- OpenVAS on Kali GNU/Linux Part 1: How to install OpenVAS
- Installation
- Update packages
- Make sure that haveged is running
- Install Openvas
- Redis
- Run gvm-setup
- Password
- Verify
- Keep your scapdata up-to-date
- Start the openvas services
- First login
- Install OpenVAS (GVM) on Kali 2019
- Install
- Config
- OpenVAS Web Client (Green Security Assistant)
- Task Wizard
- Modify gsad to listen on all interfaces
- OpenVAS Command Line Client (omp or gvm-cli)
- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- How to install Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS) on Kali Linux
- OpenVAS is now renamed Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM)
- Errors when installing and starting GVM, OpenVAS
- How to install OpenVAS (GVM)
- Setting up OpenVAS
- Configuring Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM)
- Conclusion
- Related articles:
- Recommended for you:
- 2 Comments to How to install Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS) on Kali Linux
OpenVAS on Kali GNU/Linux Part 1: How to install OpenVAS
February 28, 2021 6 minute read
OpenVAS is an opensource security scanner it started as a fork of Nessus which went from an opensource project to a closed source scanner.
I always prefer opensource software, for security tools, I even prefer it more… It nice to see/audit where the security data comes from, instead of the “magic” that is used by the close source software.
To scan for missing patches on your systems there are faster/better tools available that can be integrated into your build pipeline more easily. But OpenVAS is still a very nice network security scanner. Relying on one security tool is also not a “best security practice”.
Kali GNU/Linux has become the default Linux distribution for security auditing pen testing, it’s nice to have OpenVAS installed on your Kali GNU/Linux setup. If you just want to have OpenVAS available there is also a (virtual) appliance available from the OpenVAS developers ( Greenbone ).
You’ll find my journey to install OpenVAS on Kali GNU/Linux.
Installation
Update packages
It’s always a good idea to start with an update of your system.
Update the repository database with apt update .
Run apt upgrade to upgrade your packages.
Make sure that haveged is running
During the setup, OpenVAS will create an encryption key to create this key it’s important to have enough random data available. I had an issue (back in 2015) to create this key in the past. For this reason, I always verify that haveged daemon is running on my system when I install OpenVAS.
Install Openvas
Install OpenVAS with apt install openvas .
Redis
OpenVAS comes with its own redis service on Kali GNU/Linux. This redis service is configured to work with OpenVAS correctly.
Run gvm-setup
The openvas-setup setup script has been renamed to gvm-setup . This for marketing reasons, GVM stands for Greenbone Vulnerability Manager. As long the software remains opensource I don’t care.
Gvm-setup will set the PostgreSQL database, create the admin user and download/import all the ScapData.
Password
The gvm-setup script will display the password for the admin at the end. If you forgot to write it down you can reset the admin password with the gvmd command as the _gvm . Unfortunately, you need to use the password as an argument. So it recommended to use a shell without a history or to clear the history (or both) after the password update.
Verify
You can verify your installation with gvm-check-setup .
Keep your scapdata up-to-date
It’s import for a security scanner to keep the security data up to date. A security scanner can only know which software packages have vulnerabilities or how to verify for network exploits when it gets the security data from somewhere. For this reason, vendors must publish security data with OVAL — Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language — for example. This way security scanners can use this data to verify system/network for security issues.
To sync the security feeds on OpenVAS you can use the gvm-feed-update command, this will fetch the security data from Greenbone.
Start the openvas services
There is a gvm-start script, this will start the required services and start the web browser to the openvas login url: https://127.0.0.1:9392. This script needs to be executed as root.
For this reason, I just enable/start the required systemd services.
First login
If you rebooted your system or just started the services, you might need a few minutes to let the services startup.
Источник
Install OpenVAS (GVM) on Kali 2019
In this setup guide, we step through the process of getting OpenVAS (GVM) running on Kali 2019. Installing OpenVAS into a Kali-based system is made much easier by the inclusion of a quick setup script.
When using Kali Linux for OpenVAS scanning, resource usage should always be taken into account. Whether running Kali in a virtual machine or on bare metal, you will want to have sufficient memory and cpu available for the scanner to be optimised for speed (4 cores & 8GB should be a minimum). If you are hoping to run large numbers of parallel scans, then you will need more resources. Several performance tuning options are available in the OpenVAS scanner configuration file to better use the resources you have available. See our OpenVAS tutorial for details on modifying the configuration file.
Install
First step is to install the packages through apt install openvas .
Config
It is then a simple matter of running the configuration script to get OpenVAS configured with required services, user accounts and the latest NVT updates from the Greenbone Community Feed.
The output shown here is a bit daunting, however it is all automated. Assuming all goes well you should soon have a working and up to date OpenVAS installation. The actual time taken for this script will vary depending on download speeds as it is grabbing a fair amount of data for the signatures and CVE data.
By utilising the prebuilt configuration script we can get up and running with OpenVAS in a very short amount of time.
OpenVAS Web Client (Green Security Assistant)
Access the Greenbone Web Client using your web browser. Login with admin and the password in the script output and you will be launching a scan of your target systems within a few minutes.
Lets first check that gsad is running and listening.
Now browse to https://localhost:9392/. The Greenbone Security Assistant is a web portal front end to the GVM and OpenVAS scanner.
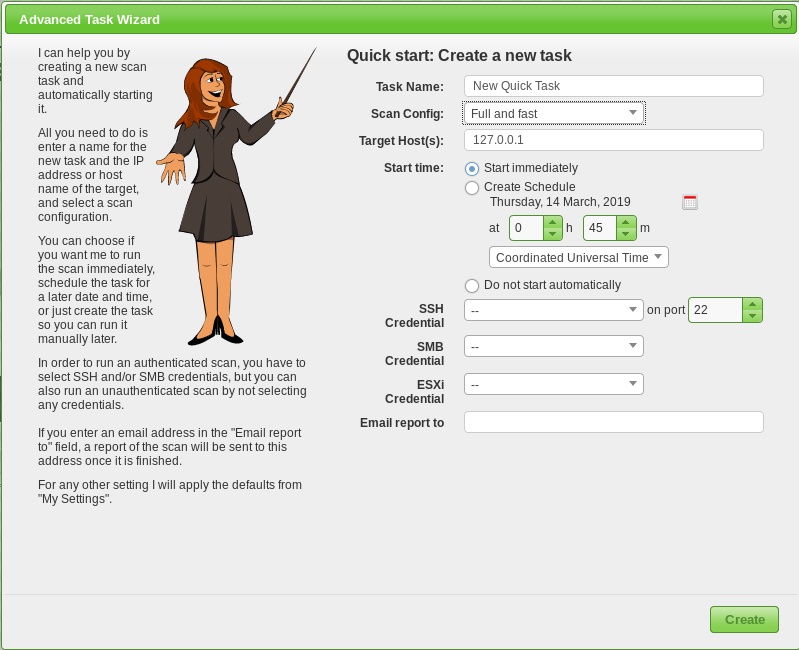
Task Wizard
The quickest way to fire off a scan is using the Task Wizard.
Enter the target and scan profile. Launch. Results are available under the reports option.
Modify gsad to listen on all interfaces
In the netstat output above, we can see that gsad is only listening on localhost . Here is how to change it so you can access the web interface over your local network.
Kali 2019 is using systemd for its services so we have to edit the following file to make the web interface listen on all interfaces.
Now change the 127.0.0.1 to 0.0.0.0 , we also need to add a new parameter to the ExecStart line. This allows remote hosts to connect to our IP address (or hostname). Otherwise, we will get the following error in the browser:
If your IP address is 192.168.1.100 then make the changes as shown below.
Now restart the service and check with netstat or ss .
Looks like we are up and running, now you can access the OpenVAS web interface from any system on your network.
OpenVAS Command Line Client (omp or gvm-cli)
Accessing OpenVAS from the command line is a powerful feature that gives you full control over scan tasks, reports and other management tasks. The current client in Kali is the omp client. Newer versions of GVM will use the gvm-cli command that is part of the gvm-tools package.
Both clients use XML to perform actions on the GVM server. The omp client has a number of command line switches, but the XML is where the real power lies.
# omp —help Usage: omp [OPTION…] — OpenVAS OMP Command Line Interface Help Options: -?, —help Show help options Application Options: -h, —host= Connect to manager on host -p, —port= Use port number -V, —version Print version. -v, —verbose Verbose messages (WARNING: may reveal passwords). —use-certs Use client certificates to authenticate. —client-cert= Client certificate. Default: /usr/var/lib/openvas/CA/clientcert.pem —client-key= Client key. Default: /usr/var/lib/openvas/private/CA/clientkey.pem —client-ca-cert= Client CA certificate. Default: /usr/var/lib/openvas/CA/cacert.pem -u, —username= OMP username -w, —password=
OMP password —config-file= Configuration file for connection parameters. -P, —prompt Prompt to exit. -O, —get-omp-version Print OMP version. -n, —name= Name for create-task. -C, —create-task Create a task. -m, —comment= Comment for create-task. -c, —config= Config for create-task. -t, —target= Target for create-task. -E, —delete-report Delete one or more reports. -D, —delete-task Delete one or more tasks. -R, —get-report Get report of one task. -F, —get-report-formats Get report formats. (OMP 2.0 only) -f, —format=
Источник
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
How to install Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS) on Kali Linux
OpenVAS is now renamed Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM)
When the OpenVAS project was created, it only consisted of a vulnerability scanning engine. Greenbone Networks received funding shortly thereafter to provide professional vulnerability scanning support. Greenbone took over development leadership, added a few software components, and turned OpenVAS into a multi-pronged vulnerability management solution that still retains the value of open and free software.
Over the years, it became apparent that the use of OpenVAS as a trademark for an open source project and funding for almost all of the project’s development had not been appreciated from outside. Therefore, after the release of the OpenVAS 9 platform, it was renamed Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) and released as Greenbone Source Edition (GSE). Since GVM 10, the term OpenVAS is used only for the scanner component, as it was at the beginning of the project.
Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) packages: https://github.com/greenbone
Errors when installing and starting GVM, OpenVAS
During the installation and launch process, I encountered quite a few errors, which, nevertheless, were resolved. Under the assumption that these errors are common to everyone (not just my particular installation), I described these errors right during the installation process, as a result of which the instructions became cluttered.
If during the installation process you do not encounter the described errors, please write about it in the comments – if the errors do not appear for everyone, then I will put them at the very end of the article, due to which, in general, the instruction will become clearer.
How to install OpenVAS (GVM)
Since the authors renamed openvas to gvm (more precisely, divided it into different packages), now the main package is gvm, when it is installed, all other necessary packages will also be obtained as dependencies.
Installation is done like this:
Setting up OpenVAS
Let’s start by setting up the Open Vulnerability Assessment Scanner (OpenVAS) for Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) solution.
It is used in Greenbone Security Manager and is a full-fledged scan engine that performs constantly updated and expanded submissions of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs).
The scanner needs a running Redis server to temporarily store the collected information on the scanned hosts. Configuring the Redis server is done like this (these commands need to be executed once):
Starting the Redis server (must be done after every computer restart):
Or, if you like, add it to startup:
The Greenbone Vulnerability Management (gvmd) service acts as an OSP client to connect to and manage scanners. openvas does not act as an OSP service – you need the OSPD-OpenVAS module for that. Actual user interfaces (like GSA or GVM-Tools) will only interact with gvmd and/or ospd-openvas, not the scanner. You can run openvas to load plugins in Redis using the following command:
but ospd-openvas will update automatically.
Please note that although you can run openvas as a non-elevated user, it is recommended that you run openvas as root because some network vulnerability tests (NVTs) require root privileges to perform certain operations, such as package spoofing. If you run openvas as a user without permission to perform these operations, the scan results are likely to be incomplete.
Since openvas will be launched from the ospd-openvas process using sudo, the following configuration is required in the sudoers file:
add this line to allow the user running ospd-openvas to run openvas as root
Replace USERNAME with your Linux username.
You can find out the username with the command:
If something does not work, then you can view the log with the command:
Configuring Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM)
Greenbone Vulnerability Manager is the central management service between security scanners and user clients.
It manages the storage of any vulnerability management configuration and scan results. Data, control commands, and workflows are accessed through the XML-based Greenbone Management Protocol (GMP). Scanners such as OpenVAS are controlled through the Open Scanner Protocol (OSP).
Deployment script (instead of openvas-setup):
This script needs to be run only once.
The script ended with an error:
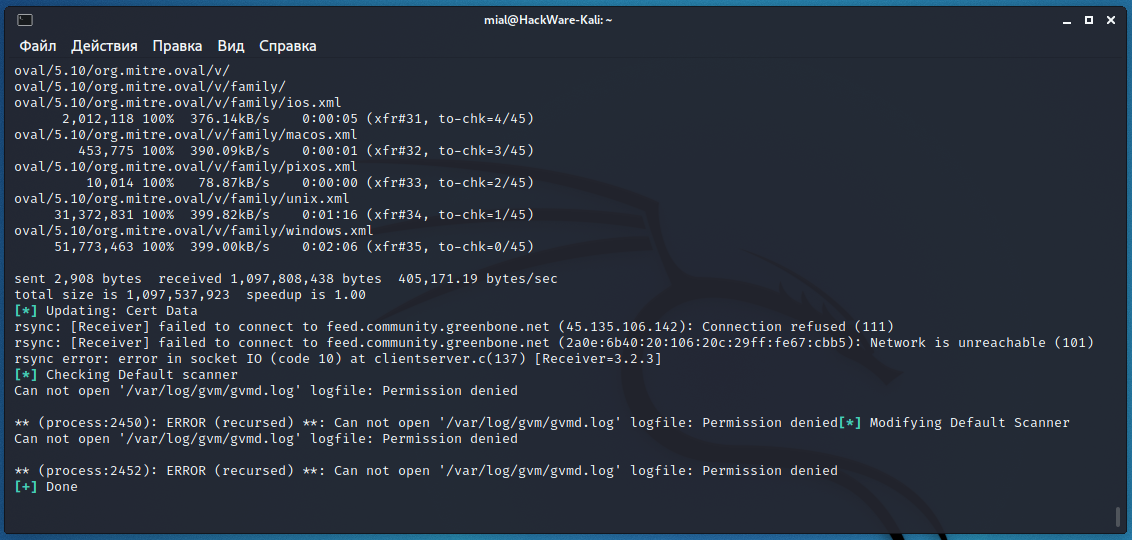
also showed an error in the fourth step:
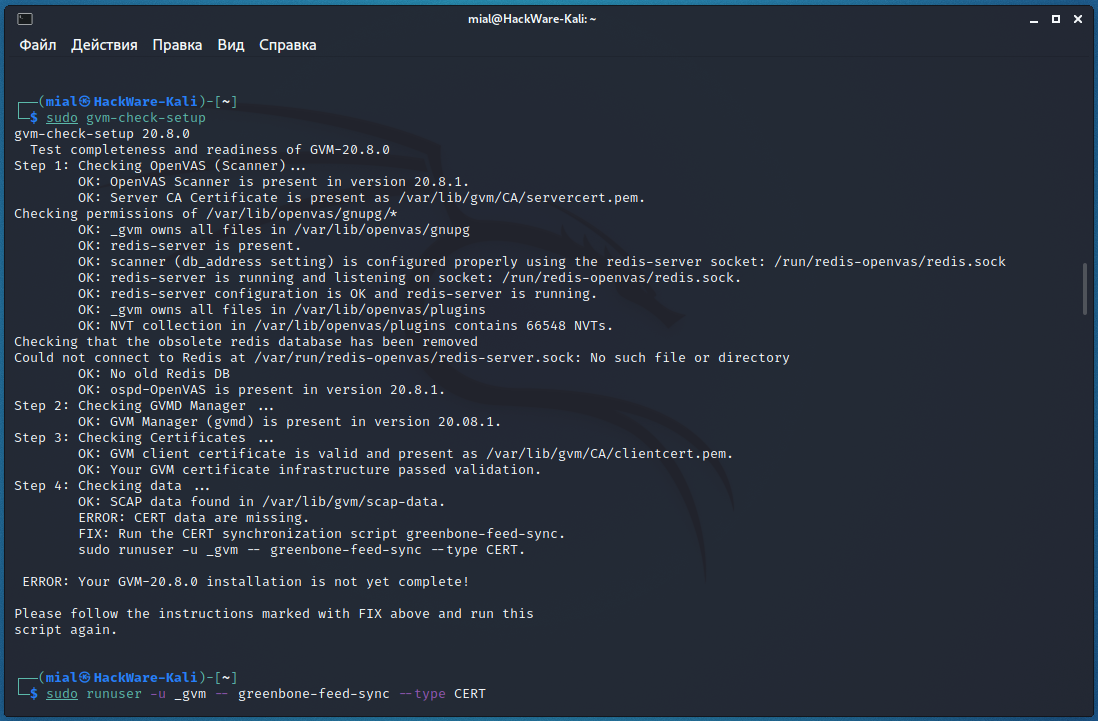
To fix the error “ERROR: CERT data are missing. FIX: Run the CERT synchronization script greenbone-feed-sync” run the following command:
Re-running the check showed an error at the fifth step:

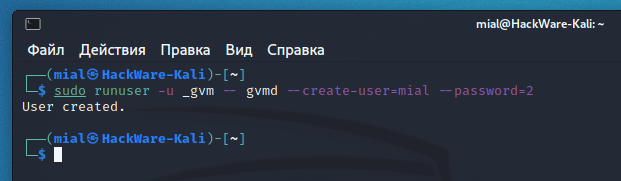
There are several errors at once, but the key one is “ERROR: No users found. You need to create at least one user to log in.”, To fix it, run a command like this:
For example, to create a user named mial and password 2:
The previous command failed:
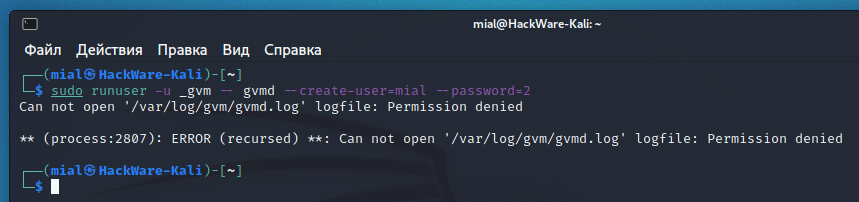
The essence of the error is that the command does not have enough permissions to write to the /var/log/gvm/gvmd.log file, even though the previous command was run with sudo. To fix the error, run the following command:
Then run the new user creation again.
And one more mistake at the seventh step:
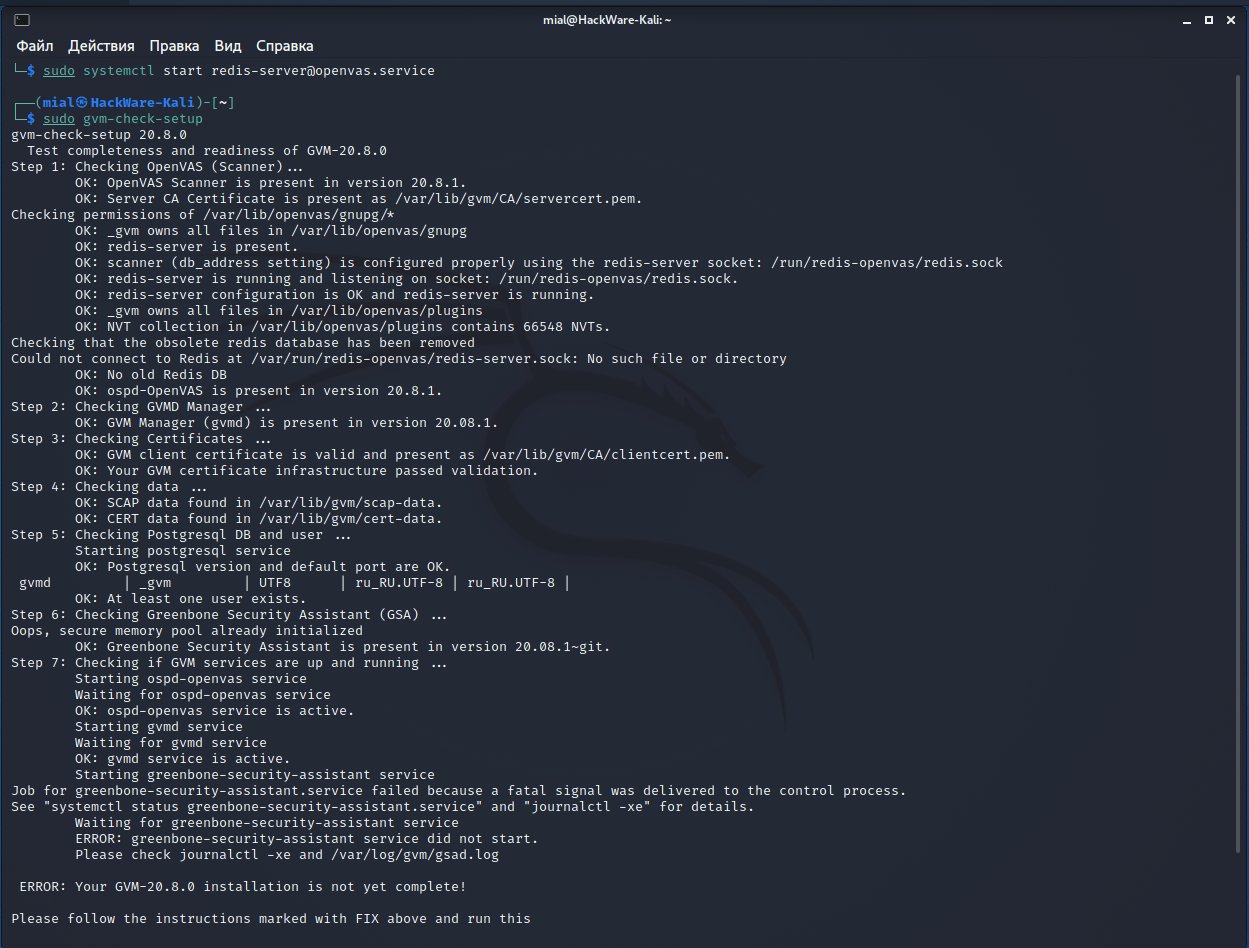
I don’t know how to solve it completely, but I know how to get around it.
Let’s move on to starting the necessary services.
Do not forget that before starting the service you need to start the Redis server, that is, type following before executing the primary command:
Main service start:
And we get the following:

The essence of the messages is that everything started fine, except for the greenbone-security-assistant, that is, gsa, that is, Web UI (Greenbone Security Assistant), that is, the web interface.
You can see the contents of the log file:
https daemon failed to start .
gsad has a —http-only option which only runs HTTP without HTTPS. Let’s use it:
Again, the next message will be displayed that something is wrong:
However, the web interface is now available at http://127.0.0.1:9392 (but not available at https://127.0.0.1:9392!).
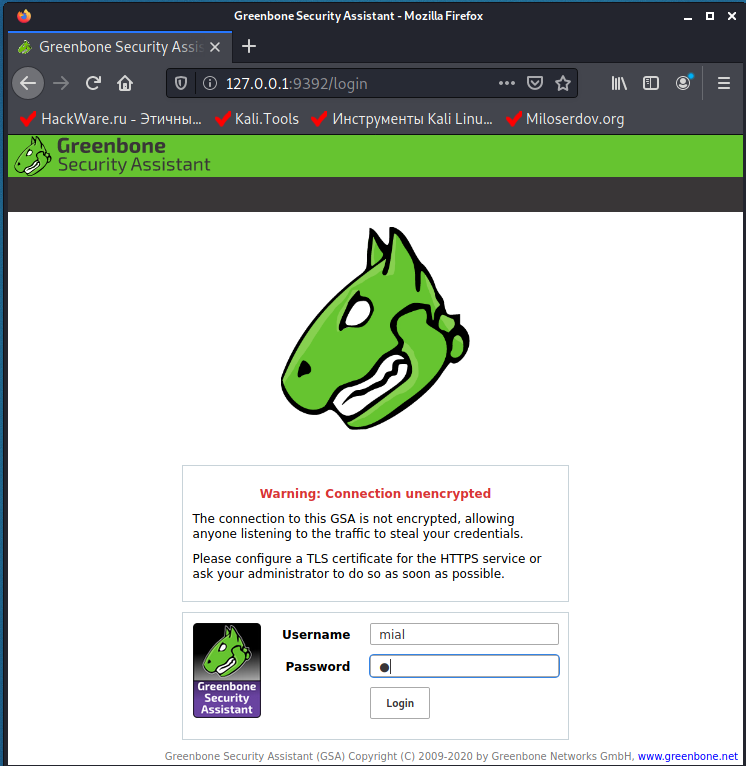
Log in using the credentials that you came up with when creating a new user.
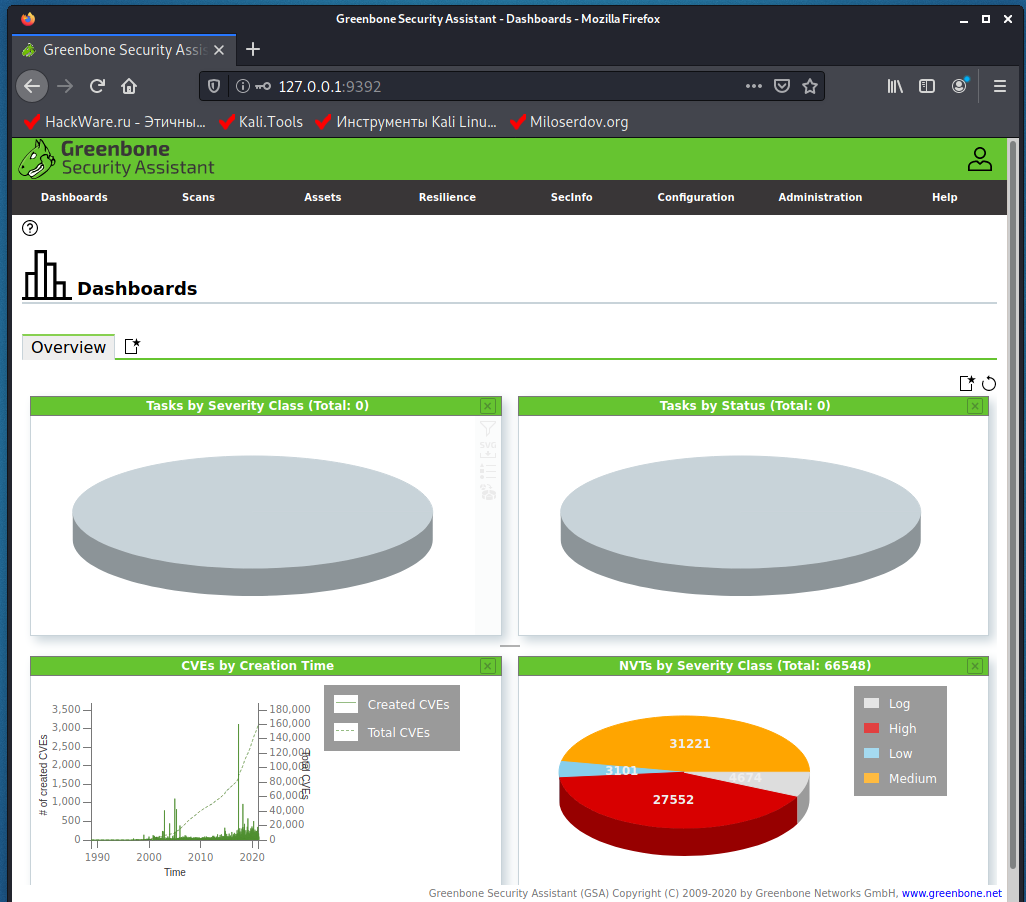
To stop the service:
In the future, sometimes run the command to update signatures:
If something does not work, then you can view the log with the command:
Conclusion
One of the following instructions will be devoted to how to work in Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS).
And do not forget to write – have you encountered the described errors during installation?
Related articles:
- Default passwords in Kali Linux (100%)
- Kali Linux Rolling post install tips (51.2%)
- How to install OWASP Mutillidae II and Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) in Kali Linux (51.2%)
- How to install and run VLC, Google Chrome, and Chromium on Kali Linux (51.2%)
- How to update Kali Linux (51.2%)
- How to install Java (JDK) on Windows and Linux (RANDOM — 50%)
Recommended for you:
2 Comments to How to install Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS) on Kali Linux
I found feed status are «update in progress» and «scap database is required» on my Open VAS GVM platform.I have tried may option to update feeds but notings works.
This is log OPEN VAS:
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 06h52.30 utc:5664: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 09h04.08 utc:1213: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 09h48.54 utc:1297: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 10h09.17 utc:1168: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 13h05.31 utc:1220: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 13h23.30 utc:1159: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 13h55.51 utc:1148: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 15h45.48 utc:1197: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 17h46.23 utc:1712: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 18h09.25 utc:1194: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-13 15h31.07 utc:1204: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h31.17 utc:2876: redis_find: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h31.17 utc:2876: get_redis_ctx: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h31.17 utc:2876: get_redis_ctx: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h37.41 utc:3412: redis_find: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h37.41 utc:3412: get_redis_ctx: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h37.41 utc:3412: get_redis_ctx: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-13 16h25.01 utc:3395: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109131026
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-13 16h34.58 utc:1214: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109131026
Hi! thanks for the tutorial!
on «sudo gvm-setup» i get this:
rsync: [generator] failed to set permissions on «/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2014/gb_fedora_2014_5004_httpd_fc19.nasl»: Function not implemented (38)
rsync: [generator] failed to set permissions on «/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2014/gb_fedora_2014_5006_json-c_fc20.nasl»: Function not implemented (38)
rsync: [generator] failed to set permissions on «/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2014/gb_fedora_2014_5015_elfutils_fc20.nasl»: Function not implemented (38)
Источник