- Linux List Processes – How to Check Running Processes
- Prerequisites
- A Quick Introduction to Linux Processes
- How to List Running Processes in Linux using the ps Command
- How to List Running Processes in Linux using the top and htop Commands
- How to Kill Running Processes in Linux
- Conclusion
- How to check running process in Linux using command line
- Check running process in Linux
- How to manage processes from the Linux terminal
- Linux pgrep command
- Linux top command
- Linux htop command to check running process in Linux
- Linux kill command
- Linux pkill command
- Linux killall command
- Linux nice and renice command
- How to List Running Processes in Linux: A Beginner’s Guide
- Introduction to Linux Processes
- How to List Running Processes in Linux?
- Utilizing the “ps” Command
- Using the “top” Command
- Running “htop” Command
- Conclusion
Linux List Processes – How to Check Running Processes
Every day, developers use various applications and run commands in the terminal. These applications can include a browser, code editor, terminal, video conferencing app, or music player.
For each of these software applications that you open or commands you run, it creates a process or task.
One beautiful feature of the Linux operating system and of modern computers in general is that they provide support for multitasking. So multiple programs can run at the same time.
Have you ever wondered how you can check all the programs running on your machine? Then this article is for you, as I’ll show you how to list, manage, and kill all the running processes on your Linux machine.
Prerequisites
- A Linux distro installed.
- Basic knowledge of navigating around the command-line.
- A smile on your face 🙂
A Quick Introduction to Linux Processes
A process is an instance of a running computer program that you can find in a software application or command.
For example, if you open your Visual Studio Code editor, that creates a process which will only stop (or die) once you terminate or close the Visual Studio Code application.
Likewise, when you run a command in the terminal (like curl ifconfig.me ), it creates a process that will only stop when the command finishes executing or is terminated.
How to List Running Processes in Linux using the ps Command
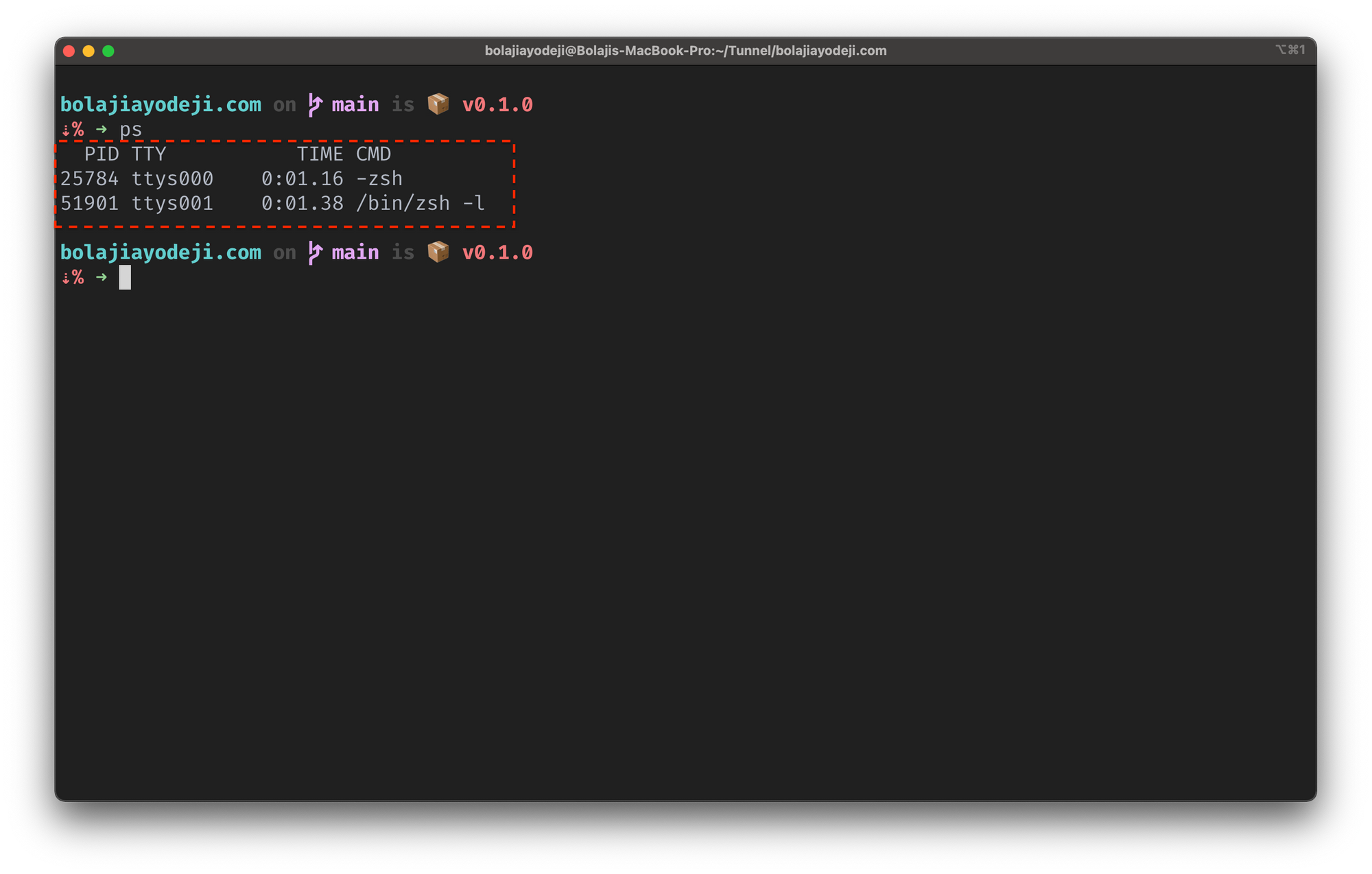
You can list running processes using the ps command (ps means process status). The ps command displays your currently running processes in real-time.
To test this, just open your terminal and run the ps command like so:
This will display the process for the current shell with four columns:
- PID returns the unique process ID
- TTY returns the terminal type you’re logged into
- TIME returns the total amount of CPU usage
- CMD returns the name of the command that launched the process.
You can choose to display a certain set of processes by using any combination of options (like -A -a , -C , -c , -d , -E , -e , -u , -X , -x , and others).
If you specify more than one of these options, then all processes which are matched by at least one of the given options will be displayed.
Type man ps in your terminal to read the manual for the ps command, which has a complete reference for all options and their uses.
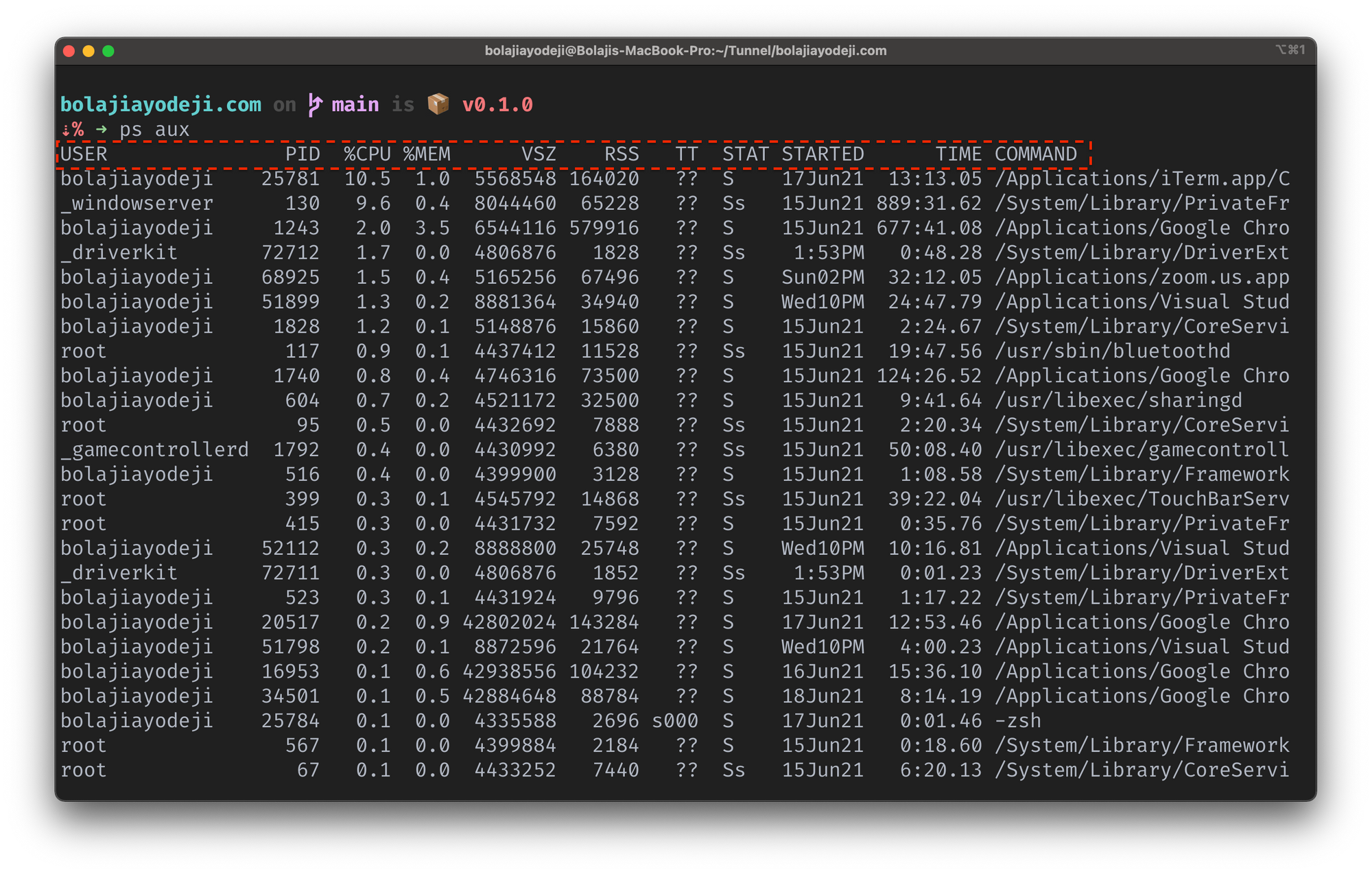
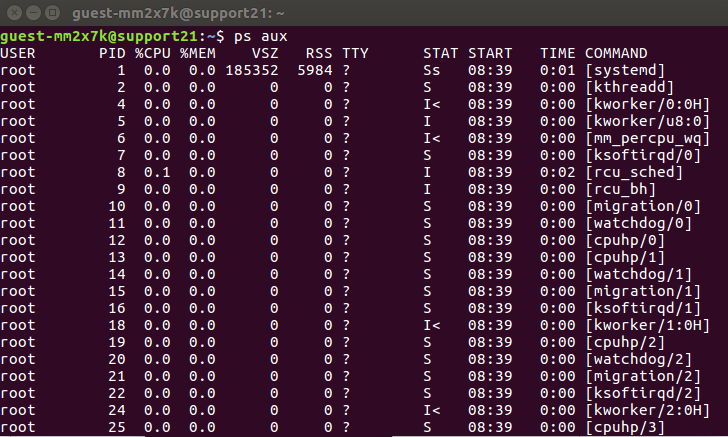
To display all running processes for all users on your machine, including their usernames, and to show processes not attached to your terminal, you can use the command below:
Here’s a breakdown of the command:
- ps : is the process status command.
- a : displays information about other users’ processes as well as your own.
- u : displays the processes belonging to the specified usernames.
- x : includes processes that do not have a controlling terminal.
This will display the process for the current shell with eleven columns:
- USER returns the username of the user running the process
- PID returns the unique process ID
- %CPU returns the percentage of CPU usage
- %MEM returns the percentage memory usage
- VSV returns the virtual size in Kbytes
- RSS returns the resident set size
- TT returns the control terminal name
- STAT returns the symbolic process state
- STARTED returns the time started
- CMD returns the command that launched the process.
How to List Running Processes in Linux using the top and htop Commands
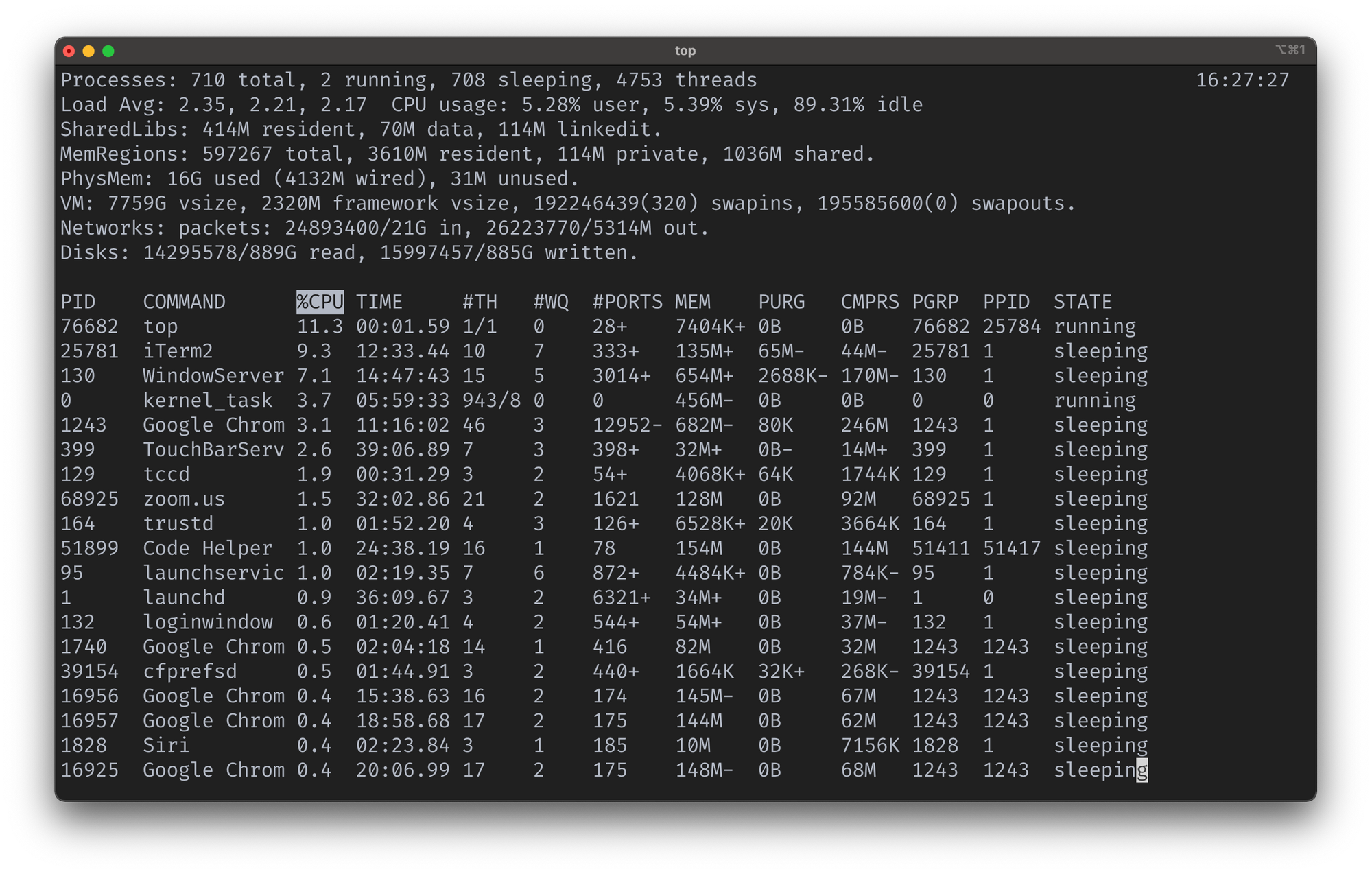
You can also use the top task manager command in Linux to see a real-time sorted list of top processes that use the most memory or CPU.
Type top in your terminal and you’ll get a result like the one you see in the screenshot below:
You can type q to exit the session.
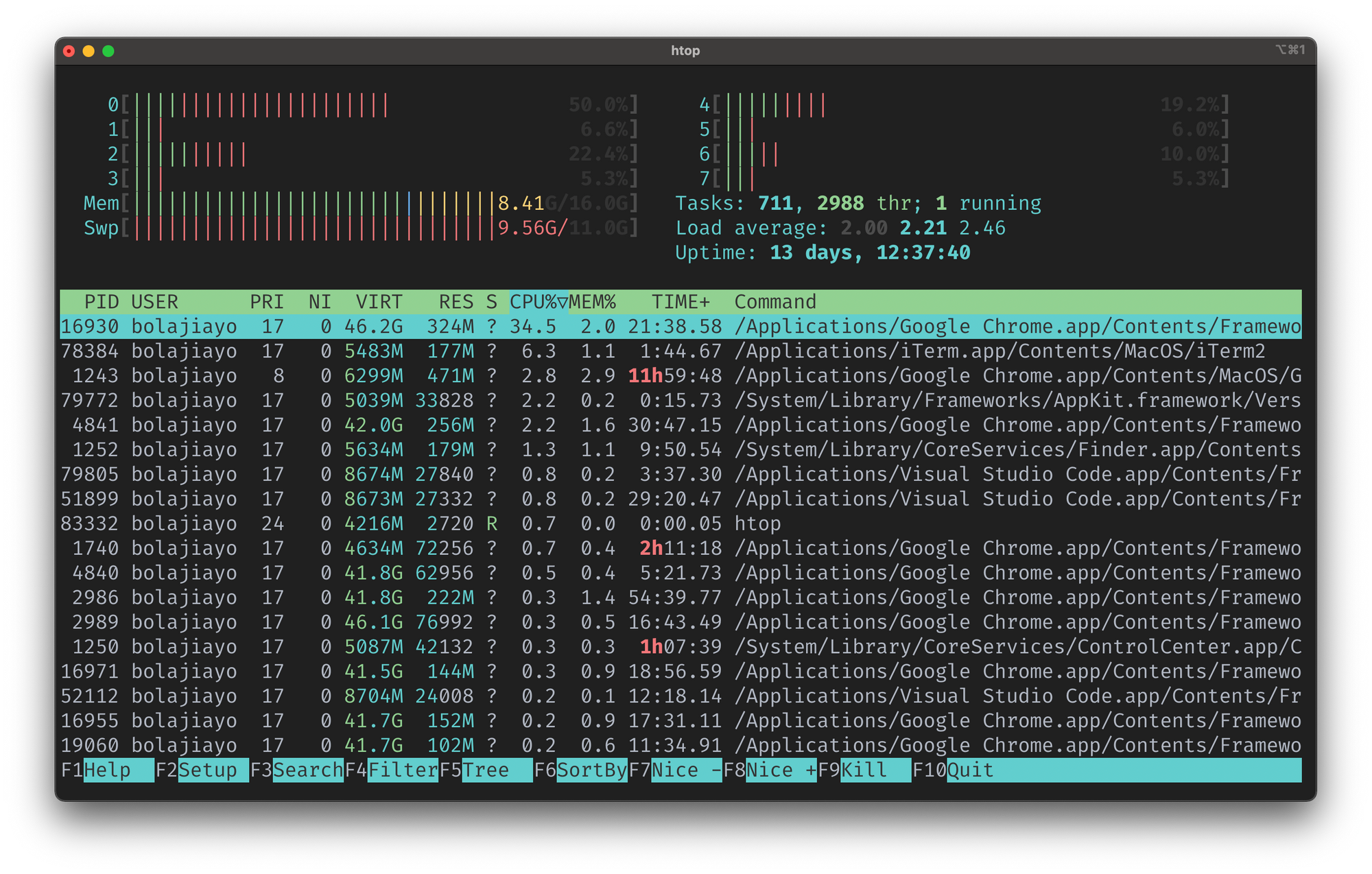
An alternative to top is htop which provides an interactive system-monitor to view and manage processes. It also displays a real-time sorted list of processes based on their CPU usage, and you can easily search, filter, and kill running processes.
htop is not installed on Linux by default, so you need to install it using the command below or download the binaries for your preferred Linux distro.
Just type htop in your terminal and you’ll get a result like the one you see in the screenshot below:
How to Kill Running Processes in Linux
Killing a process means that you terminate a running application or command. You can kill a process by running the kill command with the process ID or the pkill command with the process name like so:
To find the process ID of a running process, you can use the pgrep command followed by the name of the process like so:
To kill the iTerm2 process in the screenshot above, we will use any of the commands below. This will automatically terminate and close the iTerm2 process (application).
Conclusion
When you list running processes, it is usually a long and clustered list. You can pipe it through less to display the command output one page at a time in your terminal like so:
or display only a specific process that matches a particular name like so:
I hope that you now understand what Linux processes are and how to manage them using the ps , top , and htop commands.
Make sure to check out the manual for each command by running man ps , man top , or man htop respectively. The manual includes a comprehensive reference you can check if you need any more help at any point.
Thanks for reading – cheers! 💙
Software Engineer, Content Creator & Developer Advocate.
If you read this far, tweet to the author to show them you care. Tweet a thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
freeCodeCamp is a donor-supported tax-exempt 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization (United States Federal Tax Identification Number: 82-0779546)
Our mission: to help people learn to code for free. We accomplish this by creating thousands of videos, articles, and interactive coding lessons — all freely available to the public. We also have thousands of freeCodeCamp study groups around the world.
Donations to freeCodeCamp go toward our education initiatives and help pay for servers, services, and staff.
Источник
How to check running process in Linux using command line
I am a new system administrator for the Linux operating system. How do I check running process in Linux using the command line option?
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux terminal |
| Est. reading time | 4 mintues |
One can use the Linux command line or terminal app to display a running process, change their priorities level, delete process and more. This page shows how to use various commands to list, kill and manage process on Linux.
Check running process in Linux
The procedure to monitor the running process in Linux using the command line is as follows:
- Open the terminal window on Linux
- For remote Linux server use the ssh command for log in purpose
- Type the ps aux command to see all running process in Linux
- Alternatively, you can issue the top command or htop command to view running process in Linux
Let us see some example and usage in details.
Please note that vivek@nixcraft:
$ is my shell prompt. You need to type commands after the $ prompt.
How to manage processes from the Linux terminal
The ps command is a traditional Linux command to lists running processes. The following command shows all processes running on your Linux based server or system:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ ps -aux
vivek@nixcraft:
- root – User name
- 1 – PID (Linux process ID)
- 19:10 – Process start time
- /sbin/init splash – Actual process or command
There may be too many processes. Hence, it uses the following less command/more command as pipe to display process one screen at a time:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ ps -aux | more
vivek@nixcraft:
$ sudo ps -aux | less
Press q to exit from above Linux pagers. You can search for a particular Linux process using grep command/egrep command:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ ps aux | grep firefox
vivek@nixcraft:
$ sudo ps aux | grep vim
vivek@nixcraft:
$ sudo ps -aux | egrep ‘sshd|openvpn|nginx’
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Linux pgrep command
Many variants of Linux comes with the pgrep command to search/find process. The syntax is:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ sudo pgrep sshd
vivek@nixcraft:
$ pgrep vim
vivek@nixcraft:
$ pgrep firefox
vivek@nixcraft:
Linux top command
The top command is another highly recommended method to see your Linux servers resource usage. One can see a list of top process that using the most memory or CPU or disk.
vivek@nixcraft:
$ sudo top
vivek@nixcraft:
Linux htop command to check running process in Linux
The htop command is an interactive process viewer and recommended method for Linux users. One can see a list of top process that using the most memory or CPU or disk and more:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ sudo htop
vivek@nixcraft:
Linux kill command
Want to kill a process? Try kill command. The syntax is:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ kill pid
vivek@nixcraft:
$ kill -signal pid
Find PID using ps, pgrep or top commands. Say you want to kill a PID # 16750, run:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ kill 16750
For some reason if the process can not be killed, try forceful killing:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ kill -9 16750
OR
vivek@nixcraft:
$ kill -KILL 16750
Linux pkill command
If you wish to kill a process by name, try pkill command. The syntax is:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ pkill processName
vivek@nixcraft:
$ pkill vim
vivek@nixcraft:
$ pkill firefox
vivek@nixcraft:
$ pkill -9 emacs
vivek@nixcraft:
$ sudo pkill -KILL php7-fpm
Linux killall command
The killall command kills processes by name, as opposed to the selection by PID as done by kill command:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ killall vim
vivek@nixcraft:
$ killall -9 emacs
Linux nice and renice command
The primary purpose of the nice command is to run a process/command at a lower or higher priority. Use the renice command to alter the nice value of one or more running Linux processes. The nice value can range from -20 to 19, with 19 being the lowest priority. Say, you want to compile software on a busy Linux server. You can set a very low priority, enter:
vivek@nixcraft:
$ nice -n 13 cc -c *.c &
Set a very high priority for a kernel update. Before rebooting Linux server, run:
Источник
How to List Running Processes in Linux: A Beginner’s Guide
Need to view all running processes on your Linux server and discover which consumes your resources the most? Look no further, because, in this article, we’ll explain how to list Linux processes by using several common commands.
Introduction to Linux Processes
A process is the execution of a program. They can be launched when opening an application or when issuing a command through the command-line terminal.
A command can only generate a process. However, an application can run multiple processes for different tasks. For instance, Google Chrome will start a different process each time a new tab is opened.
Each Linux process is assigned a unique PID (process identification number). If there are no possible combinations left, the system can reuse old PIDs for newer processes.
A process can be initiated as a foreground or background process.
By default, all commands that run in the shell will start as foreground processes. As the process occupies the shell, you have to wait until it is finished before executing other commands.
If a command takes too long to complete, you can run it as a background process by adding an ampersand (&) at the end of the command so you can use the shell for other tasks.
Occasionally, processes may consume a lot of resources and need to be killed. Alternatively, times when you may want to change the priority level of a process, so the system will allocate more resources to it. Regardless of the case, all these tasks require you to do the same thing: listing the running processes on Linux.
How to List Running Processes in Linux?
There are several commands that you can use to list running processes: ps, top, and htop.
Utilizing the “ps” Command
The ps (process statuses) command produces a snapshot of all running processes. Therefore, unlike the Windows task manager, the results are static.
When this command is used without any additional argument or option, it will return a list of running processes along with four crucial columns: the PID, terminal name (TTY), running time (TIME), and the name of the command that launches the process (CMD). 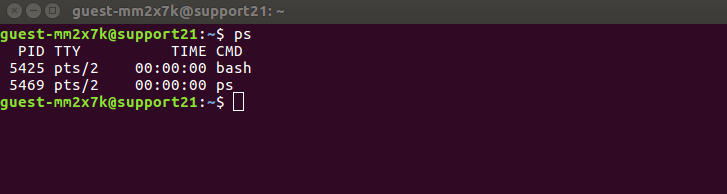
- a option outputs all running processes of all users in the system.
- u option provides additional information like memory and CPU usage percentage, the process state code, and the owner of the processes.
- x option lists all processes not executed from the terminal. A perfect example of this are daemons, which are system-related processes that run in the background when the system is booted up.
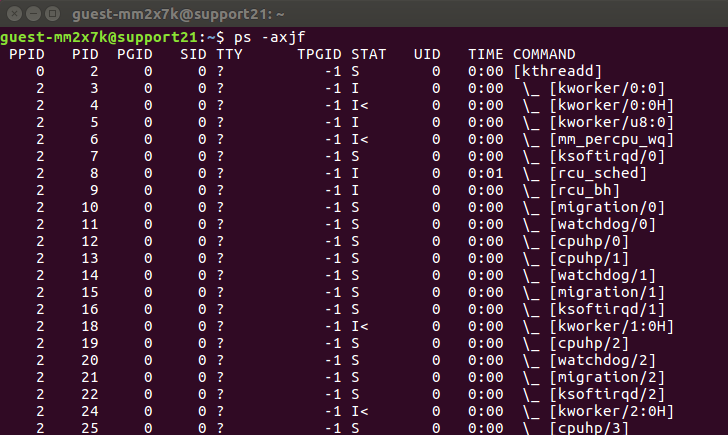
- ps -u [username] lists all running processes of a certain user.
- ps -e or ps -A displays active Linux processes in the generic UNIX format.
- ps -T prints active processes that are executed from the terminal.
- Ps -C process_name will filter the list by the process name. In addition, this command also shows all child processes of the specified process.
Using the “top” Command
The top command is used to discover resource-hungry processes. This Linux command will sort the list by CPU usage, so the process which consumes the most resources will be placed at the top.
Unlike the ps command, the output of the top command is updated periodically. That means you’ll see real-time updates for CPU usage and running time. 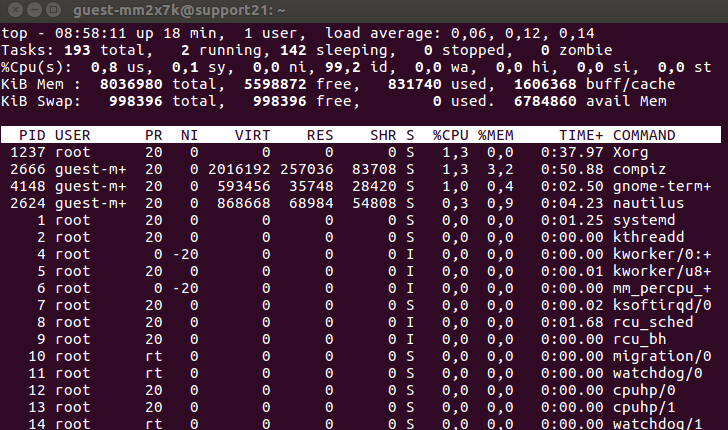
| Keys | Functions |
| k | Kills a process |
| M | Sorts the list by memory usage. |
| N | Sorts the list by PID. |
| r | Changes the priority of a process. |
| h | Displays the help window. |
| z | Displays running processes in colors. |
| d | Changes the refresh time interval. |
| c | Displays the absolute path of a process. |
| CTRL+C or q | Stops the top command. |
Keep in mind that the keys above are case sensitive, so be sure not to enable the caps lock.
Running “htop” Command
Both the htop and top command display the same information when listing your Linux processes, but the former offers user-friendly features that are great for everyday process management.
First thing first, the htop command allows you to scroll vertically and horizontally. As such, you can see the complete list of your Linux processes along with their full command lines.
What’s more, the command allows you to use a mouse to select items, kill processes without inserting their PIDs, change the priority of multiple processes easily, and so on.
Unfortunately, most Linux distributions don’t have this command right out of the box, so you need to install it manually.
If you use Ubuntu, you can install htop by running the following command:
Once installed, type htop, and you’ll get a list of all your Linux processes. 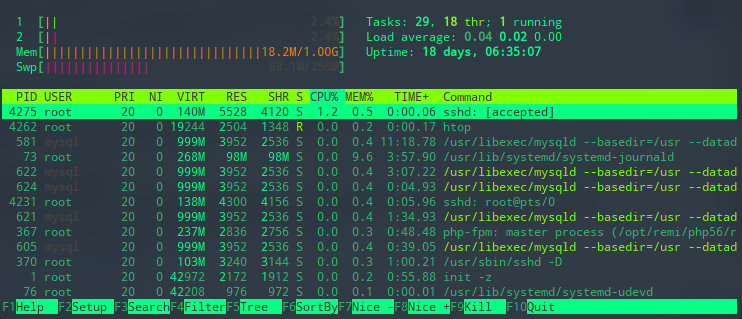
| Keys | Functions |
| F9 | To kill a process. |
| F8 | Increase the priority of a process. |
| F7 | Decrease the priority of a process. |
| F6 | Sort processes by any column. |
| F5 | Display processes in a tree view. |
| F4 | Filter the processes by name. |
| F3 | Search for a process. |
| F2 | Open htop setup. |
| F1 | Display the help menu. |
Conclusion
It is important to know how to list all running processes in your Linux operating system. The knowledge will be useful when you need to manage processes.
Let’s take a look once more at the three commands that you can use to list Linux processes:
- ps command — outputs a static view of all processes.
- top command — displays the real-time list of all running processes.
- htop command — shows the real-time result and is equipped with user-friendly features.
Which command do you prefer? Share your thoughts in the comment section below!
Domantas leads the content and SEO teams forward with fresh ideas and out of the box approaches. Armed with extensive SEO and marketing knowledge, he aims to spread the word of Hostinger to every corner of the world. During his free time, Domantas likes to hone his web development skills and travel to exotic places.
Источник