- 16 команд для проверки аппаратной части компьютера в Linux
- Информация о комплектации компьютера
- 1. lscpu
- 2. lshw – список аппаратных устройств
- 3. hwinfo – информация об аппаратуре компьютера
- 4. lspci – список устройств PCI
- 5. lsscsi — список устройств scsi
- 6. lsusb – подробный список шин и устройств usb
- 7. Inxi
- 8. lsblk — список блочных устройств
- 9. df – дисковое пространство файловых систем
- 10. Pydf – команда df, написанная на языке Python
- 11. fdisk
- 12. mount
- 13. free – проверка оперативной памяти
- 14. dmidecode
- 15. Файлы /proc
- 16. hdparm
- Заключение
- 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux
- Hardware information
- 1. lscpu
- 2. lshw — List Hardware
- 3. hwinfo — Hardware Information
- 4. lspci — List PCI
- 5. lsscsi — List scsi devices
- 6. lsusb — List usb buses and device details
- 7. Inxi
- 8. lsblk — List block devices
- 9. df — disk space of file systems
- 10. Pydf — Python df
- 11. fdisk
- 12. mount
- 13. free — Check RAM
- 14. dmidecode
- 15. /proc files
- 16. hdparm
- Summary
- 48 thoughts on “ 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux ”
- How to Display Linux Hardware Info via Command Line
- 1. lshw
- 2. Inxi
- 3. hwinfo
- 4. lscpu
- 5. lsscsi
- 6. lsblk
- 7. lsusb
- 8. lspci
- 9. Using dmesg
- 10. Using dmidecode command
- 11. hdparm
- 12. From /proc file
- 13. free
- Conclusion
16 команд для проверки аппаратной части компьютера в Linux
Информация о комплектации компьютера
Точно также, как для всего прочего, в вашей системе Linux есть много команд для получения информацию об аппаратной части вашего компьютера. Некоторые команды сообщают информацию только о конкретных компонентах оборудования, например, процессоре или памяти, а другие — выдают информацию сразу о нескольких устройствах.
В данной статье кратко рассказывается о нескольких наиболее часто используемых командах, предназначенных для получения информации и особенностях настройки различных периферийных устройств и компонентах компьютера. Среди рассматриваемых — команды lscpu, hwinfo, lshw, dmidecode, lspci и другие.
1. lscpu
Команда lscpu выдает информацию о процессоре и его составляющих. В ней нет каких-либо дополнительных параметров или функциональных возможностей.
2. lshw – список аппаратных устройств
Утилита общего назначения, которая сообщает подробную и краткую информацию о нескольких различных аппаратных устройствах, таких как процессор, память, диск, контроллеры usb, сетевые адаптеры и т.д. Команда lscpu извлекает информацию из различных файлов /proc.
Если вы хотите больше узнать о команде lshw, то обратите внимание на пост Получаем интфомацию в Linux об аппаратных частях компьютера с помощью команды lshw .
3. hwinfo – информация об аппаратуре компьютера
Утилита hwinfo является еще одной универсальной утилитой зондирования аппаратуры, которая может сообщить подробную и краткую информацию о многих различных аппаратных компонентах, причем может сообщить больше, чем утилита lshw.
4. lspci – список устройств PCI
Команда lspci выдает список всех шин PCI, а также подробную информация об устройствах, которые к ним подключены. Под эту категорию подпадают следующие устройства — адаптер vga, графическая карта, сетевой адаптер, порты usb, контроллеры sata и т.д.
Отфильтруйте информацию о конкретном устройстве с помощью команды grep.
5. lsscsi — список устройств scsi
Выдается список устройств scsi/sata, например, жестких дисков и оптических приводов.
6. lsusb – подробный список шин и устройств usb
Эта команда показывает информацию о контроллерах usb и подробные сведения о подключенных к ним устройствах. По умолчанию выдается краткая информация. Для того, чтобы о каждом порте usb получить подробную информацию, используйте параметр «-v».
В системе, информация о которой приведена выше, один порт usb используется для подключения мыши.
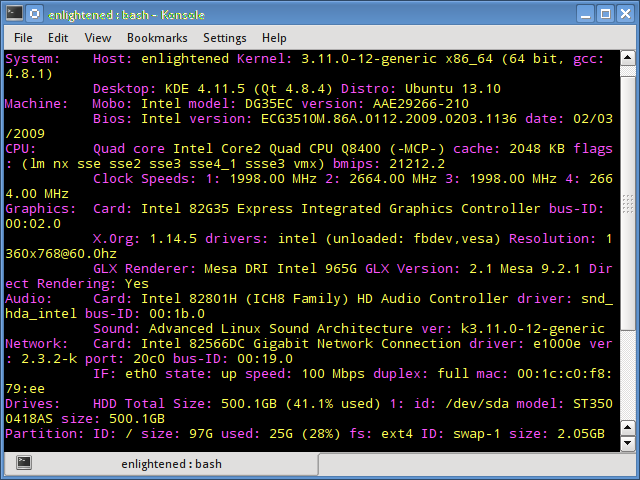
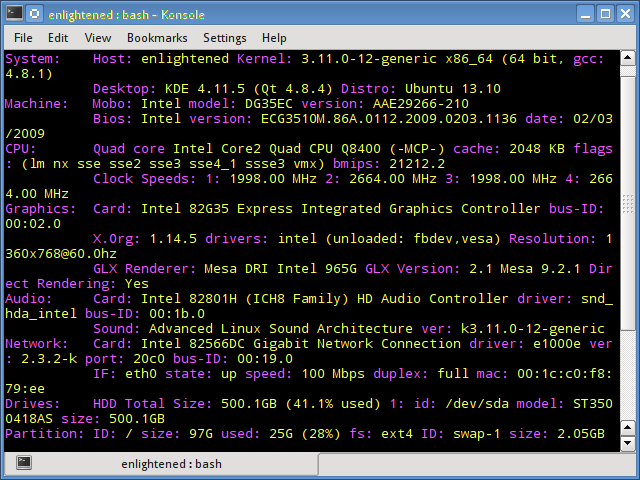
7. Inxi
Inxi является мега скриптом bash, состоящим из 10000 строк кода, с помощью которого из разных источников и команд системы будет получена подробная информация об аппаратном обеспечении и будет создан отчет в виде, позволяющим его читать пользователям, которые не являются техническими специалистами.
8. lsblk — список блочных устройств
Перечисляется информация о всех блочных устройствах, которыми являются разделы жестких дисков и других устройств хранения данных, например, оптических приводов и флэш-накопителей
9. df – дисковое пространство файловых систем
Отчеты о различных разделах, об их точках монтирования и о том, сколько в каждом разделе есть свободного места.
10. Pydf – команда df, написанная на языке Python
Улучшенный вариант команды df , написанной на языке python, который выдает информацию в цвете, что выглядит лучше, чем информация, выдаваемая командой df
11. fdisk
Fdisk является утилитой, предназначенной для изменения разделов жестких дисков, и ей также можно пользоваться для получения информации о списке имеющихся разделов.
12. mount
Команда mount используется для монтирования/демонтирования, а также для просмотра смонтированных файловых систем.
Опять же, используйте команду grep для отфильтровывания информации только о тех файловых системах, которые вам интересны
13. free – проверка оперативной памяти
С помощью команды free проверьте объем используемой, свободной и общий объема оперативной памяти, имеющейся в системе.
14. dmidecode
Команда dmidecode отличается от всех других команд. Она извлекает информацию об оборудовании, читая для этого данные из структур данных SMBOIS (которые также называются таблицами DMI).
Подробности смотрите на странице man.
15. Файлы /proc
Во многих виртуальных файлах каталога /proc содержится информация об аппаратном обеспечении и о конфигурациях. Ниже приведены некоторые из них.
Информация о процессоре/памяти
Информация о Linux/ядре
16. hdparm
Команда hdparm получает информацию об устройствах sata, например, жестких дисков.
Заключение
В каждой из команд используется чуть-чуть иной способ извлечения информации, и вам для, чтобы получить определенную информацию об оборудовании, возможно, потребуется попробовать более одной команды. Но все они есть в большинстве дистрибутивов Linux и их легко можно установить из репозиториев, используемых по умолчанию.
Для тех, кто не хочет запоминать и вводить команды, на рабочем столе есть графические инструментальные средства. Hardinfo и I-nex — некоторые из популярных инструментальных средств, с помощью которых можно получить подробную информацию о большом количестве различных аппаратных компонентов.
Источник
16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux
Hardware information
Like for every thing, there are plenty of commands to check information about the hardware of your linux system.
Some commands report only specific hardware components like cpu or memory while the rest cover multiple hardware units.
This post takes a quick look at some of the most commonly used commands to check information and configuration details about various hardware peripherals and devices.
The list includes lscpu, hwinfo, lshw, dmidecode, lspci etc.
1. lscpu
The lscpu command reports information about the cpu and processing units. It does not have any further options or functionality.
2. lshw — List Hardware
A general purpose utility, that reports detailed and brief information about multiple different hardware units such as cpu, memory, disk, usb controllers, network adapters etc. Lshw extracts the information from different /proc files.
Check out the following post to learn more about lshw
3. hwinfo — Hardware Information
Hwinfo is another general purpose hardware probing utility that can report detailed and brief information about multiple different hardware components, and more than what lshw can report.
4. lspci — List PCI
The lspci command lists out all the pci buses and details about the devices connected to them.
The vga adapter, graphics card, network adapter, usb ports, sata controllers, etc all fall under this category.
Filter out specific device information with grep.
5. lsscsi — List scsi devices
Lists out the scsi/sata devices like hard drives and optical drives.
6. lsusb — List usb buses and device details
This command shows the USB controllers and details about devices connected to them. By default brief information is printed. Use the verbose option «-v» to print detailed information about each usb port
On the above system, 1 usb port is being used by the mouse.
7. Inxi
Inxi is a 10K line mega bash script that fetches hardware details from multiple different sources and commands on the system, and generates a beautiful looking report that non technical users can read easily.
8. lsblk — List block devices
List out information all block devices, which are the hard drive partitions and other storage devices like optical drives and flash drives
9. df — disk space of file systems
Reports various partitions, their mount points and the used and available space on each.
10. Pydf — Python df
An improved df version written in python, that displays colored output that looks better than df
11. fdisk
Fdisk is a utility to modify partitions on hard drives, and can be used to list out the partition information as well.
12. mount
The mount is used to mount/unmount and view mounted file systems.
Again, use grep to filter out only those file systems that you want to see
13. free — Check RAM
Check the amount of used, free and total amount of RAM on system with the free command.
14. dmidecode
The dmidecode command is different from all other commands. It extracts hardware information by reading data from the SMBOIS data structures (also called DMI tables).
Check out the man page for more details.
15. /proc files
Many of the virtual files in the /proc directory contain information about hardware and configurations. Here are some of them
16. hdparm
The hdparm command gets information about sata devices like hard disks.
Summary
Each of the command has a slightly different method of extracting information, and you may need to try more than one of them, while looking for specific hardware details. However they are available across most linux distros, and can be easily installed from the default repositories.
On the desktop there are gui tools, for those who do not want to memorise and type commands. Hardinfo, I-nex are some of the popular ones that provide detailed information about multiple different hardware components.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
48 thoughts on “ 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux ”
How i can check memory in CPU. Example OPT, Efuse
Thanks for this. I’m just getting going on a VPS and this helped me discover they’d not given me the extra 1Gb I ordered. Very well explained.
Super happy with
inxi -Fx
more accurate than some of the other utilities.. for instance hwinfo was inaccurate for my Lenovo
Thanks for the great post!
Thank you! Your descriptions were useful and well explained!
Источник
How to Display Linux Hardware Info via Command Line
When a user works on a Linux system, in some cases, the user needs to know the information about the hardware under the operating system. This helps us to install compatible applications and utilities which adapt to hardware components of the system.
This tutorial will go through many utilities with detailed explanations of how to get the Linux hardware information.
1. lshw
The lshw stands for List Hardware. It collects the detailed information of the hardware on your system. lshw can show you the name of mainboard, CPU information, bus speed and firmware version and more.
In order to display the information of all the hardware components, run:
If you want to shorten the result, run the command with -short option:
You will receive the brief list of hardware components on your Linux system:
Display disk properties and storage device properties on Linux system by running:
You can get the brief result you may use the option -short :
This tool is also available in a GTK graphical version:
2. Inxi
Inxi is a powerful feature-rich command line tool for Linux users when they want to get the information of system hardware, CPU, RAM, Graphics card, drivers, battery, kernel, process information, and more.
By default, Inxi is not pre-installed on Linux. In order to use it, install the inxi package by running the following command:
Running inxi without any option:
The command will return the information of CPU and Memory as follows:
In order to get the graphics info, run the following command:
To show audio/sound card information, run:
To show battery data, charge, condition, plus extra information (if battery present), run the command with -B option:
3. hwinfo
The hwinfo command is a powerful tool for Linux users to get the detail of hardware components of system. It helps you collect almost of information about: CPU, USB controller, graphics controller, network devices and more.
You can use hwinfo command with —short and —devicetype options to list a specific type of information.
Display information about NIC cards and find out what eth0, eth1 stands for by running:
In order to display storage information with hwinfo command, run:
Likewise, to display list of partitions and hard disks, run the following command:
4. lscpu
The lscpu will show you all the information of your CPU such as number of CPUs, cores, threads, sockets and CPU family, caches, model and more.
You can get the detail of the CPU by running the following command:
The output of the command will be something likes this:
Moreover, if you want to view the speed of the CPU in MHz, run the command:
5. lsscsi
The lsscsi is used to list all of the SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) devices and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory express) devices on your machine.
By default, the lsscsi is not pre-installed on Ubuntu, run the following command to install:
You can simply use the command by running:
6. lsblk
The lsblk command will show you the details of all the block devices in a tree format. It gathers information from sysfs filesystem and udev database.
In order to list all of block devices and their partitions and sizes, let’s run the following command:
7. lsusb
The lsusb is a powerful tool for displaying all the information about USB devices connected to USB buses of your Linux system. The information contains: speed, class, vendor id, product id, bus of USB devices etc.
You can run the following command to get brief information:
If you want to display the specified device with Bus and Device number, run the command with ‘-s’ option. For example:
8. lspci
This standard Linux utility shows what your systems have got internally. The command is a combination of ls, the standard command to list files and PCI that is for the peripheral connection. You can also expect your results to include AGP and onboard components like your USB chipset.
The command is much helpful in diagnosing bugs related to PCI devices. Using ‘-t’ option of lspci command you can see PCI layout in a tree format.
In order to get more detailed information, use -v option with -t option:
You can just run lspci command to display basic device information:
9. Using dmesg
The dmesg command is useful to find out some info about hardware events. It displays the contents of the system log.
The following command lists all references to universal serial bus devices:
In order to display the details about physical memory that is RAM, run:
10. Using dmidecode command
Dmidecode stands for Desktop Management Interface decode, it is a powerful tool for retrieving the information of CPU, RAM, serial numbers, BIOS. The command will show you the hardware details in a human-readable format.
In order to get the Information about BIOS, run:
If you want to display the hardware components information by ID, run the command with -t option following by a number ID (DMI).
For example, the following command will show you the information of memory Device:
11. hdparm
The hdparm stands for Hard Disk Parameter. It’s a Linux command line utility used for handling hard disk devices. You can also use hdparm command to set parameters such as power management, sleep mode, drive caches, Direct Memory Access settings, etc.
For instance, in order to display information of the hard disk, run the following command:
Another example, you can use hdparm to test the speed of hard disk by running the following command:
12. From /proc file
The /proc directory contains lots of system and hardware information. You can try the following commands to get more info on devices:
The output of the command will be something likes this:
In addition, you can run some other commands in order to get information about CPU, Memory, and PCI devices respectively.
13. free
Sometimes, you want to know whether the free memory (RAM) is enough to launch or install a new program? In this case, you can use free command to get information about memory detail in your Linux system.
The free command not only shows you information about the total amount of physical RAM and swap but also free and used memory. For example:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to use Linux command line to get information about the hardware components of the system.
Thanks for reading and please leave your suggestion in the below comment section.
Источник