- Setting up a Windows Host¶
- Host Requirements¶
- Upgrading PowerShell and .NET Framework¶
- WinRM Memory Hotfix¶
- WinRM Setup¶
- WinRM Listener¶
- Setup WinRM Listener¶
- Delete WinRM Listener¶
- WinRM Service Options¶
- Common WinRM Issues¶
- HTTP 401/Credentials Rejected¶
- HTTP 500 Error¶
- Timeout Errors¶
- Connection Refused Errors¶
- Failure to Load Builtin Modules¶
- Windows SSH Setup¶
- Installing Win32-OpenSSH¶
- How to Install Ansible on Windows 10
- Install Ansible on Windows 10
- Tutorial in Detail with screenshots:
Setting up a Windows Host¶
This document discusses the setup that is required before Ansible can communicate with a Microsoft Windows host.
Host Requirements¶
For Ansible to communicate to a Windows host and use Windows modules, the Windows host must meet these requirements:
Ansible can generally manage Windows versions under current and extended support from Microsoft. Ansible can manage desktop OSs including Windows 7, 8.1, and 10, and server OSs including Windows Server 2008, 2008 R2, 2012, 2012 R2, 2016, and 2019.
Ansible requires PowerShell 3.0 or newer and at least .NET 4.0 to be installed on the Windows host.
A WinRM listener should be created and activated. More details for this can be found below.
While these are the base requirements for Ansible connectivity, some Ansible modules have additional requirements, such as a newer OS or PowerShell version. Please consult the module’s documentation page to determine whether a host meets those requirements.
Upgrading PowerShell and .NET Framework¶
Ansible requires PowerShell version 3.0 and .NET Framework 4.0 or newer to function on older operating systems like Server 2008 and Windows 7. The base image does not meet this requirement. You can use the Upgrade-PowerShell.ps1 script to update these.
This is an example of how to run this script from PowerShell:
Once completed, you will need to remove auto logon and set the execution policy back to the default of Restricted . You can do this with the following PowerShell commands:
The script works by checking to see what programs need to be installed (such as .NET Framework 4.5.2) and what PowerShell version is required. If a reboot is required and the username and password parameters are set, the script will automatically reboot and logon when it comes back up from the reboot. The script will continue until no more actions are required and the PowerShell version matches the target version. If the username and password parameters are not set, the script will prompt the user to manually reboot and logon when required. When the user is next logged in, the script will continue where it left off and the process continues until no more actions are required.
If running on Server 2008, then SP2 must be installed. If running on Server 2008 R2 or Windows 7, then SP1 must be installed.
Windows Server 2008 can only install PowerShell 3.0; specifying a newer version will result in the script failing.
The username and password parameters are stored in plain text in the registry. Make sure the cleanup commands are run after the script finishes to ensure no credentials are still stored on the host.
WinRM Memory Hotfix¶
When running on PowerShell v3.0, there is a bug with the WinRM service that limits the amount of memory available to WinRM. Without this hotfix installed, Ansible will fail to execute certain commands on the Windows host. These hotfixes should be installed as part of the system bootstrapping or imaging process. The script Install-WMF3Hotfix.ps1 can be used to install the hotfix on affected hosts.
The following PowerShell command will install the hotfix:
For more details, please refer to the Hotfix document from Microsoft.
WinRM Setup¶
Once Powershell has been upgraded to at least version 3.0, the final step is for the WinRM service to be configured so that Ansible can connect to it. There are two main components of the WinRM service that governs how Ansible can interface with the Windows host: the listener and the service configuration settings.
Details about each component can be read below, but the script ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1 can be used to set up the basics. This script sets up both HTTP and HTTPS listeners with a self-signed certificate and enables the Basic authentication option on the service.
To use this script, run the following in PowerShell:
There are different switches and parameters (like -EnableCredSSP and -ForceNewSSLCert ) that can be set alongside this script. The documentation for these options are located at the top of the script itself.
The ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1 script is intended for training and development purposes only and should not be used in a production environment, since it enables settings (like Basic authentication) that can be inherently insecure.
WinRM Listener¶
The WinRM services listens for requests on one or more ports. Each of these ports must have a listener created and configured.
To view the current listeners that are running on the WinRM service, run the following command:
This will output something like:
In the example above there are two listeners activated; one is listening on port 5985 over HTTP and the other is listening on port 5986 over HTTPS. Some of the key options that are useful to understand are:
Transport : Whether the listener is run over HTTP or HTTPS, it is recommended to use a listener over HTTPS as the data is encrypted without any further changes required.
Port : The port the listener runs on, by default it is 5985 for HTTP and 5986 for HTTPS. This port can be changed to whatever is required and corresponds to the host var ansible_port .
URLPrefix : The URL prefix to listen on, by default it is wsman . If this is changed, the host var ansible_winrm_path must be set to the same value.
CertificateThumbprint : If running over an HTTPS listener, this is the thumbprint of the certificate in the Windows Certificate Store that is used in the connection. To get the details of the certificate itself, run this command with the relevant certificate thumbprint in PowerShell:
Setup WinRM Listener¶
There are three ways to set up a WinRM listener:
Using winrm quickconfig for HTTP or winrm quickconfig -transport:https for HTTPS. This is the easiest option to use when running outside of a domain environment and a simple listener is required. Unlike the other options, this process also has the added benefit of opening up the Firewall for the ports required and starts the WinRM service.
Using Group Policy Objects. This is the best way to create a listener when the host is a member of a domain because the configuration is done automatically without any user input. For more information on group policy objects, see the Group Policy Objects documentation.
Using PowerShell to create the listener with a specific configuration. This can be done by running the following PowerShell commands:
To see the other options with this PowerShell cmdlet, see New-WSManInstance.
When creating an HTTPS listener, an existing certificate needs to be created and stored in the LocalMachine\My certificate store. Without a certificate being present in this store, most commands will fail.
Delete WinRM Listener¶
To remove a WinRM listener:
The Keys object is an array of strings, so it can contain different values. By default it contains a key for Transport= and Address= which correspond to the values from winrm enumerate winrm/config/Listeners.
WinRM Service Options¶
There are a number of options that can be set to control the behavior of the WinRM service component, including authentication options and memory settings.
To get an output of the current service configuration options, run the following command:
This will output something like:
While many of these options should rarely be changed, a few can easily impact the operations over WinRM and are useful to understand. Some of the important options are:
Service\AllowUnencrypted : This option defines whether WinRM will allow traffic that is run over HTTP without message encryption. Message level encryption is only possible when ansible_winrm_transport is ntlm , kerberos or credssp . By default this is false and should only be set to true when debugging WinRM messages.
Service\Auth\* : These flags define what authentication options are allowed with the WinRM service. By default, Negotiate (NTLM) and Kerberos are enabled.
Service\Auth\CbtHardeningLevel : Specifies whether channel binding tokens are not verified (None), verified but not required (Relaxed), or verified and required (Strict). CBT is only used when connecting with NTLM or Kerberos over HTTPS.
Service\CertificateThumbprint : This is the thumbprint of the certificate used to encrypt the TLS channel used with CredSSP authentication. By default this is empty; a self-signed certificate is generated when the WinRM service starts and is used in the TLS process.
Winrs\MaxShellRunTime : This is the maximum time, in milliseconds, that a remote command is allowed to execute.
Winrs\MaxMemoryPerShellMB : This is the maximum amount of memory allocated per shell, including the shell’s child processes.
To modify a setting under the Service key in PowerShell:
To modify a setting under the Winrs key in PowerShell:
If running in a domain environment, some of these options are set by GPO and cannot be changed on the host itself. When a key has been configured with GPO, it contains the text [Source=»GPO»] next to the value.
Common WinRM Issues¶
Because WinRM has a wide range of configuration options, it can be difficult to setup and configure. Because of this complexity, issues that are shown by Ansible could in fact be issues with the host setup instead.
One easy way to determine whether a problem is a host issue is to run the following command from another Windows host to connect to the target Windows host:
If this fails, the issue is probably related to the WinRM setup. If it works, the issue may not be related to the WinRM setup; please continue reading for more troubleshooting suggestions.
HTTP 401/Credentials Rejected¶
A HTTP 401 error indicates the authentication process failed during the initial connection. Some things to check for this are:
Verify that the credentials are correct and set properly in your inventory with ansible_user and ansible_password
Ensure that the user is a member of the local Administrators group or has been explicitly granted access (a connection test with the winrs command can be used to rule this out).
Make sure that the authentication option set by ansible_winrm_transport is enabled under Service\Auth\*
If running over HTTP and not HTTPS, use ntlm , kerberos or credssp with ansible_winrm_message_encryption: auto to enable message encryption. If using another authentication option or if the installed pywinrm version cannot be upgraded, the Service\AllowUnencrypted can be set to true but this is only recommended for troubleshooting
Ensure the downstream packages pywinrm , requests-ntlm , requests-kerberos , and/or requests-credssp are up to date using pip .
If using Kerberos authentication, ensure that Service\Auth\CbtHardeningLevel is not set to Strict .
When using Basic or Certificate authentication, make sure that the user is a local account and not a domain account. Domain accounts do not work with Basic and Certificate authentication.
HTTP 500 Error¶
These indicate an error has occurred with the WinRM service. Some things to check for include:
Verify that the number of current open shells has not exceeded either WinRsMaxShellsPerUser or any of the other Winrs quotas haven’t been exceeded.
Timeout Errors¶
These usually indicate an error with the network connection where Ansible is unable to reach the host. Some things to check for include:
Make sure the firewall is not set to block the configured WinRM listener ports
Ensure that a WinRM listener is enabled on the port and path set by the host vars
Ensure that the winrm service is running on the Windows host and configured for automatic start
Connection Refused Errors¶
These usually indicate an error when trying to communicate with the WinRM service on the host. Some things to check for:
Ensure that the WinRM service is up and running on the host. Use (Get-Service -Name winrm).Status to get the status of the service.
Check that the host firewall is allowing traffic over the WinRM port. By default this is 5985 for HTTP and 5986 for HTTPS.
Sometimes an installer may restart the WinRM or HTTP service and cause this error. The best way to deal with this is to use win_psexec from another Windows host.
Failure to Load Builtin Modules¶
If powershell fails with an error message similar to The ‘Out-String’ command was found in the module ‘Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility’, but the module could not be loaded. then there could be a problem trying to access all the paths specified by the PSModulePath environment variable. A common cause of this issue is that the PSModulePath environment variable contains a UNC path to a file share and because of the double hop/credential delegation issue the Ansible process cannot access these folders. The way around this problems is to either:
Remove the UNC path from the PSModulePath environment variable, or
Use an authentication option that supports credential delegation like credssp or kerberos with credential delegation enabled
See KB4076842 for more information on this problem.
Windows SSH Setup¶
Ansible 2.8 has added an experimental SSH connection for Windows managed nodes.
Use this feature at your own risk! Using SSH with Windows is experimental, the implementation may make backwards incompatible changes in feature releases. The server side components can be unreliable depending on the version that is installed.
Installing Win32-OpenSSH¶
The first step to using SSH with Windows is to install the Win32-OpenSSH service on the Windows host. Microsoft offers a way to install Win32-OpenSSH through a Windows capability but currently the version that is installed through this process is too old to work with Ansible. To install Win32-OpenSSH for use with Ansible, select one of these three installation options:
Manually install the service, following the install instructions from Microsoft.
Install the openssh package using Chocolatey:
How to Install Ansible on Windows 10
Know simple way to configure Ansible on Windows 10 using Windows subsystems for Linux such as Debian, Open Suse or Ubuntu.
Ansible is an open source software available for Linux Based systems such as Debian, Redhat, Ubuntu, Centos and more… Besides the free product, it also comes in an enterprise version called Ansible Tower. It was acquired by RedHat (2015) and written in Python. It is basically powerful and simple to setup tool that uses for making the automation process. It can help in configuration management, application deployment, and task automation.
This tool is capable of handling complex operations without the need of some agent on the remote machine. It can connect remotely via SSH or Powershell.
Ansible is very much able to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. For example, the user can upgrade some remote server while simultaneously detaching that from any cluster. Means many complex tasks can be done from a single point on the screen. It also has an extensible architecture which allows users to use Ansible modules to add extra functionality into it. They are mostly standalone and written in language like Python, Perl, Ruby, Bash, etcetera. So, now let’s see how to install the Ansible on Windows 10 without any virtual machine or virtualization software like VirtualBox.
Install Ansible on Windows 10
- Open the Window’s Turn Windows features on or off section.
- Select the Windows Subsystem for Linux to activate it.
- Go to the Microsoft app store.
- Search for Linux.
- Multiple Linux system will appear like Debian, Ubuntu, OpenSuse
- Select the Ubuntu or any other Linux you want to install the Ansible. Here we are using Ubuntu 18.04
- Once the Ubuntu installed on Windows 10, it will ask you to create the user.
- Now add the Ansible PPA repo on Windows 10’s Ubuntu app.
- Use installation commands to install the Ansible on Windows 10 Linux subsystem.
- Now you can run Ansible on Windows to perform different management and automation tasks.
Tutorial in Detail with screenshots:
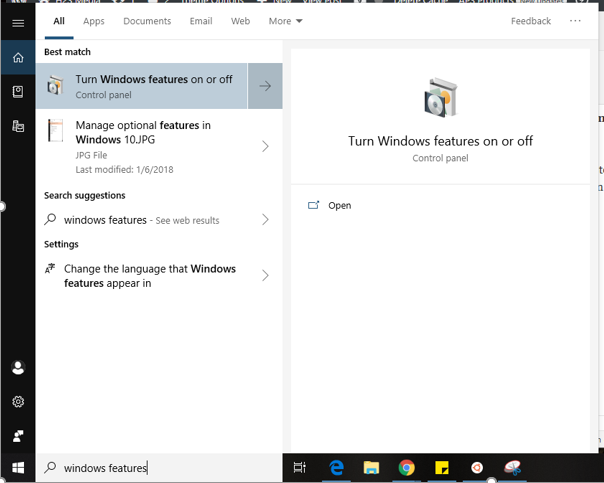
Step 1: Turn Windows features on or off
Basically, this features already on the Windows 10 and we just need to turn it on from the features option. For that just search for Windows features in the Search box. And when the “Turn Windows features on or off ” appears click on that.
Step 2: Install the Windows SubSystem for Linux
Now a window will open with a bunch of features. Scroll down and check the box of Windows Subsystem for Linux option. And after that click on the OK button.
Step 3: Open the Microsoft Store
To open the App store of Microsoft for Windows click on the search box and type Microsoft store. The moment it will appear, click on that.
Step 4: Install Ubuntu 18.04 on Windows 10
Now search for the Ubuntu and install the latest version which is 18.04. As soon as it appears, you will see GET button, click on that and install it on your Windows 10. After the installation, you will see a launch button, use that to open the Ubuntu Bash. You can install any other Linux system such as Debian, Kali Linux, and OpenSuSE to install the Ansible.
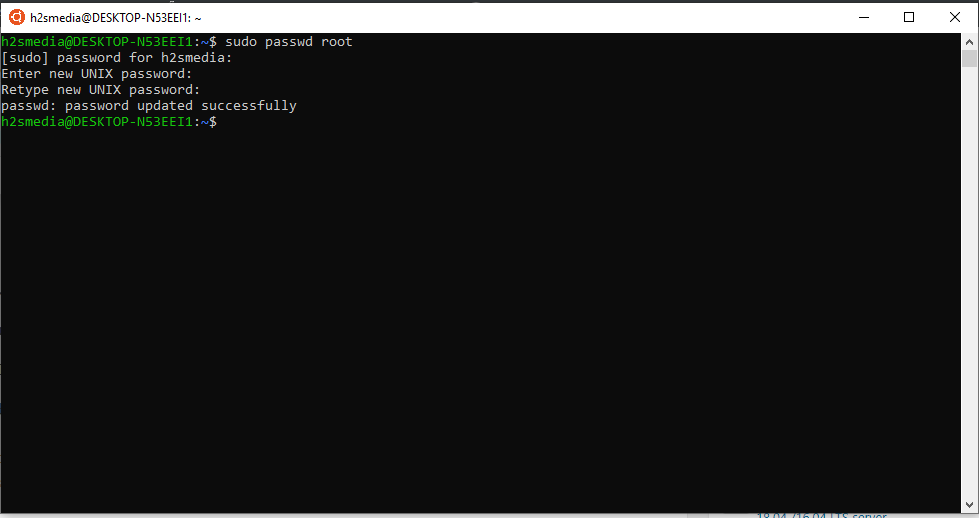
When the Ubuntu Bash opens, it will ask you to set the username and password for default user of your Ubuntu on Windows. We can also set the root account password from here. Just type sudo passwd root
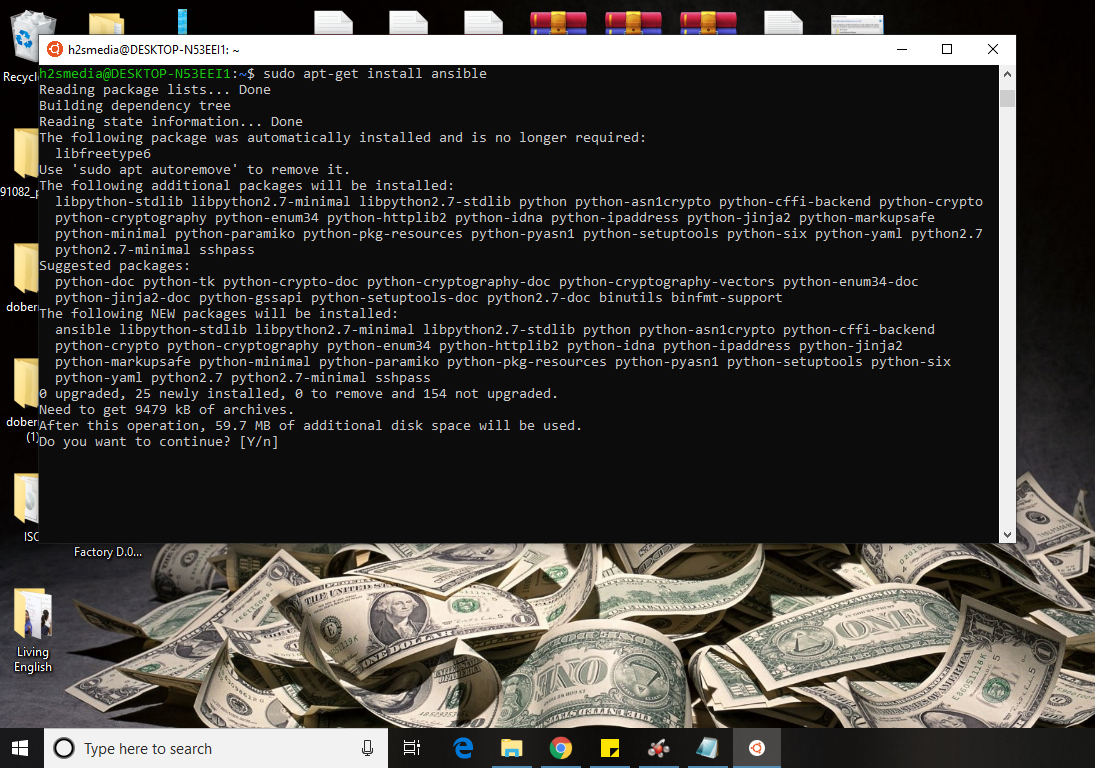
Step 6: Install Ansible on Windows
For installing and running Ansible on Windows just use the below-given commands:
Note: For older Ubuntu versions such as Ubuntu 14.04, 15.04, and 16.04, we need to add the repo of Ansible but the latest version such as Ubuntu 18.04 can get the Ansible installation files directly from via its package management.
Press Y when it asks for…
Step 7: Test Ansible on Windows
After the installation of Ansible, we will test it whether it is working or not. So, we create a demo playbook file for it.
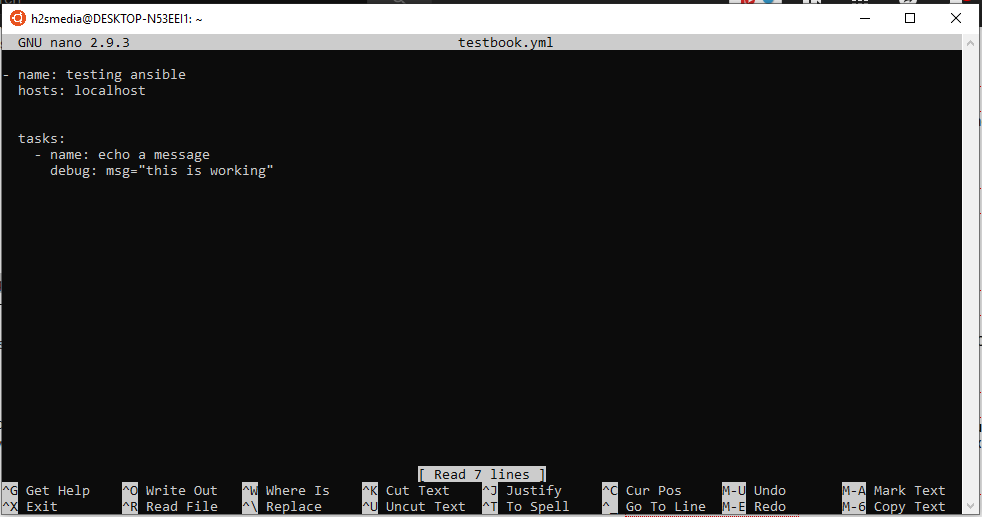
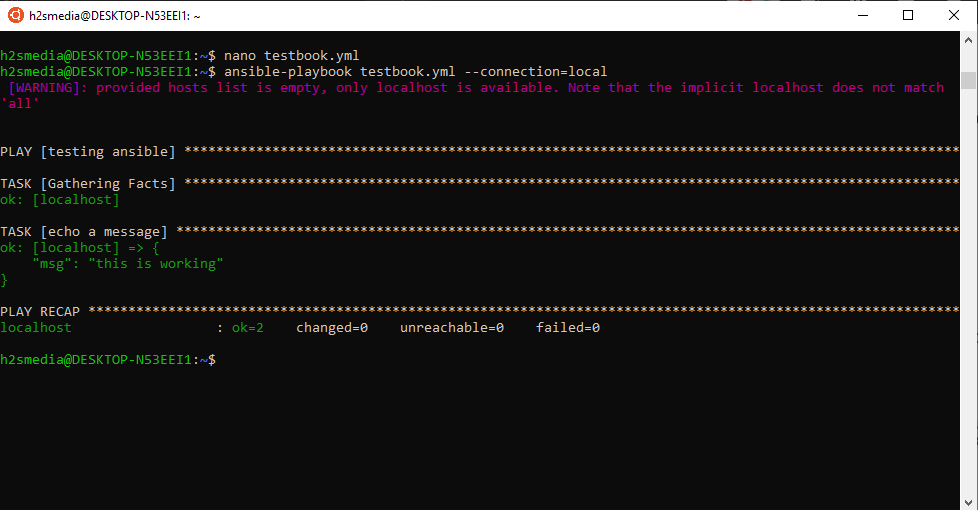
Create a file called testbook.yml
Now add the following lines into it and then exit and save the file.
Step 8: Now run the ansible command to check whether it is working or not.
Note: We are pointing the ansible to localhost because we want to test the file present on localhost.
It will prompt a message the mentioned host file is empty. So, in the next, we will also give it some demo inventory file.
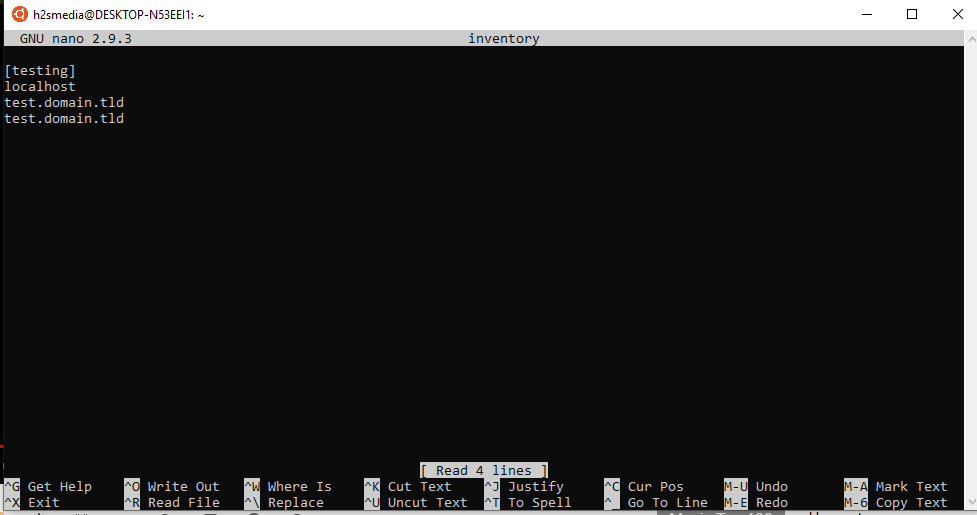
Step 9: Create a demo inventory for Ansible
Create a file with any name you want, we are using ‘inventory’. So, the command is:
Now add the following lines into it… Here we are adding some random non-existing demo domains in a group of localhost in the file for testing purpose.
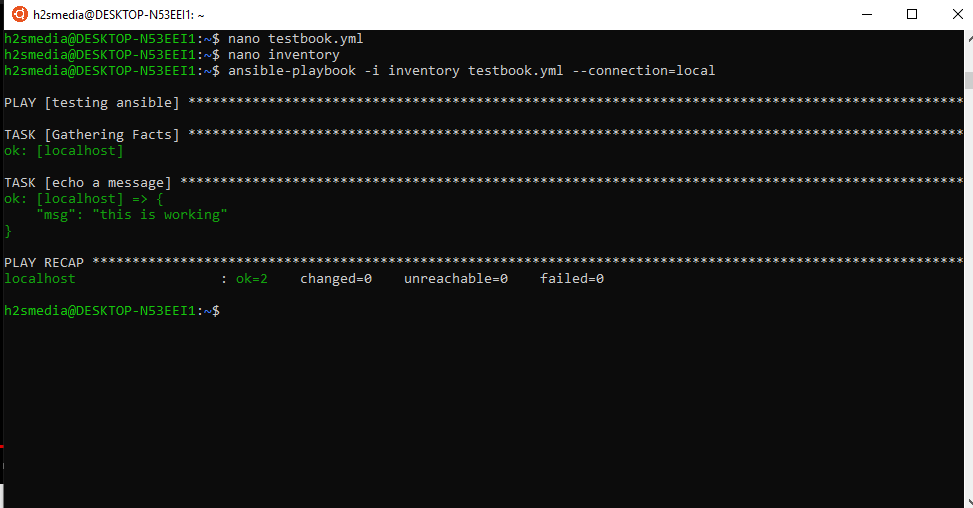
Step 10: Run the Ansible command with inventory
This time again we run the same command above but with inventory file available
This time you will see that it will not be going to show any error.
So, in this way, we can install the Ansible on Windows 10 for testing and other purposes.
Other Useful Resources: