- How to install Mods for Minecraft Forge
- How to install Minecraft Forge
- How to Install Mods for Minecraft Forge
- Introduction: How to Install Mods for Minecraft Forge
- Step 1: Make Sure You Have Already Installed Minecraft Forge.
- Step 2: Download a Mod for Minecraft Forge
- Step 3: Locate the Minecraft Application Folder
- Step 4: Place the Mod You Have Just Downloaded (.jar or .zip File) Into the Mods Folder
- Step 5: Choose Your Minecraft Mod Version
- Be the First to Share
- How To Install Forge Mods (Client Side)
- Overview
- Adding mods to Minecraft Forge
- Common Issues
- Tutorials/Creating Forge mods
- Contents
- Overview [ edit ]
- Things you are not to do [ edit ]
- First steps with Forge [ edit ]
- A note about placeholders [ edit ]
- 1. Create a folder for your project [ edit ]
- 2. Obtain a «source distribution» [ edit ]
- 3. Copy key files to your project folder [ edit ]
- 3½. A note about mappings [ edit ]
- 4. Import the gradle project [ edit ]
- 5. Designate the JDK [ edit ]
- 6. Set up workspace [ edit ]
- 7. Configure Run settings [ edit ]
- Creating a mod for Forge [ edit ]
- Identifying your mod [ edit ]
- Setting up Item Registration [ edit ]
- Creating a Custom Tool [ edit ]
- Custom Layers over Vanilla Textures [ edit ]
- Textures from Scratch [ edit ]
- Creating a Custom Mob [ edit ]
- Models from Scratch [ edit ]
How to install Mods for Minecraft Forge
This guide will explain how to install mods that have been made for the Minecraft Forge API.
1. Make sure you have already installed Minecraft Forge.
2. Download a Forge compatible mod from this site, or anywhere else!
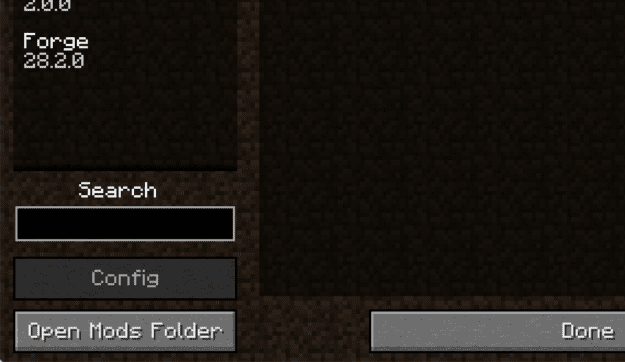
3.В Open Minecraft, click the ‘Mods’ button on the main menu, then click ‘Open Mods Folder’.
Important: Some older versions of Forge may not have the ‘Open Mods Folder’ button. If that is the case, you need to find the folder manually.
- Press the Windows key and R at the same time
- Type %appdata% and press enter
- Find the Minecraft folder and then look for the Mods folder within that
- Click on the desktop and then press Command+Shift+G all at the same time
- Type
/Library and press enter
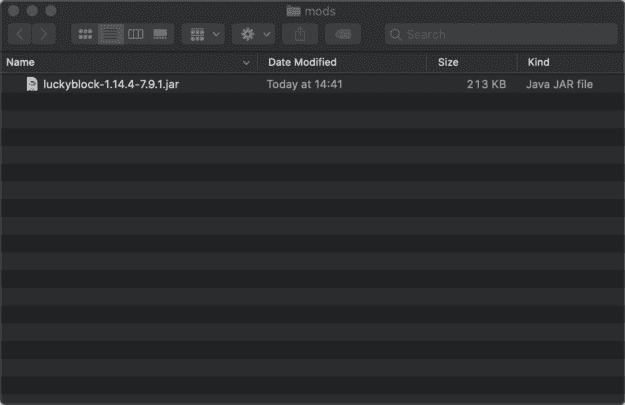
4. Place the mod you have just downloaded (.jar or .zip file) into the Mods folder.
5. Relaunch Minecraft, and you should now see the mod you have installed in the list!
How to install Minecraft Forge
Minecraft Forge is a Modding API that makes it very easy to install a number of different Minecraft mods. This guide will explain how to correctly install Forge.
1.В Visit the Forge website, choose the Minecraft version you would like to run from the sidebar on the left, then download the installer.
2. Open the .jar file you have just downloaded, make sure ‘Install client’ is selected and click OK. Once this has finished you will see a success message.
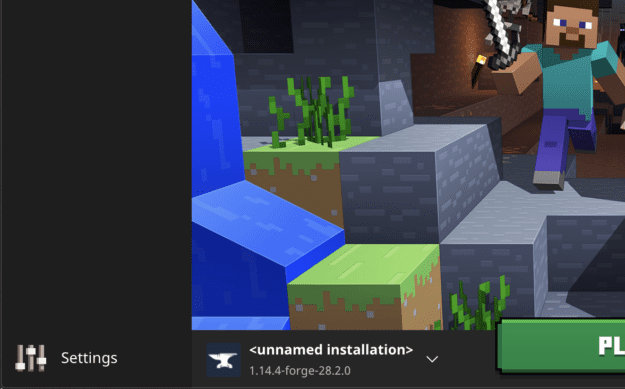
3.В Launch Minecraft and select the Forge profile then click Play.
4. You should now see the Minecraft Forge text in the lower left hand corner and a Mods button below Multiplayer.
If so, congratulations, you have successfully installed Minecraft Forge!
Click here to find out how to add mods once Forge has been installed.
How to Install Mods for Minecraft Forge
Introduction: How to Install Mods for Minecraft Forge
This guide will explain how to install mods that have been made for the Minecraft Forge API.
Step 1: Make Sure You Have Already Installed Minecraft Forge.
Download and install Minecraft Forge. Readmore: Minecraft Forge
Step 2: Download a Mod for Minecraft Forge
Download a mod for Minecraft Forge from this link Minecraft Forge, the Minecraft Forums or anywhere else!
Step 3: Locate the Minecraft Application Folder
Locate the minecraft application folder.
- On windows open Run from the start menu, type %appdata%\.minecraft\ and click Run.
- On mac open finder, hold down ALT and click Go then Library in the top menu bar. Open the folder Application Support and look for minecraft.
Step 4: Place the Mod You Have Just Downloaded (.jar or .zip File) Into the Mods Folder
Place the mod you have just downloaded (.jar or .zip file) into the Mods folder
Step 5: Choose Your Minecraft Mod Version
When you launch Minecraft and click the mods button you should now see the mod is installed.
Help you Find Minecraft Mods and download: https://wminecraft.net/minecraft-mods/
Be the First to Share
Did you make this project? Share it with us!
How To Install Forge Mods (Client Side)
Last modified on Feb 25, 2021 in General
Overview
Having a modded Minecraft server is a great way to customize your gameplay experience. However, playing with mods is not as simple as just uploading them to your server. For every mod that goes into your server, it has to be run client-side. Minecraft by default does not run mods so you need to use a mod loader, Forge. There are multiple different ways you can add mods whether you are just installing Forge and the mods manually to Minecraft or if you are using a launcher such as the Twitch Desktop App. Adding mods to your Minecraft client can be tricky, however, we will be walking you through each step of the process.
Keep in mind that in order for mods to work, you must be running Forge. You can find our guide on installing Minecraft Forge here.
Adding mods to Minecraft Forge
This section only covers how-to on the default Minecraft launcher with Forge installed.
- You need to get the mods from CurseForge or the mod author’s official site. Doing this ensures that you won’t get corrupted files or viruses.
- Once you decide on a mod you want, click the name to open the mod page.
- Open the Files tab to view the versions. To the right of the version you want, press download. It’s best to download the latest recommended update for your version of Minecraft.
- Head back to the mods page and open the Relations tab. This is very important as these are the mods you need for it to work correctly. If you don’t download the dependencies, the mod will not function properly or can cause the game to crash.
- Make sure your Minecraft client is closed.
- Press the Windows Key (Start)
- Type in %appdata% and press enter.
- Open the .minecraft folder and then enter the mods folder.
- From here, just drag in the mods that you wish to add.
- Open Minecraft again and click Play, and the mods should now be loaded. You can check this by clicking the Mods tab on the Minecraft homepage.
- Make sure your Minecraft client is closed.
- At the top of your Mac, click the Go tab and then “Go to Folder…”.
- Type in
/Library/Application Support/minecraft and click Go.
Common Issues
Minecraft Crashes on startup
Minecraft crashing on startup can be a result of a variety of different issues. If this is happening to you, you need to check that all of your mods are for the correct version of Forge, there are no duplicate mods, and that you are not missing any dependencies. You can also test to see if it is the mods crashing the game by launching it without any mods loaded. If you still can’t find out which mod is the issue, you can add the mods back one at a time. This may take a bit of time but it is effective.
Getting Mod Rejections when trying to join a server
Having a mod rejection either means that the mod is not the same version as the one from the server, or that you are missing a mod on your Minecraft client that is on your server or vice versa. Double-check that your mods folder from client-side matches with the server-side mods folder with the exception of client-side only mods.
This server has mods that require FML/Forge to be installed on the client
This means that Forge is not on your Minecraft client at all. This could be that you are just launching the wrong version. Close the client and double-check that it is running the Forge version, if you don’t see Forge under the versions you will need to reinstall it.
Tutorials/Creating Forge mods
Contents
Overview [ edit ]
Mods (short for ‘modifications’) can modify or add items, blocks, entities, and much more. Presumably, you already have an idea for a mod you want to create. If you simply want to add custom advancements, functions, loot tables, structures, recipes or tags to your game, look into how to make a Data pack, which does not require programming. Or look into how to make a resource pack if you simply want to customize textures (colors and designs), models, music, sounds, languages, splashes, fonts, or the end poem. Or perhaps you want to ‘fork’ a favorite mod to update for newer versions of Minecraft. In any case, this guide will eventually cover only the most basic elements of creating an item and creating an entity (a moving thing like a villager, sheep, zombie, etc.), and distributing the resulting mod package.
Minecraft mods consist of jar files (example: yournewmod.jar) which contain class files, JSON files, and image files, to name a few of the most common.
- Class files are specific to the Java programming language. A few Java tutorials to try are w3schools (web and mobile), SoloLearn (web and mobile), and kodevelopment(web). You will need an IDE (Integrated Development Environment) such as IntelliJ or Eclipse to read or create class files. This tutorial will focus on IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2019.
- JSON files are a means of detailing the characteristics of objects used by Java class files. JSON is much simpler than Java. You will need a text editor such as Notepad++, Vim, or Emacs to read or create JSON files. You probably already have a basic text editor on your computer, but there are many advantages to using other ones instead.
- Image files you may be familiar with include .bmp and .jpg formats, but Minecraft requires .png format (example: yournewlogo.png) in multiples of 16 pixels square (example: 16×16, 32×32, 64×64). You will need an image editor such as Paint.NET or GIMP to edit or create .png files. You probably already have MS Paint on your computer, but GIMP has so much more functionality, and Paint.NET is quite user-friendly. There are also several websites with tools for creating pixel art.
If you have been playing Minecraft Java Edition, you probably already have JRE (Java Runtime Environment). To develop a mod, you will need to find JDK (Java Development Kit), which includes the JRE and an emulator. Create a free account at oracle.com and download JDK Standard Edition version 8. Then follow the instructions for installing it, and make note of the location it installs to. Pay particular attention to the section on Updating the PATH Environment Variable.
With a Java Development Kit installed, and the IntelliJ Integrated Development Environment to manipulate Java with, you now have the tools to develop custom software that can be used in a variety of applications. While working on a mod, continue working through Java tutorials false. The lessons will enable you to put your ideas into action, while the ideas will make the lessons more interesting and memorable.
One more tool you should set up before starting a mod is the Forge MDK (Mod Development Kit). Forge is a collection of useful resources and mod loader, designed specifically to simplify compatibility between Minecraft Java Edition and multiple community-created mods. This tutorial will focus on the MDK for version 1.12.2 of Minecraft Java Edition, although Forge for 1.14.4 has been around for some time. An alternative to Forge is Fabric, but Java is still used to code mods either way.
Things you are not to do [ edit ]
There are some things that you should be careful to not do when creating a mod. Keep this list in mind:
- Don’t do anything that violates Mojang Studios’ terms of use for Minecraft.
- Don’t release Minecraft versions or modifications that allow you to play without having bought Minecraft from Mojang Studios.
- Don’t release the de-compiled source code of Minecraft in any way.
- Don’t modify existing mods without permission from that mod’s author(s). Check their License, usually available in the author’s GitHub repository. If you can’t find the license, then you do not have permission to share a modified version with anybody. You may tinker with the files for personal use only.
First steps with Forge [ edit ]
This wiki article aims to provide a foolproof walk-through of a few key elements of Forge’s tutorial: https://mcforge.readthedocs.io. Bookmark their page, as it addresses many issues this article will not. Moreover, there’s more than one valid way to achieve the desired result; this wiki article will focus on the simplest, which is probably not the most efficient or elegant. If you follow precisely the steps outlined here, you should soon have a functional mod, which you can then tinker with to your heart’s content. If you use Linux, Forge’s tutorial will probably be more useful for you. If you use Windows, read on.
A note about placeholders [ edit ]
This tutorial will use «You» to represent the User profile you are logged in with; if you copy-paste paths from this tutorial, be sure to replace «You» with your own Windows username. This tutorial will use «yournewmod» to represent sections you should replace with the mod name you choose for your project.
1. Create a folder for your project [ edit ]
Navigate to C:/Users/You/Documents and create a new folder. The name of this folder may be changed easily later.
2. Obtain a «source distribution» [ edit ]
Visit https://files.minecraftforge.net and make sure the version selected is the version for which you want to create a mod. In the large «Download Recommended» box, click on the small MDK box. A dialog box will appear, asking where you want to save the file, and what to name it. Choose any convenient location, but leave the name unchanged.
3. Copy key files to your project folder [ edit ]
Open the forge-1.16.5-. -mdk folder (with or without unzipping it first) and copy-paste the following 5 files from this folder [ more information needed ] to the project folder you created in the first step:
- the src folder
- the gradle folder
- gradlew
- gradlew.bat
- build.gradle
3½. A note about mappings [ edit ]
There are two different sets of mappings available for method names — «MCP» community-based mappings, and «Official» mappings based in part on the official Obfuscation maps (though class names are different for technical reasons). The default in the MDK has recently been changed to ‘official’, but this tutorial will use the MCP mappings for now because function parameter names are not available in the official mappings.
Change the following line in build.gradle line 34
On line 51 of ExampleMod.java, change options to gameSettings (or simply comment or delete the line)
4. Import the gradle project [ edit ]
Open/Run the IntelliJ IDEA program. In the landing screen, click on Open. A dialog box will appear, asking which file to import. Navigate to your project folder and select «build.Gradle,» then click OK.
5. Designate the JDK [ edit ]
In the next window, click in the «Gradle JVM» field and navigate to the JDK files you installed earlier. If you got version 8 update 282, select the folder named «jdk1.8.0_282.» Click OK and wait for the build to finish, displaying the results in the bottom field.
[TODO: I didn’t get another window, need to verify what happens on a fresh IDEA install]
6. Set up workspace [ edit ]
No Dependencies needed to be Installed. Move to next step as new update in Forge command setupDecompWorkspace is not needed
7. Configure Run settings [ edit ]
After refreshing, double-click the «genIntellijRuns» entry in the «fg_runs» folder. Open the «Edit configurations» window of Run settings and look approximately halfway down, for «Use classpath of module.» Click on its dropdown field, and select the option that ends with .main , then click Apply. If the settings you just finished editing were for the Minecraft Client, click on Minecraft Server and repeat the steps to set the classpath. [TODO: Is this necessary anymore? It was already set]
You can now Run the client, which will start the Launcher with your mod included. When you get to the landing menu, you can check whether your mod is present.
Creating a mod for Forge [ edit ]
Identifying your mod [ edit ]
The project as delivered with the MDK is called «examplemod» with the package name «com.example.examplemod». You will need to rename this to your own names in the following places — rename the class files — build.gradle — META-INF/mods.toml
Package names should be based on a domain name in reverse order, or a name that is not a valid domain name if you do not own a domain name.
[TODO clearer instructions, set up MODID variable]
Setting up Item Registration [ edit ]
You can create a class to put your definitions in. Here we call it RegistryHandler, though some mods have separate classes for each type of object called ModItems, ModBlocks, etc; and in principle you could just add it to the main class. Having at least one class to put them in without any non registration related code provides better organization for when you expand your mod.
In your main class, set it up to automatically be called at the appropriate time, in the public ExampleMod() constructor:
Creating a Custom Tool [ edit ]
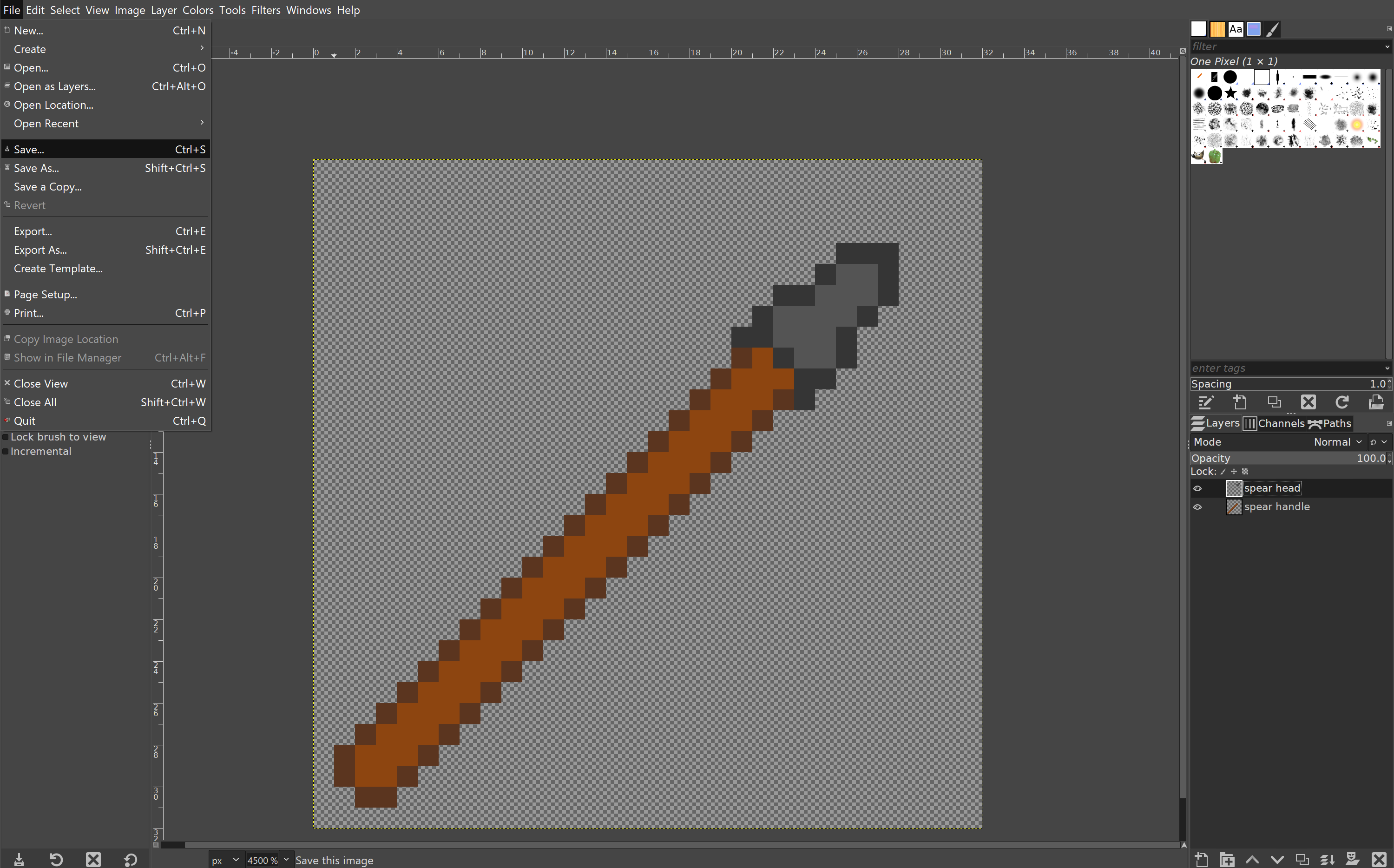
Let’s make a simple spear, with damage ability similar to a stone sword.
So, to start off with we need to make a new directory called tools in your package. Next create a new Java enum called ModItemTier. In this file you need to type a variant of the following:
Next, you need to register your item. Go to your item registry class [?] and make a new item like the one here:
The numbers are the base attack damage [added to the damage set in the ItemTier] and the speed modifier, the values chosen for the example are intermediate between a sword and an axe.
After this, you need to make a JSON file in src/main/resources/assets/examplemod/models/item called what you set earlier, like so:
Then, go to your textures folder and input the texture you will make in the next step. If you want to know more about durability I recommend this page.
Custom Layers over Vanilla Textures [ edit ]
Textures from Scratch [ edit ]
Open an image editor, preferably one that supports transparency, and create a new image, with a size that is a multiple of 16×16 (eg. 32×32, 64×64. etc.)
This example is using a 32×32 pixel image and is made in GIMP.
Create your file, making sure it is in pixels and not inches, millimetres, or any other measurement.
Create a new layer, and delete the original canvas. If you don’t do that, then your image will have a white background.
Using a brush of 1×1 pixel, start drawing your item. Make sure to use separate layers for separate parts of the item to allow changes to be made easier.
When you’re done creating your art, press file to save. If you’re using GIMP or another advanced editor, it won’t save as a .png. For GIMP, it saves as a .xcf.
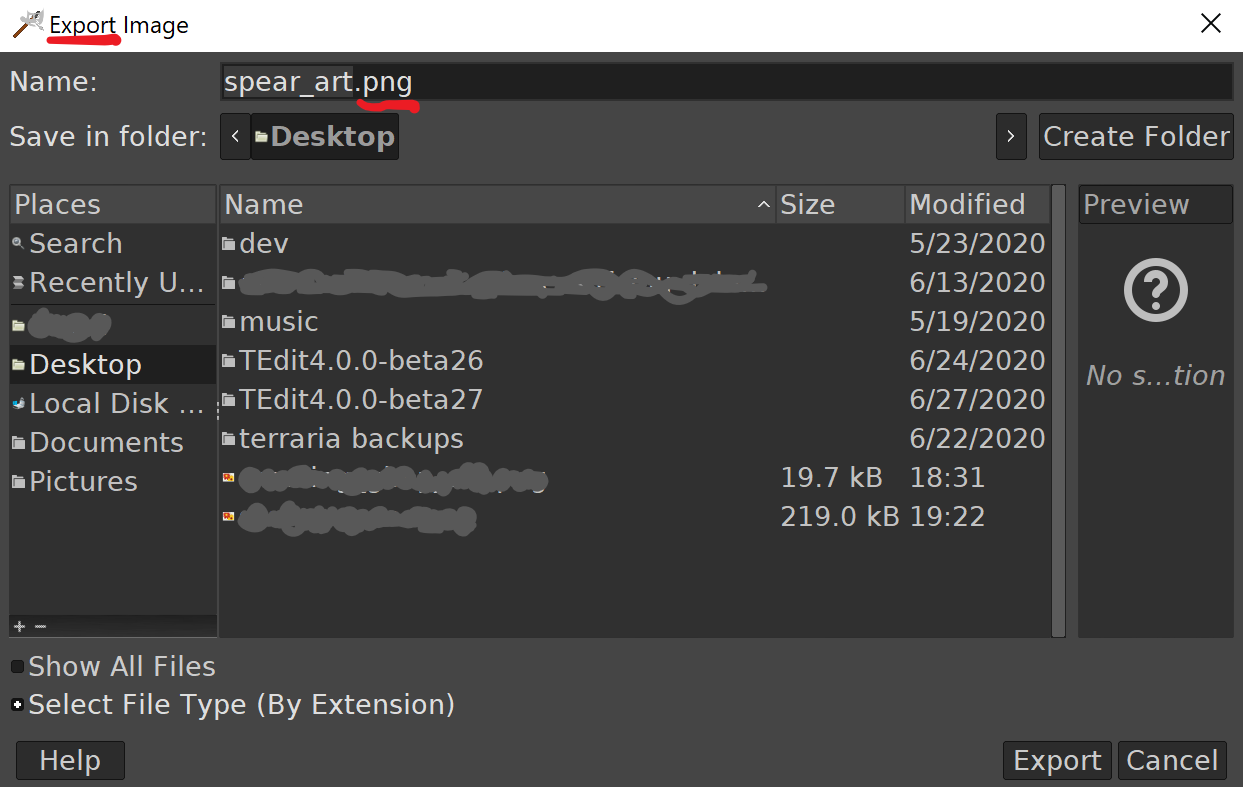
Navigate to the export dropdown or press ctrl+e on Windows or ⌘+E for macOS. This is to export the file. Make sure you export as a .png, not a .jpg or any other file extension. If it is not saved as a .png, it will have a white background and won’t look correct.
If you’re following along with this tutorial and wish to use this image, you can download this finished pixel art here.
Creating a Custom Mob [ edit ]
Models from Scratch [ edit ]
The best way to model mobs is probably blockbench (blockbench website). Blockbench is a free modeling tool, and it would be much faster and easier than taking the other approach, which is slow. If you want to model with it, simply make a cube, position it, rotate it, size it, and make your model the way you want to make it. If you need more cubes, you can easily make a new one. This is probably the best method for this. It is fast, easy, and customizable.