- Which version of Windows operating system am I running?
- Find operating system info in Windows 10
- Related links
- Find operating system info in Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1
- Related links
- Find operating system info in Windows 7
- Related links
- How to install the Microsoft Windows operating system
- Check hardware compatibility
- Genuine Windows CD, DVD, or USB thumb drive
- Installing or upgrading Windows
- Final Windows and computer configuration
- Long-term maintenance of Windows
- Operating system
- What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
- What is an Operating System?
- History Of OS
- Examples of Operating System with Market Share
- Types of Operating System (OS)
- Batch Operating System
- Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
- Real time OS
- Distributed Operating System
- Network Operating System
- Mobile OS
- Functions of Operating System
- Features of Operating System (OS)
- Advantage of using Operating System
- Disadvantages of using Operating System
- What is a Kernel?
- Features of Kennel
- Types of Kernels
Which version of Windows operating system am I running?
Find operating system info in Windows 10
To find out which version of Windows your device is running, press the Windows logo key + R, type winver in the Open box, and then select OK.
Here’s how to learn more:
Select the Start button > Settings > System > About .
Under Device specifications > System type, see if you’re running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
Under Windows specifications, check which edition and version of Windows your device is running.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate in Windows 10.
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
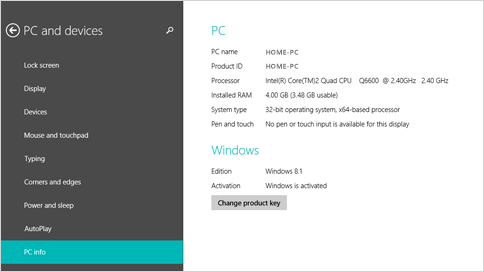
Find operating system info in Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1
To find out which version of Windows your device is running, press the Windows logo key + R, type winver in the Open box, and then select OK.
If your device is running Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1, here’s how to learn more:
If you’re using a touch device, swipe in from the right edge of the screen, tap Settings, and then tap Change PC settings. Continue to step 3.
If you’re using a mouse, point to the lower-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer up, click Settings, and then click Change PC settings.
Select PC and devices > PC info.
Under Windows you’ll see which edition and version of Windows your device is running.
Under PC > System type you’ll see if you’re running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate Windows 7 or Windows 8.1
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
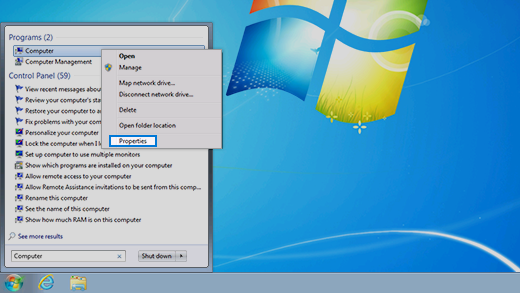
Find operating system info in Windows 7
Select the Start 
Under Windows edition, you’ll see the version and edition of Windows that your device is running.
Support for Windows 7 ended on January 14, 2020
We recommend you move to a Windows 10 PC to continue to receive security updates from Microsoft.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate Windows 7 or Windows 8.1.
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
How to install the Microsoft Windows operating system
Each version of Microsoft Windows is installed on a computer using similar steps. While there are steps in the installation process that differ between versions of Windows, the following general steps and guidelines help you install Windows on your computer.
If you are replacing the hard drive in your computer, you need to reinstall Windows again.
If you are replacing the motherboard in your computer, you may need to purchase a new licensed copy of Windows and install it. Microsoft has designed current versions of Windows to be tied to the motherboard in the computer when Windows is installed. So if you change the motherboard, the existing license, or product key, may no longer be valid.
If you want to upgrade to a newer version of Windows on your computer, the steps on this page help you with the upgrade process. The Windows installation process should recognize if you have an older version of Windows already installed on the computer and ask if you want to upgrade or perform a fresh install. The upgrade process installs the newer Windows operating system files over top the old ones and preserve your files.
The steps below are for all recent versions of Windows, including Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10. These steps would even work for earlier versions (e.g., Windows 95) as long as you’re using the disc version. The floppy diskette version is similar, but it requires additional steps.
The install guidelines for Windows for a server have additional steps based on the type of server and version of Windows.
Check hardware compatibility
Before installing or upgrading Windows on your computer, check the hardware in the computer to make sure it’s compatible with that version of Windows. Microsoft provides a Windows Compatible Products List for checking if the hardware in your computer is compatible with the chosen version of Windows.
If you find that one or more pieces of hardware in your computer are not compatible with the chosen Windows version, we recommend replacing that hardware with compatible hardware. Having compatible hardware in your computer helps ensure the Windows install or upgrade process is successful.
Genuine Windows CD, DVD, or USB thumb drive
First, you need a genuine copy of the Microsoft Windows operating system installation CD, DVD, or USB thumb drive. A genuine Windows product key is included with the installation disc, which is required to activate Windows after installation. If you have an OEM computer, the Windows product key is often on the back or side of the computer.
If you have an OEM computer (e.g., Acer, Dell, HP, etc.), the computer will not have a genuine Windows CD, DVD, or USB thumb drive. Instead, you would reinstall Windows and all the software using a hidden partition or a set of restore discs. The steps mentioned on this page would still work, but you’d need a copy of Windows. You can borrow a friends Windows disc, as long as its the same version of Windows that came with the computer and have a product key.
With early versions of Windows, you cannot download a copy of Windows to install on a computer. You must purchase a physical copy of Windows. If you are installing Windows 10, you can download the Windows 10 creation tool to create a bootable disc or USB thumb drive.
Microsoft has Windows 10 available for download only from their website. Any other site that claims to have copies of other versions of Windows should not be trusted. These copies of Windows are pirated software and could contain anything including spyware or malware.
Installing or upgrading Windows
To start the Windows install or upgrade process, you need to configure your computer to boot from a CD or DVD before booting to the hard drive. Changing the boot process forces the computer to look for the Windows installation disc before trying to boot from the hard drive.
- Open the CMOS setup.
- How to enter the BIOS or CMOS setup.
- Change the computer’s boot order. Set the CD, DVD or disc drive as the first boot device if you are trying to boot from a disc. Or, set the first boot device to your USB drive if you’re trying to boot from a USB thumb drive. If the drive is not shown, keep the disc is inserted and reboot the computer. With the disc in the drive, BIOS should recognize and include it in the list.
- Save the settings change and exit BIOS.
Once you have updated the boot order, you can begin the Windows installation process.
- Place the Windows disc in the CD/DVD drive or USB thumb drive into the back of the computer.
- Turn on or restart the computer. As the computer starts up, it should detect the installation disc or drive and show a message similar to Press any key to boot from CD. Press any key on the keyboard to have the computer boot from the Windows disc or drive.
- After the Windows install begins, there are several prompts that you need to answer. Select either Yes or the appropriate option to install Windows.
Make sure you select the Full Install option and not the Repair or Upgrade option.
If you are upgrading to a newer version of Windows, select the Upgrade option instead of the Full Install option.
- When asked which partition to install Windows onto, select the main partition, which is usually the C: drive or one labeled «Unallocated partition». If upgrading Windows, select the existing installation of Windows on the hard drive.
- You may be asked if you want to erase all contents on the hard drive, then install Windows. We recommend you choose this option, as it also formats the hard drive to allow the Windows operating system to be installed.
You can use the erase all contents option to effectively uninstall an existing version of Windows on the hard drive, then install Windows agains.
- The computer may need to restart several times during the Windows install process. The restarts are normal and if prompted to restart, select the Yes option.
- When the install process is nearly complete, the Windows configuration option screens are shown. On these screens, you may be asked to select the time zone you live in, your preferred language, and the name of the account you use to access Windows. Select the appropriate options and enter the appropriate information on each configuration screen.
The Windows install process is completed when the computer prompts you to log in or when it loads into Windows.
Final Windows and computer configuration
After Windows is installed on the computer, you need to install the drivers and related software for the hardware in the computer. You can use the installation discs that came with the hardware, or you can download the drivers from the hardware manufacturer’s website.
If you cannot download drivers because your network card is not working after installing Windows, you can download the drivers on another computer. Then, copy them to a USB thumb drive, and move them over to your computer.
It is strongly recommended that you install the latest drivers for each piece of hardware.
To determine which hardware needs drivers to be installed, check the Device Manager and look for exclamation mark «!» next to hardware devices. The exclamation point means drivers are needed for that device.
After installing the necessary hardware device drivers, install any software programs on the computer that you want to use.
Finally, download and install any available Windows updates. Updating Windows improves the performance of the operating system, the hardware in the computer, and software programs you use. It can also improve security by fixing potential security holes and flaws in Windows.
Long-term maintenance of Windows
Microsoft frequently releases new updates for Windows, so we recommend you check for and install available updates. Doing so helps keep Windows running better and keep your computer protected.
Also, periodically check for updated hardware device drivers from manufacturers’ websites. Keeping hardware drivers updated helps the hardware devices in the computer run at peak performance and improves compatibility with other computer hardware and software.
Operating system
- Download Restoro PC Repair Tool that comes with Patented Technologies (patent available here).
- Click Start Scan to find Windows issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Click Repair All to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Restoro has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
An operating system (OS) is a collection of software that manages computer hardware resources and provides common services for computer programs.
The operating system is a vital component of the system software in a computer system. Application programs usually require an operating system to function. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources.
Early computers were built to perform a series of single tasks, like a calculator. Basic operating system features were developed in the 1950s, such as resident monitor functions that could automatically run different programs in succession to speed up processing.
Operating systems did not exist in their modern and more complex forms until the early 1960s. Hardware features were added, that enabled use of runtime libraries, interrupts , and parallel processing. When personal computers became popular in the 1980s, operating systems were made for them similar in concept to those used on larger computers.
What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
What is an Operating System?
An Operating System (OS) is a software that acts as an interface between computer hardware components and the user. Every computer system must have at least one operating system to run other programs. Applications like Browsers, MS Office, Notepad Games, etc., need some environment to run and perform its tasks.
The OS helps you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language. It is not possible for the user to use any computer or mobile device without having an operating system. 
History Of OS
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage
- The General Motors Research Lab implemented the first OS in the early 1950s for their IBM 701
- In the mid-1960s, operating systems started to use disks
- In the late 1960s, the first version of the Unix OS was developed
- The first OS built by Microsoft was DOS. It was built in 1981 by purchasing the 86-DOS software from a Seattle company
- The present-day popular OS Windows first came to existence in 1985 when a GUI was created and paired with MS-DOS.
Examples of Operating System with Market Share
Following are the examples of Operating System with the latest Market Share
| OS Name | Share |
| Windows | 40.34 |
| Android | 37.95 |
| iOS | 15.44 |
| Mac OS | 4.34 |
| Linux | 0.95 |
| Chrome OS | 0.14 |
| Windows Phone OS | 0.06 |
Types of Operating System (OS)
Following are the popular types of Operating System:
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
Batch Operating System
Some computer processes are very lengthy and time-consuming. To speed the same process, a job with a similar type of needs are batched together and run as a group.
The user of a batch operating system never directly interacts with the computer. In this type of OS, every user prepares his or her job on an offline device like a punch card and submit it to the computer operator.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
Time-sharing operating system enables people located at a different terminal(shell) to use a single computer system at the same time. The processor time (CPU) which is shared among multiple users is termed as time sharing.
Real time OS
A real time operating system time interval to process and respond to inputs is very small. Examples: Military Software Systems, Space Software Systems are the Real time OS example.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems use many processors located in different machines to provide very fast computation to its users.
Network Operating System
Network Operating System runs on a server. It provides the capability to serve to manage data, user, groups, security, application, and other networking functions.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those OS which is especially that are designed to power smartphones, tablets, and wearables devices.
Some most famous mobile operating systems are Android and iOS, but others include BlackBerry, Web, and watchOS.
Functions of Operating System
Below are the main functions of Operating System: 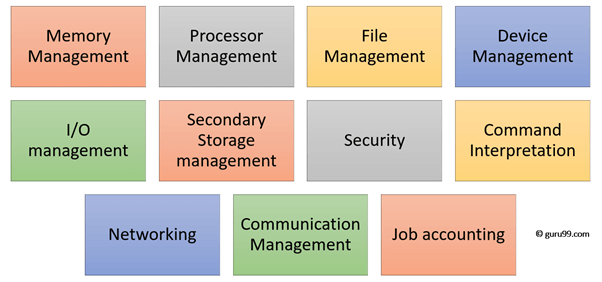
In an operating system software performs each of the function:
- Process management:- Process management helps OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
- Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of this resources.
- File management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
- Device Management: Device management keeps tracks of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of the devices.
- I/O System Management: One of the main objects of any OS is to hide the peculiarities of that hardware devices from the user.
- Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have several levels of storage which includes primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be stored in primary storage or cache so that a running program can reference it.
- Security:- Security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threat and authorized access.
- Command interpretation: This module is interpreting commands given by the and acting system resources to process that commands.
- Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors which do not share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network.
- Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resource used by various job and users.
- Communication management: Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, and another software resource of the various users of the computer systems.
Features of Operating System (OS)
Here is a list important features of OS:
- Protected and supervisor mode
- Allows disk access and file systems Device drivers Networking Security
- Program Execution
- Memory management Virtual Memory Multitasking
- Handling I/O operations
- Manipulation of the file system
- Error Detection and handling
- Resource allocation
- Information and Resource Protection

Advantage of using Operating System
- Allows you to hide details of hardware by creating an abstraction
- Easy to use with a GUI
- Offers an environment in which a user may execute programs/applications
- The operating system must make sure that the computer system convenient to use
- Operating System acts as an intermediary among applications and the hardware components
- It provides the computer system resources with easy to use format
- Acts as an intermediator between all hardware’s and software’s of the system
Disadvantages of using Operating System
- If any issue occurs in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored in your system
- Operating system’s software is quite expensive for small size organization which adds burden on them. Example Windows
- It is never entirely secure as a threat can occur at any time
What is a Kernel?
The kernel is the central component of a computer operating systems. The only job performed by the kernel is to the manage the communication between the software and the hardware. A Kernel is at the nucleus of a computer. It makes the communication between the hardware and software possible. While the Kernel is the innermost part of an operating system, a shell is the outermost one.
Features of Kennel
- Low-level scheduling of processes
- Inter-process communication
- Process synchronization
- Context switching
Types of Kernels
There are many types of kernels that exists, but among them, the two most popular kernels are:
1.Monolithic
A monolithic kernel is a single code or block of the program. It provides all the required services offered by the operating system. It is a simplistic design which creates a distinct communication layer between the hardware and software.
2. Microkernels
Microkernel manages all system resources. In this type of kernel, services are implemented in different address space. The user services are stored in user address space, and kernel services are stored under kernel address space. So, it helps to reduce the size of both the kernel and operating system.