- Windows Authentication
- Overview
- New in IIS 7.5
- Compatibility
- Setup
- Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
- Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Vista or Windows 7
- How To
- How to enable Windows authentication for a Web site, Web application, or Web service
- How to enable Extended Protection for Windows authentication
- Configuration
- Attributes
- Child Elements
- Configuration Sample
- Sample Code
- Настройка аутентификации Windows при расположении веб-сервера IIS и рабочих серверов на разных машинах
- Описание проблемы
- Решение проблемы
- Расположение веб-сервера IIS и рабочих серверов 1С на разных машинах
Windows Authentication
Overview
The element defines configuration settings for the Internet Information Services (IIS) 7 Windows authentication module. You can use Windows authentication when your IIS 7 server runs on a corporate network that is using Microsoft Active Directory service domain identities or other Windows accounts to identify users. Because of this, you can use Windows authentication whether or not your server is a member of an Active Directory domain.
Windows authentication (formerly named NTLM, and also referred to as Windows NT Challenge/Response authentication) is a secure form of authentication because the user name and password are hashed before being sent across the network. When you enable Windows authentication, the client browser sends a strongly hashed version of the password in a cryptographic exchange with your Web server.
Windows authentication supports two authentication protocols, Kerberos and NTLM, which are defined in the
element. When you install and enable Windows authentication on IIS 7, the default protocol is Kerberos. The element can also contain a useKernelMode attribute that configures whether to use the kernel mode authentication feature that is new to Windows Server 2008.
Windows authentication is best suited for an intranet environment for the following reasons:
- Client computers and Web servers are in the same domain.
- Administrators can make sure that every client browser is Internet Explorer 2.0 or later.
- HTTP proxy connections, which are not supported by NTLM, are not required.
- Kerberos version 5 requires a connection to Active Directory, which is not feasible in an Internet environment.
New in IIS 7.5
The element was introduced in IIS 7.5, which allows you to configure the settings for the new extended protection features that have been integrated into Windows authentication.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The element was added in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The element was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The element replaces portions of the IIS 6.0 AuthType and AuthFlags metabase properties. |
Setup
The default installation of IIS 7 and later does not include the Windows authentication role service. To use Windows authentication on IIS, you must install the role service, disable Anonymous authentication for your Web site or application, and then enable Windows authentication for the site or application.
After you install the role service, IIS 7 commits the following configuration settings to the ApplicationHost.config file.
Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager.
- In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features.
- In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next.
- On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), expand Web Server, expand Security, and then select Windows Authentication. Click Next.
.
- On the Select features page, click Next.
- On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
- On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, expand World Wide Web Services, expand Security, and then select Windows Authentication.
- Click OK.
- Click Close.
Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager.
- In the Server Manager hierarchy pane, expand Roles, and then click Web Server (IIS).
- In the Web Server (IIS) pane, scroll to the Role Services section, and then click Add Role Services.
- On the Select Role Services page of the Add Role Services Wizard, select Windows Authentication, and then click Next.
- On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows Vista or Windows 7
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows Features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, then World Wide Web Services, then Security.
- Select Windows Authentication, and then click OK.
How To
How to enable Windows authentication for a Web site, Web application, or Web service
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then the site, application, or Web service for which you want to enable Windows authentication.
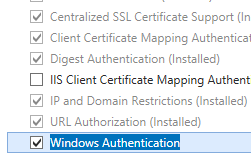
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Windows Authentication, and then click Enable in the Actions pane.
How to enable Extended Protection for Windows authentication
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then the site, application, or Web service for which you want to enable Extended Protection for Windows authentication.
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Windows Authentication.
Click Enable in the Actions pane.
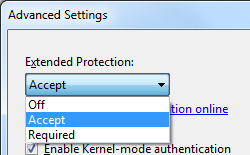
Click Advanced Settings in the Actions pane.
When the Advanced Settings dialog box appears, select one of the following options in the Extended Protection drop-down menu:
- Select Accept if you want to enable extended protection while providing down-level support for clients that do not support extended protection.
- Select Required if you want to enable extended protection without providing down-level support.
Click OK to close the Advanced Settings dialog box.
Configuration
The element is configurable at the site, application, or virtual directory level in the ApplicationHost.config file.
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| authPersistNonNTLM | Optional Boolean attribute. |
Specifies whether IIS automatically reauthenticates every non-NTLM (for example, Kerberos) request, even those on the same connection. False enables multiple authentications for the same connections.
Note: A setting of true means that the client will be authenticated only once on the same connection. IIS will cache a token or ticket on the server for a TCP session that stays established.
The default is false .
Setting this flag to true specifies that authentication persists only for a single request on a connection. IIS resets the authentication at the end of each request, and forces reauthentication on the next request of the session.
The default value is false .
Specifies whether Windows authentication is enabled.
The default value is false .
Specifies whether Windows authentication is done in kernel mode. True specifies that Windows authentication uses kernel mode.
Kernel-mode authentication may improve authentication performance and prevent authentication problems with application pools that are configured to use a custom identity.
As a best practice, do not disable this setting if you use Kerberos authentication and have a custom identity on the application pool.
The default is true .
Child Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| extendedProtection | Optional element. |
Specifies extended protection options for Windows authentication.
Note: This element was added in IIS 7.5.
Specifies security support providers used for Windows authentication.
Configuration Sample
The following default element is configured at the root ApplicationHost.config file in IIS 7.0, and disables Windows authentication by default. It also defines the two Windows authentication providers for IIS 7.0.
The following example enables Windows authentication and disables Anonymous authentication for a Web site named Contoso.
Sample Code
The following examples disable Anonymous authentication for a site named Contoso, then enable Windows authentication for the site.
Настройка аутентификации Windows при расположении веб-сервера IIS и рабочих серверов на разных машинах
Описание проблемы
Не работает аутентификация операционной системы (windows) через IIS при использовании тонкого клиента или веб-клиента.
С точки зрения пользователей, будет видно окно с запросом логина и пароля.
Проблема может заключаться в том, что методы операционной системы в силу различных причин возвращают описание текущего пользователя сеанса в таком представлении, которое не совпадает ни с одним пользователем в списке пользователей информационной базы 1С
Решение проблемы
На сервере 1С включить технологический журнал, используя следующую настройку:
Воспроизвести ситуацию с неудачной аутентификацией операционной системы. Авторизоваться под пользователем операционной системы, указанным в свойствах пользователя 1С.
Открыть технологический журнал рабочего процесса и найти событие EXCP со следующим описанием: «Идентификация пользователя не выполнена
Неправильное имя или пароль пользователя»
Обратите внимание на предшествующее ему событие CONN и значение свойства DstUserName2 — именно в таком виде пользователь должен быть указан в свойствах пользователя информационной базы.
04:45.940011-0,CONN,2,process=rphost,t:clientID=60,Txt=Srvr: SrcUserName1: svc-1c@DOMAIN701.COM
04:45.940012-0,CONN,2,process=rphost,t:clientID=60,Txt=Srvr: DstUserName1: testuser2@DOMAIN701.COM(DOMAIN701.COM\testuser2)
04:45.971001-0,CONN,2,process=rphost,t:clientID=60,Txt=Srvr: DstUserName2: DOMAIN701\testuser2(DOMAIN701\testuser2)
04:46.205021-0,EXCP,2,process=rphost,p:processName=trade,t:clientID=60,t:applicationName=WebServerExtension,t:computerName=webserver,t:connectID=19,Exception=a01f465c-ed70-442e-ada5-847668d7a41c,Descr=’src\VResourceInfoBaseServerImpl.cpp(991):
a01f465c-ed70-442e-ada5-847668d7a41c: Идентификация пользователя не выполнена
Неправильное имя или пароль пользователя’
Заменить значение свойства «Пользователь» пользователя информационной базы согласно следующему формату «\\» + [Имя пользователя из свойства DstUserName2 без скобок].
Проверить работоспособность аутентификации средствами операционной системы, войдя в информационную базу, используя веб-клиент.
Расположение веб-сервера IIS и рабочих серверов 1С на разных машинах
В некоторых случаях, несмотря на корректно указанного пользователя операционной системы в пользователе информационной базы, при попытке входа в опубликованную базу через браузер аутентификация операционной системы не проходит. Такая ситуация может возникать, если веб-сервер IIS и сервер 1с находятся на разных машинах. В таком случае в технологическом журнале рабочего процесса можно наблюдать следующую картину:
56:39.487001-0,CONN,2,process=rphost,p:processName=accounting,t:clientID=39,t:applicationName=WebServerExtension,t:computerName=webserver,t:connectID=16,Txt=Srvr: SrcUserName1: winserver1c$@DOMAIN701.COM
56:39.487002-0,CONN,2,process=rphost,p:processName=accounting,t:clientID=39,t:applicationName=WebServerExtension,t:computerName=webserver,t:connectID=16,Txt=Srvr: DstUserName1: testuser2@DOMAIN701.COM(DOMAIN701.COM\testuser2)
56:39.596004-0,CONN,2,process=rphost,p:processName=accounting,t:clientID=39,t:applicationName=WebServerExtension,t:computerName=webserver,t:connectID=16,Txt=Srvr: DstUserName2: NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON(NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON )
56:39.659003-0,EXCP,2,process=rphost,p:processName=accounting,t:clientID=39,t:applicationName=WebServerExtension,t:computerName=webserver,t:connectID=16,Exception=a01f465c-ed70-442e-ada5-847668d7a41c,Descr=’src\VResourceInfoBaseServerImpl.cpp(991):
a01f465c-ed70-442e-ada5-847668d7a41c: Идентификация пользователя не выполнена
Неправильное имя или пароль пользователя’
При возникновении такой ситуации необходимо проверить следующие настройки:
1) Убедиться, что процессы сервера 1С запущены от имени доменной учетной записи, входящей в группу Domain Users.
2) Убедиться, что веб-сервер IIS настроен корректно.
В публикации информационной базы найти настройки аутентификации
В настройках аутентификации отключить анонимную аутентификацию и включить Windows-аутентификацию. В Windows-аутентификации упорядочить доступных провайдеров так, чтобы на первом месте был Negotiate.
Пул приложений публикации не нуждается в настройках, в нем можно оставить все по умолчанию.
После изменения настроек перезапустить веб-сервер с помощью команды iisreset в командной строке.
3) Убедиться, что в контроллере домена в свойствах компьютера, на котором запущен веб-сервер, на вкладке делегирование установлено «Доверять компьютеру делегирование любых служб (только Kerberos)»
Для этого откройте оснастку Active Directory Users and Computers (dsa.msc), в компьютерах найдите веб-сервер, перейдите в его свойства и на вкладке Делегирование установить значение «Доверять компьютеру делегирование любых служб (только Kerberos)» и нажать применить.
4) Убедиться, что на клиенте в свойствах обозревателя разрешена встроенная проверка подлинности Windows.
После выполнения всех действий необходимо перезагрузить клиентский компьютер (рабочие серверы перезагрузки не требуют) и убедиться, что аутентификация операционной системы успешно выполняется.
Важно: аутентификации Windows при расположении веб-сервера IIS и рабочих серверов на разных машинах в тонком клиенте работает, начиная с версии 8.3.10.2620 (для тестирования).
 .
.