- ИТ База знаний
- Полезно
- Навигация
- Серверные решения
- Телефония
- Корпоративные сети
- Как отформатировать разделы диска в Linux
- Проверка разделов
- Форматирование раздела диска в Linux
- Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой ext4
- Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой FAT32
- Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой NTFS
- Монтирование раздела диска в Linux
- Понимание файловой системы Linux
- Linux Hard Disk Format Command
- Step #1 : Partition the new disk using fdisk command
- Step#2 : Format the new disk using mkfs.ext3 command
- Step#3 : Mount the new disk using mount command
- Step#4 : Update /etc/fstab file
- Task: Label the partition
ИТ База знаний
Курс по Asterisk
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Как отформатировать разделы диска в Linux
4 минуты чтения
Перед использованием раздел диска необходимо отформатировать и смонтировать. Процесс форматирования также может быть выполнен по ряду других причин, таких как изменение файловой системы, исправление ошибок или удаление всех данных.
Мини — курс по виртуализации
Знакомство с VMware vSphere 7 и технологией виртуализации в авторском мини — курсе от Михаила Якобсена
В этом руководстве вы узнаете, как форматировать и монтировать разделы диска в Linux с использованием файловой системы ext4, FAT32 или NTFS.
Проверка разделов
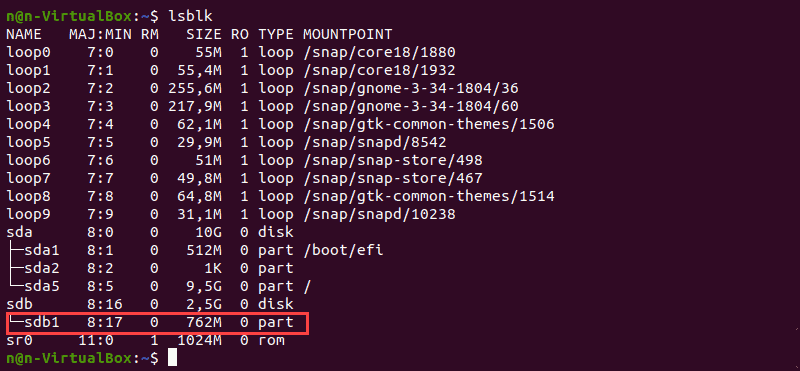
Перед форматированием найдите раздел, который хотите отформатировать. Для этого запустите команду lsblk , которая отображает блочные устройства. Блочные устройства — это файлы, которые представляют такие устройства, как жесткие диски, RAM-диски, USB-накопители и CD/ROM.
Терминал покажет список всех блочных устройств, а также информацию о них:
- NAME — имена устройств
- MAJ:MIN — старший или младший номер устройства
- RM — является ли устройство съемным (1, если да, 0, если нет)
- SIZE — размер устройства
- RO — доступно ли устройство только для чтения
- TYPE — тип устройства
- MOUNTPOINT — точка монтирования устройства
В качестве примера мы будем использовать раздел /dev/sdb1 .
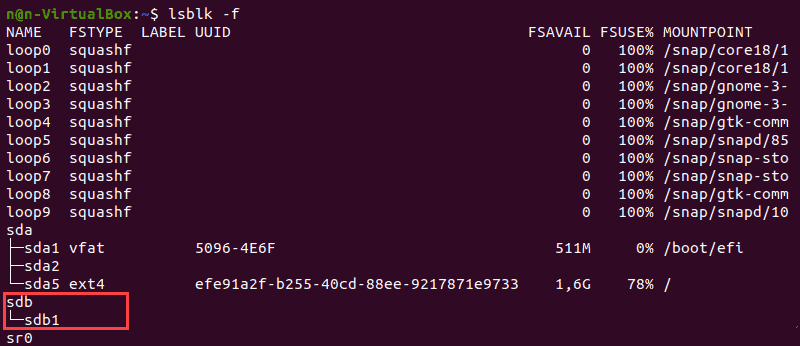
Команда lsblk без дополнительных параметров не отображает информацию о файловых системах устройств.
Чтобы отобразить список, содержащий информацию о файловой системе, добавьте параметр -f :
Терминал покажет список всех блочных устройств. Разделы, не содержащие информации об используемой файловой системе, являются неформатированными разделами.
Форматирование раздела диска в Linux
В зависимости от типа файловой системы существует три способа форматирования разделов диска с помощью команды mkfs :
Общий синтаксис форматирования разделов диска в Linux:
Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой ext4
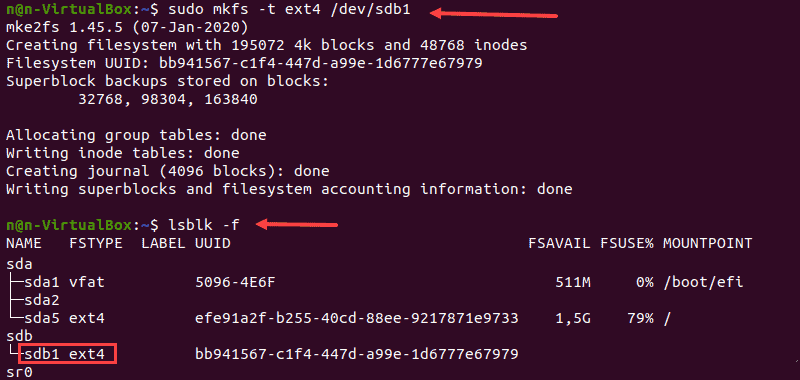
1. Отформатируйте раздел диска с файловой системой ext4, используя следующую команду:
2. Затем проверьте изменение файловой системы с помощью команды:
Терминал покажет список блочных устройств.
3. Найдите нужный раздел и убедитесь, что он использует файловую систему ext4.
Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой FAT32
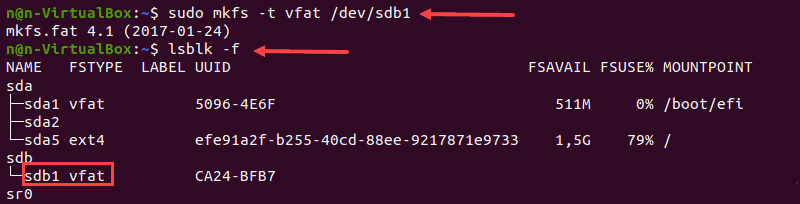
1. Чтобы отформатировать диск в файловой системе FAT32, используйте:
2. Снова запустите команду lsblk , чтобы проверить изменение файловой системы и найти нужный раздел в списке.
Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой NTFS
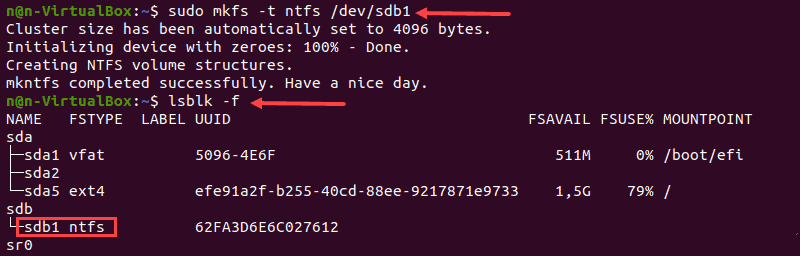
1. Запустите команду mkfs и укажите файловую систему NTFS для форматирования диска:
Терминал покажет подтверждающее сообщение, когда процесс форматирования завершится.
2. Затем проверьте изменение файловой системы, используя:
3. Найдите нужный раздел и убедитесь, что он использует файловую систему NFTS.
Монтирование раздела диска в Linux
Перед использованием диска создайте точку монтирования и смонтируйте к ней раздел. Точка монтирования — это каталог, используемый для доступа к данным, хранящимся на дисках.
1. Создайте точку монтирования, введя:
2. После этого смонтируйте раздел с помощью следующей команды:
Примечание. Замените [mountpoint] предпочтительной точкой монтирования (пример: /usr/media ).
Если процесс завершился успешно, вывода нет.

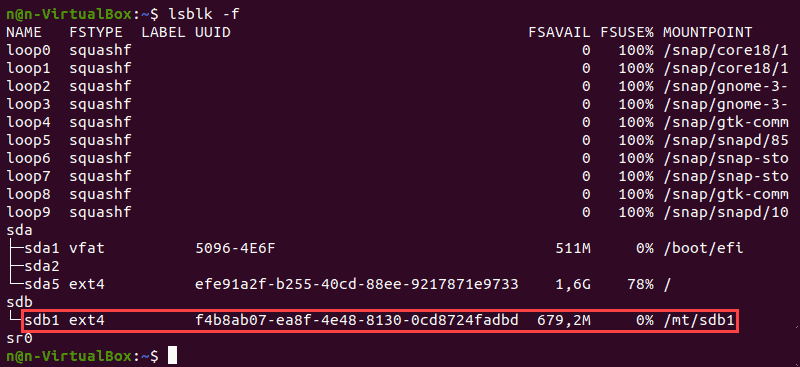
3. Убедитесь, что раздел смонтирован, используя следующую команду:
Понимание файловой системы Linux
Выбор правильной файловой системы перед форматированием диска для хранения имеет решающее значение. Каждый тип файловой системы имеет разные ограничения размера файла или разную совместимость с операционной системой.
Наиболее часто используемые файловые системы: FAT32, NTFS и ext4
Их основные особенности и отличия:
| Файловая система | Поддерживаемый размер файла | Совместимость | Идеальное использование |
| FAT32 | до 4 ГБ | Windows, Mac, Linux | Для максимальной совместимости |
| NTFS | 16 EiB — 1 КB | Windows, Mac (только для чтения), большинство дистрибутивов Linux | Для внутренних дисков и системного файла Windows |
| Ext4 | 16 GiB — 16 TiB | Windows, Mac, Linux (для доступа требуются дополнительные драйверы) | Для файлов размером более 4 ГБ |
Мини — курс по виртуализации
Знакомство с VMware vSphere 7 и технологией виртуализации в авторском мини — курсе от Михаила Якобсена
Источник
Linux Hard Disk Format Command
Q. I’ve installed a new 250GB SATA hard disk on our office CentOS Linux server. How do I format a hard disk under Linux operating system from a shell prompt?
A. . There are total 4 steps involved for hard disk upgrade and installation procedure:
Step #1 : Partition the new disk using fdisk command
Following command will list all detected hard disks:
# fdisk -l | grep ‘^Disk’
Output:
A device name refers to the entire hard disk. For more information see Linux partition naming convention and IDE drive mappings.
To partition the disk – /dev/sdb, enter:
# fdisk /dev/sdb
The basic fdisk commands you need are:
- m – print help
- p – print the partition table
- n – create a new partition
- d – delete a partition
- q – quit without saving changes
- w – write the new partition table and exit
Step#2 : Format the new disk using mkfs.ext3 command
To format Linux partitions using ext2fs on the new disk:
# mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Step#3 : Mount the new disk using mount command
First create a mount point /disk1 and use mount command to mount /dev/sdb1, enter:
# mkdir /disk1
# mount /dev/sdb1 /disk1
# df -H
Step#4 : Update /etc/fstab file
Open /etc/fstab file, enter:
# vi /etc/fstab
Append as follows:
Save and close the file.
Task: Label the partition
You can label the partition using e2label. For example, if you want to label the new partition /backup, enter
# e2label /dev/sdb1 /backup
You can use label name insted of partition name to mount disk using /etc/fstab:
LABEL=/backup /disk1 ext3 defaults 1 2
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
yah thats good for understand………
i have 48TB storage server in raid 5, how do i format this server?
to format the corresponding hdd you need a RAM(Random Access Memory) 1 YB(yota byte)
1YB=1024 ZB
1ZB=1024 XB
1XB=1024 PB
1PB=1024 TB
LOL, I’ve got 1 UB (UnniByte) RAM on my Server
1UB=1024YB
1YB=1024 ZB
1ZB=1024 XB
1XB=1024 PB
1PB=1024 TB
Is it possible to format my 1.4 MB floppy now?
I have 90’90 power of per zylions! So what? You’ve only got a pint of milk. does your processor register .
Use LVM directly or read this tutorial which explains how to create partition larger than 2TB
How do I format a harddisk using linux system call
thank you fro valuable information
how to format a disk by cpp programe?is there any sample code ?
Thank you very much this valuable information.
/dev/sdb1 /disk1 ext3 defaults 1 2
The above line what is mean by defaults and what is 1 2 ?
can u explain those two things !
This is directly from the arch linux (amazing) documentation:
- The first number is “dump”: used by the dump utility to decide when to make a backup. Dump checks the entry and uses the number to decide if a file system should be backed up. Possible entries are 0 and 1. If 0, dump will ignore the file system; if 1, dump will make a backup. Most users will not have dump installed, so they should put 0 for the entry.
- The second number is “pass”: used by fsck to decide which order filesystems are to be checked. Possible entries are 0, 1 and 2. The root file system should have the highest priority 1 – all other file systems you want to have checked should have a 2. File systems with a value 0 will not be checked by the fsck utility.
IN my system both WINDOWS-XP and LINUX , I’ve installed. after that
I want to format the linux OS from my system.
so please send to me tricks or method on Email addr., so i can remove LUNUX OS from my system.
BY both method (i)Text command and
(ii)without Text command.
Hey man I also have same problem .did u got any methods to remove . please help man
verrrrrrrrry useful i’ve searched for 2 days for this thanks
Thank you very much this valuable information. Very useful this
Thanks
B. Sathish.
I have installed CentOS ..
now i want my disk to be fully formatted like a new one. with no files on it..
i remember doing it by booting in DOS mode in Win98..
Please tell how can i do it..
Thank you.
nice and clear.
Excellent and easy. Thanx
Nice information and esp. the link that you posted for Anikat. Information really useful pal. Thanks a ton..
Regards
Charanjit Singh Cheema
Thank you, this is the kind of fast reference that one is always looking for
Well, this saved me an hour of banging my head against the wall… well written! thanks!
Yes. Very useful. Thanks.
help me to see the out put of the php programe, i have php 2007 developer
Very simple and useful, thanks 🙂
Great. Searched for a long time to find this, very well done. Thanks!
Can any one tell me what the mean by 1,2 in default and when i create a raid partition is there any change in default charcter or it is sama as ” default” .
IN my Laptop both WINDOWS-XP and LINUX, i’ve safe the problem in windows hal.dll file is corrupted.
so please send to me tricks or method on Email addr.
Good Recipe for what I did in UNIX for years with the simple format command.
You boiled it down to an excellent example…
very helpfull , thanks.
very first command (fdisk /dev/sdb) failed. message is “Unable to open /dev/sdb”. any suggestions?
Is there any software to bound two NIC to use on ip address for both NICs.
Thank you very much these are very good and easy way commands to understand for the people.
how to format linex form my system plz reply solution at my email
thanks alot . that was really usefull
how many formatting for window and linux
plz sand ams on my email address
I deleted the panel in ubuntu by mistake.. how can i get the default panels?
The above steps are so good and easy to format
Thank u Very much for your Formating steps.
a very nice article. thank you for sharing.
how do installed linux …. with command . tell me all command….
IN my system both WINDOWS-XP and LINUX , I’ve installed. after that
I want to format the linux OS from my system.
so please send to me tricks or method on Email addr., so i can remove LUNUX OS from my system.
BY both method (i)Text command and
(ii)without Text command.
Good article.
Note: this works on centos 5.5 … fyi.
This is beautiful. There are some who care out there..
IN my system both WINDOWS-XP and LINUX , I’ve installed. after that
I want to format the linux OS from my system.
so please send to me tricks or method on Email addr., so i can remove LUNUX OS from my system.
BY both method
(i)Text command and
(ii)without Text command.
Источник




