- How can I install Wi-Fi drivers in Kali Linux?
- How to install all drivers in kali linux
- Prerequisites
- Installation
- DPI/PPI
- Verify Driver Installation
- Hashcat
- Benchmarking
- Troubleshooting
- OpenCL Loaders
- Querying GPU Information
- How to install all drivers in kali linux
- System Requirements
- Installation Prerequisites
- Preparing for the Installation
- Kali Linux Installation Procedure
- Language
- Network
- User Accounts
- Clock
- Encrypted LVM
- Proxy Information
- Metapackages
- Boot Information
- Reboot
- Post Installation
How can I install Wi-Fi drivers in Kali Linux?
I installed Kali Linux on my Sony Vaio laptop (model number SVF142C1WW), but I had no wireless out of the box. Ethernet works fine, and I can connect to wireless networks normally from Windows running on the same machine.
I found this video on Google which suggested I install the compatible wireless driver. I downloaded it from kernel.org, extracted it to
/Desktop and ran the following commands:
After these commands, my wireless NIC seems to be recognized (see iwconfig output below), but I can’t see any available wireless networks. Also, the driver disappears after restarting, and I have to run the commands again and reinstall to get the NIC to show up in iwconfig again.
I found one more thing, and now I’m totally confused.
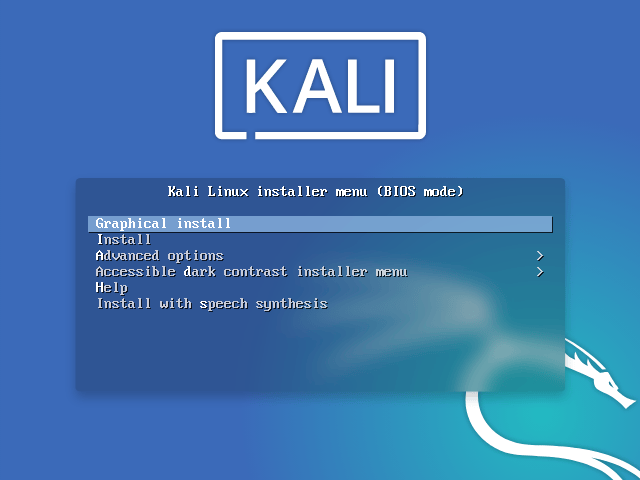
See, while installing Kali Linux this is the menu you get in the beginning:
I went into the option Kali Graphical Install to install Kali Linux.
I believed to run live Kali, and I have to go in Kali — Boot Persistent. I went into that, and I got Kali desktop. And I found out that Wi-Fi drivers were perfectly fine and they were working well. I can connect to any Wi-Fi connections and all Wi-Fi connections were showing.
What is this?
And there is one more thing. While installing Kali Linux, inbetween I got an error message saying the following.
But after I ran some update and upgrade commands, it is present in /lib/firmware .
Источник
How to install all drivers in kali linux
Do not attempt this in a VM. It is possible in theory, however this likely will not work and we do not recommend that users attempt this.
This document explains how to install NVIDIA GPU drivers and CUDA support, allowing integration with popular penetration testing tools.
This guide is also for a dedicated card (desktops users), not Optimus (notebook users). We do not have the hardware in order to write up the guide. So we are looking for community contribution to help out. If you have the hardware, and expertise, please edit this guide!
Prerequisites
First, you’ll need to ensure that your card supports CUDA.
GPUs with a CUDA compute capability > 5.0 are recommended, but GPUs with less will still work.
Let’s determine the exact GPU installed, and check the kernel modules it’s using:
Notice how Kernel driver in use & Kernel modules are using nouveau? This is the open source driver for nVidia. This guide covers installing the close source, from NVIDIA.
There is a package called nvidia-detect which will fail to detect the driver due to Kali being a rolling distribution and requires a stable release.
Installation
Once the system has rebooted from doing an OS upgrade, we will proceed to install the Drivers, and the CUDA toolkit (allowing for tool to take advantage of the GPU).
During installation of the drivers the system created new kernel modules, so a reboot is required:
DPI/PPI
Upon Kali starting back up, certain things may appear different than what is expected.
- If certain things are smaller, this could because of HiDPI.
- However, if certain things are larger, this could because the DPI is incorrect.
Verify Driver Installation
Now that our system should be ready to go, we need to verify the drivers have been loaded correctly. We can quickly verify this by running the nvidia-smi tool.
You can see our hardware has been detected we are using nvidia rather than nouveau drive now.
Hashcat
With the output displaying our driver and GPU correctly, we can now dive into benchmarking (using the CUDA toolkit). Before we get too far ahead, let’s double check to make sure hashcat and CUDA are working together.
It appears everything is working, let’s go ahead and run hashcat’s inbuilt benchmark test.
Benchmarking
There are a multitude of configurations to improve cracking speed, not mentioned in this guide. However, we encourage you to take a look at the hashcat documentation for your specific cases.
Troubleshooting
In the event setup isn’t going as planned, we’ll install clinfo for detailed troubleshooting information.
OpenCL Loaders
It may be necessary to check for additional packages that may be conflicting with our setup. Let’s first check to see what OpenCL Loader we have installed. The NVIDIA OpenCL Loader and the generic OpenCL Loader will both work for our system.
If mesa-opencl-icd is installed, we should remove it:
Since we have determined that we have a compatible ICD loader installed, we can easily determine which loader is currently being used.
As expected, our setup is using the open source loader that was installed earlier. Now, let’s get some detailed information about the system.
Querying GPU Information
We’ll use nvidia-smi once again, but with a much more verbose output.
It looks like our GPU is being recognized correctly, so let’s use glxinfo to determine if 3D Rendering is enabled.
The combination of these tools should assist the troubleshooting process greatly. If you still experience issues, we recommend searching for similar setups and any nuances that may affect your specific system.
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: g0tmi1k
Источник
How to install all drivers in kali linux
Installing Kali Linux (single boot) on your computer is an easy process. This guide will cover the basic install (which can be done on bare metal or guest VM), with the option of encrypting the partition. At times, you may have sensitive data you would prefer to encrypt using Full Disk Encryption (FDE). During the setup process you can initiate an LVM encrypted install on either Hard Disk or USB drives.
First, you’ll need compatible computer hardware. Kali Linux is supported on amd64 (x86_64/64-Bit) and i386 (x86/32-Bit) platforms. Where possible, we would recommend using the amd64 images. The hardware requirements are minimal as listed in the section below, although better hardware will naturally provide better performance. You should be able to use Kali Linux on newer hardware with UEFI and older systems with BIOS.
Our i386 images, by default use a PAE kernel, so you can run them on systems with over 4 GB of RAM.
In our example, we will be installing Kali Linux in a fresh guest VM, without any existing operating systems pre-installed. We will explain other possible scenarios throughout the guide.
System Requirements
The installation requirements for Kali Linux will vary depending on what you would like to install and your setup. For system requirements:
- On the low end, you can set up Kali Linux as a basic Secure Shell (SSH) server with no desktop, using as little as 128 MB of RAM (512 MB recommended) and 2 GB of disk space.
- On the higher end, if you opt to install the default Xfce4 desktop and the kali-linux-default metapackage, you should really aim for at least 2 GB of RAM and 20 GB of disk space.
- When using resource-intensive applications, such as Burp Suite, they recommend at least 8 GB of RAM(and even more if it large web application!) or using simultaneous programs at the same time.
Installation Prerequisites
This guide will make also the following assumptions when installing Kali Linux:
- Using the amd64 installer image.
- CD/DVD drive / USB boot support.
- Single disk to install to.
- Connected to a network (with DHCP & DNS enabled) which has outbound Internet access.
We will be wiping any existing data on the hard disk, so please backup any important information on the device to an external media.
Preparing for the Installation
Download Kali Linux (We recommend the image marked Installer).
Burn The Kali Linux ISO to DVD or image Kali Linux Live to USB drive. (If you cannot, check out the Kali Linux Network Install).
Backup any important information on the device to an external media.
Ensure that your computer is set to boot from CD/DVD/USB in your BIOS/UEFI.
Kali Linux Installation Procedure
- To start your installation, boot with your chosen installation medium. You should be greeted with the Kali Linux Boot screen. Choose either Graphical install or Install (Text-Mode). In this example, we chose the Graphical install.
If you’re using the live image instead, you will see another mode, Live, which is also the default boot option.
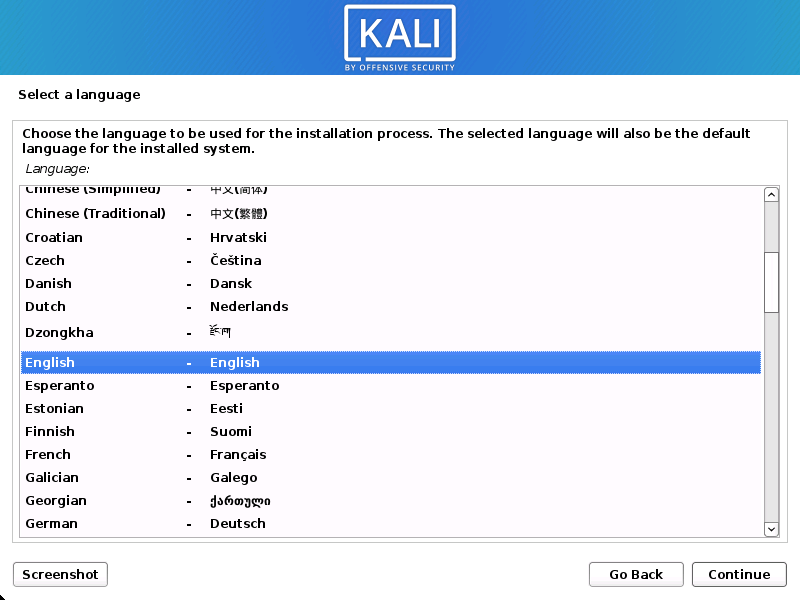
Language
- Select your preferred language. This will be used for both the setup process and once you are using Kali Linux.
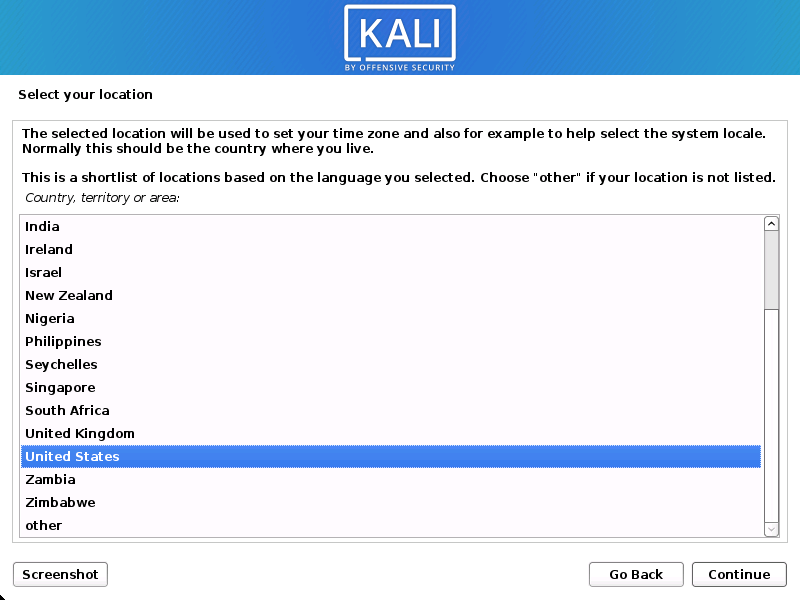
- Specify your geographic location.
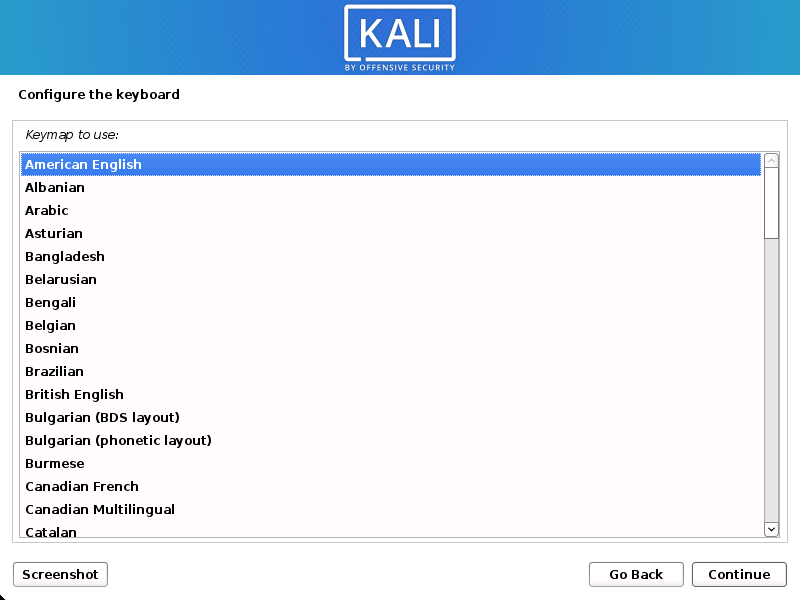
- Select your keyboard layout.
Network
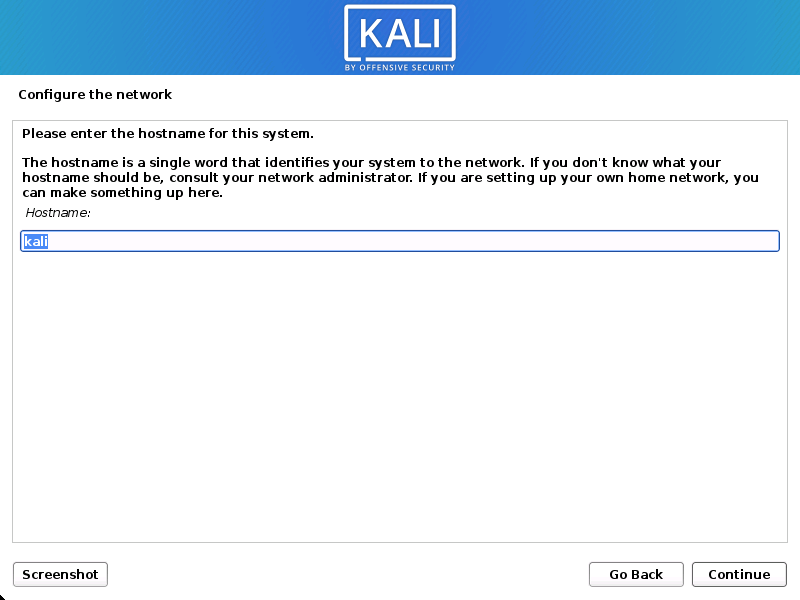
- The setup will now probe your network interfaces, looks for a DHCP service, and then prompt you to enter a hostname for your system. In the example below, we’ve entered kali as our hostname.
If there is no network access with DHCP service detected, you may need to manually configure the network information or do not configure the network at this time.
- If there isn’t a DHCP service running on the network, it will ask you to manually enter the network information after probing for network interfaces, or you can skip.
- If Kali Linux doesn’t detect your NIC, you either need to include the drivers for it when prompted, or generate a custom Kali Linux ISO with them pre-included.
- If the setup detects multiple NICs, it may prompt you which one to use for the install.
- If the chosen NIC is 802.11 based, you will be asked for your wireless network information before being prompted for a hostname.
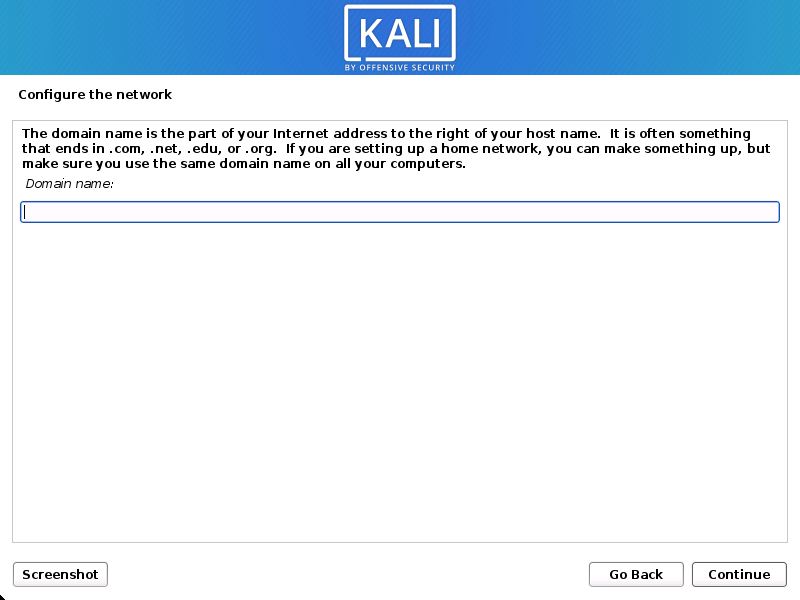
- You may optionally provide a default domain name for this system to use (values may be pulled in from DHCP or if there is an existing operating systems pre-existing).
User Accounts
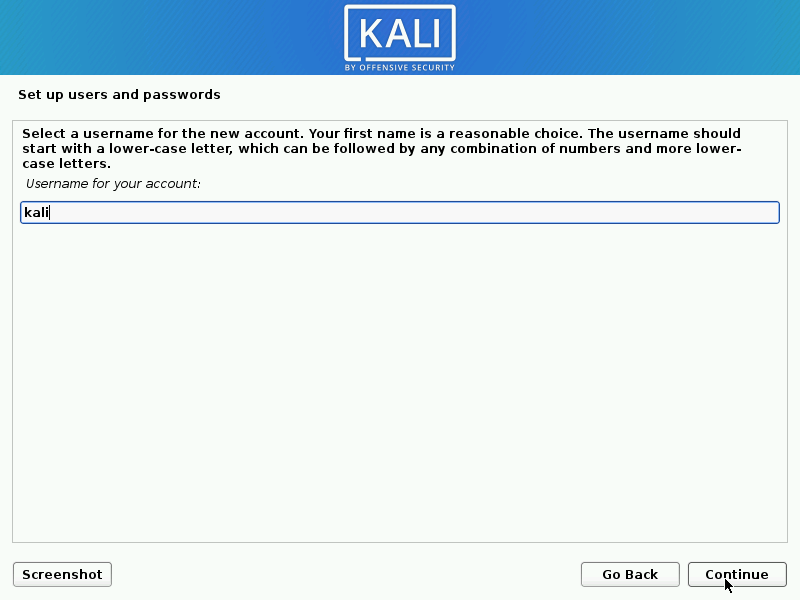
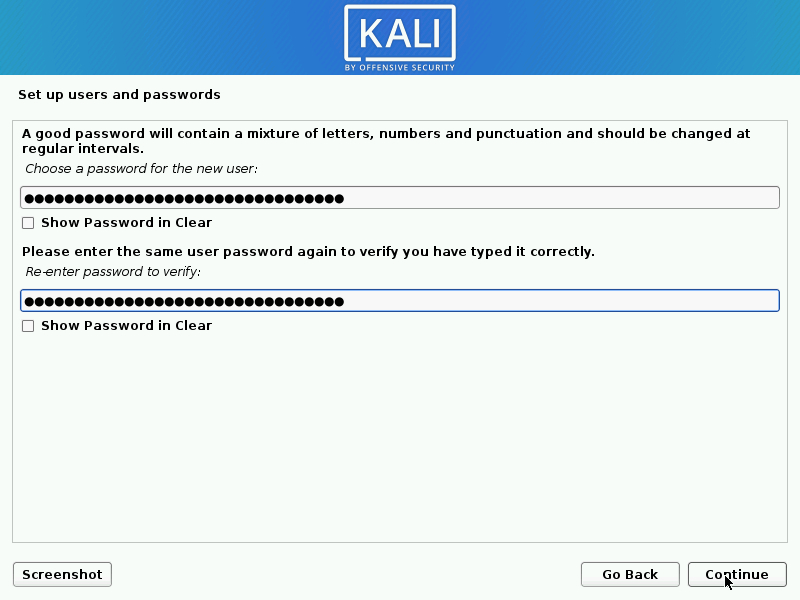
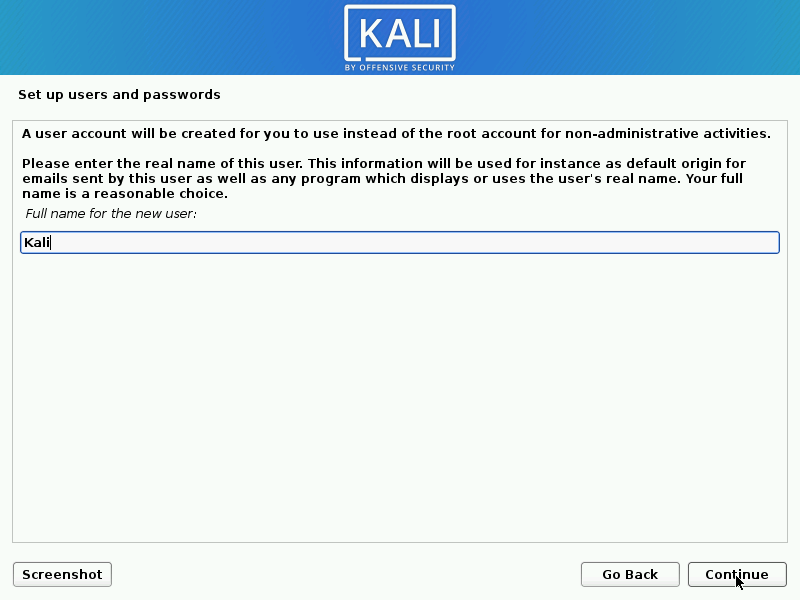
- Next, create the user account for the system (Full name, username and a strong password).
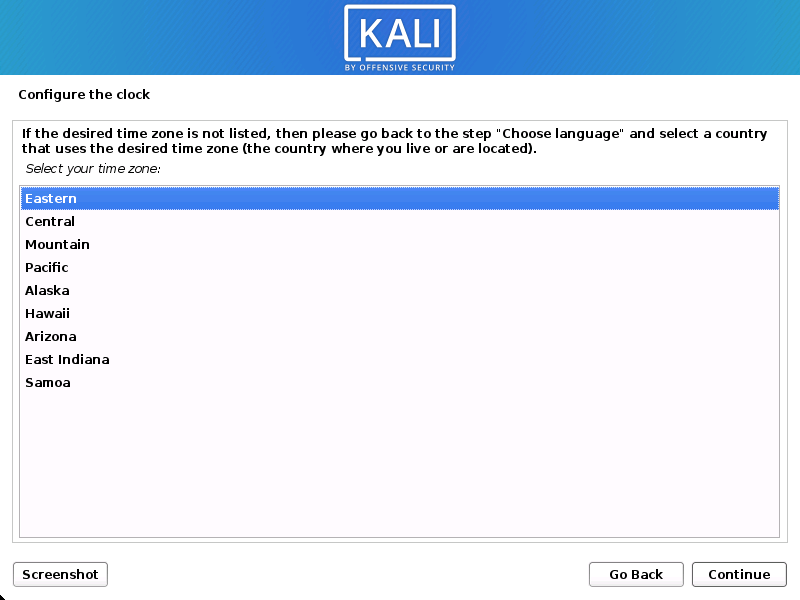
Clock
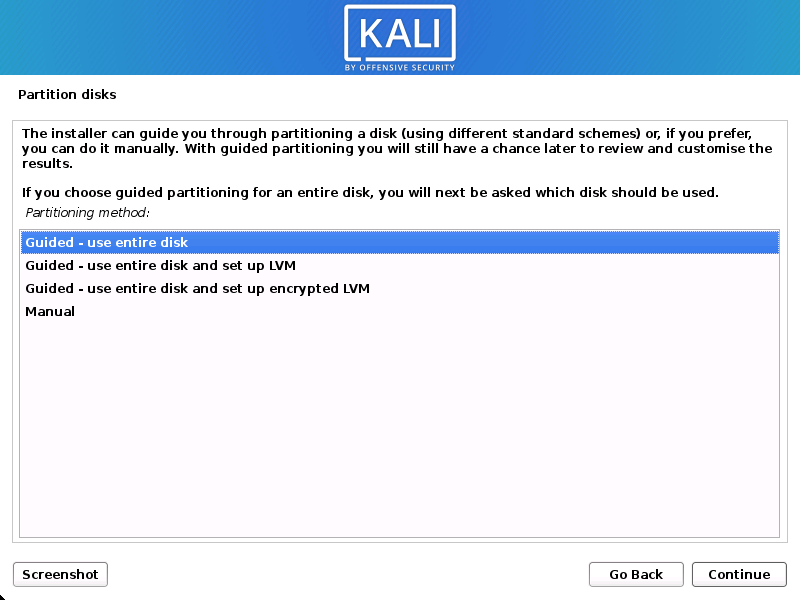
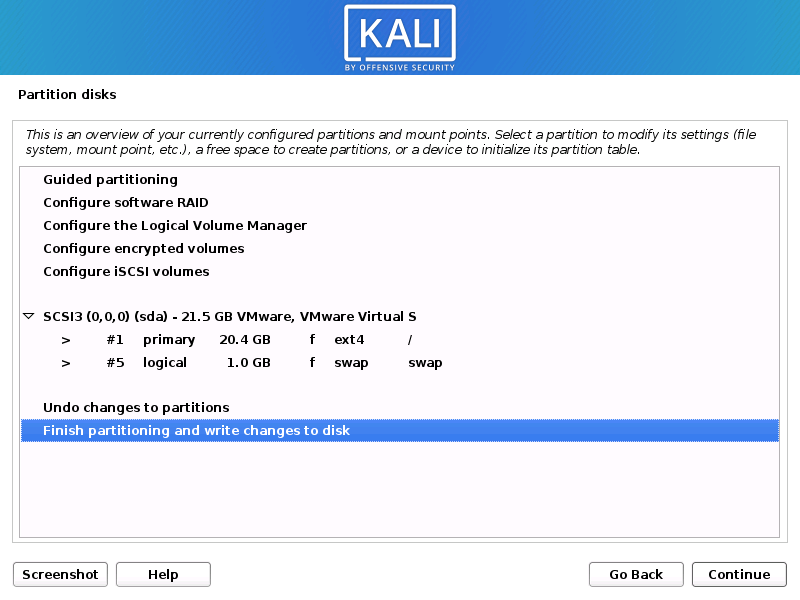
- The installer will now probe your disks and offer you various choices, depending on the setup.
In our guide, we are using a clean disk, so we have four options to pick from. We will select Guided — the entire disk, as this is the single boot installation for Kali Linux, so we do not want any other operating systems installed, so we are happy to wipe the disk.
If there is an pre-existing data on the disk, you will have have an extra option (Guided — use the largest continuous free space) than the example below. This would instruct the setup not to alter any existing data, which is perfect for for dual-booting into another operating system. As this is not the case in this example, it is not visible.
Experienced users can use the “Manual” partitioning method for more granular configuration options, which is covered more in our BTRFS guide.
If you want to encrypt Kali Linux, you can enable Full Disk Encryption (FDE), by selecting Guided — used entire disk and setup encrypted LVM. When selected, later on in the setup (not in this guide) prompt you to enter a password (twice). You will have to enter this password every time you start up Kali Linux.
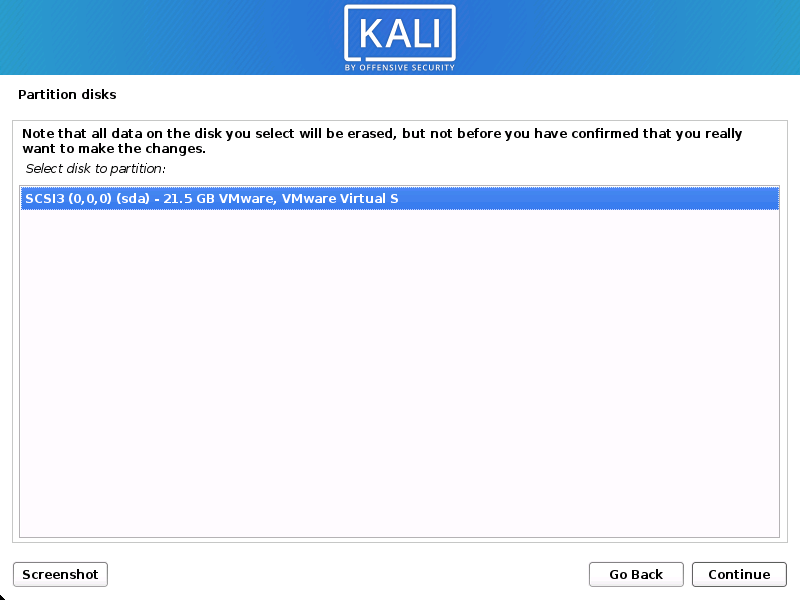
- Select the disk to be partitioned.
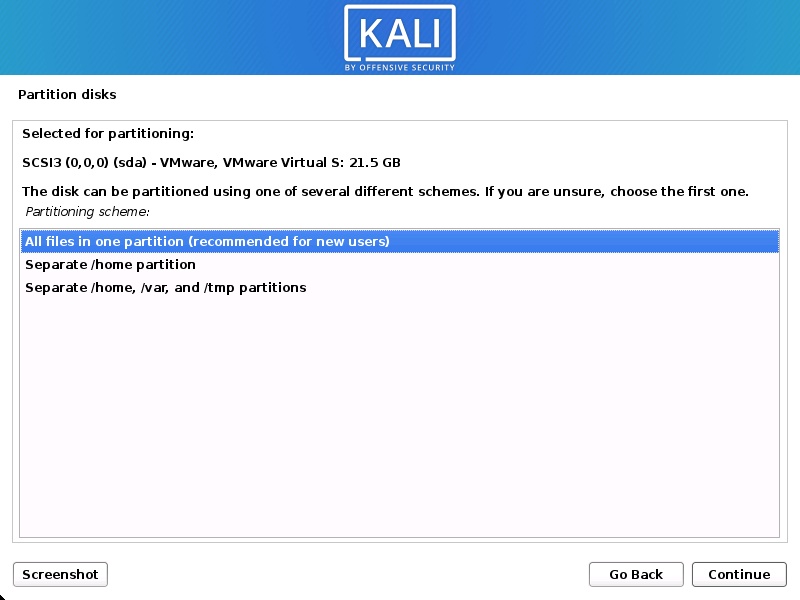
- Depending on your needs, you can choose to keep all your files in a single partition — the default — or to have separate partitions for one or more of the top-level directories.
If you’re not sure which you want, you want “All files in one partition”.
- Next, you’ll have one last chance to review your disk configuration before the installer makes irreversible changes. After you click Continue, the installer will go to work and you’ll have an almost finished installation.
Encrypted LVM
If enabled in the previous step, Kali Linux will now start to perform a secure wipe of the hard disk, before asking you for a LVM password.
Please sure a strong password, else you will have to agree to the warning about a weak passphrase.
This wipe may take “a while” (hours) depending on the size and speed of the drive.
If you wish to risk it, you can skip it.
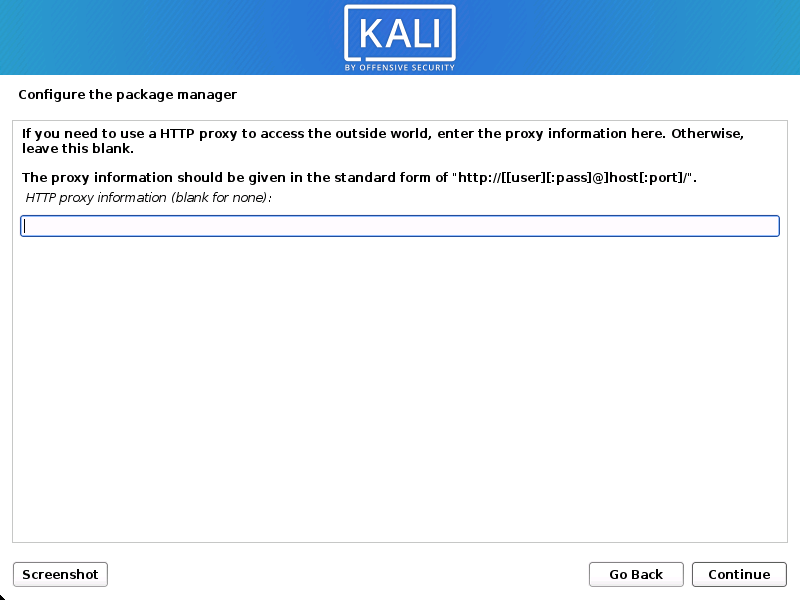
Proxy Information
- Kali Linux uses a central repository to distribute applications. You’ll need to enter any appropriate proxy information as needed.
Metapackages
If network access was not setup, you will want to continue with setup when prompt.
If you are using the Live image, you will not have the following stage.
- Next you can select which metapackages you would like to install. The default selections will install a standard Kali Linux system and you don’t really have to change anything here.
Please refer to this guide if you prefer to change the default selections.
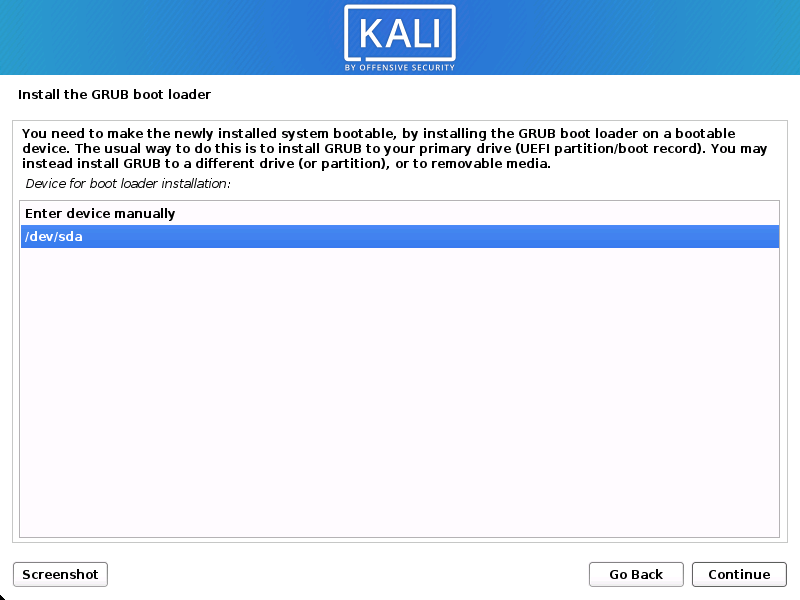
Boot Information
- Next confirm to install the GRUB boot loader.
- Select the hard drive to install the GRUB bootloader in (it does not by default select any drive).
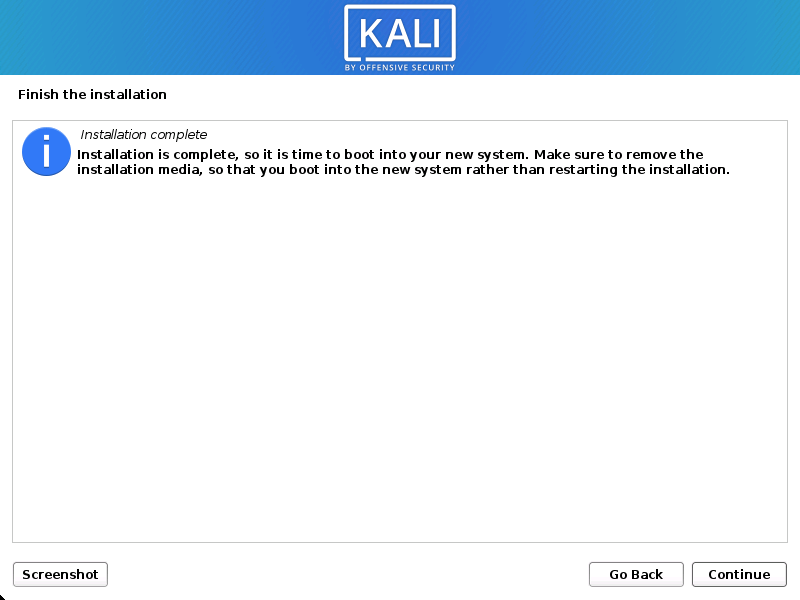
Reboot
- Finally, click Continue to reboot into your new Kali Linux installation.
Post Installation
Now that you’ve completed installing Kali Linux, it’s time to customize your system.
The General Use section has more information and you can also find tips on how to get the most out of Kali Linux in our User Forums.
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: gamb1t
Источник