- Htop linux установка centos
- Htop в centos
- How to install htop on CentOS Linux 8
- How to install htop on CentOS 8 using yum
- Turn on EPEL repo on CentOS 8
- CentOS Linux 8 install htop
- Find information about htop package
- Installing htop on CentOS 8
- How to use htop command
- One can use a monochrome color scheme, run:
- Want to see the tree view by default when running htop? Try:
- CentOS htop keyboard shortcut keys
- Other keyboard shortcuts
- How to get help about htop
- Optional: Linux hide processes when using htop
- Conclusion
- linux-notes.org
- Установка HTOP в RHEL, CentOS и Fedora Linux
- Сравнение между Htop и top
- Установка HTOP на RHEL / CentOS 5.x/6.x/7.x, Fedora 12/13/14/15/16/17/18/19/20
- Как использовать Htop команду
- Измените выход интервала обновления
- Функциональные клавиши Htop
- Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
- Htop – An Interactive Process Viewer for Linux
- Install Htop in Linux
- How to Install htop on CentOS 8
- Advantages of htop over top include
- Install htop on CentOS 8
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
Htop linux установка centos
Всем привет, сегодня хочу рассказать как в centos htop добавить. Напомню htop это утилита командной строки, которая в реальном времени показывает вам загрузку всех ваших ресурсов и процессов нагружающих систему, некий такой аля мониторинг ресурсов в Windows. Ниже рассмотрим установку для разных версий. Если же у вас много хостов, то целесообразно использовать уже специальные серверы мониторинга, по типу Zabbix
Htop в centos
Давайте посмотрим, каким же методом вы можете произвести инсталляцию htop в centos, так как после установки Centos 7, хотелось бы видеть, кто и сколько кушает.
Для 32 битной версии
## For RHEL 5, CentOS 5 & Fedora ##
# wget http://packages.sw.be/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.2-2.el5.rf.i386.rpm
# rpm -ihv rpmforge-release*.rf.i386.rpm
## For RHEL 6 and CentOS 6
# wget http://packages.sw.be/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.2-2.el6.rf.i686.rpm
# rpm -ihv rpmforge-release*.rf.i686.rpm
## For RHEL 6 and CentOS 7
# wget http://packages.sw.be/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.2-2.el7.rf.i686.rpm
# rpm -ihv rpmforge-release*.rf.i686.rpm
Для 64 битной версии
## For RHEL 5, CentOS 5 & Fedora ##
# wget http://packages.sw.be/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.2-2.el5.rf.x86_64.rpm
# rpm -ihv rpmforge-release*.rf.x86_64.rpm
## For RHEL 6 and CentOS 6
# wget http://packages.sw.be/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.2-2.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm
# rpm -ihv rpmforge-release*.rf.x86_64.rpm
## For RHEL 6 and CentOS 7
# wget http://packages.sw.be/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.2-2.el7.rf.x86_64.rpm
# rpm -ihv rpmforge-release*.rf.x86_64.rpm
Как видите установка htop на centos весьма простое действие, занимающее пару минут.
Источник
How to install htop on CentOS Linux 8
How to install htop on CentOS 8 using yum
The procedure for installing htop CentOS Linux 8 is as follows:
- Open the terminal window.
- For remote CentOS 8 server login using ssh command.
- Turn on EPEL repo
- Execute sudo yum search htop command to search for htop on CentOS
- Run sudo yum install htop to install htop in CentOS 8
- Update sudo yum update htop to upgrade htop to the latest version in CentOS 8
Let us see all steps and examples in details.
Turn on EPEL repo on CentOS 8
Make sure EPEL repo enabled and installed on CentOS 8. If not, run:
vivek@centos8-box:$ sudo yum -y install epel-release
vivek@centos8-box:$ sudo yum repolist
Please note that vivek@centos8-box:$ is my shell prompt. You need to type all commands after that prompt. Also you can use the dnf command instead of yum on CentOS 8.
CentOS Linux 8 install htop
It is important that you know how to search for any packages. Therefore type the following command to search for htop package using yum command:
vivek@centos8-box:$ sudo yum search htop
Sample outputs:
Find information about htop package
Run the following command:
vivek@centos8-box:$ sudo yum info htop
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Installing htop on CentOS 8
First, make sure you system is up to date:
vivek@centos8-box:$ sudo yum update
vivek@centos8-box:$ sudo yum upgrade
Finally, run the following to install htop on CentOS:
vivek@centos8-box:$ sudo yum install htop
Installing htop on CentOS Enterprise Linux 8 server
How to use htop command
One can use a monochrome color scheme, run:
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop -C
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop —no-color
Want to see the tree view by default when running htop? Try:
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop -t
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop —tree
Let us see only processes of a given user named vivek:
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop -u vivek
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop —user=vivek
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop —user=nginx
Limit and show process for only the given PIDs:
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop -p PID
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop -p PID1,PID2
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop —pid=PID,[,PID,PID. ] vivek@centos8-box:$ htop -p 1992
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop -p 1244,2233
CentOS htop keyboard shortcut keys
The following commands are supported while in htop:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Up arrow key | Select (highlight) the previous process in the process list. Scroll the list if necessary. |
| Down arrow key | Select (highlight) the next process in the process list. Scroll the list if necessary. |
| Left arrow key | Scroll the process list left. |
| Right arrow key | Scroll the process list right. |
| PgUp, PgDn | Scroll the process list up or down one window. |
| Home | Scroll to the top of the process list and select the first process. |
| End | Scroll to the bottom of the process list and select the last process. |
| s | Trace process system calls: if strace(1) is installed, pressing this key will attach it to the currently selected process, presenting a live update of system calls issued by the process. |
| l | Display open files for a process: if lsof(1) is installed, pressing this key will display the list of file descriptors opened by the process. |
Other keyboard shortcuts
| u | Show only processes owned by a specified user. |
| M | Sort by memory usage (top compatibility key). |
| P | Sort by processor usage (top compatibility key). |
| T | Sort by time (top compatibility key). |
| F | “Follow” process: if the sort order causes the currently selected process to move in the list, make the selection bar follow it. This is useful for monitoring a process: this way, you can keep a process always visible on screen. When a movement key is used, “follow” loses effect. |
| K | Hide kernel threads: prevent the threads belonging the kernel to be displayed in the process list. (This is a toggle key.) |
| H | Hide user threads: on systems that represent them differently than ordinary processes (such as recent NPTL-based systems), this can hide threads from userspace processes in the process list. (This is a toggle key.) |
| p | Show full paths to running programs, where applicable. (This is a toggle key.) |
| Ctrl-L | Rfresh the screen. |
| F1 | See this help menu. |
How to get help about htop
Simply pass the —help option. For example:
vivek@centos8-box:$ htop —help
vivek@centos8-box:$ man htop
Optional: Linux hide processes when using htop
Set up hidepid=2 option as described here:
$ sudo mount -o remount,rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,hidepid=2 /proc
$ htop
Conclusion
This page showed you how to install and use htop on CentOS Unix server. It has many more option. Hence, see the htop home page online here or read man page.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
linux-notes.org
Установка HTOP в RHEL, CentOS и Fedora Linux
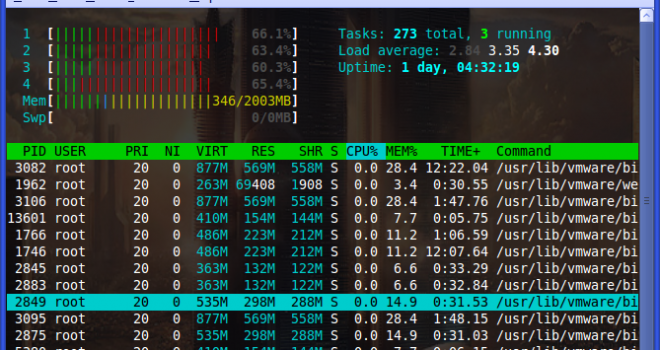
Htop является интерактивным режимом реального времени и системой-мониторинга «процесс-зритель» который написанный для Linux. Он предназначен для замены программы top в Unix. Она показывает часто обновленный список процессов, запущенных на компьютере, как правило. В отличие от top, HTOP предоставляет полный список процессов, запущенных. Htop использует цвет и дает визуальную информацию о процессоре, своп и состояние памяти.
Сравнение между Htop и top
— В «Htop» вы можете прокручивать список по вертикали и горизонтали, чтобы увидеть все процессы и все командные строки.
— В «top» возможна задержка для каждого неназначенной нажатой клавиши (особенно раздражает, когда несколько ключей управляющие последовательности вызывают аварии).
— ‘HTOP’ стартует быстрее (‘top’, кажется, собирать данные в течение некоторого времени перед отображением).
— В «Htop» вам не нужно набирать номер процесса, чтобы убить процесс, в ‘top’ вы должны знать его.
— В «Htop» вам не нужно набирать номер процесса или значение приоритета для изменить приоритет процесса, в «top» вы делаете это.
— ‘HTOP «поддерживает работу мыши.
— ‘top’ старше, следовательно, больше привыкли к нему.
Установка HTOP на RHEL / CentOS 5.x/6.x/7.x, Fedora 12/13/14/15/16/17/18/19/20
На RHEL, CentOS, инструмент HTOP не доступен в репозитории yum по умолчанию. Таким образом, мы подключим репозиторий RPMForge.
Узнать какая разрядность ОС можно выполнив команду:
После включения хранилище RPMForge установить HTOP можно выполнив yum команду:
Установка Htop из исходного кода
Если вы предпочитаете устанавливать Htop от соусе, загрузить исходный код и скомпилировать его:
Как использовать Htop команду
После установки, просто введите HTOP в терминале, чтобы запустить его, и обратите внимание на большой текстовый режим график в верхней части дисплея:
Нажмите «F2», чтобы увидеть меню настройки HTOP :
Если вы хотите увидеть список процессов в виде древо процессов то используйте «F5» или «Т»
Измените выход интервала обновления
Чтобы изменить интервал обновления выхода Htop, используйте D-опции командной строки. «htop -d x». Где х упоминается в thenths секунд.
Функциональные клавиши Htop
На этом подошла тема «Установка HTOP в RHEL, CentOS и Fedora Linux» к завершению.
Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
Этот сайт использует Akismet для борьбы со спамом. Узнайте, как обрабатываются ваши данные комментариев.
Источник
Htop – An Interactive Process Viewer for Linux
This article is the continuation of our Linux system monitoring series, today we’re talking about the most popular monitoring tool called htop, which is just reached version 3.0.5 and comes with some cool new features.

Htop is an interactive real-time process monitoring application for Linux/Unix-like systems and also a handy alternative to top command, which is a default process monitoring tool that comes pre-installed on all Linux operating systems.
Htop has numerous other user-friendly features, which are not available under the top command and they are:
- In htop, you can scroll vertically to view the full process list and scroll horizontally to view the full command lines.
- It starts very quickly as compared to the top because it doesn’t wait to fetch data during startup.
- In htop, you can kill more than one process at once without inserting their PIDs.
- In htop, you no longer needed to enter the process number or priority value to re-nice a process.
- Press “e” to print the set of environment variables for a process.
- Use the mouse to select list items.
Install Htop in Linux
The htop packages are mostly available in all modern Linux distributions and can be installed using the default package manager from your system.
Источник
How to Install htop on CentOS 8
If you are looking to monitor your system interactively, then the htop command should be one of your best options. An improvement of its predecessor top command, htop is an interactive process viewer and system monitor that displays resource-usage metrics in color and allows you to easily keep tabs on your system’s performance.
It displays information about CPU & RAM utilization, tasks being carried out, load average and uptime. Additionally, htop displays a list of all the running processes and can also display these processes in a tree-like format.
Advantages of htop over top include
- Colored output resource usage statistics.
- The ability to end or kill processes without typing their PIDs.
- Htop allows mouse usage, unlike top which doesn’t support it.
- Better performance than top command.
Let’s now jump in and see how to install this handy feature.
Install htop on CentOS 8
By default, htop comes pre-installed on CentOS8. However, if by any chance the tool is missing on your system, installation is an easy 3 step process.
1. The first step in the installation of the Htop tool is to enable the EPEL repository. To do so, run:
After the installation of the EPEL repository, update the system.
2. To install htop tool, simply run the command:

After the installation is complete, you can find more information about htop by running the command.

3. To launch htop, simply run the command.

Additionally, you can pass some arguments to the command. For example, to list the processes of a user. let’s say tecmint run the command.

To get help with the command usage, simply run.

Alternatively, you can view the man pages by running:
Conclusion
In this article, you learned how to install htop on CentOS 8 and how to use the command to retrieve system statistics.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник