- Подключение Linux Ubuntu 20.04, 20.10, 21.04 к Forti VPN
- Предыстория
- Решение
- Альтернативное решение
- FortiClient 7.0
- Overview
- FortiClient Unifies Endpoint Features
- Consistent web filtering policy enforcement on and off campus
- Установка клиента Fortinet SSL VPN без графического интерфейса в Linux (centos)
- Bits and Bytes
- Not just another Tech site
- Forticlient – SSLVPN .deb packages
- 269 thoughts on “ Forticlient – SSLVPN .deb packages ”
Подключение Linux Ubuntu 20.04, 20.10, 21.04 к Forti VPN
Предыстория
Так уж получилось, что для удаленного доступа к работе приходится использовать Forti VPN.
В Windows за подключение отвечает отдельное приложение, а в Ubuntu 18.04 раньше использовал пакет из репозитория openfortivpn и GUI клиент с сайта https://hadler.me/linux/openfortigui/ .
Не феншуйно, но работало. Времени искать более правильное решение не было.
Сейчас, когда только-только вышла Ubuntu 20.04 работающего без ошибок GUI Forti VPN клиента еще не выпустили.
Прежде всего в репозитории я нашел для GNOME пакет network-manager-fortisslvpn-gnome. В результате его установки в настройках подключения появился пункт настройки VPN и возможность выбора типа подключения.
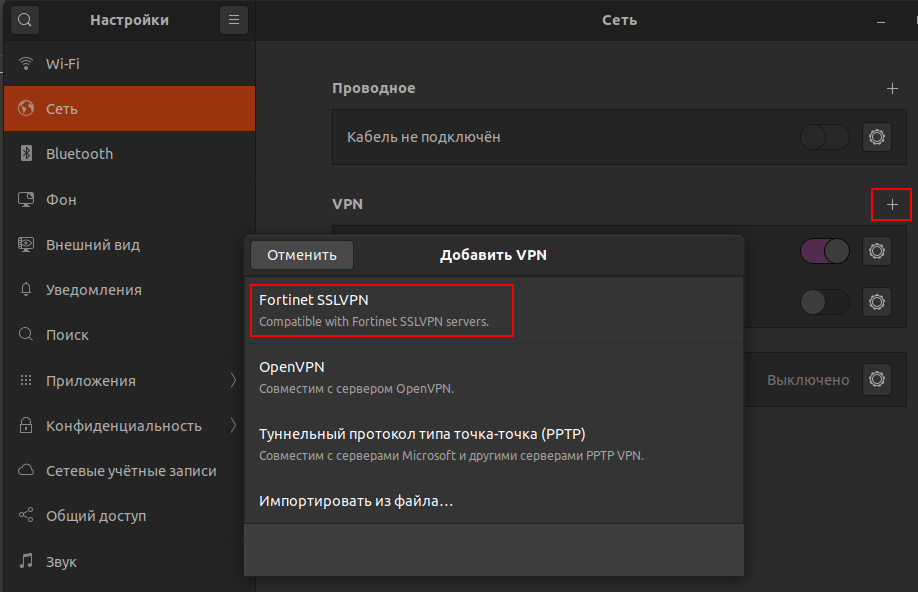
Безусловно это вселяло надежду, что получится отказаться от громоздкого GUI приложения.
После создания и настройки нового подключения появляется соответствующий пункт в панели управления.
Но вот незадача, не подтягиваются DNS сервера от DHCP сервера. После многих часов поиска ответа на вопрос что же происходит привели меня к следующему выводу. Оказалось, что наш VPN-cервер Forti использует SSL для шифрования, а его использование по умолчанию отключено в systemd.
Решение
Итого, чтобы настроить подключение к Forti VPN с шифрованием SSL и корректным использованием DNS серверов нужно:
1 — Установить network-manager-fortisslvpn-gnome
sudo apt-get install network-manager-fortisslvpn-gnome
2 — Открываем файл /etc/systemd/resolved.conf . Далее ищем строчку DNSOverTLS, раскомментируем ее и присваиваем значение opportunistic. Потом раскомментируем строку Domains и прописываем доменное имя DNS-сервера. После чего дописываем DNS.
[Resolve]
DNS=X.X.X.X
DNS=Y.Y.Y.Y
#FallbackDNS=
Domains=corp.yourdomain.com
#LLMNR=no
#MulticastDNS=no
#DNSSEC=no
DNSOverTLS=opportunistic
#Cache=yes
#DNSStubListener=yes
#ReadEtcHosts=yes
3. Перезапускаем systemd
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart systemd-networkd
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved
Затем переподключаем соединение или для избежания доп проблем вообще перезагружаемся.
Все, при новом подключении к VPN серверу DNS серверы должны начать использоваться системой.
Альтернативное решение
Есть всегда альтернативный способ прописать DNS-серверы вручную и для этого нужно:
1 — Установить resolvconf
sudo apt-get install resolvconf
2 — Затем открыть один из файлов в папке /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d (head или tail)
3 — После чего прописать в файл информацию о DNS серверах.
Источник
FortiClient 7.0
Fortinet Fabric Agent for Visibility, Control, and ZTNA
Overview
FortiClient Unifies Endpoint Features
FortiClient is a Fabric Agent that that delivers protection, compliance, and secure access in a single, modular lightweight client. A Fabric Agent is a bit of endpoint software that runs on an endpoint, such as a laptop or mobile device, that communicates with the Fortinet Security Fabric to provide information, visibility, and control to that device. It also enables secure, remote connectivity to the Security Fabric.
The FortiClient Fabric Agent can:
- Report to the Security Fabric on the status of a device, including applications running and firmware version.
- Send any suspicious files to a Fabric Sandbox.
- Enforce application control, USB control, URL filtering, and firmware upgrade policies.
- Provide malware protection and application firewall service.
- Enable the device to connect securely to the Security Fabric over either VPN (SSL or IPsec) or ZTNA tunnels, both encrypted. The connection to the Security Fabric can either be a FortiGate Next-generation Firewall or SASE service.
FortiClient is offered with several levels of capabilities, with increasing levels of protection. It integrates with many key components of the Fortinet Security Fabric and is centrally managed by the Enterprise Management Server (EMS).
| Zero Trust Agent with Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) | The Zero Trust Agent supports ZTNA tunnels, single sign-on (SSO), and device posture check to FortiOS access proxy |
| Central Management via EMS or FortiClient Cloud | Centralized FortiClient deployment and provisioning that allows administrators to remotely deploy endpoint software and perform controlled upgrades. Makes deploying FortiClient configuration to thousands of clients an effortless task with the click of a button. |
Vulnerability dashboard helps manage an organization’s attack surface. All vulnerable endpoints are easily identified for administrative action.
Windows AD integration helps sync an organization’s AD structure into EMS so the same organization units (OUs) can be used for endpoint management. Realtime Endpoint Status always provides current information on endpoint activity and security events.
Powered by FortiGuard Labs research, the web filtering function monitors all web browser activities to enforce web security and acceptable usage policy with 75+ categories. It works across all supported operating systems and works with Google SafeSearch. The endpoint web filtering profile can be synchronized from FortiGate for consistent policy enforcement. Administrators can set black/white lists, on-/off-net policies, and import FortiGate web filtering policies for consistent enforcement.
FortiClient now supports a web filter plugin that improves detection and enforcement of web filter rules on HTTPS sites with encrypted traffic.
| ZTNA Edition Features | This edition includes all the features in the ZTNA Edition plus the following: |
|---|---|
| AI-powered Next-Generation Antivirus (NGAV) | Anti-malware leverages FortiGuard Content Pattern Recognition Language (CPRL), machine learning, and AI to protect endpoints against malware. The pattern-based CPRL is highly effective in detecting and blocking polymorphic malware. It also blocks attack channels and malicious websites. |
| FortiClient Cloud Sandbox | FortiClient natively integrates with FortiSandbox. FortiClient automatically submits files to the connected FortiSandbox for real-time analysis. Sandbox analysis results are automatically synchronized with EMS. Administrators can see detailed information and behavior activities of submitted objects including graphic visualization of the full process tree. |
| Automated Endpoint Quarantine | When triggered by security events, automated endpoint quarantine automates policy-based response. For example, it can automatically quarantine a suspicious or compromised endpoint to contain incidents and prevent outbreaks. |
| Application Firewall | The application firewall provides the ability to monitor, allow, or block application traffic by categories. It uses the same categories as FortiGate, enabling consistent application traffic control. It leverages FortiGuard anti-botnet, IPS, and application control intelligence and can prevent the use of unwanted applications including proxy apps and HTTPS messaging apps. |
| Application Inventory |