- How to Install PuTTY on Linux
- How to Install PuTTY on Linux
- Install PuTTy on Ubuntu
- Install PuTTy on Debian
- Install PuTTy on Arch Linux
- Install PuTTy on CentOS, Red Hat & Fedora
- Install PuTTy from Source Code in Linux
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Установка PuTTY в Linux
- Установка PuTTy в Linux
- How to Install PuTTY on Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions
- Installing Putty on Ubuntu Linux
- Installing Putty on other Linux distributions
- How To Install & use Putty in Ubuntu Linux
- How to Use Putty to access Cloud VMs via Keys
- How to Install PuTTY on Linux (Ubuntu / Fedora / Arch / Manjaro)
- Installing PuTTy on Linux distributions
How to Install PuTTY on Linux
PuTTY is a free and open-source cross-platform SSH and telnet client that even after being around for over 20 years remains one of the most popular SSH clients being used especially on the Windows platform.
Linux distros ship with SSH capabilities built into their terminal but in real-world environments, I have seen PuTTY being used instead of the default Linux systems more time than I cared to count.
The quickest reasons that come to mind for such scenarios include:
- Familiarity: users are more comfortable using an SSH client they got familiar with while using Windows.
- Debug mode: Connection to serial pots and raw sockets is more user-friendly with PuTTY.
- Convenience: PuTTY has a GUI that undeniably makes it easier to use especially by SSH and/or terminal newbies.
It is possible for your own reasons for wanting to use PuTTY on GNU/Linux is different. It doesn’t really matter. Here are the steps to take in order to install PuTTY on Linux distro of your choice.
How to Install PuTTY on Linux
PuTTY is available to install from the default official repositories in most Linux distributions. For instance, you can install PuTTY on Ubuntu and its derivative distros via the universe repository.
Install PuTTy on Ubuntu
First, you’ll have to enable the universe repository so that you can access its packages, update your system to recognize its new access rights, and then run the install command.
Launch PuTTY to see that its UI mirrors that of the windows version. Happy you 🙂

Install PuTTy on Debian
Just like for Ubuntu, PuTTY is available for Debian and all its distros via aptitude (i.e. using apt-get) as shown.
Install PuTTy on Arch Linux
Arch Linux and its derivatives can also install PuTTY from the default repositories.
Install PuTTy on CentOS, Red Hat & Fedora
PuTTY is available to install via the distro’s default package manager.
Install PuTTy from Source Code in Linux
It’s possible that you want to get your hands ‘dirty‘ and build the SSH client from scratch yourself. You’re in luck because it is open-source and the source code is available for free here.
That’s all folks! You’re now equipped with the knowledge to install PuTTY on any Linux distro, in any environment. Now learn how to use putty with this useful putty tips and tricks.
Do you use a different SSH or telnet client? Tell us about it in the comments section below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Установка PuTTY в Linux
Утилита PuTTY заметно выделяется среди огромного количества существующих на рынке SSH-клиентов. В данный момент это бесспорно самый популярный клиент для подключения к удалённому компьютерному узлу и управления ним.
PuTTy станет незаменимым помощником в случае, когда необходимо выполнять администрирование Linux удалённо либо просто подключиться из среды Windows к ОС семейства Unix. В этой статье мы рассмотрим как выполняется установка PuTTy Linux.
Обратим внимание на несколько особенностей:
- Простая установка во всех наиболее распространённых ОС.
- Удалённое администрирование из под Windows или Linux.
- Работа через последовательный порт.
- Поддержка работы с VPN.
- Поддержка IPv6.
- Использование клиентов SCP-SFTP.
- Перенаправление портов.
- Разные варианты аутентификации (в том числе и с открытым ключом).
- Сжатие данных, применяемое до окончания процесса аутентификации.
Разработчики программ используют PuTTy для создания локальной среды, а администраторы сетей — для удалённой настройки маршрутизаторов и управления Linux.
Кроме открытого исходного кода у PuTTy есть ряд других преимуществ перед другими клиентами SSH. Пакет программы состоит только из исполняемых файлов, что исключает привязку к DLL, версии ОС и другим приложениям.
PuTTy ориентирован не только на удобство использования, но и на безопасность. Технология реализует только клиентскую сторону соединения, остальная работа производится на сервере.
Установка PuTTy в Linux
Установка PuTTy в Ubuntu проста и не вызовет сложностей даже у начинающих пользователей Linux. Запустите терминал (сочетание клавиш для быстрого запуска приложения: Ctrl+Alt+T):
Убедитесь, что репозиторий universe активен. Выполните следующую команду:
sudo add-apt-repository universe
Убедившись, что репозиторий включён, обновите Ubuntu, используя команду:
sudo apt update
Далее установите PuTTy:
sudo apt install putty
После этого утилиту можно найти в главном меню и запустить:
Для других операционных систем установка утилиты не очень сильно отличается. Все операции выполняются с помощью команды sudo.
sudo apt-get install putty
sudo dnf install putty
sudo pacman -S putty
Интерфейс PuTTy практически идентичен в любой операционной системе.
Источник
How to Install PuTTY on Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions
Last updated June 26, 2019 By Abhishek Prakash 20 Comments
If I am not wrong, Putty is perhaps the most popular SSH client for Windows.
In IT companies, the development environment is usually on a remote Linux system while the developers use Windows as their local system. Putty is used for connecting to the remote Linux system from the Windows machine.
Putty is not limited to Windows only. You can also use this open source software on Linux and macOS.
But wait! Why would you use a separate SSH client on Linux when you already have the ‘real’ Linux terminal with you? There are several reasons why you would want to use Putty on Linux.
- You have used Putty for so long on Windows that you are more comfortable with it.
- You find it difficult to manually edit SSH config file to save the various SSH sessions. You prefer Putty’s graphical way of storing SSH connection.
- You want to debug by connecting to raw sockets and serial ports.
Whatever may be the reason, if you want to use Putty on Ubuntu or any other Linux, you can certainly do so. Let me show you how to do that.
Installing Putty on Ubuntu Linux
The good news for the Ubuntu users is that Putty is available in the universe repository of Ubuntu.
To install Putty on Ubuntu, you should first make sure that the universe repository is enabled.
Once you have the universe repository enabled, you should update Ubuntu with this command:
After this, you can install Putty with this command:
Once installed, you can start Putty by finding it in the menu.
As you can see in the screenshot below, the Linux version of Putty looks the same as the Windows version. That’s a relief because you won’t have to fiddle around trying to find your way through a new and changed settings .
When you enter the remote system’s hostname or IP address and connect to it, Putty will utilize the already saved SSH keys in your home directory.
Installing Putty on other Linux distributions
Putty is available for Debian so you just need to use apt-get or aptitude for installing it.
Putty is also available for Fedora/Red Hat and can be installed using the default package manager.
You can also easily install Putty in Arch Linux based distributions.
Remember that Putty is an open source software. You can also install it via source code if you really want to. You can get the source code of Putty from the link below.
I would always prefer the native Linux terminal over an SSH client like Putty. I feel more at home with the GNOME terminal or Terminator. However, it’s up to an individual’s choice to use the default terminal or Putty in Linux
What do you use for managing multiple SSH connections on Linux?
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
How To Install & use Putty in Ubuntu Linux
System Admins who had worked on Windows Operating system, surely they have used putty software to ssh UNIX like systems. When they migrated to Ubuntu Desktop , they might require putty to manage their UNIX and Linux systems.
PuTTY is the most popular Windows SSH client. It supports flexible terminal setup, mid-session reconfiguration using Ctrl-rightclick, multiple X11 authentication protocols, and various other interesting things not provided by ssh in an xterm. Putty also supports various protocols like Telnet, SCP, rlogin, SFTP and Serial.
In this article we will go through installations steps of putty in Ubuntu 14.04 / 16.04 LTS / 18.04 LTS
Step1) Issue the below Command to install Putty
Open the terminal on your ubuntu system and run below apt-get command to install putty ( Putty Debian package available in the default package repositories).
$ sudo apt-get install putty -y
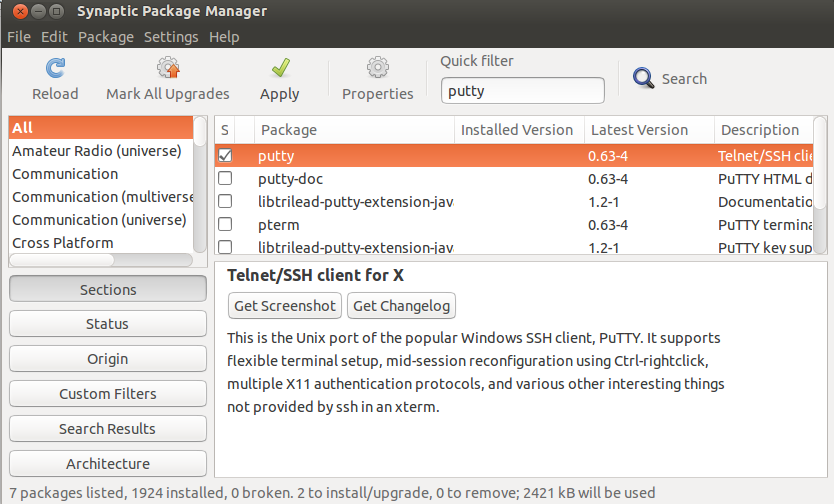
Alternate way to install putty is via GUI ( Synaptic Package Manager), In case Synaptic is not installed the first install it via below command,
$ sudo apt-get install synaptic -y
Once the synaptic is installed then open the Synaptic Package Manager , search putty as shown below :
Click on putty Select ‘Mark for Installation’ option & then click on apply.
Step:2 Now Access the Putty SSH Client
Click on PuTTY SSH Client
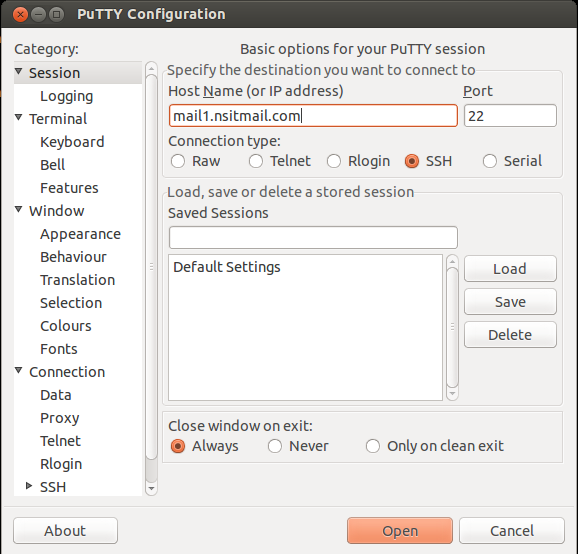
Enter Remote Server’s IP Address or Hostname.
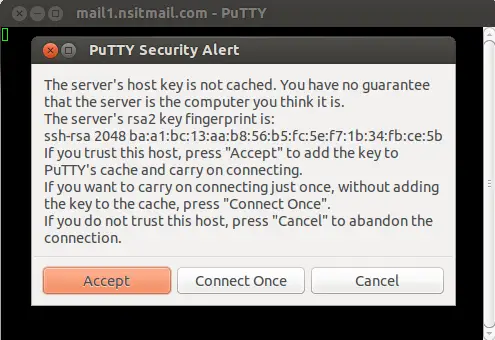
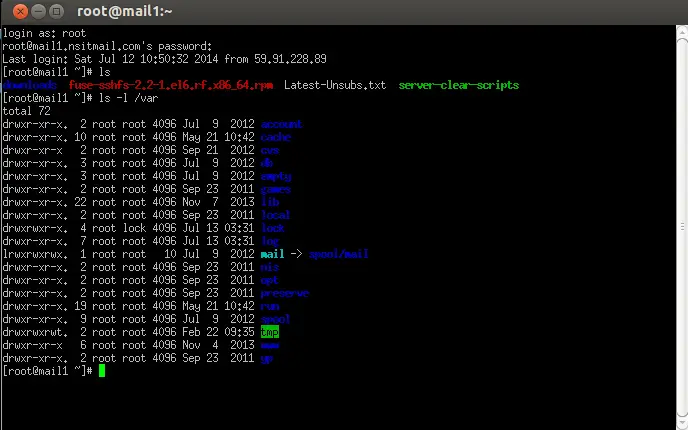
Click On Accept , then it will ask for User Name & Password as shown below :
How to Use Putty to access Cloud VMs via Keys
Let’s suppose you want to access your public cloud VMs via putty using their private SSH keys, so for that refer the below steps:
1) Access the Putty
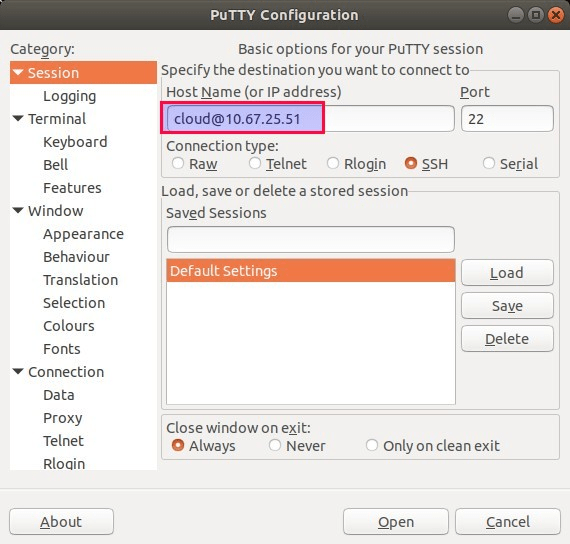
2) Enter User Name and External IP address of your Cloud VM in ‘Host Name’ field
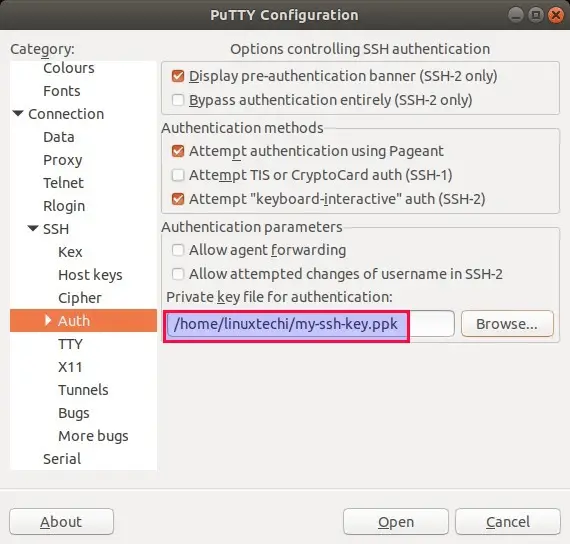
Here User name is the same user for which SSH keys are generated. By default SSH keys are generated in .pem format and putty don’t accept .pem ssh private keys, so it is recommended covert .pem ssh keys into .ppk format. One of the easiest way to convert keys into .ppk is via PuTTYgen utility, example is shown below. Puttygen utility will be installed automatically when we install putty.
$ puttygen my-ssh-key.pem -o my-ssh-key.ppk
3) From SSH Tab, choose ‘Auth’ and then browse .ppk format ssh key,
Now click on Open to start the SSH session with your cloud VM, After the successful Connection to your Cloud VM, run the commands and other tasks that you want to do and to come out of VM or disconnect from VM type exit command.
That’s all from this guide, please do share your feedback and comments.
Источник
How to Install PuTTY on Linux (Ubuntu / Fedora / Arch / Manjaro)
PuTTY stands out from the huge number of existing SSH clients. It is by far the most popular client for connecting to and controlling a remote computer at the moment.
PuTTy will become an indispensable assistant in the case when you need to administer Linux remotely or just connect from the Windows environment to the Unix OS. In this article I will show you how to install PuTTy on popular Linux distributions.
Besides open source, PuTTy has a number of other advantages over other SSH clients. The utility package consists only of executable files, which excludes linking to DLL, OS version and other applications. PuTTy is focused not only on usability, but also on security. The technology implements only the client side of the connection, the rest of the work is done on the server.
Installing PuTTy on Linux distributions
Installing PuTTy is simple and straightforward, even for novice Linux users.
- Open a terminal with the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + T .
- Next, install the PuTTy utility in Ubuntu, for this enter or paste this command into the terminal: Debian:Arch Linux / Manjaro:Fedora / Red Hat:
Сonfirm the installation.
If you have problems installing on Ubuntu, make sure the universe repository is active. To do this, run the following command:
Update Ubuntu using the command:
I would be grateful if you shared this information
Источник