- Русские Блоги
- Установка и использование GDB на Mac
- Как установить gdb (debugger) в Mac OSX El Capitan?
- 8 ответов
- Вариант 1: подписания бинарными
- Альтернатива 2: Используйте устаревшую опцию для taskgated
- How to setup gdb and Eclipse to debug C++ files on macOS Catalina
- Thomas Vitale
- Install gdb
- Install gdb 8.3 (recommended)
- Install gdb 8.0.1
- Generate a certificate
- Troubleshooting the certificate generation
- Sign the certificate for gdb
- Create a gdb command file
- Set Eclipse for using gdb
- Troubleshooting the Eclipse configuration
- Conclusion
Русские Блоги
Установка и использование GDB на Mac
0,1 фон
Gdb — это инструмент для отладки кода. Он по-прежнему поддерживается в Mac, но из-за самой системы MacOS и несовместимых версий во время использования будут возникать различные проблемы. В этой статье подробно описан процесс установки из Gdb, настройки цепочки для ключей и отладки с помощью VScode.
Версия 0.2
Версия для Mac: macOS High Sierra 10.13.6
Установка 1 Гб
Самый быстрый способ — использовать brew для установки, команда выглядит следующим образом.
В настоящее время (2018.11.2) brew install будет устанавливать версию 8.2 по умолчанию, но при последующем использовании возникли некоторые проблемы (Mac high Sierra и gdb 8.0 и выше несовместимы во многих местах, и это настоятельно не рекомендуется), поэтому не рекомендуется Используйте эту версию. Я рекомендую использовать версию 8.0, 8.0 устанавливается следующим образом.
Нажмите на эту ссылку, чтобы загрузить исходный установочный пакет 8.0http://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gdb/gdb-8.0.tar.gz Затем распакуйте его. Войдите в распакованный каталог и выполните следующие команды по порядку.
Если все идет хорошо, вы можете увидеть, что версия GDB 8.0.
2 Настройте разрешения отладки
Если вы отлаживаете программу прямо сейчас, вы столкнетесь со следующей ошибкой.
Это связано с тем, что ядро Darwin не позволяет отлаживать другие процессы без специальных разрешений. Отладка процесса означает полный контроль над процессом. Поэтому по умолчанию это запрещено. Поэтому лучший способ позволить gdb контролировать другие процессы — это подписать его сертификатом, которому доверяет система.
2.1 Создать сертификат
- Команда + пробел, введите брелок доступа.
- Нажмите Доступ к цепочке для ключей в меню-> Ассистент сертификата-> Трансцендировать сертификат
- Введите следующую информацию
- Имя: gdb_codesign
- Тип удостоверения: самоподписанный корневой сертификат
- Тип сертификата: подпись кода
- Проверено: позвольте мне переопределить эти настройки по умолчанию
- Затем продолжайте, пока не появится «Укажите местоположение сертификата», выберите систему и завершите.
- Затем выберите «Система» на левой боковой панели и выберите «Мой сертификат» ниже, чтобы увидеть созданный сертификат, а затем дважды щелкните. Разверните пункт «Доверие» и выберите «Всегда доверять».
- Закройте окно, вам необходимо подтвердить пароль.
2.2 Подписание GDB
Выполните следующую команду в Терминале
В противном случае подпись не вступит в силу.
3 Использование GDB в VScode
GDB мощный, но он работает лучше с хорошим визуальным интерфейсом vscode.
Источник
Как установить gdb (debugger) в Mac OSX El Capitan?
Как установить gdb (отладчик) в Mac OSX El Capitan ? Я попытался установить gdb, но потерпел неудачу пару раз.
я следовал этому URL:http://ntraft.com/installing-gdb-on-os-x-mavericks/, MAC не позволяет устанавливать MacPorts.
может ли кто-нибудь помочь мне в этом отношении.
8 ответов
существует два решения проблемы, и они оба упомянуты в других ответах на этот вопрос и как заставить gdb работать с помощью macports под OSX 10.11 El Capitan?, но чтобы прояснить некоторую путаницу, вот мое резюме (как ответ, так как он получил немного длинный комментарий):
какая альтернатива более безопасна, я думаю, сводится к выбору между 1) доверяя самозаверяющим сертификатам и 2) предоставляя пользователям больше преференции.
Вариант 1: подписания бинарными
если используется альтернатива подписи, отключение SIP для добавления опции-p в taskgated не требуется.
обратите внимание, что с этой альтернативой, отладка разрешена только для пользователей _developer группа.
использование codesign для подписи с помощью сертификата с именем gdb-cert :
codesign -s gdb-cert /opt/local/bin/ggdb
(используя MacPorts стандартный путь, принять по мере необходимости)
обратите внимание, что вы нужно перезапустить приложение keychain и служба taskgated во время и после процесса (самый простой способ — перезагрузить.)
Альтернатива 2: Используйте устаревшую опцию для taskgated
в соответствии с ответом @user14241, отключив SIP и добавив опцию-p в taskgated вариант. Обратите внимание, что при использовании этой опции, подписание двоичного файла не требуется, а также обходит диалог проверки подлинности в качестве члена группы инструментов разработчика ( _developer ).
после добавления опции-p (разрешить группы procmod и procview) в taskgated вам также необходимо добавьте пользователей, которым должно быть разрешено использовать gdb в группу procmod.
перезагрузить в режиме восстановления, откройте терминал и выполните команду csrutil disable
перезагрузите машину и отредактируйте /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.taskgated.plist , добавив the -p opion:
перезагрузка в режиме восстановления для повторного использования SIP ( csrutil enable )
перезагрузите машину и добавьте пользователя USERNAME для группа procmod :
sudo dseditgroup -o edit -a USERNAME -t user procmod
альтернатива это не включает добавление пользователей в группы-это сделайте исполняемый файл setgid procmod, что составляет procmod эффективный идентификатор группы любого пользователя, выполняющего двоичный файл setgid (предлагается в https://apple.stackexchange.com/a/112132)
Сначала установите Homebrew:
/usr/bin/ruby -e «$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)»
запустите этого : brew install gdb
Это не обязательно решает вопрос, но если вы используете Mac OS X, то вы, вероятно, можете использовать lldb Домашняя страница LLDB . Это очень похоже на gdb и даже руководство по использованию команд, которые вы используете на gdb .
вот сообщение в блоге объясняет это очень хорошо:
и то, как я заставляю его работать:
создайте сертификат подписи кодирования через Открыть Брелок:
1.1 в меню выберите связка > сертификат помощника > создать сертификат.
1.2 следуйте указаниям мастера, чтобы создать сертификат и назовем его gdb.cert тип личности Самоподписанный Корень, а тип сертификата —Подписывание Кода и выберите Let Me override defaults.
1.3 нажмите несколько раз на Далее, пока не дойдете до укажите местоположение для экрана сертификата, затем установите брелок to система.
установить gdb через Homebrew: brew install gdb
перезагрузка taskgated : sudo killall taskgated && exit
откройте окно терминала и введите sudo codesign -vfs gdb.cert /usr/local/bin/gdb
на моем Mac OS X El Capitan я использую homebrew для установки gdb:
затем я следую инструкции здесь:https://sourceware.org/gdb/wiki/BuildingOnDarwin, в разделе 2.1. Метод для Mac OS X 10.5 (Leopard) и более поздних версий.
как только вы получите версию macports gdb установлен вам нужно будет отключить SIP, чтобы сделать правильные изменения в /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.taskgated.plist . Чтобы отключить SIP, необходимо перезагрузиться в режиме восстановления и выполнить следующую команду:
перезагрузите. Затем вам нужно будет отредактировать нижнюю часть com.apple.taskgated.plist такой:
тогда вам придется перезапустить, чтобы изменения вступили в силу. Тогда вы должны reenable глоток. The для установка macports на самом деле ggdb . Вам нужно будет код sign ggdb следуя инструкциям здесь:
единственный способ заставить подпись кода работать-это запустить ggdb С sudo . Удачи!
кажется, что MacPorts может быть установлен в El Capitan прямо сейчас: https://www.macports.org/install.php Тогда вы, вероятно, можете установить gdb по ссылке, которую вы упомянули.
просто потратил несколько дней, пытаясь заставить это работать на High Sierra 10.13.1. Версия gdb 8.1 от homebrew не будет работать независимо от того, что я пытался. Закончилась установка gdb 8.0.1 через macports, и это чудесным образом сработало (после прыжка через все другие необходимые обручи, связанные с кодовым дизайном и т. д.).
одна дополнительная проблема заключается в том, что в Eclipse вы получите посторонние одинарные кавычки вокруг всех ваших аргументов программы, которые можно обойти, предоставив споры внутри .вместо этого gdbinit.
Источник
How to setup gdb and Eclipse to debug C++ files on macOS Catalina
Using gdb debugger on macOS is no longer straightforward since Xcode stopped using it and replaced it with lldb. For macOS Catalina, there are several steps to follow to make it work. In this article, I’ll show you how.
Thomas Vitale
Using gdb debugger on macOS is no longer straightforward since Xcode stopped using it and replaced it with lldb. Starting from Mavericks (macOS 10.9), there are several steps to follow to make it work.
- Install gdb
- Install gdb 8.3 (recommended)
- Install gdb 8.0.1
- Generate a certificate
- Troubleshooting the certificate generation
- Sign the certificate for gdb
- Create a gdb command file
- Set Eclipse for using gdb
- Troubleshooting the Eclipse configuration
Install gdb
The easiest way to install gdb is by using Homebrew: «the missing package manager for macOS». If you don’t have it installed, open your Terminal prompt and write this command:
Once you have Homebrew, you can install gdb. If you’re using High Sierra (macOS 10.13) or later, be aware that gdb 8.1 and 8.2 are not compatible. You can either use gdb 8.0.1 or one of the latest versions, starting from 8.3. In this tutorial, I’m going to use gdb 8.3.
Install gdb 8.3 (recommended)
To install the latest version of gdb, run this command:
Verify that the operation was successfull by running:
Take note of the version: you’ll need it later. In my case, it is 8.3.
Install gdb 8.0.1
Should you decide to do so, you can install gdb version 8.0.1 in this way.
The pinning operation makes sure that brew doesn’t upgrade gdb to newer versions.
In case you have already a newer version of gdb, you first need to unlink the other version before installing the old one.
To check out your gdb version, run:
Take note of the version: you’ll need it later. In my case, it is 8.3.
Generate a certificate
Installing gdb is not enough. If you try debugging a file, you’ll get an error since the Darwin kernel doesn’t allow gdb to control another process without having special rights. For security reasons, this is the default behaviour.
To give gdb those permissions, you need to generate a self-signed certificate.
- Launch Keychain Access application: Applications > Utilities > Keychain Access.
- From the Keychains list on the left, right-click on the System item and select Unlock Keychain «System».
- From the toolbar, go to Keychain Access > Certificate Assistant > Create a Certificate.
- Choose a name (e.g. gdb-cert).
- Set Identity Type to Self Signed Root.
- Set Certificate Type to Code Signing.
- Check the Let me override defaults checkbox.
- At this point, you can go on with the installation process until you get the Specify a Location For The Certificate dialogue box. Here you need to set Keychain to System. Finally, you can click on the Create button.
- After these steps, you can see the new certificate under System keychains. From the contextual menu of the newly created certificate (right-click on it) select the Get info option. In the dialogue box, expand the Trust item and set Code signing to Always Trust.
- Then, from the Keychains list on the left, right-click on the System item and select Lock Keychain «System».
- Finally, reboot your system.
Troubleshooting the certificate generation
At the end of the procedure to generate a certificate, you might get the following error message:
This kind of error has bothered a lot of macOS users over the past years, I don’t know why Apple has not replaced it with a more meaningful message yet. It seems that the error is related to the creation of the certificate in the System keychain. Here there are a few things you can try to solve the problem.
- Be sure that your System keychain is unlocked. If it is and you’re still getting the same error, than you can use a workaround. Create the certificate in the login keychain and then drag and drop the newly created certificate, the public key and the private key from the login keychain to the System keychain.
- If the drag-and-drop option doesn’t work for you, then find your certificate in the login keychain, select it, then choose File -> Export items from the toolbar and save the certificate somewhere on your disk. Then, go in the System folder, choose File -> Import items from the toolbar and select your certificate. Finally, delete the certificate originally created in the login folder (it’s not done automatically).
Notice that once you have created the certificate using one of the previous workarounds, you still need to go through steps 9 to 11 of the prior section.
I hope that one of the solutions worked well for you. Please leave a comment if you are encountering any other error during the procedure.
Sign the certificate for gdb
It’s time to sign the certificate. If you’re using maOS Mojave (10.14) or later, create a gdb-entitlement.xml file. This will tell the operating system which operations the gdb process has to be trusted. In this case, just for debugging.
Then, open your Terminal prompt, go to the directory where you saved the xml file and run:
If you’re using macOS High Sierra (10.13) or older, you don’t need an entitlement configuration. Instead, you need to run this command:
where gdb-cert is the name of your certificate and gdbPath is the full path to your gdb binary file. If you have installed gdb as explained before (using Homebrew), the path should be: /usr/local/Cellar/gdb/version/bin/gdb (replace version with the actual version of your gdb installation, e.g. /usr/local/Cellar/gdb/8.3/bin/gdb).
Create a gdb command file
If you are on macOS Sierra (10.12) or later, you need to do this extra step.
In the home directory, create a new file called .gdbinit and write the following command in it:
Alternatively, from the Terminal, you can do that by running this:
Now you can use gdb for debugging files on your Mac. If you use Eclipse, follow the next step.
Set Eclipse for using gdb
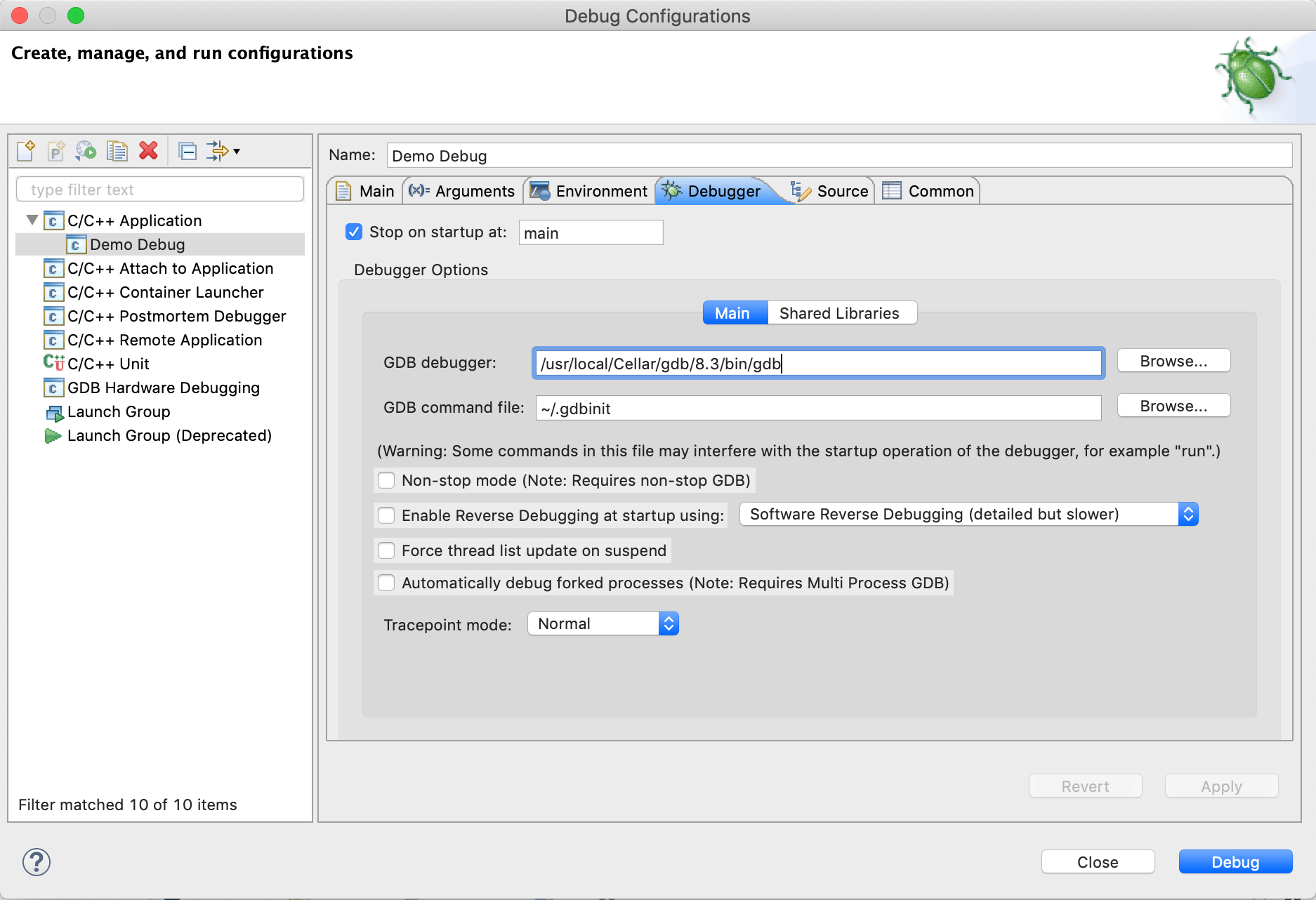
If you want to configure gdb for a specific project in Eclipse, you need to set some options:
- Go to Run > Debug Configurations.
- Select a launch configuration from the list on the left (e.g. C/C++ Application)
- Open the Debugger tab from the menu on the right
- Set GDB debugger to the full path of your gdb binary file (the same used for signing the certificate)
- Set GDB command file to the full path of your .gdbinit file:
/.gdbinit (or the extended form /Users/yourname/.gdbinit, where yourname is your username)
In case you want to define a default configuration for gdb to be used in any Eclipse project, these are the steps to follow:
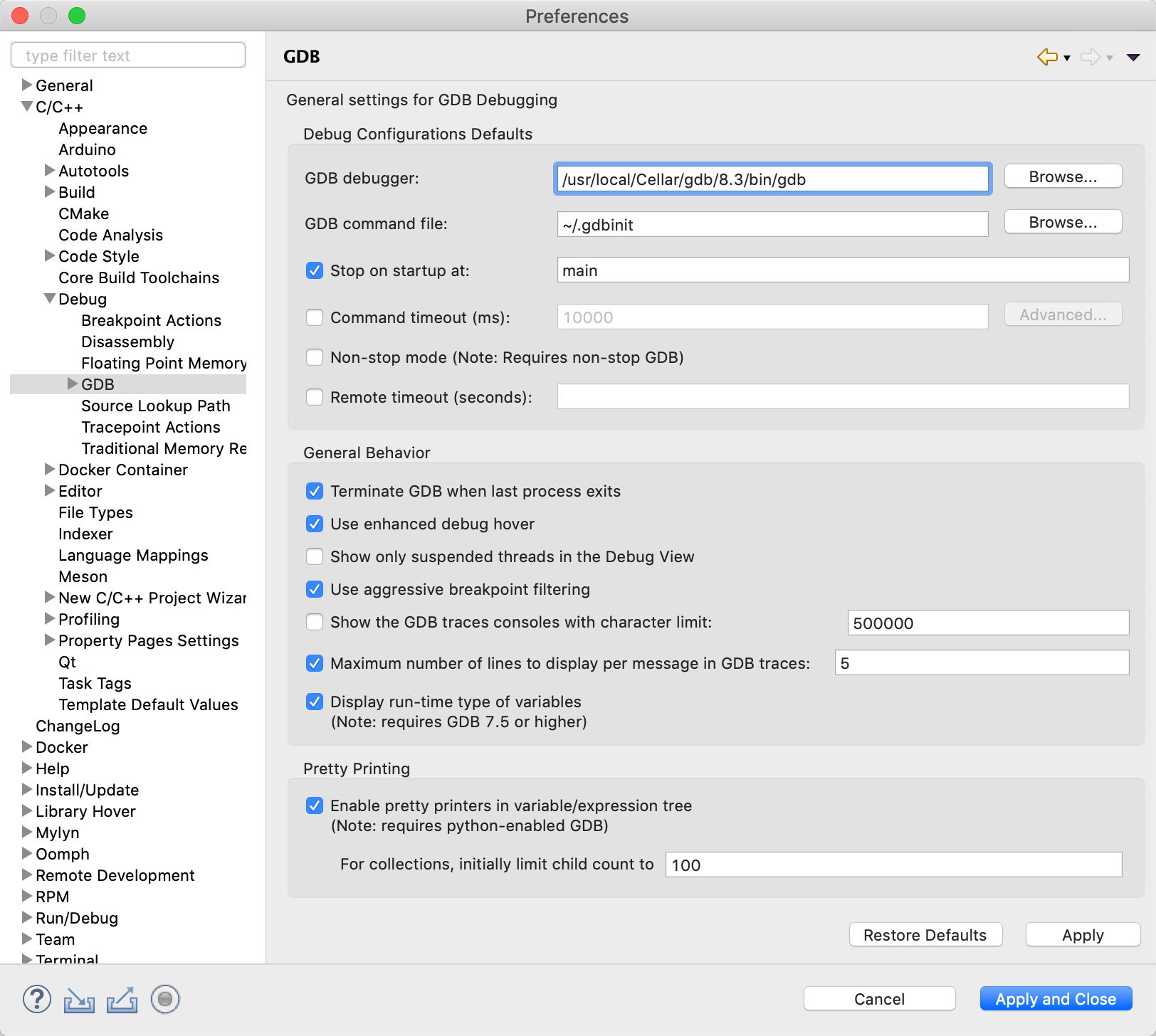
- Go to Eclipse > Preferences
- From the left menu select C/C++ > Debug > GDB
- Set GDB debugger to the full path of your gdb binary file (the same used for signing the certificate)
- Set GDB command file to the full path of your .gdbinit file:
/.gdbinit (or the extended form /Users/yourname/.gdbinit, where yourname is your username)
Now, you can debug files from inside Eclipse using gdb.
Troubleshooting the Eclipse configuration
If there is no GDB option in Eclipse > Preferences > C/C++ > Debug, then you need first to debug any C/C++ project. So, open any project and start a debugging session either by clicking the Debug icon on the toolbar. The operation will fail since you haven’t configured gdb yet, but in this way, you will be able to see the gdb option in the main Preferences window.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, I’ve shown you how to install gdb and use it to debug a C/C++ application on macOS.
Special thanks to those people who helped me improve this article by commenting with suggestions and tips.
Источник





