- Manage auditing and security log
- Reference
- Possible values
- Best practices
- Location
- Default values
- Policy management
- Group Policy
- Security considerations
- Vulnerability
- Countermeasure
- Potential impact
- Управление журналом аудита и безопасности Manage auditing and security log
- Справочные материалы Reference
- Возможные значения Possible values
- Рекомендации Best practices
- Location Location
- Значения по умолчанию Default values
- Управление политикой Policy management
- Групповая политика Group Policy
- Вопросы безопасности Security considerations
- Уязвимость Vulnerability
- Противодействие Countermeasure
- Возможное влияние Potential impact
- How to get Security Log with non-administrative user
- SHOWTIME
- Manage auditing and security log
- Get-WinEvent VS Get-EventLog
- Non-administrator access to DC Event logs
Manage auditing and security log
Applies to
Describes the best practices, location, values, policy management, and security considerations for the Manage auditing and security log security policy setting.
Reference
This policy setting determines which users can specify object access audit options for individual resources such as files, Active Directory objects, and registry keys. These objects specify their system access control lists (SACL). A user who is assigned this user right can also view and clear the Security log in Event Viewer. For more info about the Object Access audit policy, see Audit object access.
Possible values
- User-defined list of accounts
- Administrators
- Not Defined
Best practices
- Before removing this right from a group, investigate whether applications are dependent on this right.
- Generally, assigning this user right to groups other than Administrators is not necessary.
Location
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment
Default values
By default this setting is Administrators on domain controllers and on stand-alone servers.
The following table lists the actual and effective default policy values for the most recent supported versions of Windows. Default values are also listed on the policy’s property page.
| Server type or GPO | Default value |
|---|---|
| Default Domain Policy | Not defined |
| Default Domain Controller Policy | Administrators |
| Stand-Alone Server Default Settings | Administrators |
| Domain Controller Effective Default Settings | Administrators |
| Member Server Effective Default Settings | Administrators |
| Client Computer Effective Default Settings | Administrators |
Policy management
This section describes features, tools, and guidance to help you manage this policy.
A restart of the computer is not required for this policy setting to be effective.
Any change to the user rights assignment for an account becomes effective the next time the owner of the account logs on.
Audits for object access are not performed unless you enable them by using the Local Group Policy Editor, the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), or the Auditpol command-line tool.
For more information about the Object Access audit policy, see Audit object access.
Group Policy
Settings are applied in the following order through a Group Policy Object (GPO), which will overwrite settings on the local computer at the next Group Policy update:
- Local policy settings
- Site policy settings
- Domain policy settings
- OU policy settings
When a local setting is greyed out, it indicates that a GPO currently controls that setting.
Security considerations
This section describes how an attacker might exploit a feature or its configuration, how to implement the countermeasure, and the possible negative consequences of countermeasure implementation.
Vulnerability
Anyone with the Manage auditing and security log user right can clear the Security log to erase important evidence of unauthorized activity.
Countermeasure
Ensure that only the local Administrators group has the Manage auditing and security log user right.
Potential impact
Restricting the Manage auditing and security log user right to the local Administrators group is the default configuration.
Warning:В В If groups other than the local Administrators group have been assigned this user right, removing this user right might cause performance issues with other applications. Before removing this right from a group, investigate whether applications are dependent on this right.
Управление журналом аудита и безопасности Manage auditing and security log
Область применения Applies to
В этой статье описываются лучшие методики, расположение, значения, управление политиками и вопросы безопасности для параметра политики безопасности «Управление аудитом и журналом безопасности». Describes the best practices, location, values, policy management, and security considerations for the Manage auditing and security log security policy setting.
Справочные материалы Reference
Этот параметр политики определяет, какие пользователи могут указывать параметры аудита доступа к объектам для отдельных ресурсов, таких как файлы, объекты Active Directory и ключи реестра. This policy setting determines which users can specify object access audit options for individual resources such as files, Active Directory objects, and registry keys. Эти объекты указывают свои системные списки управления доступом (SACL). These objects specify their system access control lists (SACL). Пользователь, которому назначено это право, также может просмотреть и очистить журнал безопасности в окне просмотра событий. A user who is assigned this user right can also view and clear the Security log in Event Viewer. Дополнительные сведения о политике аудита доступа к объектам см. в этой теме. For more info about the Object Access audit policy, see Audit object access.
Константа: SeSecurityPrivilege Constant: SeSecurityPrivilege
Возможные значения Possible values
- Определяемый пользователей список учетных записей User-defined list of accounts
- Администраторы Administrators
- Не определено Not Defined
Рекомендации Best practices
- Перед удалением этого права из группы необходимо выяснить, зависят ли приложения от этого права. Before removing this right from a group, investigate whether applications are dependent on this right.
- Как правило, назначать это право пользователю группам, кроме администраторов, не требуется. Generally, assigning this user right to groups other than Administrators is not necessary.
Location Location
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment
Значения по умолчанию Default values
По умолчанию этот параметр является администратором на контроллерах домена и на автономных серверах. By default this setting is Administrators on domain controllers and on stand-alone servers.
В следующей таблице перечислены фактические и эффективные значения политики по умолчанию для последних поддерживаемых версий Windows. The following table lists the actual and effective default policy values for the most recent supported versions of Windows. Значения по умолчанию также можно найти на странице свойств политики. Default values are also listed on the policy’s property page.
| Тип сервера или объект групповой политики Server type or GPO | Значение по умолчанию Default value |
|---|---|
| Default Domain Policy Default Domain Policy | Не определено Not defined |
| Политика контроллера домена по умолчанию Default Domain Controller Policy | Администраторы Administrators |
| Параметры по умолчанию для автономного сервера Stand-Alone Server Default Settings | Администраторы Administrators |
| Действующие параметры по умолчанию для контроллера домена Domain Controller Effective Default Settings | Администраторы Administrators |
| Действующие параметры по умолчанию для рядового сервера Member Server Effective Default Settings | Администраторы Administrators |
| Действующие параметры по умолчанию для клиентского компьютера Client Computer Effective Default Settings | Администраторы Administrators |
Управление политикой Policy management
В этом разделе описаны компоненты, средства и рекомендации, которые помогут в управлении этой политикой. This section describes features, tools, and guidance to help you manage this policy.
Для активации этого параметра политики не требуется перезагрузка компьютера. A restart of the computer is not required for this policy setting to be effective.
Изменения прав пользователя вступают в силу при его следующем входе в учетную запись. Any change to the user rights assignment for an account becomes effective the next time the owner of the account logs on.
Аудит доступа к объектам не выполняется, если их не включить с помощью редактора локальных групповых политик, консоли управления групповыми политиками (GPMC) или средства командной строки Auditpol. Audits for object access are not performed unless you enable them by using the Local Group Policy Editor, the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), or the Auditpol command-line tool.
Дополнительные сведения о политике аудита доступа к объектам см. в этой теме. For more information about the Object Access audit policy, see Audit object access.
Групповая политика Group Policy
Параметры применяются в следующем порядке с помощью объекта групповой политики (GPO), который будет перезаписывать параметры на локальном компьютере при следующем обновлении групповой политики: Settings are applied in the following order through a Group Policy Object (GPO), which will overwrite settings on the local computer at the next Group Policy update:
- Параметры локальной политики Local policy settings
- Параметры политики сайта Site policy settings
- Параметры политики домена Domain policy settings
- Параметры политики подразделения OU policy settings
Если локальный параметр затеняется, это означает, что в настоящее время этот параметр контролируется GPO. When a local setting is greyed out, it indicates that a GPO currently controls that setting.
Вопросы безопасности Security considerations
В этом разделе описывается, каким образом злоумышленник может использовать компонент или его конфигурацию, как реализовать меры противодействия, а также рассматриваются возможные отрицательные последствия их реализации. This section describes how an attacker might exploit a feature or its configuration, how to implement the countermeasure, and the possible negative consequences of countermeasure implementation.
Уязвимость Vulnerability
Любой пользователь с правом на управление аудитом и журналом безопасности может очистить журнал безопасности, чтобы удалить важные признаки несанкционированной деятельности. Anyone with the Manage auditing and security log user right can clear the Security log to erase important evidence of unauthorized activity.
Противодействие Countermeasure
Убедитесь, что только у локальной группы администраторов есть право на управление аудитом и журналом безопасности. Ensure that only the local Administrators group has the Manage auditing and security log user right.
Возможное влияние Potential impact
Настройка по умолчанию ограничивает права пользователя журнала аудита и безопасности только локальной группой администраторов. Restricting the Manage auditing and security log user right to the local Administrators group is the default configuration.
Предупреждение: Если группе, кроме локальной группы администраторов, назначено это право пользователя, удаление этого права пользователя может привести к проблеме производительности в других приложениях. Warning: If groups other than the local Administrators group have been assigned this user right, removing this user right might cause performance issues with other applications. Перед удалением этого права из группы необходимо выяснить, зависят ли приложения от этого права. Before removing this right from a group, investigate whether applications are dependent on this right.
How to get Security Log with non-administrative user
Привет Хабр! Читайте под катом как получить доступ к логу безопасности Windows без прав администратора. Эта будет не первая статья на Хабре связанная с логами Windows и наверно не самая оригинальная, но на мой взгляд я потратил слишком много времени на поиск простого решения для чтения логов обычным пользователем, вот я и решил поделиться «историей своего успеха».
Также пришлось сравнить скорость работы Powershell командлетов Get-WinEvent и Get-EventLog.
Все что находится под катом актуально для Windows Server 2008R2/2012R2, Windows 10 Pro (1809), на других версиях я не проверял, думаю что с продуктами 2016 и 2019 годов ситуация аналогичная.
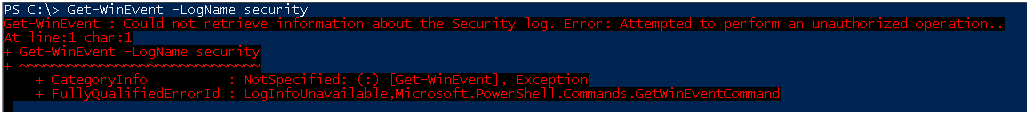
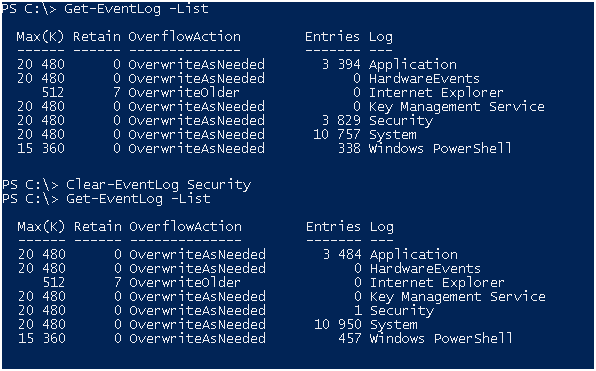
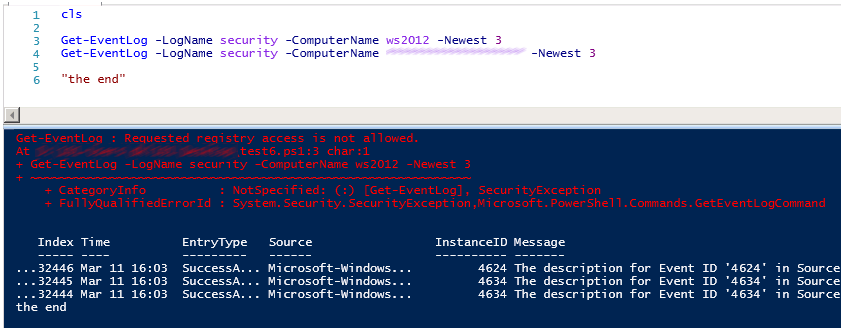
И так, по умолчанию у рядового пользователя прав на чтение логов безопасности нет.
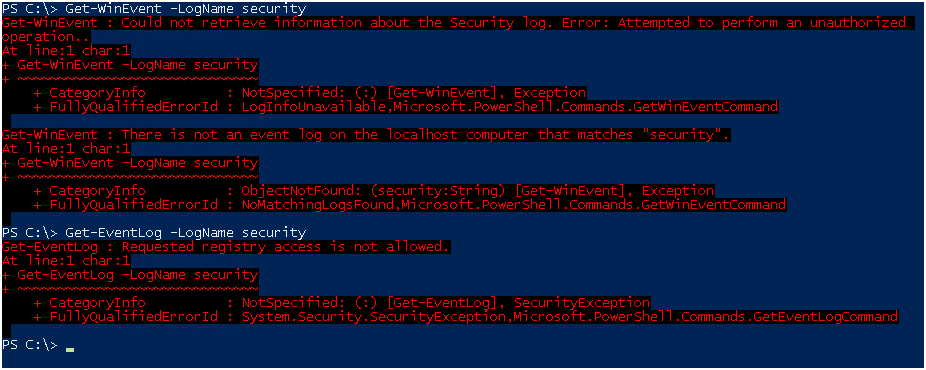
При попытке получить логи вы получите ошибку.
И через Event Viewer в доступе также будет отказано.
SHOWTIME
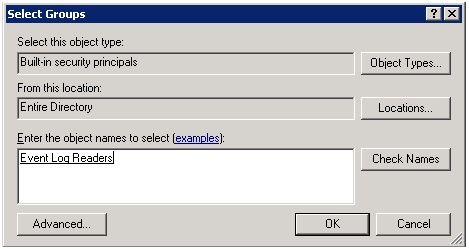
Добавим пользователя в локальную группу Event Log Readers.
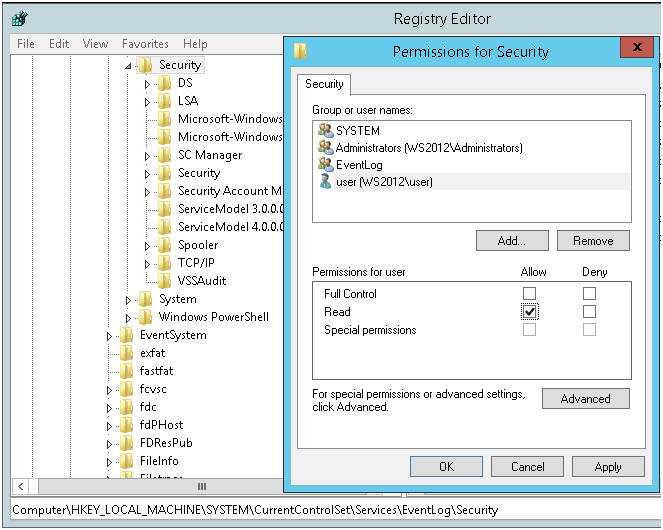
Далее предоставляем права на чтение ветки реестра MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Eventlog\Security.
Без изменения прав на эту ветку реестра, прочитать параметры лога безопасности не получится, соответственно не получится узнать место расположение и имя файла с логами. Security, это единственный раздел сервиса Eventlog который не наследует права доступа от корня.
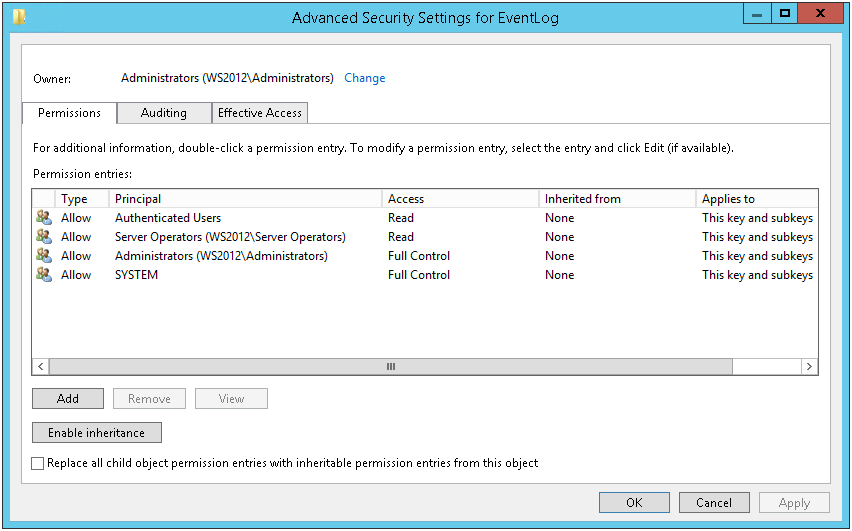
Вот как выглядят права для MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Eventlog.
Проверяем, оба командлета Get-WinEvent и Get-EventLog работают!
Позже вернусь к сравнению этих командлетов…
Manage auditing and security log
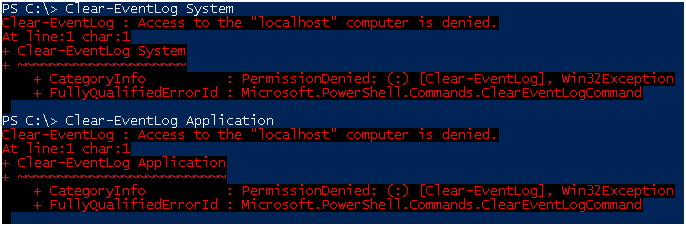
Если пользователю необходимо предоставить права на отчистку лога, вам придется отредактировать групповую политику. Пользователю или группе пользователей необходимо добавить права Manage auditing and security log.
Находится данная группа тут Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment.
Более подробно про Manage auditing and security log можно прочитать тут
This policy setting determines which users can specify object access audit options for individual resources such as files, Active Directory objects, and registry keys. These objects specify their system access control lists (SACL). A user who is assigned this user right can also view and clear the Security log in Event Viewer. For more info about the Object Access audit policy, see Audit object access.
Проверяем, все работает как и было обещано, логи были отчищены…
Другие логии отчистить прав нету.
Честно говоря, не могу придумать сценарий где пользователю нужно выдать права на отчистку логов безопасности, но такая возможность присутствует.
Get-WinEvent VS Get-EventLog
Пришло время сравнить эти два командлета
The Get-EventLog cmdlet gets events and event logs on the local and remote computers.
You can use the cmdlet’s parameters and property values to search for events. This cmdlet gets events that match the specified property values.
The cmdlets that contain the EventLog noun work only on classic event logs. To get events from logs that use the Windows Event Log technology in Windows Vista and later Windows versions, use Get-WinEvent.
The Get-WinEvent cmdlet gets events from event logs, including classic logs, such as the System and Application logs, and the event logs that are generated by the Windows Event Log technology introduced in Windows Vista. It also gets events in log files generated by Event Tracing for Windows (ETW).
Without parameters, a Get-WinEvent command gets all the events from all the event logs on the computer. To interrupt the command, press CTRL + C.
Get-WinEvent also lists event logs and event log providers. You can get events from selected logs or from logs generated by selected event providers. And, you can combine events from multiple sources in a single command. This cmdlet allows you to filter events by using XPath queries, structured XML queries, and simplified hash-table queries
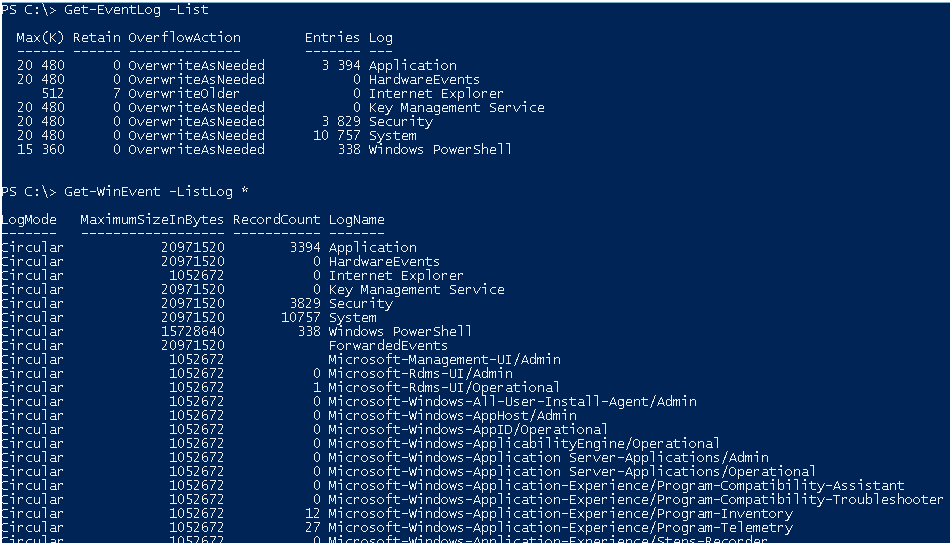
Согласно описания, Get-WinEvent умеет работать с большим количеством журналов которые появились в WIndows Vista.
Для наглядности вот списки с которыми работают эти командлеты, вывод для Get-WinEvent я остановил.
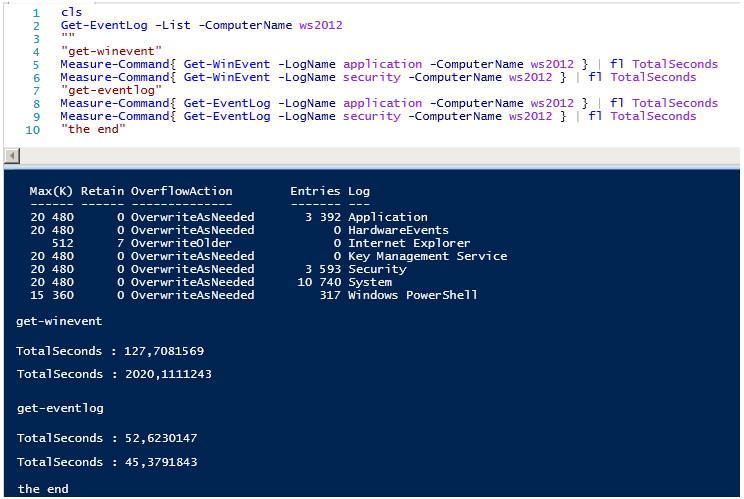
Но есть одно но, производительность имеет значение, сравните время выполнения запросов.
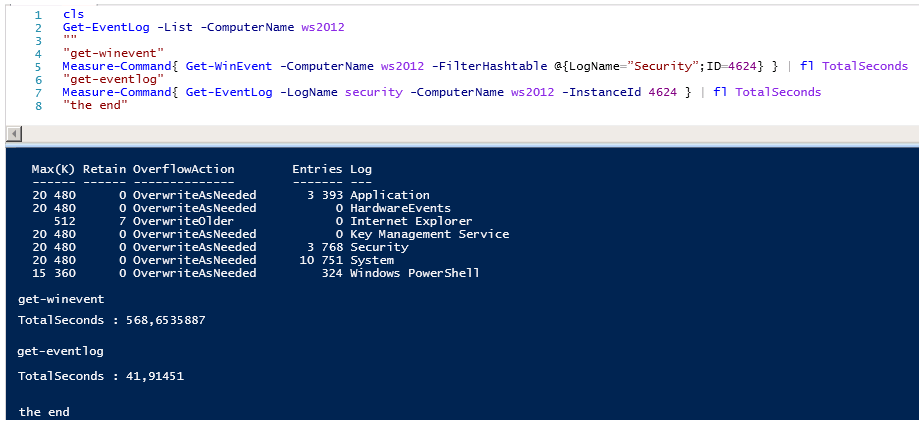
Время работы Get-WinEvent просто поражает, обратите внимание на количество записей в логах Applocation и Security, количество событий примерно одинаковое 3400-3600, но при этом разница по времени выполнения почти 20 раз…
Get-WinEvent тратит 127 секунд против 52 секунд Get-EventLog для чтения событий Application.
И шах и мат, Get-WinEvent тратит 2020 секунд против 45 секунд Get-EventLog для чтения событий Security.
Если выполнить те же команды локально все выглядит не так уж и плохо, но даже локально Get-EventLog работает с логами безопасности в 50 раз быстрее чем Get-WinEvent.
И еще один пример, уже чуть более осмысленный, получения событий с кодом 4624 An account was successfully logged on.
Что тут сказать, цифры не врут…
Non-administrator access to DC Event logs
И на заключение я оставил тему получения доступа к логам безопасности на домен контроллере.
Все выше написанное актуально и для домен контроллера с некоторыми поправками.
1 — Группу Event Log Readers вы найдете в объектах Built-in security principals.
Добавляя пользователя в данную группу вы даете права только на чтение логов на домен контроллерах.
И не забывайте что на каждом из домен контроллеров необходимо дать права на чтение ветки реестра MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Eventlog\Security.
Вот пример, прочитать лог рядового сервера разрешений нет, если вам нужно читать логи с других машин домена, используйте групповые политики, для добавления пользователей или групп пользователей в локальные группы Event Log Readers.
2 – Для добавления прав на отчистку логов необходимо редактировать политику Default Domain Controllers Policy.
3 – Для разрешения запуска заданий от имени пользователя на домен контроллере необходимо также редактировать Default Domain Controllers Policy и дать пользователю права Log on as a batch job.
4 — Будьте предельно внимательными при редактировании дефолтных политик домена!
Краткий список ресурсов, которые мне помогли: