- How To Format USB Drive in Linux Command Line
- Step 1 – Attach USB to System
- Step 2 – Format USB Drive in Linux
- Conclusion
- how to format an usb drive in fat16/fat32/ntfs from linux command line
- Install dosfstools Package
- Format USB drives In FAT32 Or NTFS Format In Arch Linux
- Format USB drives In FAT32 Or NTFS Format In Arch Linux
- Format USB drive in FAT32
- Format USB drive in NTFS
- Set label name to USB drives
- Форматирование флешки Linux различными способами
- Форматирование USB-накопителя через командную строку
- Через графический интерфейс
- Инструмент GParted
- Вывод
How To Format USB Drive in Linux Command Line
USB formatting is the process of erasing all data from the disk and prepare it for use. Sometimes we are required to change the filesystem on our USB drive, In that case, we have to format the USB drive with the new filesystem type. Formatting a USB drive in Ubuntu using Terminal commands is much easier than formatting it in Windows systems.
This tutorial will help Ubuntu (Linux) users with the simple steps for format a USB flash drive using the command line.
Step 1 – Attach USB to System
Insert a USB drive into your system and identify your USB drive correctly. This is the step you need to take care, because you may format the wrong disk if not correctly identify your disk.
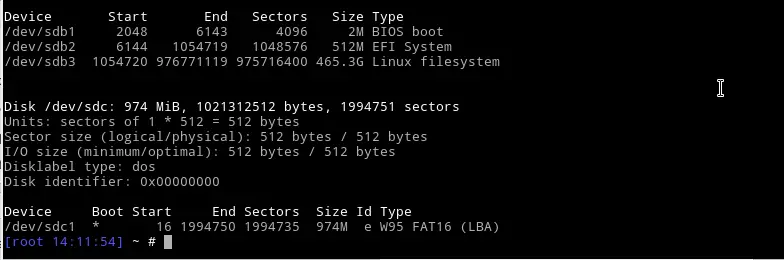
Now, You can see that the USD drive is attached as /dev/sdc1 device. Which is mounted on /media/tecadmin.
Step 2 – Format USB Drive in Linux
Whenever we attach a USB drive in Ubuntu, it is automatically mounted to the system. We can not format any disk on Linux systems that are already mounted. So first un-mount /dev/sdc1 USB drive on your system.
Now, Use one of the following commands as per the file system you want. To format a USB drive, most of the users prefer VFAT and NTFS file systems because they can be easily used on the Windows operating system.
- Format with vFat File System
- Format with NTFS File System
- Format with EXT4 File System
Similarly, you can format a USB Flash drive with any required file system.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned to format a USB drive on a Linux system via the command-line interface.
Источник
how to format an usb drive in fat16/fat32/ntfs from linux command line
One of the reasons of having to use an usb drive is to transfer files between different machines, usually with different operating systems. Unfortunately, there are still enough Windows machines out in the wild that reads only specific file systems in formats such as FAT32 or NTFS.
This means you will need to format your USB drives in formats that is understood by MS Windows. These may be either FAT16, FAT32 or NTFS file system formats. We will see how you can format an usb drive in any file system format from the Linux command line.
The command that is used to create a new file system is called mkfs in Linux. You can use this to create file systems on any disk, drive or partitions on the system. This utility supports many different file systems, including the FAT ones.
Install dosfstools Package
The support for the FAT file systems are provided by the dosfstools package. Most Linux distros should have this installed by default. If it is not installed, then you will need to install this first using your package manager installation process (apt-get, pacman, emerge etc).
The mkfs utility is only a front-end to the underlying file system builders, which means you can only use those utilities directly as well. The mkfs utility takes a command line option –type (or -t) to specify the file system type to be used.
In order for the system to format the drive, the system should be able to identify the device correctly. You also will need to know the device name for the USB drive. We will assume that the usb is loaded at /dev/sdc for the examples below.
Note: You can use the fdisk command to find the device. Use the fdisk -l command, which will print out all the devices identified by the machine.
In order to create a FAT16 file system on the device, you use one of the following commands.
bash# mkfs -t fat /dev/sdc1
bash# mkfs.fat -F 16 -I /dev/sdc1
There are several different commands, which are all symlinks to mkfs.fat command or utility. There are several different (legacy) names to the tools, which are all available by symlinks. You can use mkdosfs, mkfs.msdos, mkfs.dos, mkfs.fat or mkfs.vfat all of which does the same thing.
If you want to set the block size to 32 then you specify 32 as the value to the -F command line option.
bash# mkfs.fat -F 32 -I /dev/sdc
If you want to use the NTFS for formatting instead of the FAT32, then you can specify that using the same command line options as above….but using NTFS instead.
bash# mkfs.ntfs /dev/sdc1
bash# mkfs -t ntfs /dev/sdc1
All of these commands do support additional options, that will allow you to set or specify several other formatting values. You can specify sector size, volume labels, compression, indexing etc etc. These advanced options vary between the FAT and NTFS formats. You can check manual page of these utilities to find the additional options that they support.
Источник
Format USB drives In FAT32 Or NTFS Format In Arch Linux
Today, we will see how to format USB drives in FAT or NTFS file system in Arch Linux and its derivatives like Antergos and Manjaro Linux. There are many GUI tools available to get this job done. However, some of you might wondering if there is any way to format the usb drives from command line. No worries! This tutorial will teach you how. The following are the two commands that I use throughout this guide to format the USB drives in FAT or NTFS format.
As the name implies, mkfs.vfat will format an USB drive in FAT, and mkfs.ntfs will format the USB drive in NTFS format.
These two utilities comes preinstalled with most Linux distributions. However, these two aren’t available in my Arch Linux minimal system. After a few google search, I came to know that I must install the following two packages in-order to use those commands.
They are available in the default repositories of Arch Linux. So, you can install them by running the following command using Pacman as shown below.
To install ntfsprogs, run:
Now, let us see how to format an USB drive in MSDOS file system. The commands are same for almost all Linux distributions.
Format USB drives In FAT32 Or NTFS Format In Arch Linux
First, we will see how to format the usb drive in FAT.
Format USB drive in FAT32
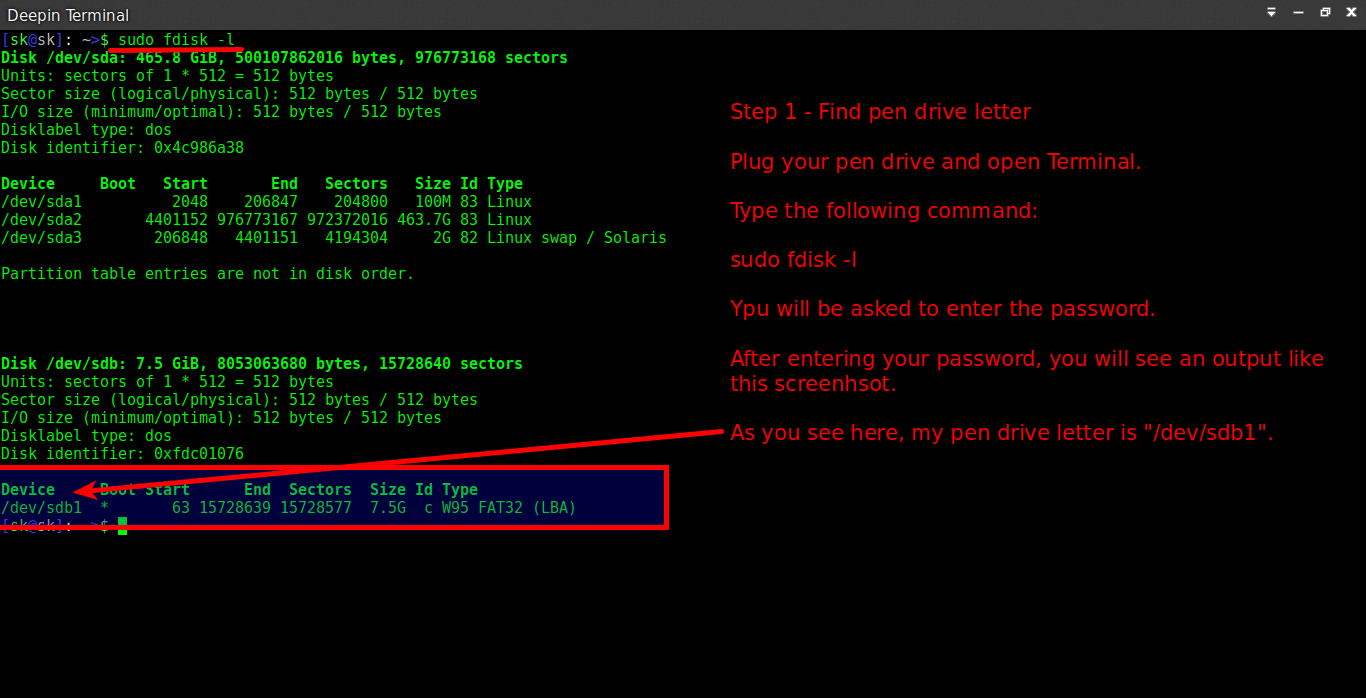
First we will find out the USB drive name (This is what we say Drive letter in Windows OS).
It’s very simple, but at the same time you should be very careful if you are using dual-booting with Windows. If you don’t be careful, you might format one of your windows partitions accidentally.
We can easily find out our disk drive letters using fdisk command.
Plug your USB drive and run the following command to display the partition table.
Sample output:
As you see in the above output, I have two disks. One is my local hard disk (500 GB), and another one is my USB drive (8 GB).
Again, I warn you please be careful if you are using dual boot with Windows or if you have multiple OSs in the single hard drive. If you use dual boot, this command will also display the Windows drives names like /dev/sdb1, /dev/sdc1 etc., in the above result. Just make sure you are formatting the correct drive.
As I mentioned in the above screenshot, my USB drive name is /dev/sdb1.
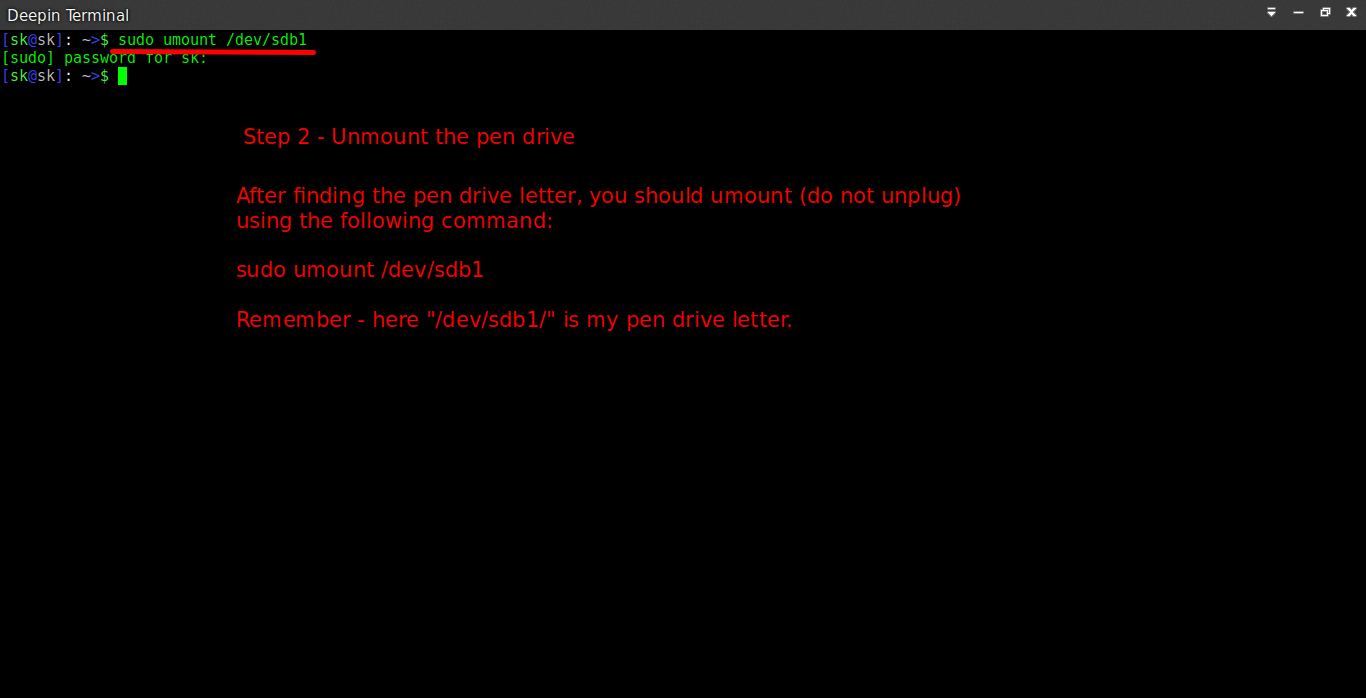
Once you find out the USB drive name, unmount it. Because you can’t format a mounted drive. Do not un-plug, just unmount the USB drive.
To unmount the drive, run:
Sample output:
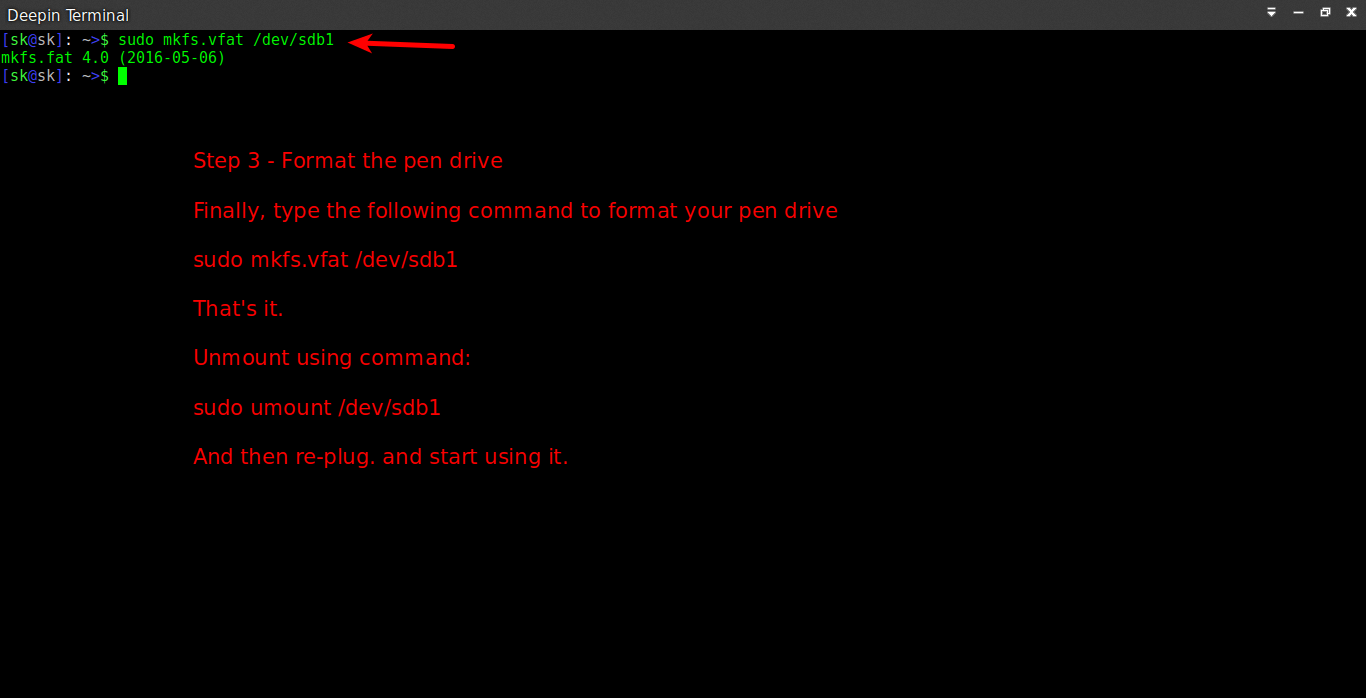
Finally, format the USB drive in FAT32 using command:
Sample output:
After formatting the drive, just unmount using it command:
Again, re-plug the USB drive to start using the it.
For further details, refer man pages.
Format USB drive in NTFS
Similarly, To format the drive in NTFS, just run:
For more options, refer man pages.
Set label name to USB drives
To set drive label name use ‘-n’ flag.
For example, the following command will format my USB drive in FAT32 format and set label name for my USB drive as «sk».
Please note that lowercase labels might not work properly with DOS or Windows. So, use upper case label name.
And, that’s all for now. You know now how to format an USB drive in MSDOS filesystem in Arch Linux. Hope this helps. If you find this guide helpful, please share it on your social, prpfessional networks and support OSTechNix.
Источник
Форматирование флешки Linux различными способами
В очередной раз требуется отформатировать USB-накопитель, чтобы изменить файловую систему, полностью стереть данные или избавиться от вируса, заражающего их. Существуют различные способы форматирования USB-накопителя.
Мы предлагаем рассмотреть несколько в этой статье, чтобы вы могли увидеть, какой из них подходит именно вам. Вы можете отформатировать USB как через командную строку, так и через графический интерфейс, в зависимости от того, что вам удобно.
Команды и процедуры, описанные в этой статье, были выполнены в Ubuntu 18.04 LTS.
Подробный обзор дистрибутива Ubuntu в данной статье.
Форматирование USB-накопителя через командную строку
Форматирование USB-накопителя очень просто с помощью командной строки. Даже новичок может отформатировать USB-накопитель с помощью простого процесса и команд, которые мы здесь описываем.
- Правильно определить USB-накопитель, чтобы избежать случайного форматирования любого другого накопителя. Откройте приложение «Терминал» с помощью сочетания клавиш Ctrl + Alt + Tи введите следующую команду:
$ df -h
Последняя строка в выводе перечисляет / dev / sdb1 как наш USB-накопитель.
- Используйте следующую команду для форматирования USB в соответствии с файловой системой VFAT:
$ sudo mkfs.vfat / dev / sdb1
Вы будете использовать местоположение в соответствии с выводом, полученным из команды df -h.
- Вы можете отформатировать только отключенный USB-накопитель, в противном случае вы получите следующее сообщение:
Поэтому, пожалуйста, отключите диск с помощью следующей команды:
$ sudo umount / dev / sdb1
Теперь, когда вы запустите команду форматирования от имени пользователя root, ваш USB-накопитель будет успешно отформатирован.
Через графический интерфейс
Вы можете отформатировать USB-накопитель через графический интерфейс вашей системы Ubuntu следующим образом:
- Откройте диспетчер файлов и затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши имя USB-накопителя.
- Выберите опцию «Формат» в контекстном меню. Следующий диалог откроется.
- Укажите имя тома для вашего USB-накопителя. На изображении выше мы ввели USB как имя тома.
Вы можете удалить существующие данные на USB-накопителе, нажав кнопку «Стереть». В этом случае существующие данные в вашей системе будут перезаписаны, а процесс форматирования займет немного больше времени. Вы также можете указать файловую систему, которую вы хотите иметь на USB-накопителе.
- Нажмите кнопку «Далее», расположенную в верхнем правом углу.
Следующее диалоговое окно «Подтвердить детали». Убедитесь, что вы форматируете нужный объем, просматривая информацию о местоположении. Это предотвратит форматирование любого нежелательного хранилища.
- Нажмите кнопку «Формат» после подтверждения деталей.
Ваш USB-накопитель будет отформатирован и готов к использованию в соответствии с указанным вами именем тома, файловой системой и параметрами стирания данных.
Инструмент GParted
Вы также можете отформатировать USB-накопитель с помощью инструмента под названием Gparted. Выполните следующие шаги, чтобы установить и использовать этот инструмент:
- Откройте Терминал через CTRL + ALT + Tили через Ubuntu Dash.
- Введите следующую команду для установки инструмента с открытым исходным кодом GParted:
$ sudo apt-get install gparted
- Введите y при появлении запроса опции ay / n для продолжения установки.
Инструмент GParted будет установлен в вашей системе.
- Чтобы получить доступ к GParted со своего рабочего стола, найдите его через Dash следующим образом:
- Нажмите на значок GParted, чтобы открыть приложение.
- Вам будет предложено предоставить аутентификацию для пользователя root. Введите пароль и нажмите «Аутентификация».
Инструмент откроется, отображая разделы / dev / sda жесткого диска по умолчанию.
- Поскольку мы хотим просмотреть сведения о съемных носителях, выберите их в раскрывающемся списке, расположенном в верхнем правом углу. Теперь вы сможете увидеть разделы съемных носителей следующим образом:
- Вам необходимо отключить USB-накопитель перед его форматированием. Выберите раздел USB, который вы хотите отформатировать, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Unmount».
- Теперь, когда вы щелкнете правой кнопкой мыши по разделу USB, опция « Форматировать» станет активной. Нажмите «Форматировать в», а затем выберите файловую систему, которую вы хотите использовать для вашего USB-накопителя.
Мы выбрали ntfs в этом примере. Эта операция будет добавлена как ожидающая операция.
- Чтобы применить эту операцию, щелкните значок галочки на верхней панели, чтобы применить все операции.
- Появится следующее диалоговое окно с запросом подтверждения о применении всех ожидающих операций. Нажмите кнопку Применить, когда вы уверены в своем выборе.
Начнется процесс форматирования.
Вы будете уведомлены, когда операции будут завершены следующим образом:
- Нажмите кнопку Закрыть; Теперь у вас есть отформатированный USB-накопитель с указанной вами файловой системой.
Вывод
Прочитав эту статью, вы, возможно, нашли способ отформатировать USB-накопитель для лучшего использования.
Во-первых, вы можете использовать по своему усмотрению командную строку. Во-вторых, пользовательский интерфейс, который является прекрасной альтернативой. И наконец, мощный инструмент редактирования разделов GParted.
Каждый вариант хорош по своему, а вам остается только выбрать подходящий.
Источник