- How to check your computer uptime on Windows 10
- How to check PC uptime using Task Manager
- How to check PC uptime using Control Panel
- How to check PC uptime using Command Prompt
- Using WMIC
- Using System Information
- How to check PC uptime using PowerShell
- More Windows 10 resources
- The Dell XPS 15 is our choice for best 15-inch laptop
- Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
- Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
- These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
- How to get the system uptime in Windows? [closed]
- 3 Answers 3
- 1: By using the Task Manager
- 2: By using the System Information Utility
- 3: By using the Uptime Utility
- 3.1: By using the old Uptime Utility
- 4: By using the NET STATISTICS Utility
- 5: By Using the Event Viewer
- 5.1: Eventlog via PowerShell
- 6: Programmatically, by using GetTickCount64
- 7: By using WMI
- 8: The new uptime.exe for Windows XP and up
- Windows uptime (аптайм) как узнать?
How to check your computer uptime on Windows 10
On Windows 10, understanding how long a device has been up and running can be useful information in a number of scenarios. For example, when troubleshooting problems, you may want to know if a reboot was recently applied, or if your computer is acting up while working on an important project, and you suspect a restart is required.
Whatever the reason, Windows 10 doesn’t make it obvious to see your system uptime, but it’s not impossible to find either, as you can deduce this information using Task Manager, Control Panel, Command Prompt, and PowerShell.
In this Windows 10 guide, we walk you through four simple ways to check your device uptime without involving scripts or restarting.
How to check PC uptime using Task Manager
Perhaps the easiest way to check your device uptime is using Task Manager with these steps:
- Open Start.
Search for Task Manager and click the top result to open the experience.
Quick Tip: You can also open Task Manager using the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keyboard shortcut, or by right-clicking the taskbar and selecting Task Manager from the menu.
Select the CPU section.
Once you complete these steps, you’ll see your device uptime on the right side, at the bottom of the page.
How to check PC uptime using Control Panel
Another easy way to determine your system uptime is to check your network adapter status with these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Control Panel and click the top result to open the experience.
Click on Network and Internet.
Click on Network and Sharing Center.
Click the Change adapter settings option in the left pane.
Double-click the network adapter connected to the internet.
After completing the steps, you can deduce your computer uptime using the «Duration» information, which indicates the uptime from the network connection that resets every time the device starts. (Of course, these methods work as long as you didn’t reset your network connection since the last time you booted the device.)
How to check PC uptime using Command Prompt
If you want to use Command Prompt to check your device uptime, you have at least two ways to do it.
Using WMIC
To check your computer uptime using Command Prompt, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and click the Run as administrator option.
Type the following command to query the device’s last boot time and press Enter:
wmic path Win32_OperatingSystem get LastBootUpTime
Once you complete these steps, you’ll notice an output that can look intimidating, but it’s not difficult to decode so you can understand your device uptime.
For example, the LastBootUpTime 20181219104602.500000-300 can be broken down using the info below.
- Year: 2018.
- Month: 12.
- Day: 19.
- Hour: 10.
- Minutes: 46.
- Seconds: 02.
- Milliseconds: 500000.
- GMT: -300 (5 hours ahead of GMT).
This means that the computer has been up and running since December 19, 2018, at 10:46 AM. If you want to be more specific, just subtract the last boot time with the current time to deduce the number of days, hours, and minutes the device has been in operation.
Using System Information
You can also see your system uptime with a more user-friendly format using the System Information tool with these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and click the Run as administrator option.
Type the following command to query the device’s last boot time and press Enter:
systeminfo | find «System Boot Time»
Using the System Information tool, you can quickly find out the last time your system rebooted in an easy-to-read format. Also, like the wmic command, you can subtract the last boot time with the current time to determine the number of days, hours, and minutes the device has been running.
How to check PC uptime using PowerShell
It’s also possible to check your device uptime using PowerShell with these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and click the Run as administrator option.
Type the following command to query the device uptime and press Enter:
(get-date) — (gcim Win32_OperatingSystem).LastBootUpTime
After completing these steps, you’ll get the uptime information on a list format with the days, hours, and minutes.
This guide outlines several ways to check your device uptime, but it’s important to note that there are many other methods to find the same information using Command Prompt and PowerShell scripts. However, these are the most straightforward methods.
In addition, while these instructions are focused on Windows 10, these methods have been around for a long time, which means they’ll also work on Windows 8.1 and Windows 7.
More Windows 10 resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10, visit the following resources:
The Dell XPS 15 is our choice for best 15-inch laptop
For a lot of people, a 15-inch laptop is a perfect size that offers enough screen for multitasking, and in a lot of cases, some extra performance from powerful hardware. We’ve rounded up the best of the best at this size.
Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
Halo: The Master Chief Collection is more popular than ever, but some fans don’t agree with the live service approach 343 Industries has taken with it. Here’s why those elements are, at the end of the day, great for the game and for Halo overall.
Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
Microsoft announced this week that it was expanding Surface Duo availability to nine new commercial markets. While Surface Duo is undoubtedly a work in progress, this is not a sign of a disaster. It’s also doesn’t mean that Surface Duo is selling a ton either. Instead, the reason for the expansion is a lot more straightforward.
These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
Instant computer — just add a screen. That’s the general idea behind the ultra-portable PC, but it can be hard to know which one you want. Relax, we have you covered!
How to get the system uptime in Windows? [closed]
Want to improve this question? Update the question so it’s on-topic for Stack Overflow.
Closed 8 years ago .
I am using windows 7 and xp. I want to know the uptime of the system.
What is the command / procedure for getting the uptime?
3 Answers 3
Following are eight ways to find the Uptime in Windows OS.
1: By using the Task Manager
In Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, the Task Manager has been beefed up to show additional information about the system. One of these pieces of info is the server’s running time.
- Right-click on the Taskbar, and click Task Manager. You can also click CTRL + SHIFT + ESC to get to the Task Manager.
- In Task Manager, select the Performance tab.
The current system uptime is shown under System or Performance ⇒ CPU for Win 8/10.
2: By using the System Information Utility
The systeminfo command line utility checks and displays various system statistics such as installation date, installed hotfixes and more. Open a Command Prompt and type the following command:
You can also narrow down the results to just the line you need:
3: By using the Uptime Utility
Microsoft have published a tool called Uptime.exe. It is a simple command line tool that analyses the computer’s reliability and availability information. It can work locally or remotely. In its simple form, the tool will display the current system uptime. An advanced option allows you to access more detailed information such as shutdown, reboots, operating system crashes, and Service Pack installation.
Read the following KB for more info and for the download links:
To use it, follow these steps:
- Download uptime.exe from the above link, and save it to a folder, preferably in one that’s in the system’s path (such as SYSTEM32).
- Open an elevated Command Prompt window. To open an elevated Command Prompt, click Start, click All Programs, click Accessories, right-click Command Prompt, and then click Run as administrator. You can also type CMD in the search box of the Start menu, and when you see the Command Prompt icon click on it to select it, hold CTRL + SHIFT and press ENTER .
- Navigate to where you’ve placed the uptime.exe utility.
- Run the uptime.exe utility. You can add a /? to the command in order to get more options.
It does not offer many command line parameters:
3.1: By using the old Uptime Utility
There is an older version of the «uptime.exe» utility. This has the advantage of NOT needing .NET. (It also has a lot more features beyond simple uptime.)
4: By using the NET STATISTICS Utility
Another easy method, if you can remember it, is to use the approximate information found in the statistics displayed by the NET STATISTICS command. Open a Command Prompt and type the following command:
The statistics should tell you how long it’s been running, although in some cases this information is not as accurate as other methods.
5: By Using the Event Viewer
Probably the most accurate of them all, but it does require some clicking. It does not display an exact day or hour count since the last reboot, but it will display important information regarding why the computer was rebooted and when it did so. We need to look at Event ID 6005, which is an event that tells us that the computer has just finished booting, but you should be aware of the fact that there are virtually hundreds if not thousands of other event types that you could potentially learn from.
Note: BTW, the 6006 Event ID is what tells us when the server has gone down, so if there’s much time difference between the 6006 and 6005 events, the server was down for a long time.
Note: You can also open the Event Viewer by typing eventvwr.msc in the Run command, and you might as well use the shortcut found in the Administrative tools folder.
- Click on Event Viewer (Local) in the left navigation pane.
- In the middle pane, click on the Information event type, and scroll down till you see Event ID 6005. Double-click the 6005 Event ID, or right-click it and select View All Instances of This Event.
- A list of all instances of the 6005 Event ID will be displayed. You can examine this list, look at the dates and times of each reboot event, and so on.
- Open Server Manager tool by right-clicking the Computer icon on the start menu (or on the Desktop if you have it enabled) and select Manage. Navigate to the Event Viewer.
5.1: Eventlog via PowerShell
6: Programmatically, by using GetTickCount64
GetTickCount64 retrieves the number of milliseconds that have elapsed since the system was started.
7: By using WMI
8: The new uptime.exe for Windows XP and up
Like the tool from Microsoft, but compatible with all operating systems up to and including Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016, this uptime utility does not require an elevated command prompt and offers an option to show the uptime in both DD:HH:MM:SS and in human-readable formats (when executed with the -h command-line parameter).
Windows uptime (аптайм) как узнать?
К сожалению, в Операционной системе Windows uptime штатной команды нет как в Unix — системах. Но посмотреть сколько проработал компьютер, или когда он был включен, возможность есть. Опишу несколько способов как узнать в Windows uptime:
1. Через команду systeminfo (самый удобный на мой взгляд способ):
Чтобы ее выполнить, нужно запустить командную строку (для Windows XP: Пуск -> Выполнить -> cmd , для Windows 7: Пуск -> в строке поиска пишем cmd и кликаем на найденный вариант , через горячие клавиши для всех Windows: Win + R cmd ).
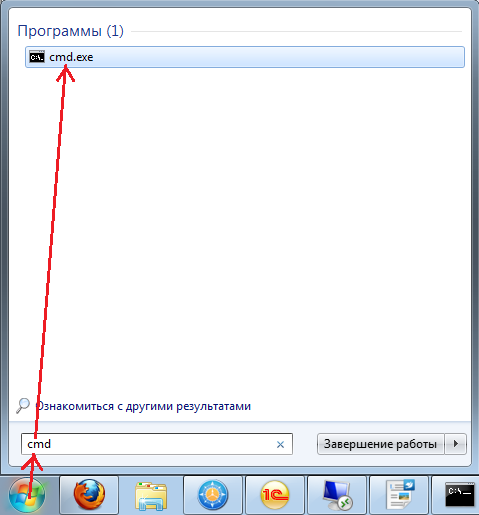

В командной строке запускаем команду systeminfo и где-то среди первых строк результата ищем что-то типа «Время загрузки системы:» («System Boot Time:» ) в Windows 7 , или «Время работы системы:» в Windows XP . В Windows 7 эта команда показывает дату и время когда система загрузилась, а в Windows XP промежуток времени прошедший с момента загрузки.

2. Команда net statistics workstation , или net statistics server , или net stats srv , в первой строке показывает с каких пор снимается статистика;
3. В Windows 7 , в диспетчере задач ( Ctrl + Shift + Esc ), на вкладке «Быстродействие» («Performance» ) ближе к низу есть строка «Время работы» («Up Time») :

Как на все эти данные влияют режимы (спящий и ждущий режим компьютера) не проверено.
Такими простыми действиями мы можем проверить узнать uptime в Windows Xp и Windows 7.














