- How to get the Windows 10 May 2020 Update
- How to get the Windows 10 May 2020 Update
- Semi-Annual Channel released for commercial customers
- Keeping you protected and productive
- Patching
- AltServerPatcher — sideload IPA from Windows
- What is AltServerPatcher?
- How to sign IPA on Windows using AltServerPatcher
- Sideload IPA files using AltStore app on Mac
- How to patch on Windows?
- 4 Answers 4
How to get the Windows 10 May 2020 Update
Windows 10 continues to play a key role in how we learn, live and work during these unique times, and we want to ensure a high quality and reliable experience, while also delivering you the latest innovations. In mid-April, we announced the initial availability of the Windows 10 May 2020 Update through the Windows Insider Program’s Release Preview ring, allowing us to both monitor and improve the quality of the release. Based on affirmative preview feedback, today we are pleased to announce that we are starting to make the May 2020 Update available. In this blog, we will cover how you can get the update and choose when to install, and availability for commercial organizations to begin targeted deployments.
How to get the Windows 10 May 2020 Update
To ensure you continue to have a reliable, productive experience with your Windows 10 devices, we are taking a measured and phased approach to how we offer the May Update, initially limiting availability to those devices running Windows 10, versions 1903 and 1909 who seek the update via Windows Update.
Beginning today, the May 2020 Update is available for customers who would like to install this latest release. If you are ready to install the update, open your Windows Update settings (Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update) and select Check for updates. Once the update appears, you can select Download and install. (Note: You may not see Download and install on your device as we are slowly throttling up this availability over the coming weeks, or your device might have a compatibility issue for which a safeguard hold is in place until we are confident that you will have a good update experience.) Once the download is complete and the update is ready to install, we’ll notify you so that you can pick the right time to finish the installation and reboot your device, ensuring the update does not disrupt your activities. This new “Download and install” capability is available for devices running Windows 10, version 1903 or version 1909. For more information on the new user update controls and how to get the May 2020 Update, watch this video.
Semi-Annual Channel released for commercial customers
Today’s release of the May 2020 Update (Windows 10, version 2004) marks the start of the 18-months servicing support lifecycle. If you’re an IT administrator, we recommend that you begin targeted deployments to validate that the apps, devices and infrastructure used by your organization work as expected with the new release and features. Windows 10, version 2004 is available through Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), Windows Update for Business and the Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC) for phased deployment using Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager or other systems management software. For information about the latest features for commercial customers, see “What’s new for IT pros in Windows 10, version 2004.” For insights on how to update, see the Windows IT Pro Blog post on feature updates while working remote. If you’re curious about Windows Server, version 2004, which was also released today, see the Windows Server Containers blog.
Keeping you protected and productive
Given all the recent changes to work and home life, we are focused on meeting you where you are and helping you adapt to these new challenges. We have often noted that being on the latest version of Windows 10 provides you with the latest features, security improvements and control. This is even more true today. The May 2020 Update offers many new features that can save you time, make you more productive and help you have fun – in addition to further enhancing your control and choices related to updates. Find out more in the “What’s new in the Windows 10 May 2020 Update” blog.
We will closely monitor the May 2020 Update experience and share timely information on the current rollout status and known issues (open and resolved) across both feature and monthly updates via the Windows release health dashboard and @WindowsUpdate. As always, please continue to tell us about your experience by providing comments or suggestions via Feedback Hub.
Patching
An application that has been installed using the Microsoft Windows Installer can be upgraded by reinstalling an updated installation package (.msi file), or by applying a Windows Installer patch (an .msp file) to the application.
A Windows Installer patch (.msp file) is a self-contained package that contains the updates to the application and describes which versions of the application can receive the patch. Patches contain at a minimum, two database transforms and can contain patch files that are stored in the cabinet file stream of the patch package. For more information about the parts of a Windows Installer patch package, see Patch Packages.
Servicing applications by delivering a Windows Installer patch, rather than a complete installation package for the updated product can have advantages. A patch can contain an entire file or only the file bits necessary to update part of the file. This can enable the user to download an upgrade patch that is much smaller than the installation package for the entire product. An update using a patch can preserve a user customization of the application through the upgrade.
**Windows Installer 4.5 and later:В В **
Beginning with Windows Installer 4.5, developers can mark components in a patch with the msidbComponentAttributesUninstallOnSupersedence value in the Component table. If a subsequent patch is installed, marked with the msidbPatchSequenceSupersedeEarlier value in its MsiPatchSequence table to supersede the first patch, Windows Installer 4.5 and later can unregister and uninstall components marked msidbComponentAttributesUninstallOnSupersedence to prevent leaving behind unused components on the computer. If the component is not marked with with this bit, installation of the superseding patch can leave an unused component on the computer. Setting the MSIUNINSTALLSUPERSEDEDCOMPONENTS property has the same effect as setting this bit for all components.
**Windows Installer 3.0 and later:В В **
Developers who use Windows Installer 3.0, and author patch packages that have the MsiPatchSequence table can create patch packages that do the following:
- Use the product baseline cached by the installer to more easily service applications with smaller delta patches. For more information about using the product baseline, see Reducing Patch Size.
- Skip actions associated with specific tables that are unmodified by the patch. This can significantly reduce the time required to install the patch. For more information about which tables can be skipped, see Patch Optimization.
- Create and install patches that can be uninstalled singly, and in any order, without having to uninstall and reinstall the entire application and other patches. For more information about uninstalling patches, see Removing Patches.
- Apply patches in a constant order regardless of the order that the patches are provided to the system. For more information about how the Windows Installer determines the sequence used to apply patches, see Sequencing Patches.
- Apply patches to an application that has been installed in a per-user-managed context. For more information, see Patching Per-User Managed Applications.
**Windows Installer 2.0:В В **
The MsiPatchSequence table is not supported. Beginning with Windows Installer 3.0, patch packages can contain information that describes the patching sequence for the patch relative to other updates and additional descriptive information.
The recommended method for creating a patch package is to use patch creation tools such as Msimsp.exe and Patchwiz.dll. Developers can generate a patch creation file as described in the section: Creating a Patch Package. The creation of a small update patch is described in the section: A Small Update Patching Example.
Microsoft Windows Installer accepts a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) as a valid source for a patch. For more information about how to install a patch located on a Web server, see Downloading and Installing a Patch From the Internet.
A single Windows Installer patch (.msp file) can be applied to the installation package when installing an application for the first time. For more information, see Patching Initial Installations.
It is not possible to eliminate all circumstances when the application of a patch may require access to the original installation source. However, to minimize the possibility that your patch will require access to the original source, adhere to the points listed in the following section: Preventing a Patch from Requiring Access to the Original Installation Source.
To minimize the possibility that your patch is not broken by a subsequent customization transform, typically the patch is installed first, followed by the customization. Installing customization transforms first, and then the patch, may break the customization. For more information about patching customized applications, see Patching Customized Applications.
AltServerPatcher — sideload IPA from Windows
Cydia Impactor is not working for a few months and because of frequent certificate revokes installing apps using 3rd party App Stores is also a pain. Mac users can download AltDeploy tool to sign IPA files, and AltServerPatcher app for Windows can help you to sideload IPA without revokes.
What is AltServerPatcher?
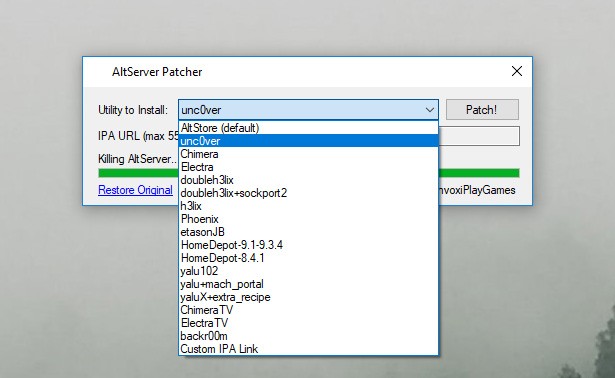
AltServerPatcher is a utility that patches AltServer to install any IPA from a web URL. This is an effective replacement of Cydia Impactor for Windows. The application doesn’t sign IPA files itself. It offers presets allowing you to sideload common jailbreaks, such as unc0ver, Phoenix, or h3lix.
AltServerPatcher is packed with links to IPA files containing unc0ver, Chimera, Electra, doubleh3lix, doubleh3lix + sockport2, h3lix, Phoenix, etasonJB, Home Depot (9.1-9.3.4), Home Depot (8.4.1), yalu102, yalu + mach_portal, yaluX + extra_recipe, ChimeraTV, ElectraTV, and backr00m.
Additionally, you can provide own link to IPA file that will be downloaded, signed, and sideloaded to your iOS devices using AltServer. Before patching, AltServerPatcher creates a backup of AltServer.exe that can be restored from the app itself. If something goes wrong simply reinstall AltServer.
This is not a perfect solution or typical Cydia Impactor alternative, but it works and you can sideload any IPA file to your device without revokes. Of course, the free Apple certificate has the same limitations you know from Impactor. The sideloaded apps will work only for 7 days.
AltServer allows you to install max 3 apps on your device. Apps that have been installed using non-developer Apple IDs (instead of $99/year Apple developer account) are only valid for 7 days, at which point they will no longer open. Every 7 days after signing, it’s required to repeat the install process, however, you do not have to delete the apps. All settings and game saves will be available.
How to sign IPA on Windows using AltServerPatcher
Preparing the platform to sign and sideload IPA files on Windows using AltServerPatcher, and AltServer is easy. Download all tools to sign IPA on Windows. Works also on iOS 8.0 & 12.1.2, iOS 13.
Step 1. Download AltServer Windows, and install the app.
Step 2. Install the newest version of iTunes+iCloud.
Step 3. Download AltServerPatcher for Windows, and extract the ZIP file.
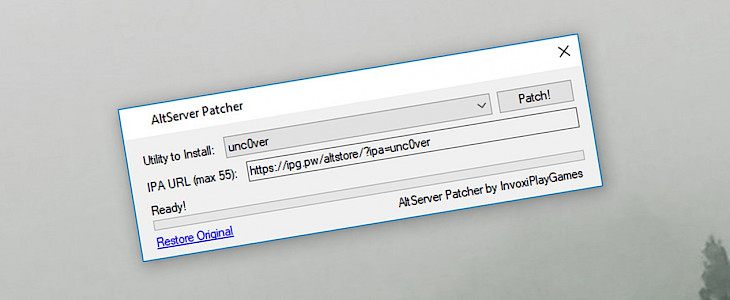
Step 4. Open AltServerPatch.exe and select utility to install.
Step 5. Alternatively, provide your own URL to IPA file (max 55 characters).
Step 6. Click Start to patch AltServer.exe.
Step 7. Open AltServer app and select «Install AltStore» from System Tray.
Step 8. Provide your Apple ID and password (or app-specific password).
Step 8. Navigate to Settings → General → Device Management.
Step 10. Find the newly installed App Certificate and trust it.
Step 11. Run the installed app from your iPhone.
If you have any issues installing IPA files temporarily disable Windows Security’s «Real-Time Protection» in Windows Defender or any other antivirus software you are using.
When you have enabled two-factor authentication for your Apple ID, AltServer is not allowed to sign in with your normal password. Instead, you must go to appleid.apple.com and create a new “App-Specific password”. You can then use this new password when AltServer asks for your Apple ID.
Sideload IPA files using AltStore app on Mac
AltStore software introduces itself as an AppStore like alternative. In reality, this is an IPA signing platform based on libraries provided by Cydia Impactor. By default, you can use the free software to install only iOS emulators, but with a patch by Hiraku, you can also force it to sideload IPA files.
Step 1. Download AltStore app for Mac OS.
Step 2. Open the DMG file and move the app to the Applications folder.
Step 3. Download AltStore hack script to Desktop.
Step 4. Open Terminal app.
Step 5. Execute command in the console
Step 6. Select unc0ver to sideload the app on your device and Enter.
Step 7. Enable the ability to open Patched AltStore from anywhere in Gatekeeper.
Step 8. Open AltServer app from Applications folders.
Step 9. Install Mail Plug-in from the menu.
Step 10. Next, go to Mail → Preferences → General → Manage Plug-ins…
Step 11. Activate AltPlugin.mailbundle plugin.
Step 12. Connect your iPhone to Mac via USB cable.
Step 13. Install AltStore app from the menu and select a connected device.
Step 14. Provide your Apple ID and password.
Step 15. unc0ver IPA will be downloaded on your Mac and sideloaded on the device.
Step 16. Trust the certificate in Settings → General → Device Management.
How to patch on Windows?
Given a (source) patch file, what’s the easiest way to apply this patch on the source files under Windows?
A GUI tool where I can visually compare the unchanged-changed source lines would be great.
4 Answers 4
Patch for Windows is what you’re looking for.
Thanks to Macke, a good way to apply a patch file under Windows OS is using Git. As I understood, Git is a version control solution like SVN.
Here is a guideline to apply a patch :
- First of all, download the latest release of the Windows Git Edition here : GIT
- With the cmd prompt, change directory to the patch file and files to patch
- Now you can use the following command line :
Thank you Macke
Not that since Git 2.3.3 (March 2015), you can use git apply —unsafe-paths to use git apply outside a git repo.
» git apply » was not very careful about reading from, removing, updating and creating paths outside the working tree (under —index / —cached ) or the current directory (when used as a replacement for GNU patch).
The documentation now includes:
By default, a patch that affects outside the working area (either a Git controlled working tree, or the current working directory when » git apply » is used as a replacement of GNU patch) is rejected as a mistake (or a mischief).
When git apply is used as a «better GNU patch», the user can pass the —unsafe-paths option to override this safety check.
This option has no effect when —index or —cached is in use.
So if you have git installed, git apply could help, even outside of any git repo.