- 10 Commands to Collect System and Hardware Info in Linux
- 1. How to View Linux System Information
- 2. How to View Linux System Hardware Information
- 3. How to View Linux CPU Information
- 4. How to Collect Linux Block Device Information
- 5. How to Print USB Controllers Information
- 6. How to Print PCI Devices Information
- 7. How to Print SCSI Devices Information
- 8. How to Print Information about SATA Devices
- 9. How to Check Linux File System Information
- 10. How to Check Linux Hardware Components Info
- Summary
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux
- Hardware information
- 1. lscpu
- 2. lshw — List Hardware
- 3. hwinfo — Hardware Information
- 4. lspci — List PCI
- 5. lsscsi — List scsi devices
- 6. lsusb — List usb buses and device details
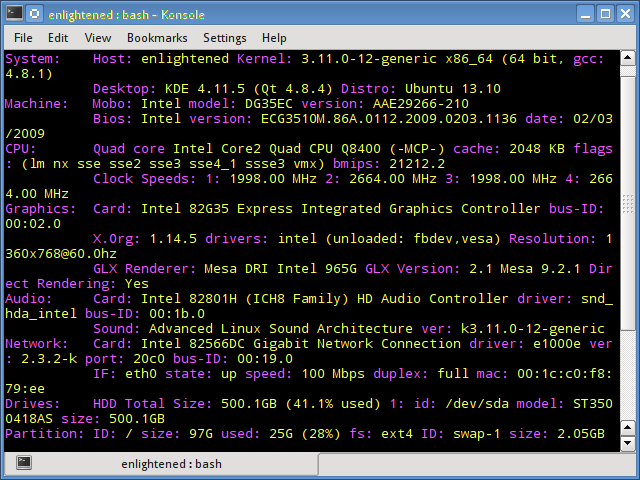
- 7. Inxi
- 8. lsblk — List block devices
- 9. df — disk space of file systems
- 10. Pydf — Python df
- 11. fdisk
- 12. mount
- 13. free — Check RAM
- 14. dmidecode
- 15. /proc files
- 16. hdparm
- Summary
- 48 thoughts on “ 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux ”
- How to Display Linux Hardware Info via Command Line
- 1. lshw
- 2. Inxi
- 3. hwinfo
- 4. lscpu
- 5. lsscsi
- 6. lsblk
- 7. lsusb
- 8. lspci
- 9. Using dmesg
- 10. Using dmidecode command
- 11. hdparm
- 12. From /proc file
- 13. free
- Conclusion
10 Commands to Collect System and Hardware Info in Linux
It is always a good practice to know the hardware components of your Linux system is running on, this helps you to deal with compatibility issues when it comes to installing packages, drivers on your system using yum, dnf, or apt.

Therefore in these tips and tricks series, we shall look at some useful commands that can help you to extract information about your Linux system and hardware components.
1. How to View Linux System Information
To know only the system name, you can use the uname command without any switch that will print system information or the uname -s command will print the kernel name of your system.
To view your network hostname, use the ‘-n’ switch with the uname command as shown.
To get information about kernel-version, use the ‘-v’ switch.
To get the information about your kernel release, use the ‘-r’ switch.
To print your machine hardware name, use the ‘-m’ switch:
All this information can be printed at once by running the ‘uname -a’ command as shown below.
2. How to View Linux System Hardware Information
Here you can use the lshw tool to gather vast information about your hardware components such as cpu, disks, memory, usb controllers, etc.
lshw is a relatively small tool and there are few options that you can use with it while extracting information. The information provided by lshw was gathered from different /proc files.
Note: Do remember that the lshw command is executed by the superuser (root) or sudo user.
To print information about your Linux system hardware, run this command.
You can print a summary of your hardware information by using the -short option.
If you wish to generate output as an html file, you can use the option -html.

3. How to View Linux CPU Information
To view information about your CPU, use the lscpu command as it shows information about your CPU architecture such as a number of CPUs, cores, CPU family model, CPU caches, threads, etc from sysfs and /proc/cpuinfo.
4. How to Collect Linux Block Device Information
Block devices are storage devices such as hard disks, flash drives, etc. lsblk command is used to report information about block devices as follows.
If you want to view all block devices on your system then include the -a option.
5. How to Print USB Controllers Information
The lsusb command is used to report information about USB controllers and all the devices that are connected to them.
You can use the -v option to generate detailed information about each USB device.
6. How to Print PCI Devices Information
PCI devices may include usb ports, graphics cards, network adapters, etc. The lspci tool is used to generate information concerning all PCI controllers on your system plus the devices that are connected to them.
To print information about PCI devices run the following command.
Use the -t option to produce output in a tree format.
Use the -v option to produce detailed information about each connected device.
7. How to Print SCSI Devices Information
To view all your scsi/sata devices, use the lsscsi command as follows. If you do not have the lsscsi tool installed, run the following command to install it.
After installation, run the lsscsi command as shown:
Use the -s option to show device sizes.
8. How to Print Information about SATA Devices
You can find some information about sata devices on your system as follows using the hdparm utility. In the example below, I used the block device /dev/sda1 which is the hard disk on my system.
To print information about device geometry in terms of cylinders, heads, sectors, size, and the starting offset of the device, use the -g option.
9. How to Check Linux File System Information
To gather information about file system partitions, you can use the fdisk command. Although the main functionality of the fdisk command is to modify file system partitions, it can also be used to view information about the different partitions on your file system.
You can print partition information as follows. Remember to run the command as a superuser or else you may not see any output.
10. How to Check Linux Hardware Components Info
You can also use the dmidecode utility to extract hardware information by reading data from the DMI tables.
To print information about memory, run this command as a superuser.
To print information about the system, run this command.
To print information about BIOS, run this command.
To print information about the processor, run this command.
Summary
There are many other ways you can use to obtain information about your system hardware components. Most of these commands use files in the /proc directory to extract system information.
Hope you find these tips and tricks useful and remember to post a comment in case you want to add more information to this or if you face any difficulties in using any of the commands. Remember to always stay connected to Tecmint.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux
Hardware information
Like for every thing, there are plenty of commands to check information about the hardware of your linux system.
Some commands report only specific hardware components like cpu or memory while the rest cover multiple hardware units.
This post takes a quick look at some of the most commonly used commands to check information and configuration details about various hardware peripherals and devices.
The list includes lscpu, hwinfo, lshw, dmidecode, lspci etc.
1. lscpu
The lscpu command reports information about the cpu and processing units. It does not have any further options or functionality.
2. lshw — List Hardware
A general purpose utility, that reports detailed and brief information about multiple different hardware units such as cpu, memory, disk, usb controllers, network adapters etc. Lshw extracts the information from different /proc files.
Check out the following post to learn more about lshw
3. hwinfo — Hardware Information
Hwinfo is another general purpose hardware probing utility that can report detailed and brief information about multiple different hardware components, and more than what lshw can report.
4. lspci — List PCI
The lspci command lists out all the pci buses and details about the devices connected to them.
The vga adapter, graphics card, network adapter, usb ports, sata controllers, etc all fall under this category.
Filter out specific device information with grep.
5. lsscsi — List scsi devices
Lists out the scsi/sata devices like hard drives and optical drives.
6. lsusb — List usb buses and device details
This command shows the USB controllers and details about devices connected to them. By default brief information is printed. Use the verbose option «-v» to print detailed information about each usb port
On the above system, 1 usb port is being used by the mouse.
7. Inxi
Inxi is a 10K line mega bash script that fetches hardware details from multiple different sources and commands on the system, and generates a beautiful looking report that non technical users can read easily.
8. lsblk — List block devices
List out information all block devices, which are the hard drive partitions and other storage devices like optical drives and flash drives
9. df — disk space of file systems
Reports various partitions, their mount points and the used and available space on each.
10. Pydf — Python df
An improved df version written in python, that displays colored output that looks better than df
11. fdisk
Fdisk is a utility to modify partitions on hard drives, and can be used to list out the partition information as well.
12. mount
The mount is used to mount/unmount and view mounted file systems.
Again, use grep to filter out only those file systems that you want to see
13. free — Check RAM
Check the amount of used, free and total amount of RAM on system with the free command.
14. dmidecode
The dmidecode command is different from all other commands. It extracts hardware information by reading data from the SMBOIS data structures (also called DMI tables).
Check out the man page for more details.
15. /proc files
Many of the virtual files in the /proc directory contain information about hardware and configurations. Here are some of them
16. hdparm
The hdparm command gets information about sata devices like hard disks.
Summary
Each of the command has a slightly different method of extracting information, and you may need to try more than one of them, while looking for specific hardware details. However they are available across most linux distros, and can be easily installed from the default repositories.
On the desktop there are gui tools, for those who do not want to memorise and type commands. Hardinfo, I-nex are some of the popular ones that provide detailed information about multiple different hardware components.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
48 thoughts on “ 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux ”
How i can check memory in CPU. Example OPT, Efuse
Thanks for this. I’m just getting going on a VPS and this helped me discover they’d not given me the extra 1Gb I ordered. Very well explained.
Super happy with
inxi -Fx
more accurate than some of the other utilities.. for instance hwinfo was inaccurate for my Lenovo
Thanks for the great post!
Thank you! Your descriptions were useful and well explained!
Источник
How to Display Linux Hardware Info via Command Line
When a user works on a Linux system, in some cases, the user needs to know the information about the hardware under the operating system. This helps us to install compatible applications and utilities which adapt to hardware components of the system.
This tutorial will go through many utilities with detailed explanations of how to get the Linux hardware information.
1. lshw
The lshw stands for List Hardware. It collects the detailed information of the hardware on your system. lshw can show you the name of mainboard, CPU information, bus speed and firmware version and more.
In order to display the information of all the hardware components, run:
If you want to shorten the result, run the command with -short option:
You will receive the brief list of hardware components on your Linux system:
Display disk properties and storage device properties on Linux system by running:
You can get the brief result you may use the option -short :
This tool is also available in a GTK graphical version:
2. Inxi
Inxi is a powerful feature-rich command line tool for Linux users when they want to get the information of system hardware, CPU, RAM, Graphics card, drivers, battery, kernel, process information, and more.
By default, Inxi is not pre-installed on Linux. In order to use it, install the inxi package by running the following command:
Running inxi without any option:
The command will return the information of CPU and Memory as follows:
In order to get the graphics info, run the following command:
To show audio/sound card information, run:
To show battery data, charge, condition, plus extra information (if battery present), run the command with -B option:
3. hwinfo
The hwinfo command is a powerful tool for Linux users to get the detail of hardware components of system. It helps you collect almost of information about: CPU, USB controller, graphics controller, network devices and more.
You can use hwinfo command with —short and —devicetype options to list a specific type of information.
Display information about NIC cards and find out what eth0, eth1 stands for by running:
In order to display storage information with hwinfo command, run:
Likewise, to display list of partitions and hard disks, run the following command:
4. lscpu
The lscpu will show you all the information of your CPU such as number of CPUs, cores, threads, sockets and CPU family, caches, model and more.
You can get the detail of the CPU by running the following command:
The output of the command will be something likes this:
Moreover, if you want to view the speed of the CPU in MHz, run the command:
5. lsscsi
The lsscsi is used to list all of the SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) devices and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory express) devices on your machine.
By default, the lsscsi is not pre-installed on Ubuntu, run the following command to install:
You can simply use the command by running:
6. lsblk
The lsblk command will show you the details of all the block devices in a tree format. It gathers information from sysfs filesystem and udev database.
In order to list all of block devices and their partitions and sizes, let’s run the following command:
7. lsusb
The lsusb is a powerful tool for displaying all the information about USB devices connected to USB buses of your Linux system. The information contains: speed, class, vendor id, product id, bus of USB devices etc.
You can run the following command to get brief information:
If you want to display the specified device with Bus and Device number, run the command with ‘-s’ option. For example:
8. lspci
This standard Linux utility shows what your systems have got internally. The command is a combination of ls, the standard command to list files and PCI that is for the peripheral connection. You can also expect your results to include AGP and onboard components like your USB chipset.
The command is much helpful in diagnosing bugs related to PCI devices. Using ‘-t’ option of lspci command you can see PCI layout in a tree format.
In order to get more detailed information, use -v option with -t option:
You can just run lspci command to display basic device information:
9. Using dmesg
The dmesg command is useful to find out some info about hardware events. It displays the contents of the system log.
The following command lists all references to universal serial bus devices:
In order to display the details about physical memory that is RAM, run:
10. Using dmidecode command
Dmidecode stands for Desktop Management Interface decode, it is a powerful tool for retrieving the information of CPU, RAM, serial numbers, BIOS. The command will show you the hardware details in a human-readable format.
In order to get the Information about BIOS, run:
If you want to display the hardware components information by ID, run the command with -t option following by a number ID (DMI).
For example, the following command will show you the information of memory Device:
11. hdparm
The hdparm stands for Hard Disk Parameter. It’s a Linux command line utility used for handling hard disk devices. You can also use hdparm command to set parameters such as power management, sleep mode, drive caches, Direct Memory Access settings, etc.
For instance, in order to display information of the hard disk, run the following command:
Another example, you can use hdparm to test the speed of hard disk by running the following command:
12. From /proc file
The /proc directory contains lots of system and hardware information. You can try the following commands to get more info on devices:
The output of the command will be something likes this:
In addition, you can run some other commands in order to get information about CPU, Memory, and PCI devices respectively.
13. free
Sometimes, you want to know whether the free memory (RAM) is enough to launch or install a new program? In this case, you can use free command to get information about memory detail in your Linux system.
The free command not only shows you information about the total amount of physical RAM and swap but also free and used memory. For example:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to use Linux command line to get information about the hardware components of the system.
Thanks for reading and please leave your suggestion in the below comment section.
Источник