- Debian Ubuntu “netstat: command not found” Error Solution and Netstat Installation
- Search Netstat Packages
- Install Netstat with Net-Tools Package
- Alternatives of Netstat
- What is Netstat-Nat Package
- How to Install netstat Command in Linux
- How to Install netstat Command in Linux
- Using netstat Command in Linux
- Conclusion
- How to Install netstat Command in Linux
- How to Install netstat Command in Linux
- How to Use netstat Command in Linux
- 1. Viewing the Network Routing Table
- 2. Display Network Interface Statistics
- 3. Show Network Connections
- 4. Show Network Services
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- How to Use Netstat Command in Linux to Check a Specific Port
- Listing All Ports and Sockets Using netstat:
- Listing All the Listening Ports and Sockets with netstat:
- Listing All the Listening TCP Ports with netstat:
- Listing All the Listening UDP Ports with netstat:
- Find out What Service Name Represent What Port:
- How to Get Help with netstat:
Debian Ubuntu “netstat: command not found” Error Solution and Netstat Installation
Ubuntu is most used Linux distributions. Canonical provides enterprise support for Ubuntu desktops and servers. netstat is easy to use tool for network operations. In this tutorial we will look how to solve netstat: command not found error and install netstat tool to the Ubuntu and Debian.
Search Netstat Packages
Ubuntu and Debian systems uses deb packages which is managed with apt online package manager. We will use apt to search netstat related package.

Install Netstat with Net-Tools Package
As we see in previous step netstat search listed a lot of package names. The package which provides netstat command is net-tools and we will install is with apt install .
Alternatives of Netstat
If we need or want to check alternative to the netstat we can look following commands.
What is Netstat-Nat Package
When searching for netstat command apt will list netstat-nat package which provides network related commands focused on NAT . We can get detailed information about netstat-nat package with the following command.

Источник
How to Install netstat Command in Linux
The netstat command generates displays that show network status and protocol statistics. It is a cross-platform utility available for Linux, macOS, or Windows systems. Which is very helpful troubleshooting the network configuration and issues. Identifying the application using ports on a system.
The latest Linux operating systems have default installed this tool. But some of the minimal installation may not contain this tool in your system. In that case, this tutorial will help you to install netstat command on Linux system.
How to Install netstat Command in Linux
Generally the net-tools package provides the netstat command for most of the popular Linux distributions. Use one of the below command to install the netstat command on your system.
- Install netstat on Fedora & CentOS/RHEL 8 systems: Use dnf command line package manager to install netstat from default package repositories.
- Install netstat onn CentOS/RHEL 7 systems: For older version of Redhat based systems, use yum package manager to install netstat tool.
- How to Install netstat on Debian/Ubuntu: Use apt package manager to install netstat on Ubuntu and Debian systems form official repositories.
- Install netstat on Arch systems:
- Install netstat on OpenSuse:
Using netstat Command in Linux
Netstat is a widely used command line utility for printing network connections, routing table, interfaces and interfaces statistics. Personally, I use this command for displaying PID/Program name for socket or listening server sockets on a systems.
My frequently used command is:
The above command help me find services running on various ports. With this its easier to identify if any service is listing on any port or not. The command parameters are:
- -t – is used to print TCP connections
- -u – is used to print UDP connections
- -l – Print all listening server sockets
- -p – Print all PID/Program name for sockets
- -n – Don’t resolve names from IPs
Conclusion
This tutorial describes you to how to install missing netstat command on your Linux system. Additionally shared my favorite use case of the netstat command.
Источник
How to Install netstat Command in Linux
Netstat – derived from the words network and statistics – is a command-line utility used by system administrators for analyzing network statistics. It displays a whole manner of statistics such as open ports and corresponding addresses on the host system, routing table, and masquerade connections.
In this article, we will walk you through how you can install the netstat command in different Linux distributions.
How to Install netstat Command in Linux
The package that contains netstat is called net-tools. On modern systems, the netstat utility comes pre-installed and there’s no need to install it.
On older systems, however, you are likely to bump into an error when you run the netstat command. Therefore, to install netstat on Linux distributions, run the command.
Once installed, run the command below to check the version of netstat installed.
How to Use netstat Command in Linux
You can invoke the netstat command on any of the Linux distributions to get different statistics on your network.
1. Viewing the Network Routing Table
You use the -r flag to show the network routing table to get something similar to the output below.

The -n option forces netstat to print addresses separated by dots instead of using symbolic network names. The option is useful for avoiding address lookups over a network.
2. Display Network Interface Statistics
Use the -i flag to get an output of statistics of a network interface that is configured. The -a option prints all present interfaces in the kernel.

3. Show Network Connections
The netstat command utility supports options that display active or passive sockets using the options -t , -n , and -a . The flags show RAW, UDP, TCP, or UNIX connection sockets. Adding the -a option, it will sow sockets ready for connection.

4. Show Network Services
To list services, their current state, and their corresponding ports, run the command.

In this article, we shed light on how you can install netstat command and how it is used to checking a wide array of network statistics. It’s also important to point out that netstat has been deprecated and instead ss utility has taken its place in displaying more refined network statistics.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
How to Use Netstat Command in Linux to Check a Specific Port
netstat command is a part of the net-tools utility package on Debian 9 Stretch. It may not be installed by default on your Debian 9 Stretch operating system. The net-tools package is available in the official package repository of Debian 9 Stretch. So installing it is very easy.
First update the apt package repository cache of your Debian 9 Stretch machine with the following command:
The apt package repository cache should be updated.
Now run the following command to install the net-tools utility on Debian 9 Stretch:
net-tools should be installed.
Now check whether netstat is working with the following command:
Listing All Ports and Sockets Using netstat:
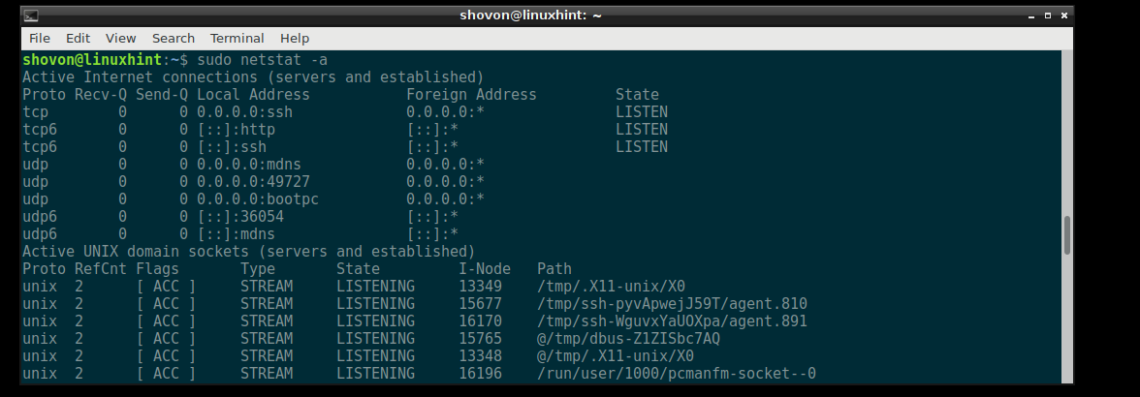
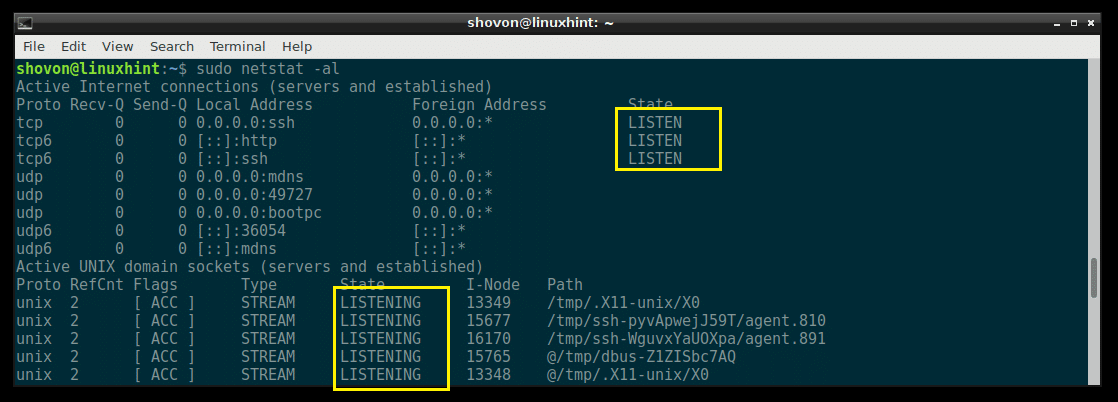
You can list all the opened ports and connected sockets on your Debian 9 machine with the following command:
As you can see, all the opened ports and sockets are listed. It’s a very long list.
Listing All the Listening Ports and Sockets with netstat:
You can use netstat to see a list of all the ports and sockets that are listening with the following command:
As you can see, all the ports and sockets on your Debian 9 machine is listed. It’s a long list.
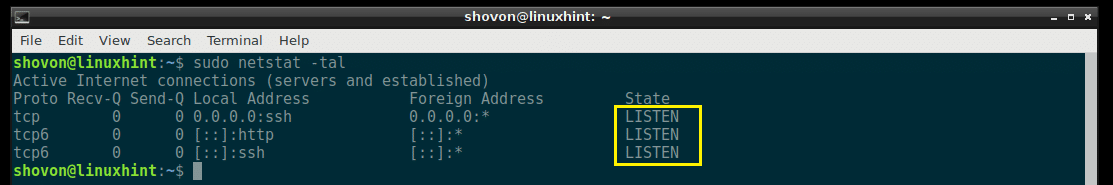
Listing All the Listening TCP Ports with netstat:
You can list all the TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) ports that are listening using netstat with the following command:
As you can see, all the TCP ports that are listening is listed.
In the output of netstat, all the common ports are replaced by the service name by default. For example, the port 80 by default is the port for the HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol), which we all are familiar with. So in the output of netstat, it is shown as http instead of port 80 as you can see in the marked section of the screenshot below.
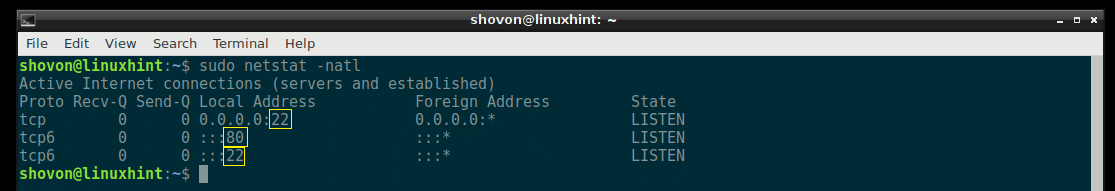
If you need the port number, not the service name, then you can run the following netstat command:
As you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below, the service names are replaced by the port number.
Listing All the Listening UDP Ports with netstat:
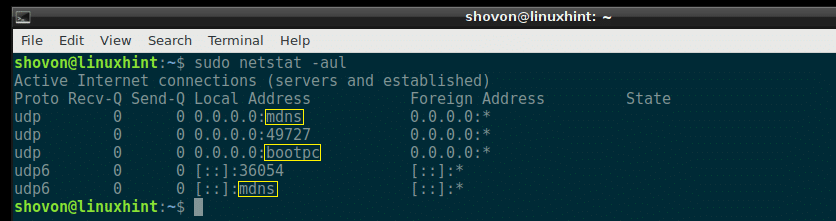
If you want to list all the UDP (User Datagram Protocol) ports that are listening on your Debian 9 machine, you can do so with the following netstat command:
All the listening UDP ports should be listed. Just like the TCP port example, the common port numbers are replaced by the service names by default here as well, as you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below.
But the ports that are not common are not replaced by the service names as you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below.
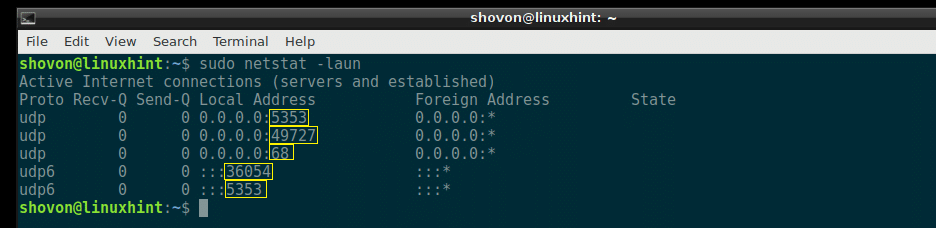
If you want all the ports to be displayed, not the service name as before, then run the following netstat command:
As you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below, the service names are replaced by the UDP port number.
Find out What Service Name Represent What Port:
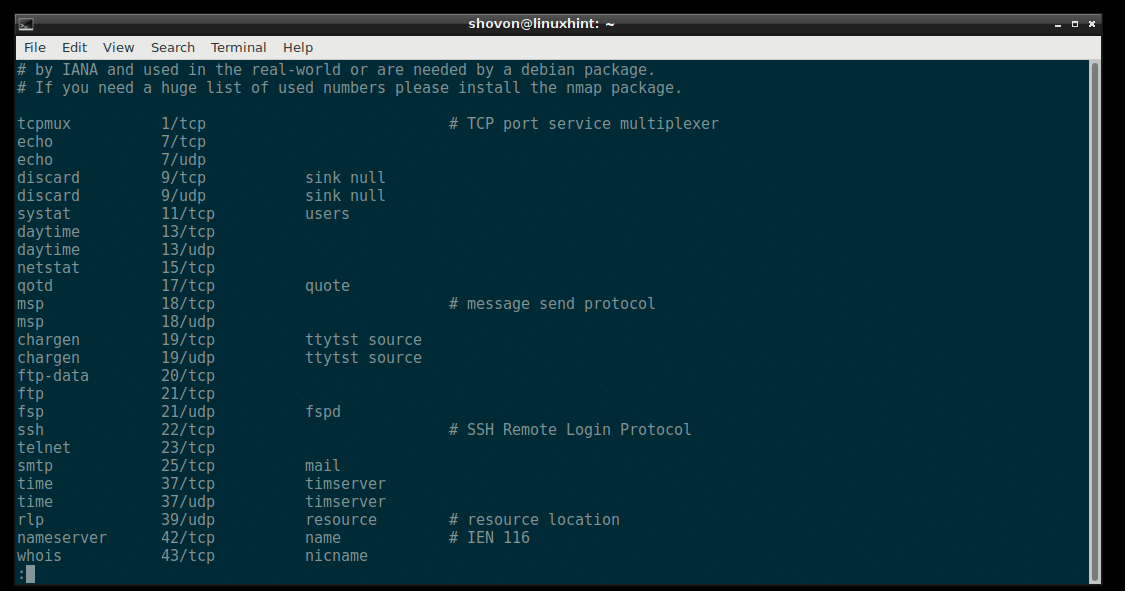
Debian 9 Stretch has a service file which can be found at /etc/services
You can open the service file /etc/services with the following command:
The contents of the /etc/services file:
The /etc/services file contains a long list of service name, and the port number and protocol of that specific service that a client or server may use. Programs on Linux system such as netstat uses this file to resolve the port numbers to service names and vice versa.
The service name, port number and protocol of the SSH service in /etc/services file:
How to Get Help with netstat:
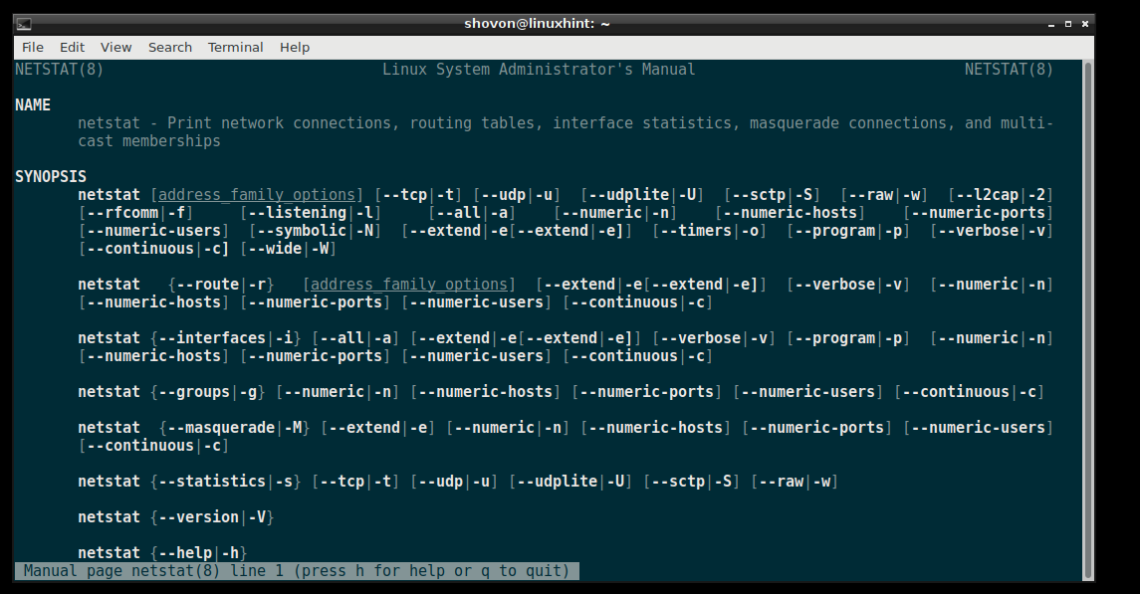
On Debian 9 Stretch, if you need any help with the netstat command, you can just go to the manpage of netstat and you should be able to get a clear documentation of what netstat command line options are available and what they do.
To go to the manpage of netstat, run the following command:
The netstat manpage:
That’s how you show listening ports on Debian 9 Stretch with netstat. Thanks for reading this article.
Источник