- Settings¶
- Checklist¶
- Git Extensions¶
- Commit dialog¶
- Appearance¶
- Revision Links¶
- Colors¶
- Start Page¶
- Git Config¶
- Build server integration¶
- Scripts¶
- Hotkeys¶
- Shell Extension¶
- Advanced¶
- Confirmations¶
- Detailed¶
- Browse repository window¶
- Diff Viewer¶
- Plugins¶
- Auto compile SubModules¶
- Periodic background fetch¶
- Create local tracking branches¶
- Delete obsolete branches¶
- Find large files¶
- Gerrit Code Review¶
- GitFlow¶
- Github¶
- Impact Graph¶
- Statistics¶
- Gource¶
- Proxy Switcher¶
- Release Notes Generator¶
- Create Bitbucket Pull Request¶
Settings¶
The settings dialog can be invoked at any time by selecting Settings from the Tools menu option.
The following buttons are always available on any page of the Settings dialog. Sometimes the Cancel button has no effect for the page — this will be noted on the page in the area next to the buttons.
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| OK | Save any entered changes made in any settings page and close the Settings dialog. |
| Cancel | Any entered changes in any settings page are not saved. The Settings dialog is closed. |
| Apply | Any entered changes in any settings page are saved. |
Settings that are specific to Git Extensions and apply globally will be stored in a file called GitExtensions.settings either in the user’s application data path or with the program. The location is dependant on the IsPortable setting in the GitExtensions.exe.config file that is with the program. Settings that are specific to Git Extensions but apply to only the current repository will be stored in a file of the same name, GitExtensions.settings , but in either the root folder of the repository or the .git folder of the repository, depending on whether or not they are distributed with that repository. The settings that are used by Git are stored in the configuration files of Git. The global settings are stored in the file called .gitconfig in the user directory. The local settings are stored in the .git\config file of the repository.
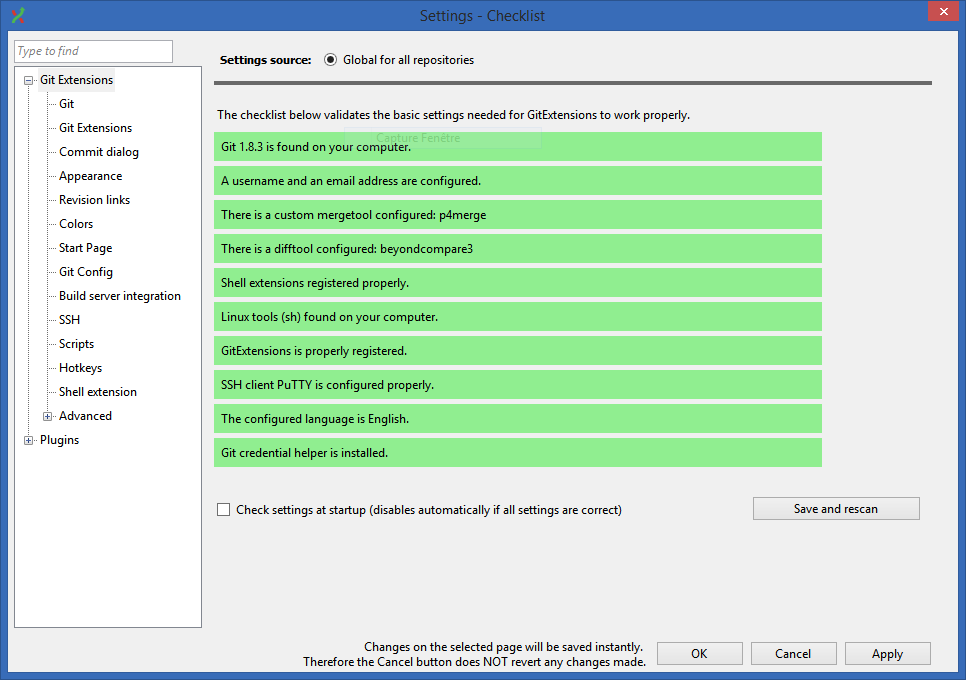
Checklist¶
This page is a visual overview of the minimal settings that Git Extensions requires to work properly. Any items highlighted in red should be configured by clicking on the highlighted item.
This page contains the following settings and buttons.
Check settings at startup ¶
Forces Git Extensions to re-check the minimal set of required settings the next time Git Extensions is started. If all settings are ‘green’ this will be automatically unchecked.
Save and rescan ¶
Saves any setting changes made and re-checks the settings to see if the minimal requirements are now met.
This page contains the settings needed to access git repositories. The repositories will be accessed using external tools. For Windows usually “Git for Windows” or Cygwin are used. Git Extensions will try to configure these settings automatically.
Git ¶ Command used to run git (git.cmd or git.exe) ¶
Needed for Git Extensions to run Git commands. Set the full command used to run git (“Git for Windows” or Cygwin). Use the Browse button to find the executable on your file system.
Path to Linux tools (sh). ¶
A few linux tools are used by Git Extensions. When Git for Windows is installed, these tools are located in the bin directory of Git for Windows. Use the Browse button to find the directory on your file system. Leave empty when it is in the path.
Environment ¶ Change HOME ¶
This button opens a dialog where the HOME directory can be changed.
The global configuration file used by git will be put in the HOME directory. On some systems the home directory is not set or is pointed to a network drive. Git Extensions will try to detect the optimal setting for your environment. When there is already a global git configuration file, this location will be used. If you need to relocate the home directory for git, click the Change HOME button to change this setting. Otherwise leave this setting as the default.
Git Extensions¶
This page contains general settings for Git Extensions.
Performance ¶ Show number of changed files on commit button ¶
When enabled, the number of pending commits are shown on the toolbar as a figure in parentheses next to the Commit button. Git Extensions must be stopped and restarted to activate changes to this option.
Show current working directory changes in revision graph ¶
When enabled, two extra revisions are added to the revision graph. The first shows the current working directory status. The second shows the staged files. This option can cause slowdowns when browsing large repositories.
Use FileSystemWatcher to check if index is changed ¶
Using the FileSystemWatcher to check index state improves the performance in some cases. Turn this off if you experience refresh problems in commit log.
Show stash count on status bar in browse window ¶
When you use the stash a lot, it can be useful to show the number of stashed items on the toolbar. This option causes serious slowdowns in large repositories and is turned off by default.
Check for uncommitted changes in checkout branch dialog ¶
Git Extensions will not allow you to checkout a branch if you have uncommitted changes on the current branch. If you select this option, Git Extensions will display a dialog where you can decide what to do with uncommitted changes before swapping branches.
Limit number of commits that will be loaded in list at start-up ¶
This number specifies the maximum number of commits that Git Extensions will load when it is started. These commits are shown in the Commit Log window. To see more commits than are loaded, then this setting will need to be adjusted and Git Extensions restarted.
Behaviour ¶ Close Process dialog when process succeeds ¶
When a process is finished, close the process dialog automatically. Leave this option off if you want to see the result of processes. When a process has failed, the dialog will automatically remain open.
Show console window when executing git process ¶
Git Extensions uses command line tools to access the git repository. In some environments it might be useful to see the command line dialog when a process is executed. An option on the command line dialog window displayed allows this setting to be turned off.
Use patience diff algorithm ¶
Use the Git ‘patience diff’ algorithm instead of the default. This algorithm is useful in situations where two files have diverged significantly and the default algorithm may become ‘misaligned’, resulting in a totally unusable conflict file.
Include untracked files in stash ¶
If checked, when a stash is performed as a result of any action except a manual stash request, e.g. checking out a new branch and requesting a stash then any files not tracked by git will also be saved to the stash.
Follow renames in file history (experimental) ¶
Try to follow file renames in the file history.
Follow exact renames and copies only ¶
Follow file renames and copies for which similarity index is 100%. That is when a file is renamed or copied and is commited with no changes made to its content.
Open last working dir on startup ¶
When starting Git Extensions, open the last used repository (bypassing the Start Page).
Play Special Startup Sound ¶
Play a sound when starting Git Extensions. It will put you in a good moooooood!
Default clone destination ¶
Git Extensions will pre-fill destination directory input with value of this setting on any form used to perform repository clone.
Revision grid quick search timeout [ms] ¶
The timeout (milliseconds) used for the quick search feature in the revision graph. The quick search will be enabled when you start typing and the revision graph has the focus.
Email settings for sending patches ¶ SMTP server name ¶
SMTP server to use for sending patches.
SMTP port number to use.
Check this box if the SMTP server uses SSL or TLS.
Commit dialog¶
This page contains settings for the Git Extensions Commit dialog.
Behaviour ¶ Provide auto-completion in commit dialog ¶
Enables auto-completion in commit dialog message box. Auto-completion words are taken from the changed files shown by the commit dialog. For each file type there can be configured a regular expression that decides which words should be considered as candidates for auto-completion. The default regular expressions included with Git Extensions can be found here: https://github.com/gitextensions/gitextensions/blob/master/GitExtensions/AutoCompleteRegexes.txt You can override the default regular expressions by creating an AutoCompleteRegexes.txt file in the Git Extensions installation directory.
Show errors when staging files ¶
If an error occurs when files are staged (in the Commit dialog), then the process dialog showing the results of the git command is shown if this setting is checked.
Ensure the second line of commit message is empty ¶
Enforces the second line of a commit message to be blank.
Compose commit messages in Commit dialog ¶
If this is unchecked, then commit messages cannot be entered in the commit dialog. When the Commit button is clicked, a new editor window is opened where the commit message can be entered.
Number of previous messages in commit dialog ¶
The number of commit messages, from the top of the current branch, that will be made available from the Commit message combo box on the Commit dialog.
Remember ‘Amend commit’ checkbox on commit form close ¶
Remembers the state of the ‘Amend commit’ checkbox when the ‘Commit dialog’ is being closed. The remembered state will be restored on the next ‘Commit dialog’ creation. The ‘Amend commit’ checkbox is being unchecked after each commit. So, when the ‘Commit dialog’ is being closed automatically after commiting changes, the ‘Amend commit’ checkbox is going to be unchecked first and its state will be saved after that. Therefore the checked state is remembered only if the ‘Commit dialog’ is being closed by an user without commiting changes.
Show additional buttons in commit button area ¶
Tick the boxes in this sub-group for any of the additional buttons that you wish to have available below the commit button. These buttons are considered additional to basic functionality and have consequences if you should click them accidentally, including resetting unrecorded work.
Appearance¶
This page contains settings that affect the appearance of the application.
General ¶ Show relative date instead of full date ¶
Show relative date, e.g. 2 weeks ago, instead of full date. Displayed on the commit tab on the main Commit Log window.
Show current branch in Visual Studio ¶
Determines whether or not the currently checked out branch is displayed on the Git Extensions toolbar within Visual Studio.
Auto scale user interface when high DPI is used ¶
Automatically resize controls and their contents according to the current system resolution of the display, measured in dots per inch (DPI).
Truncate long filenames ¶
This setting affects the display of filenames in a component of a window e.g. in the Diff tab of the Commit Log window. The options that can be selected are:
- None — no truncation occurs; a horizontal scroll bar is used to see the whole filename.
- Compact — no horizontal scroll bar. Filenames are truncated at both start and end to fit into the width of the display component.
- Trimstart — no horizontal scroll bar. Filenames are truncated at the start only.
- FileNameOnly — the path is always removed, leaving only the name of the file, even if there is space for the path.
Author images ¶ Get author image from gravatar.com ¶
If checked, gravatar will be accessed to retrieve an image for the author of commits. This image is displayed on the commit tab on the main Commit Log window.
The display size of the user image.
The number of days to elapse before gravatar is checked for any changes to an authors image.
No image service ¶
If the author has not set up their own image, then gravatar can return an image based on one of these services.
Clear image cache ¶
Clear the cached avatars.
Fonts ¶ Code font ¶
Change the font used for the display of file contents.
Change the font used on Git Extensions windows and dialogs.
Change the font used for entering a commit message in the Commit dialog.
Language ¶ Language (restart required) ¶
Choose the language for the Git Extensions interface.
Dictionary for spelling checker ¶
Choose the dictionary to use for the spelling checker in the Commit dialog.
Revision Links¶
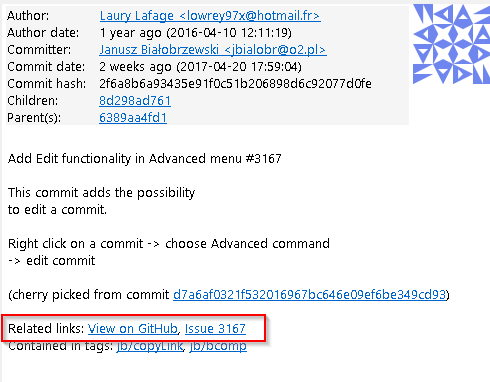
You can configure here how to convert parts of a revision data into clickable links. These links will be located under the commit message on the Commit tab in the Related links section.
The most common case is to convert an issue number given as a part of commit message into a link to the coresponding issue-tracker page. The screenshot below shows an example configuration for GitHub issues.

Lists all the currently defined Categories. Click the Add button to add a new empty Category. The default name is ‘new’. To remove a Category select it and click the Remove button.
This is the Category name used to match the same categories defined on different levels of the Settings.
Indicates whether the Category is enabled or not. Disabled categories are skipped while creating links.
It is possible to use data from remote’s URL to build a link. This way, links can be defined globally for all repositories sharing the same URL schema.
Regex to filter which remotes to use. Leave blank to create links not depending on remotes. If full names of remotes are given then matching remotes are sorted by its position in the given Regex.
Only use the first match ¶
Check if you want to create links only for the first matching remote.
Define whether to search in URL , Push URL or both.
Revision data ¶ Search in ¶
Define which parts of the revision should be searched for matches.
Regular expression used for matching text in the chosen revision parts. Each matched fragment will be used to create a new link. More than one fragment can be used in a single link by using a capturing group. Matches from the Remote data group go before matches from the Revision data group. A capturing group value can be passed to a link by using zero-based indexed placeholders in a link format definition e.g. <0>.
Nested pattern can be used when only a part of the text matched by the Search pattern should be used to format a link. When the Nested pattern is empty, matches found by the Search pattern are used to create links.
List of links to be created from a single match. Each link consists of the Caption to be displayed and the URI to be opened when the link is clicked on. In addition to the standard zero-based indexed placeholders, the %COMMIT_HASH% placeholder can be used to put the commit’s hash into the link. For example: https://github.com/gitextensions/gitextensions/commit/%COMMIT_HASH%
Colors¶
This page contains settings to define the colors used in the application.
Revision graph ¶ Multicolor branches ¶
Displays branch commits in different colors if checked. If unchecked, all branches are shown in the same color. This color can be selected.
Striped branch change ¶
When a new branch is created from an existing branch, the common part of the history is shown in a ‘hatch’ pattern.
Draw branch borders ¶
Outlines branch commits in a black border if checked.
Draw non relatives graph gray ¶
Show commit history in gray for branches not related to the current branch.
Draw non relatives text gray ¶
Show commit text in gray for branches not related to the current branch.
Highlight authored revisions ¶
Highlight all the revisions authored by the same author as the author of the currently selected revision (matched by email). If there is no revision selected, then the current user’s email is used to match revisions to be highlighted.
Color to show tags in.
Color to show branch names in.
Color remote branch ¶
Color to show remote branch names in.
Color other label ¶
Color to show other labels in.
Color authored revisions ¶
Color to show authored revisions in.
Application Icon ¶ Icon style ¶
Change icons. Useful for recognising various open instances.
Changes color of the selected icons.
Difference View ¶ Color removed line ¶
Highlight color for lines that have been removed.
Color added line ¶
Highlight color for lines that have been added.
Color removed line highlighting ¶
Highlight color for characters that have been removed in lines.
Color added line highlighting ¶
Highlight color for characters that have been added in lines.
Highlight color for a section.
Start Page¶
This page allows you to add/remove or modify the Categories and repositories that will appear on the Start Page when Git Extensions is launched. Per Category you can either configure an RSS feed or add repositories. The order of both Categories, and repositories within Categories, can be changed using the context menus in the Start Page. See Start Page for further details.
Lists all the currently defined Categories. Click the Add button to add a new empty Category. The default name is ‘new’. To remove a Category select it and click Remove. This will delete the Category and any repositories belonging to that Category.
This is the Category name displayed on the Start Page.
Specify the type: an RSS feed or a repository.
Enter the URL of the RSS feed.
For each repository defined for a Category, shows the path, title and description. To add a new repository, click on a blank line and type the appropriate information. The contents of the Path field are shown on the Start Page as a link to your repository if the Title field is blank. If the Title field is non-blank, then this text is shown as the link to your repository. Any text in the Description field is shown underneath the repository link on the Start Page.
An RSS Feed can be useful to follow repositories on GitHub for example. See this page on GitHub: https://help.github.com/articles/about-your-profile/. You can also follow commits on public GitHub repositories by:
- In your browser, navigate to the public repository on GitHub.
- Select the branch you are interested in.
- Click on the Commits tab.
- You will find a RSS icon next to the words “Commit History”.
- Copy the link
- Paste the link into the RSS Feed field in the Settings — Start Page as shown above.
Your Start Page will then show each commit — clicking on a link will open your browser and take you to the commit on GitHub.
Git Config¶
This page contains some of the settings of Git that are used by and therefore can be changed from within Git Extensions.
If you change a Git setting from the Git command line using git config then the same change in setting can be seen inside Git Extensions. If you change a Git setting from inside Git Extensions then that change can be seen using git config —get .
Git configuration can be global or local configuration. Global configuration applies to all repositories. Local configuration overrides the global configuration for the current repository.
User name shown in commits and patches.
User email shown in commits and patches.
Editor that git.exe opens (e.g. for editing commit message). This is not used by Git Extensions, only when you call git.exe from the command line. By default Git will use the built in editor.
Merge tool used to solve merge conflicts. Git Extensions will search for common merge tools on your system.
Path to mergetool ¶
Path to merge tool. Git Extensions will search for common merge tools on your system.
Command that Git uses to start the merge tool. Git Extensions will try to set this automatically when a merge tool is chosen. This setting can be left empty when Git supports the mergetool (e.g. kdiff3).
Keep backup (.orig) after merge ¶
Check to save the state of the original file before modifying to solve merge conflicts. Refer to Git configuration setting `mergetool.keepBackup` .
Diff tool that is used to show differences between source files. Git Extensions will search for common diff tools on your system.
Path to difftool ¶
The path to the diff tool. Git Extensions will search for common diff tools on your system.
Command that Git uses to start the diff tool. This setting should only be filled in when Git doesn’t support the diff tool.
Path to commit template ¶
A path to a file whose contents are used to pre-populate the commit message in the commit dialog.
Line endings ¶ Checkout/commit radio buttons ¶
Choose how git should handle line endings when checking out and checking in files. Refer to https://help.github.com/articles/dealing-with-line-endings/#platform-all
Files content encoding ¶
The default encoding for files content.
Build server integration¶
This page allows you to configure the integration with build servers. This allows the build status of each commit to be displayed directly in the revision log, as well as providing a tab for direct access to the Build Server build report for the selected commit.
General ¶ Enable build server integration ¶
Check to globally enable/disable the integration functionality.
Show build status summary in revision log ¶
Check to show a summary of the build results with the commits in the main revision log.
Build server type ¶
Select an integration target.
AppVeyor ¶ Account name ¶
AppVeyor account name. You don’t have to enter it if the projects you want to query for build status are public.
AppVeyor API token. Requiered if the Account name is entered. See https://ci.appveyor.com/api-token
Projects names separated with ‘|’, e.g. gitextensions/gitextensions|jbialobr/gitextensions
Display tests results in build status summary for every build result ¶
Include tests results in the build status summary for every build result.
Display GitHub pull requests builds ¶
Display build status for revisions which GitHub pull requests are based on. If you have fetched revisions from other users’ forks, GitExtensions will show a build status for those revisions for which a build was performed as a part of a pull request’s check.
Token to allow access the GitHub API. You can generate your private token at https://github.com/settings/tokens
Jenkins ¶ Jenkins server URL ¶
Enter the URL of the server (and port, if applicable).
Enter the name of the project which tracks this repository in Jenkins.
TeamCity ¶ TeamCity server URL ¶
Enter the URL of the server (and port, if applicable).
Enter the name of the project which tracks this repository in TeamCity. Multiple project names can be entered separated by the | character.
Build Id Filter ¶
Enter a regexp filter for which build results you want to retrieve in the case that your build project creates multiple builds. For example, if your project includes both devBuild and docBuild you may wish to apply a filter of “devBuild” to retrieve the results from only the program build.
Team Foundation ¶ Tfs server (Name or URL) ¶
Enter the URL of the server (and port, if applicable).
Team collection name ¶ Project name ¶
Enter the name of the project which tracks this repository in Tfs.
Build definition name ¶
Use first found if left empty.
This page allows you to configure the SSH client you want Git to use. Git Extensions is optimized for PuTTY. Git Extensions will show command line dialogs if you do not use PuTTY and user input is required (unless you have configured SSH to use authentication with key instead of password). Git Extensions can load SSH keys for PuTTY when needed.
Specify which ssh client to use ¶ PuTTY ¶
Use PuTTY as SSH client.
Use OpenSSH as SSH client.
Other ssh client ¶
Use another SSH client. Enter the path to the SSH client you wish to use.
Configure PuTTY ¶ Path to plink.exe ¶
Enter the path to the plink.exe executable.
Path to puttygen ¶
Enter the path to the puttygen.exe executable.
Path to pageant ¶
Enter the path to the pageant.exe executable.
Automatically start authentication ¶
If an SSH key has been configured, then when accessing a remote repository the key will automatically be used by the SSH client if this is checked.
Scripts¶
This page allows you to configure specific commands to run before/after Git actions or to add a new command to the User Menu. The top half of the page summarises all of the scripts currently defined. If a script is selected from the summary, the bottom half of the page will allow modifications to the script definition.
A hotkey can also be assigned to execute a specific script. See Hotkeys .
Adds a new script. Complete the details in the bottom half of the screen.
Removes a script.
Changes order of scripts.
The name of the script.
If checked, the script is active and will be performed at the appropriate time (as determined by the On Event setting).
Ask for confirmation ¶
If checked, then a popup window is displayed just before the script is run to confirm whether or not the script is to be run. Note that this popup is not displayed when the script is added as a command to the User Menu (On Event setting is ShowInUserMenuBar).
Run in background ¶
If checked, the script will run in the background and Git Extensions will return to your control without waiting for the script to finish.
Add to revision grid context menu ¶
If checked, the script is added to the context menu that is displayed when right-clicking on a line in the Commit Log page.
If checked, the command is started through a powershell.exe process. If the Run in background is checked, the powershell console is closed after finishing. If not, the powershell console is left for the user to close it manually.
Enter the command to be run. This can be any command that your system can run e.g. an executable program, a .bat script, a Python command, etc. Use the Browse button to find the command to run.
Enter any arguments to be passed to the command that is run. The Help button displays items that will be resolved by Git Extensions before executing the command e.g.
Select when this command will be executed, either before/after certain Git commands, or displayed on the User Menu bar.
Select an icon to be displayed in a menu item when the script is marked to be shown in the user menu bar.
Hotkeys¶
This page allows you to define keyboard shortcuts to actions when specific pages of Git Extensions are displayed. The HotKeyable Items identifies a page within Git Extensions. Selecting a Hotkeyable Item displays the list of commands on that page that can have a hotkey associated with them.
The Hotkeyable Items consist of the following pages
- Commit: the page displayed when a Commit is requested via the Commit User Menu button or the Commands/Commit menu option.
- Browse: the Commit Log page (the page displayed after a repository is selected from the Start Page).
- RevisionGrid: the list of commits on the Commit Log page.
- FileViewer: the page displayed when viewing the contents of a file.
- FormMergeConflicts: the page displayed when merge conflicts are detected that need correcting.
- Scripts: shows scripts defined in Git Extensions and allows shortcuts to be assigned. Refer Scripts .
Hotkey ¶
After selecting a Hotkeyable Item and the Command, the current keyboard shortcut associated with the command is displayed here. To alter this shortcut, click in the box where the current hotkey is shown and press the new keyboard combination.
Click to apply the new keyboard combination to the currently selected Command.
Sets the keyboard shortcut for the currently selected Command to ‘None’.
Reset all Hotkeys to defaults ¶
Resets all keyboard shortcuts to the defaults (i.e. the values when Git Extensions was first installed).
Shell Extension¶
When installed, Git Extensions adds items to the context menu when a file/folder is right-clicked within Windows Explorer. One of these items is Git Extensions from which a further (cascaded) menu can be opened. This settings page determines which items will appear on that cascaded menu and which will appear in the main context menu. Items that are checked will appear in the cascaded menu.
To the right side of the list of check boxes is a preview that shows you how the Git Extensions menu items will be arranged with your current choices.
By default, what is displayed in the context menu also depends on what item is right-clicked in Windows Explorer; a file or a folder (and whether the folder is a Git repository or not). If you want Git Extensions to always include all of its context menu items, check the box Always show all commands .
Advanced¶
This page allows advanced settings to be modified. Clicking on the ‘+’ symbol on the tree of settings will display further settings. Refer Confirmations .
Checkout ¶ Always show checkout dialog ¶
Always show the Checkout Branch dialog when swapping branches. This dialog is normally only shown when uncommitted changes exist on the current branch
Use last chosen «local changes» action as default action. ¶
This setting works in conjunction with the ‘Git Extensions/Check for uncommitted changes in checkout branch dialog’ setting. If the ‘Check for uncommitted changes’ setting is checked, then the Checkout Branch dialog is shown only if this setting is unchecked. If this setting is checked, then no dialog is shown and the last chosen action is used.
General ¶ Don’t show help images ¶
In the Pull, Merge and Rebase dialogs, images are displayed by default to explain what happens with the branches and their commits and the meaning of LOCAL, BASE and REMOTE (for resolving merge conflicts) in different merge or rebase scenarios. If checked, these Help images will not be displayed.
Always show advanced options ¶
In the Push, Merge and Rebase dialogs, advanced options are hidden by default and shown only after you click a link or checkbox. If this setting is checked then these options are always shown on those dialogs.
Check for release candidate versions ¶
Include release candidate versions when checking for a newer version.
Use Console Emulator for console output in command dialogs ¶
Using Console Emulator for console output in command dialogs may be useful the running command requires an user input, e.g. push, pull using ssh, confirming gc.
Auto normalise branch name ¶
Controls whether branch name should be automatically normalised as per git branch naming rules. If enabled, any illegal symbols will be replaced with the replacement symbol of your choice.
Confirmations¶
This page allows you to turn off certain confirmation popup windows.
Don’t ask to confirm to ¶ Amend last commit ¶
If checked, do not display the popup warning about the rewriting of history when you have elected to amend the last committed change.
Commit when no branch is currently checked out ¶
When commiting changes and there is no branch currently being checked out, then GitExtensions warns you and proposes to checkout or create a branch. Enable this option to continue working with no warning.
Apply stashed changes after successful pull ¶
In the Pull dialog, if Auto stash is checked, then any changes will be stashed before the pull is performed. Any stashed changes are then re-applied after the pull is complete. If this setting is checked, the stashed changes are applied with no confirmation popup.
Apply stashed changes after successful checkout ¶
In the Checkout Branch dialog, if Stash is checked, then any changes will be stashed before the branch is checked out. If this setting is checked, then the stashed changes will be automatically re-applied after successful checkout of the branch with no confirmation popup.
Add a tracking reference for newly pushed branch ¶
When you push a local branch to a remote and it doesn’t have a tracking reference, you are asked to confirm whether you want to add such a reference. If this setting is checked, a tracking reference will always be added if it does not exist.
Push a new branch for the remote ¶
When pushing a new branch that does not exist on the remote repository, a confirmation popup will normally be displayed. If this setting is checked, then the new branch will be pushed with no confirmation popup.
Update submodules on checkout ¶
When you check out a branch from a repository that has submodules, you will be asked to update the submodules. If this setting is checked, the submodules will be updated without asking.
If enabled, then when conflicts are detected GitExtensions will start the Resolve conflicts dialog automatically without any prompt.
Commit changes after conflicts have been resolved ¶
Enable this option to start the Commit dialog automatically after all conflicts have been resolved.
Confirm for the second time to abort a merge ¶
When aborting a merge, rebase or other operation that caused conflicts to be resolved, an user is warned about the consequences of aborting and asked if he/she wants to continue. If the user chooses to continue the aborting operation, then he/she is asked for the second time if he/she is sure that he/she wants to abort. Enable this option to skip this second confirmation.
Detailed¶
This page allows detailed settings to be modified. Clicking on the ‘+’ symbol on the tree of settings will display further settings.
Push window ¶ Get remote branches directly from the remote ¶
Git caches locally remote data. This data is updated each time a fetch operation is performed. For a better performance GitExtensions uses the locally cached remote data to fill out controls on the Push dialog. Enable this option if you want GitExtensions to use remote data recieved directly from the remote server.
Merge window ¶ Add log messages ¶
If enabled, then in addition to branch names, git will populate the log message with one-line descriptions from at most the given number actual commits that are being merged. See https://git-scm.com/docs/git-merge#git-merge—logltngt
Browse repository window¶
Enable to move the commit details panel from the tab pages at the bottom of the window to the top right corner.

Show the Console tab in the Browse Repository window.
Console settings ¶ Console style ¶
Choose one of the predefined terminals.
Console font size.
Diff Viewer¶
Remember in the GitExtensions settings the latest chosen value of the ‘Ignore whitespaces’ preference. Use the remembered value the next time GitExtensions is opened.
Remember the ‘Show nonprinting characters’ preference ¶
Remember in the GitExtensions settings the latest chosen value of the ‘Show nonprinting characters’ preference. Use the remembered value the next time GitExtensions is opened.
Remember the ‘Show entire file’ preference ¶
Remember in the GitExtensions settings the latest chosen value of the ‘Show entire file’ preference. Use the remembered value the next time GitExtensions is opened.
Remember the ‘Number of context lines’ preference ¶
Remember in the GitExtensions settings the latest chosen value of the ‘Number of context lines’ preference. Use the remembered value the next time GitExtensions is opened.
Omit uninteresting changes from combined diff ¶
Open Submodule Diff in separate window ¶
If enabled then double clicking on a submodule in the Diff file list opens a new instance of GitExtensions with the submodule as the selectect repository. If disabled, the File history window is opened for the double clicked submodule.
Show file differences for all parents in browse dialog ¶
Enable this option to see diff against each of the revision parents, combined diff including.
Plugins¶
Plugins provide extra functionality for Git Extensions.
Auto compile SubModules¶
This plugin proposes (confirmation required) that you automatically build submodules after they are updated via the GitExtensions Update submodules command.
Enter true to enable the plugin, or false to disable.
Path to msbuild.exe ¶
Enter the path to the msbuild.exe executable.
Enter any arguments to msbuild.
Periodic background fetch¶
Enter the git command and its arguments into the edit box. The default command is fetch —all , which will fetch all branches from all remotes. You can modify the command if you would prefer, for example, to fetch only a specific remote, e.g. fetch upstream .
Fetch every (seconds) ¶
Enter the number of seconds to wait between each fetch. Enter 0 to disable this plugin.
Refresh view after fetch ¶
If checked, the commit log and branch labels will be refreshed after the fetch. If you are browsing the commit log and comparing revisions you may wish to disable the refresh to avoid unexpected changes to the commit log.
Fetch all submodules ¶
If checked, also perform git fetch –all recursively on all configured submodules as part of the periodic background fetch.
Create local tracking branches¶
This plugin will create local tracking branches for all branches on a remote repository. The remote repository is specified when the plugin is run.
Delete obsolete branches¶
This plugin allows you to delete obsolete branches i.e. those branches that are fully merged to another branch. It will display a list of obsolete branches for review before deletion.
Delete obsolete branches older than (days) ¶
Select branches created greater than the specified number of days ago.
Branch where all branches should be merged ¶
The name of the branch where a branch must have been merged into to be considered obsolete.
Find large files¶
Finds large files in the repository and allows you to delete them.
Find large files bigger than (Mb) ¶
Specify what size is considered a ‘large’ file.
Gerrit Code Review¶
The Gerrit plugin provides integration with Gerrit for GitExtensions. This plugin has been based on the git-review tool.
GitFlow¶
The GitFlow plugin provides high-level repository operations for Vincent Driessen’s branching model
Github¶
This plugin will create an OAuth token so that some common GitHub actions can be integrated with Git Extensions.
For more information see: https://github.com/
The token generated and retrieved from GitHub.
Impact Graph¶
This plugin shows in a graphical format the number of commits and counts of changed lines in the repository performed by each person who has committed a change.
Statistics¶
This plugin provides various statistics (and a pie chart) about the current Git repository. For example, number of commits by author, lines of code per language.
Specifies extensions of files that are considered code files.
Directories to ignore (EndsWith) ¶
Ignore these directories when calculating statistics.
Ignore submodules when calculating statistics (true/false).
Gource¶
Gource is a software version control visualization tool.
For more information see: http://gource.io/
Enter the path to the gource software.
Enter any arguments to gource.
Proxy Switcher¶
This plugin can set/unset the value for the http.proxy git config file key as per the settings entered here.
The user name needed to access the proxy.
The password attached to the username.
Proxy Server URL.
Proxy Server port number.
Release Notes Generator¶
This plugin will generate ‘release notes’. This involves summarising all commits between the specified from and to commit expressions when the plugin is started. This output can be copied to the clipboard in various formats.
Create Bitbucket Pull Request¶
If your repository is hosted on Atlassian Bitbucket Server then this plugin will enable you to create a pull request for Bitbucket from Git Extensions
The username required to access Bitbucket.
The password required to access Bitbucket.
Specify the base URL to Bitbucket ¶
The URL from which you will access Bitbucket.
Disable SSL verification ¶
Check this option if you do not require SSL verification to access Bitbucket Server.
Источник