- How to tar a file in Linux using command line
- How to tar a file in Linux using command line
- How to create tar a file in Linux
- How to exclude directories and files when using tar
- How do I view files stored in an archive?
- How do I extracting an archive?
- Conclusion
- 18 Tar Command Examples in Linux
- 1. Create tar Archive File in Linux
- 2. Create tar.gz Archive File in Linux
- 3. Create tar.bz2 Archive File in Linux
- 4. Untar tar Archive File in Linux
- 5. Uncompress tar.gz Archive File in Linux
- 6. Uncompress tar.bz2 Archive File in Linux
- 7. List Content of tar Archive File in Linux
- 8. List Content tar.gz Archive File in Linux
- 9. List Content tar.bz2 Archive File in Linux
- 10. Untar Single file from tar File in Linux
- 11. Untar Single file from tar.gz File in Linux
- 12. Untar Single file from tar.bz2 File in Linux
- 13. Untar Multiple files from tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 File
- 14. Extract Group of Files using Wildcard in Linux
- 15. Add Files or Directories to tar Archive File in Linux
- 16. Add Files or Directories to tar.gz and tar.bz2 Files
- 17. How To Verify tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 Archive File
- 18. Check the Size of the tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 Archive File
- Tar Usage and Options
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Команда tar в Linux
- Синтаксис команды tar
- Как пользоваться tar
- 1. Создание архива tar
- 2. Просмотр содержимого архива
- 3. Распаковка архива tar Linux
- 3. Работа со сжатыми архивами
- Выводы
How to tar a file in Linux using command line
How to tar a file in Linux using command line
The procedure is as follows to tar a file in Linux:
- Open the terminal app in Linux
- Compress an entire directory by running tar -zcvf file.tar.gz /path/to/dir/ command in Linux
- Compress a single file by running tar -zcvf file.tar.gz /path/to/filename command in Linux
- Compress multiple directories file by running tar -zcvf file.tar.gz dir1 dir2 dir3 command in Linux
How to create tar a file in Linux
Say you want to compress an entire directory named /home/vivek/data/:
$ tar -czvf file.tar.gz /home/vivek/data/
To compress multiple directories and files, execute:
$ tar -czvf file.tar.gz /home/vivek/data/ /home/vivek/pics/ /home/vivek/.accounting.db
One can use bzip2 compression instead of gzip by passing the -j option to the tar command:
$ tar -c j vf file.tar. bz2 /home/vivek/data/
Where,
- -c : Create a new archive
- -v : Verbose output
- -f file.tar.gz : Use archive file
- -z : Filter the archive through gzip
- -j : Filter the archive through bzip2
How to exclude directories and files when using tar
You can exclude certain files when creating a tarball. The syntax is:
$ tar -zcvf archive.tar.gz —exclude=’dir1′ —exclude=’regex’ dir1
For example, exclude
/Downloads/ directory:
$ tar -czvf /nfs/backup.tar.gz —exclude=»Downloads» /home/vivek/
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
How do I view files stored in an archive?
Now you have an archive, to list the contents of a tar or tar.gz file using the tar command:
$ tar -ztvf file.tar.gz
$ tar -jtvf file.tar.bz2
How do I extracting an archive?
You can extract an archive or tarball with the tar command. The syntax is:
$ tar -xzvf file.tar.gz
$ tar -xjvf file.tar.bz2
Want to extract the contents of the archive into a specific directory such as /home/vivek/backups/? Try passing the -C DIR option:
$ tar -xzvf my.tar.gz -C /home/vivek/backups/
$ tar -xjvf archive.tar.bz2 -C /tmp/
- -x : Extract files from an archive
- -t : List the contents of an archive
- -v : Verbose output
- -f file.tar.gz : Use archive file
- -C DIR : Change to DIR before performing any operations
- —exclude : Exclude files matching PATTERN/DIR/FILENAME
Conclusion
You learned how to tar a file in Linux using tar command. For more info please tar command help page here.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
18 Tar Command Examples in Linux
The Linux “tar” stands for tape archive, which is used by a large number of Linux/Unix system administrators to deal with tape drives backup.
The tar command is used to rip a collection of files and directories into a highly compressed archive file commonly called tarball or tar, gzip and bzip in Linux.
The tar is the most widely used command to create compressed archive files and that can be moved easily from one disk to another disk or machine to machine.

In this article, we will be going to review and discuss various tar command examples including how to create archive files using (tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2) compression, how to extract archive file, extract a single file, view content of the file, verify a file, add files or directories to the existing archive file, estimate the size of tar archive file, etc.
The main purpose of this guide is to provide various tar command examples that might be helpful for you to understand and become an expert in tar archive manipulation.
1. Create tar Archive File in Linux
The below example command will create a tar archive file tecmint-14-09-12.tar for a directory /home/tecmint in the current working directory. See the example command in action.
Let’s discuss each option used in the above command to create a tar archive file.
- c – Creates a new .tar archive file.
- v – Verbosely show the .tar file progress.
- f – File name type of the archive file.
2. Create tar.gz Archive File in Linux
To create a compressed gzip archive file we use the option as z. For example, the below command will create a compressed MyImages-14-09-12.tar.gz file for the directory /home/MyImages. (Note: tar.gz and tgz both are similar).
3. Create tar.bz2 Archive File in Linux
The bz2 feature compresses and creates an archive file less than the size of the gzip. The bz2 compression takes more time to compress and decompress files than gzip, which takes less time.
To create a highly compressed tar file we use the option j. The following example command will create a Phpfiles-org.tar.bz2 file for a directory /home/php. (Note: tar.bz2 and tbz is similar to tb2).
4. Untar tar Archive File in Linux
To untar or extract a tar file, just issue the following command using option x (extract). For example, the below command will untar the file public_html-14-09-12.tar in the present working directory.
If you want to untar in a different directory then use option as -C (specified directory).
5. Uncompress tar.gz Archive File in Linux
To Uncompress tar.gz archive file, just run the following command. If we would like to untar in different directories, just use option -C and the directory path, as shown in the above example.
6. Uncompress tar.bz2 Archive File in Linux
To Uncompress the highly compressed tar.bz2 file, just use the following command. The below example command will untar all the .flv files from the archive file.
7. List Content of tar Archive File in Linux
To list the contents of the tar archive file, just run the following command with option t (list content). The below command will list the content of the uploadprogress.tar file.
8. List Content tar.gz Archive File in Linux
Use the following command to list the content of the tar.gz file.
9. List Content tar.bz2 Archive File in Linux
To list the content of the tar.bz2 file, issue the following command.
10. Untar Single file from tar File in Linux
To extract a single file called cleanfiles.sh from cleanfiles.sh.tar use the following command.
11. Untar Single file from tar.gz File in Linux
To extract a single file tecmintbackup.xml from the tecmintbackup.tar.gz archive file, use the command as follows.
12. Untar Single file from tar.bz2 File in Linux
To extract a single file called index.php from the file Phpfiles-org.tar.bz2 use the following option.
13. Untar Multiple files from tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 File
To extract or untar multiple files from the tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 archive file. For example, the below command will extract “ file 1” “ file 2” from the archive files.
14. Extract Group of Files using Wildcard in Linux
To extract a group of files we use wildcard-based extracting. For example, to extract a group of all files whose pattern begins with .php from a tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 archive file.
15. Add Files or Directories to tar Archive File in Linux
To add files or directories to the existing tar archive files we use the option r (append). For example, we add file xyz.txt and directory php to the existing tecmint-14-09-12.tar archive file.
16. Add Files or Directories to tar.gz and tar.bz2 Files
The tar command doesn’t have an option to add files or directories to an existing compressed tar.gz and tar.bz2 archive file. If we do try will get the following error.
17. How To Verify tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 Archive File
To verify any tar or compressed archived file we use the option W (verify). To do this, just use the following examples of commands. (Note: You cannot do verification on a compressed ( *.tar.gz, *.tar.bz2 ) archive file).
18. Check the Size of the tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 Archive File
To check the size of any tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 archive file, use the following command. For example, the below command will display the size of the archive file in Kilobytes (KB).
Tar Usage and Options
- c – create an archive file.
- x – extract an archive file.
- v – show the progress of the archive file.
- f – filename of the archive file.
- t – viewing the content of the archive file.
- j – filter archive through bzip2.
- z – filter archive through gzip.
- r – append or update files or directories to the existing archive files.
- W – Verify an archive file.
- wildcards – Specify patterns in UNIX tar command.
That’s it for now, hope the above tar command examples are enough for you to learn, and for more information please use the man tar command.
If you are looking to split any large tar archive file into multiple parts or blocks, just go through this article:
If we’ve missed any examples please do share with us via the comment box and please don’t forget to share this article with your friends. This is the best way to say thanks…..
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Команда tar в Linux
В качестве инструмента для архивации данных в Linux используются разные программы. Например архиватор Zip Linux, приобретший большую популярность из-за совместимости с ОС Windows. Но это не стандартная для системы программа. Поэтому хотелось бы осветить команду tar Linux — встроенный архиватор.
Изначально tar использовалась для архивации данных на ленточных устройствах. Но также она позволяет записывать вывод в файл, и этот способ стал широко применяться в Linux по своему назначению. Здесь будут рассмотрены самые распространенные варианты работы с этой утилитой.
Синтаксис команды tar
Синтаксис команд для создания и распаковки архива практически не отличается (в том числе с утилитами сжатия bzip2 или gzip). Так, чтобы создать новый архив, в терминале используется следующая конструкция:
tar опции архив.tar файлы_для_архивации
Для его распаковки:
tar опции архив.tar
Функции, которые может выполнять команда:
| Функция | Длинный формат | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| -A | —concatenate | Присоединить существующий архив к другому |
| -c | —create | Создать новый архив |
| -d | —diff —delete | Проверить различие между архивами Удалить из существующего архива файл |
| -r | —append | Присоединить файлы к концу архива |
| -t | —list | Сформировать список содержимого архива |
| -u | —update | Обновить архив более новыми файлами с тем же именем |
| -x | —extract | Извлечь файлы из архива |
При определении каждой функции используются параметры, которые регламентируют выполнение конкретных операций с tar-архивом:
| Параметр | Длиннный формат | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| -C dir | —directory=DIR | Сменить директорию перед выполнением операции на dir |
| -f file | —file | Вывести результат в файл (или на устройство) file |
| -j | —bzip2 | Перенаправить вывод в команду bzip2 |
| -p | —same-permissions | Сохранить все права доступа к файлу |
| -v | —verbose | Выводить подробную информацию процесса |
| —totals | Выводить итоговую информацию завершенного процесса | |
| -z | —gzip | Перенаправить вывод в команду gzip |
А дальше рассмотрим примеры того, как может применяться команда tar Linux.
Как пользоваться tar
1. Создание архива tar
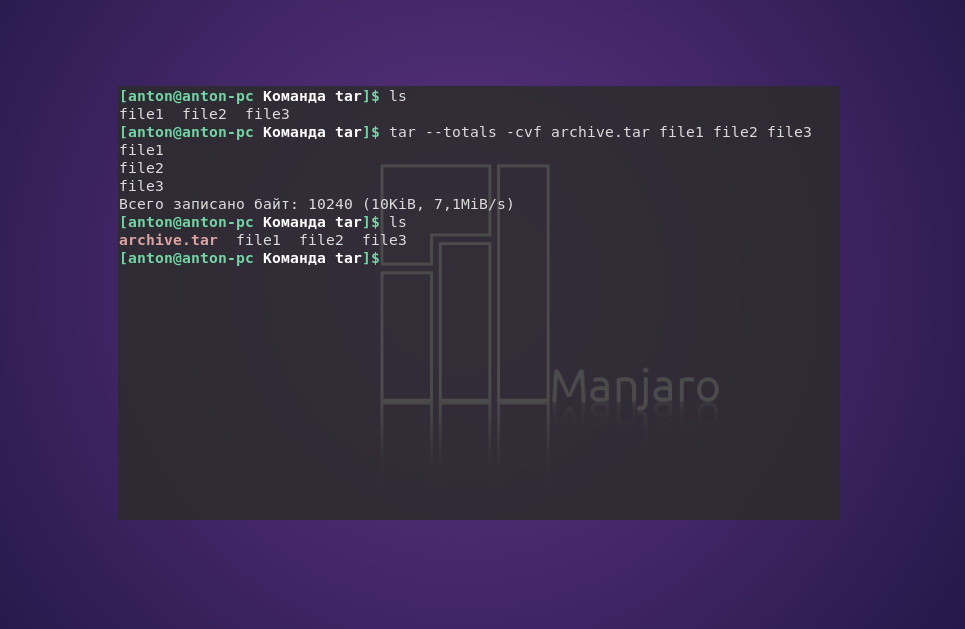
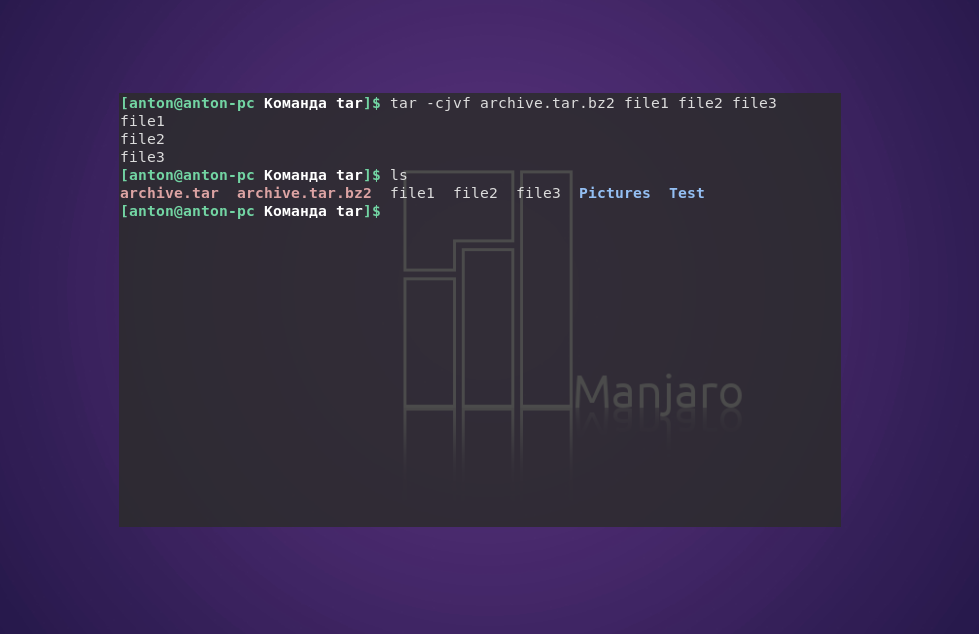
С помощью следующей команды создается архив archive.tar с подробным выводом информации, включающий файлы file1, file2 и file3:
tar —totals —create —verbose —file archive.tar file1 file2 file3
Но длинные опции и параметры можно заменить (при возможности) однобуквенными значениями:
tar —totals -cvf archive.tar file1 file2 file3
2. Просмотр содержимого архива
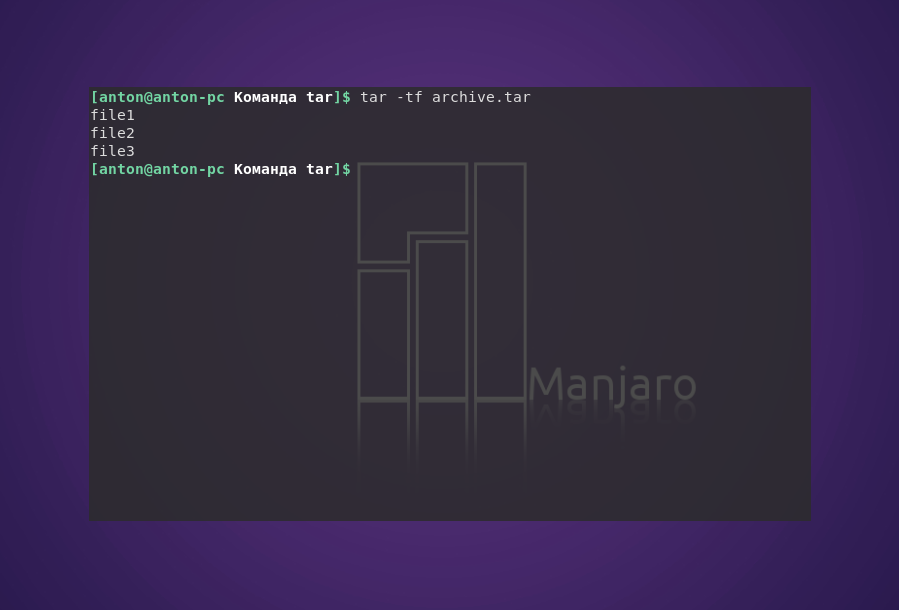
Следующая команда выводит содержимое архива, не распаковывая его:
tar -tf archive.tar
3. Распаковка архива tar Linux
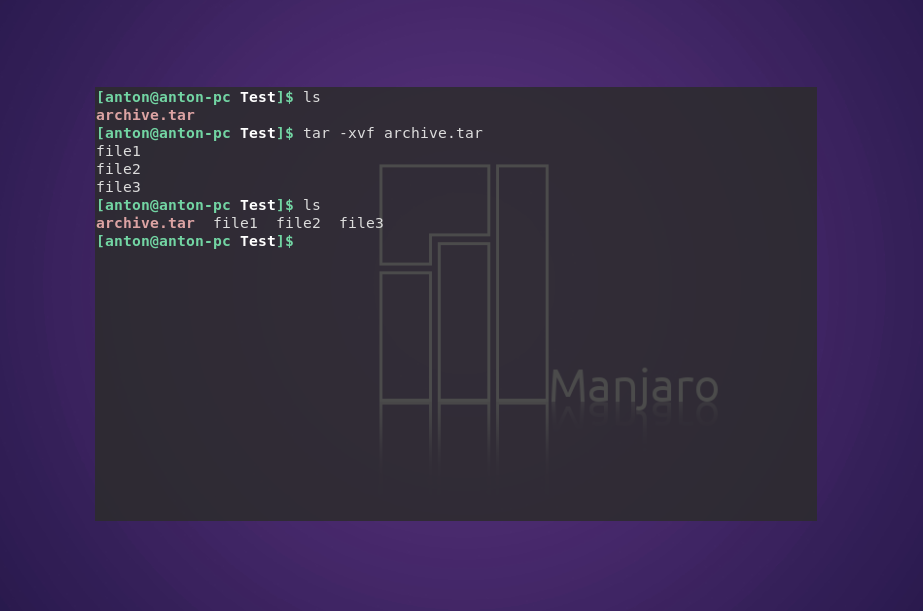
Распаковывает архив test.tar с выводом файлов на экран:
tar -xvf archive.tar
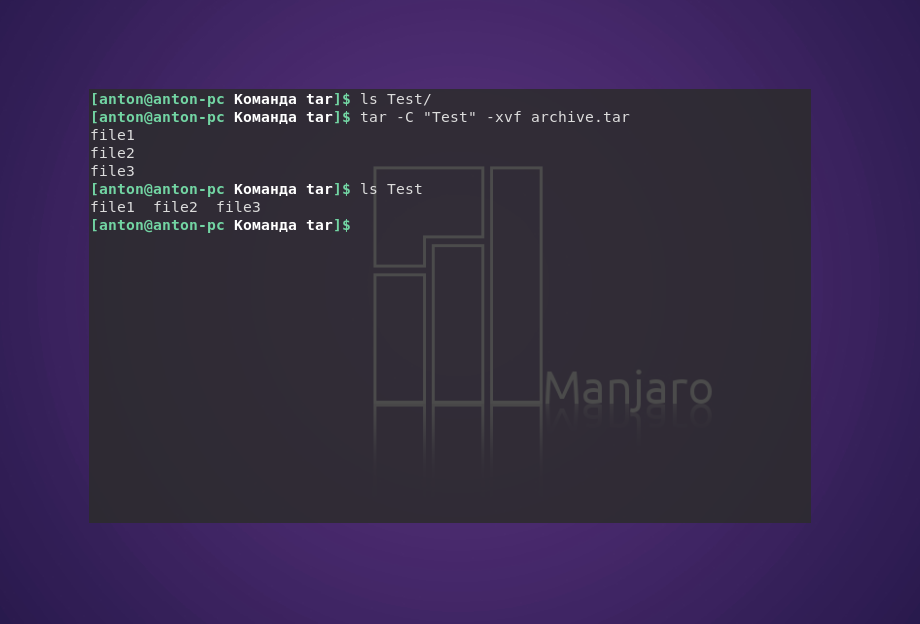
Чтобы сделать это в другой каталог, можно воспользоваться параметром -C:
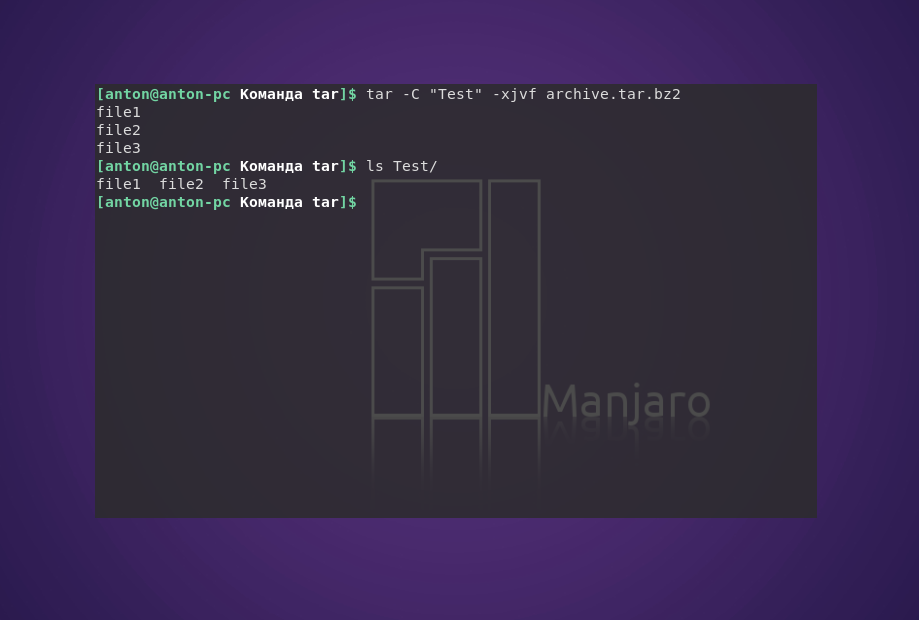
tar -C «Test» -xvf archive.tar
3. Работа со сжатыми архивами
Следует помнить, что tar только создаёт архив, но не сжимает. Для этого используются упомянутые компрессорные утилиты bzip2 и gzip. Файлы, сжатые с их помощью, имеют соответствующие расширения .tar.bz2 и .tar.gz. Чтобы создать сжатый архив с помощью bzip2, введите:
tar -cjvf archive.tar.bz2 file1 file2 file3
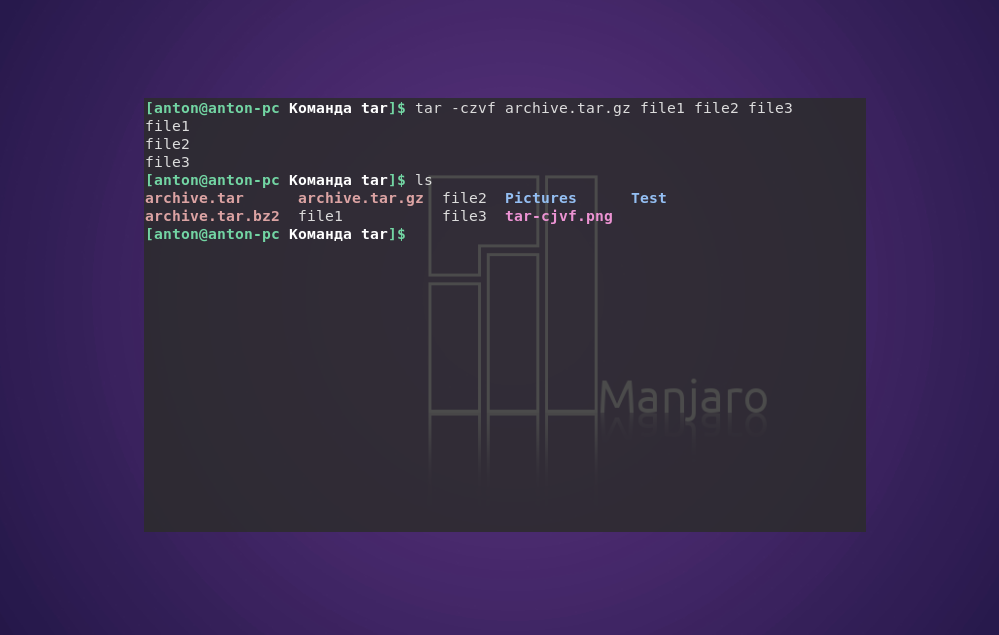
Синтаксис для gzip отличается одной буквой в параметрах, и меняется окончание расширения архива:
tar -czvf archive.tar.gz file1 file2 file3
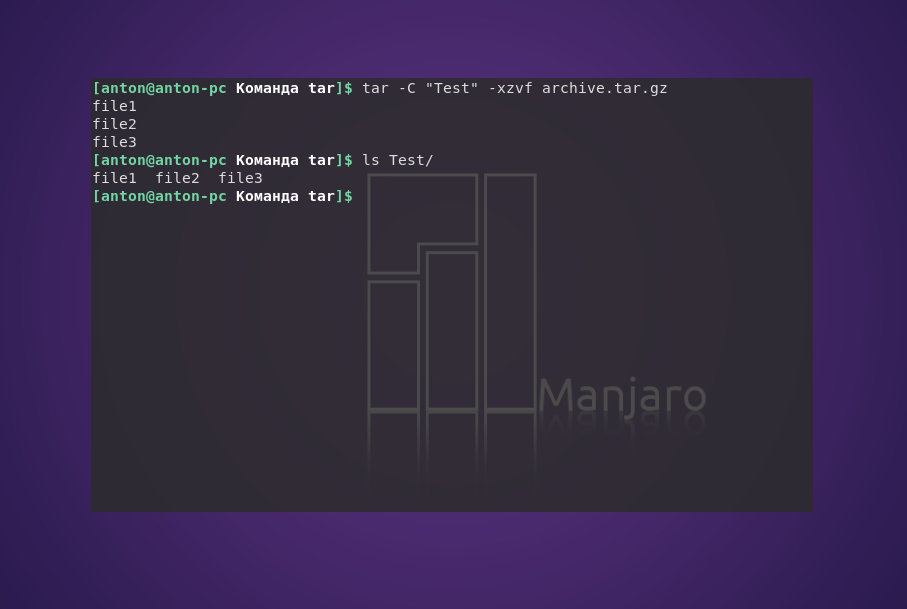
При распаковке tar-архивов с таким расширением следует указывать соответствующую опцию:
tar -C «Test» -xjvf arhive.tar.bz2
tar -xzvf archive.tar.gz
На заметку: архиватор tar — одна из немногих утилит в GNU/Linux, в которой перед использованием однобуквенных параметров, стоящих вместе, можно не ставить знак дефиса.
Выводы
В этой статье была рассмотрена команда tar Linux, которая используется для архивации файлов и поставляется по умолчанию во всех дистрибутивах. В её возможности входит создание и распаковка архива файлов без их сжатия. Для сжатия утилита применяется в связке с популярными компрессорами bzip2 и gzip.
Источник