- Install foca kali linux
- This page details the steps to install Win-Kex in under 2 minutes.
- Installation
- Prerequisites
- Install Kali Linux in WSL2
- Install Win-KeX
- Run Win-KeX
- Win-KeX supports three modes:
- Optional Steps:
- Enjoy Win-KeX!
- Install DVWA on Kali Linux (Step-by-Step)
- Pre-requisites to install DVWA
- Step 1: Download Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA)
- Step 2: Configure DVWA
- Step 3: Install MySQL on Kali Linux
- Step 4: Configure MySQL Database
- Step 5: Install PHP
- Step 6: Configure Apache Server
- Step 7: Access DVWA on Your Browser
- Conclusion
- Related Posts
- Install foca kali linux
- System Requirements
- Installation Prerequisites
- Preparing for the Installation
- Kali Linux Installation Procedure
- Language
- Network
- User Accounts
- Clock
- Encrypted LVM
- Proxy Information
- Metapackages
- Boot Information
- Reboot
- Post Installation
Install foca kali linux
This page details the steps to install Win-Kex in under 2 minutes.
Installation
All installation steps, up to the point where we install Win-Kex, are also explained in the 5 minute video guide by the amazing NetworkChuck:
Prerequisites
- Running Windows 10 version 2004 or higher
- Using Windows Terminal
Install Kali Linux in WSL2
- Open PowerShell as administrator and run:
-
Open PowerShell as administrator and run:
Download and install the WSL2 Linux Kernel from here: https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel
Open PowerShell as administrator and run: wsl —set-default-version 2
Install Kali Linux from the Microsoft Store
Note: to upgrade an existing WSL1 kali-linux installation, type: wsl —set-version kali-linux 2
Run Kali and finish the initial setup
Install Win-KeX
Run Win-KeX
Win-KeX supports three modes:
Window Mode:
To start Win-KeX in Window mode with sound support, run
Refer to the Win-KeX Win usage documentation for further information.
Enhanced Session Mode:
To start Win-KeX in Enhanced Session Mode with sound support and arm workaround, run
Refer to the Win-KeX ESM usage documentation for further information.
Seamless mode:
To start Win-KeX in Seamless mode with sound support, run
Refer to the Win-KeX SL usage documentation for further information.
Optional Steps:
- If you have the space, why not install “Kali with the lot”?: sudo apt install -y kali-linux-large
Choose amongst these options:
Basic Win-KeX in window mode with sound:
Advanced Win-KeX in window mode with sound — Kali icon and start in kali home directory:
Copy the kali-menu.png icon across to your windows picture directory and add the icon and start directory to your WT config:
Basic Win-KeX in seamless mode with sound:
Advanced Win-KeX in seamless mode with sound — Kali icon and start in kali home directory:
Copy the kali-menu.png icon across to your windows picture directory and add the icon and start directory to your WT config:
Basic Win-KeX in ESM mode with sound:
Advanced Win-KeX in ESM mode with sound — Kali icon and start in kali home directory:
Copy the kali-menu.png icon across to your windows picture directory and add the icon and start directory to your WT config:
For more information, ask for help via:
or consult the manpage via:
or join us in the Kali Forums
Enjoy Win-KeX!
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: Re4sonИсточник
Install DVWA on Kali Linux (Step-by-Step)
Table of Contents
In this tutorial, I will give you a step-by-step guide on how to set up and install DVWA on your Kali Linux system.
When starting as a penetration tester, you will need a pentesting-lab to test out your penetration skills. One such system is the Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA). DVWA is a vulnerable web application developed using PHP and MySQL that allows ethical hackers to test out their hacking skills and security tools.
It’s also an excellent guide for professional web developers with security in mind. They can use it to learn which features of a web application are easy to exploit. Some of the most common web vulnerabilities demonstrated by this application include Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), File Inclusion, SQL injection, Bruteforce attacks, and much more.
Pre-requisites to install DVWA
This tutorial assumes that you already have a Kali Linux Server Up and Running.
Step 1: Download Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA)
To get started, we will need to clone the DVWA GitHub into our /var/www/html directory. That is the location where Localhost files are stored in Linux systems. Launch the Terminal and change our directory to the /var/www/html directory with the command below.
Sample Output:
Once in this directory, we will clone the DVWA GitHub repository with the command below.
Sample Output:
After cloning, we can rename the DVWA folder to dvwa . That is not mandatory, but it makes work easier when executing multiple commands.
Step 2: Configure DVWA
After downloading cloning DVWA in our /var/www/html directory, we still need to do some minor configurations. To get started, let’s set read, write, and execute permissions to the DVWA directory. Execute the command below.
Sample Output:
After successfully executing the command, we need to set up the user and password required to access the database. Change directory to point to the config directory with the command below.
When you run the ls command to view the files inside the directory, you will see the config.inc.php.dist file. That is the original file containing the default configurations. We won’t edit it. Instead, we will create a copy of this file called config.inc.php and the original config.inc.php.dist file will act as our backup in case things go wrong.
Execute the command below.
Sample Output:
Run the command below to open the newly created file with nano editor and make the necessary changes, as shown in the image below. We will set db_user as user and db_password as pass. Feel free to use a different username or password.
Sample Output:
Save the file ( Ctrl + O , then Enter ) and Exit (Ctrl + X). That’s it! We are done configuring the DVWA Web application. Let’s move on and configure the database (MySQL).
Step 3: Install MySQL on Kali Linux
By default, MySQL comes pre-installed on Kali Linux. If that’s not the case for you or maybe you messed up with MySQL, we can go ahead and install it manually. If you have worked with Debian-based distributions, MySQL comes in two packages:
In our case, we will need to install the mysql-server. However, there is a catch. If you try using the command apt install mysql-server you will most likely get the error «Package mysql-server is not available, but is referred to by another package. E: Package ‘mysql-server’ has no installation candidate.» That’s because the package mysql-server is referred to default-mysql-server in Kali Linux and also in the latest release of Debian (Debian 10). Therefore, use the command below:
Sample output:
Step 4: Configure MySQL Database
Start the Mysql service with the command below:
You can check whether the service is running using the systemctl status command below.
Sample Output:
Login to the MySQL database using the command below as root. If you have another name set for the superuser in your system, use it instead of root.
You will see a prompt to enter the password. Just hit Enter since we haven’t set any password. MySQL will open, as shown in the image below:
We will create a new user with the username and password set in our DVWA application configuration file. In my case, the username was ‘ user ,’ and the password was ‘ pass .’ The server we are using is Localhost (127.0.0.1). Use the command below.
Sample Output:
We need to grant this new user privilege over the dvwa database. Execute the command below.
Up to this point, we are through with configuring both the DVWA application and the MySQL database. Type exit to close the database.
Step 5: Install PHP
PHP comes installed in Kali Linux. However, if you want to install a particular version, you can do it manually from the Terminal. In this post, we will install PHP 7.4 which is the latest release as of writing this post. Follow the steps below.
First, update your system and add the SURY PHP PPA repository by executing the commands below.
Sample output:
After successfully adding the repository, use the command below to install PHP 7.4
Sample output:
To install additional PHP extensions, use the syntax below where xxx stands for the extension name.
Sample output:
Step 6: Configure Apache Server
Now, we need to configure the server. Use the command below to change your location on the Terminal to point to /etc/php/7.3/apache2 directory.
In the /etc/php/7.4/apache2 , when you execute the ls command, you will see a file called php.ini . That is the file we will edit to configure our localhost server. Use the command below to open it using the nano editor.
Scroll down and look for these two lines: allow_url_fopen and allow_url_include . Set them both as On. Save the file ( Ctrl + O , then Enter ) and Exit ( Ctrl + X ).
Start Apache server using the command below:
To check whether the service started successfully, use the status command.
Sample Output:
Step 7: Access DVWA on Your Browser
That’s it! We now have everything configured, and we can proceed to launch DVWA. Open your browser and enter the URL:
That will open the setup.php web page as shown in the image:
You might see the errors colored in red as in the image above. Don’t panic! Scroll down and click the Create / Reset Database button.
That will create and configure the database. After some time, you will be redirected to the DVWA login page. Log in with these credentials:
- Username — admin
- Password — password
Once logged in, you will see the DVWA main page. On the left panel, we have the different types of attacks you can exploit and the DVWA Security button that allows you to choose the desired security level — Low, Medium, High, or Impossible.
Conclusion
That is how we install DVWA on Kali Linux. Pretty easy, right? DVWA is an excellent resource for both beginners getting started with Penetration Testing and experts. All you need to do is change the security levels depending on your skills. Feel free to share the vulnerability you found interesting to exploit with our readers in the comments section.
Related Posts
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Perform a quick search across GoLinuxCloud
If my articles on GoLinuxCloud has helped you, kindly consider buying me a coffee as a token of appreciation.
For any other feedbacks or questions you can either use the comments section or contact me form.
Thank You for your support!!
Источник
Install foca kali linux
Installing Kali Linux (single boot) on your computer is an easy process. This guide will cover the basic install (which can be done on bare metal or guest VM), with the option of encrypting the partition. At times, you may have sensitive data you would prefer to encrypt using Full Disk Encryption (FDE). During the setup process you can initiate an LVM encrypted install on either Hard Disk or USB drives.
First, you’ll need compatible computer hardware. Kali Linux is supported on amd64 (x86_64/64-Bit) and i386 (x86/32-Bit) platforms. Where possible, we would recommend using the amd64 images. The hardware requirements are minimal as listed in the section below, although better hardware will naturally provide better performance. You should be able to use Kali Linux on newer hardware with UEFI and older systems with BIOS.
Our i386 images, by default use a PAE kernel, so you can run them on systems with over 4 GB of RAM.
In our example, we will be installing Kali Linux in a fresh guest VM, without any existing operating systems pre-installed. We will explain other possible scenarios throughout the guide.
System Requirements
The installation requirements for Kali Linux will vary depending on what you would like to install and your setup. For system requirements:
- On the low end, you can set up Kali Linux as a basic Secure Shell (SSH) server with no desktop, using as little as 128 MB of RAM (512 MB recommended) and 2 GB of disk space.
- On the higher end, if you opt to install the default Xfce4 desktop and the kali-linux-default metapackage, you should really aim for at least 2 GB of RAM and 20 GB of disk space.
- When using resource-intensive applications, such as Burp Suite, they recommend at least 8 GB of RAM(and even more if it large web application!) or using simultaneous programs at the same time.
Installation Prerequisites
This guide will make also the following assumptions when installing Kali Linux:
- Using the amd64 installer image.
- CD/DVD drive / USB boot support.
- Single disk to install to.
- Connected to a network (with DHCP & DNS enabled) which has outbound Internet access.
We will be wiping any existing data on the hard disk, so please backup any important information on the device to an external media.
Preparing for the Installation
Download Kali Linux (We recommend the image marked Installer).
Burn The Kali Linux ISO to DVD or image Kali Linux Live to USB drive. (If you cannot, check out the Kali Linux Network Install).
Backup any important information on the device to an external media.
Ensure that your computer is set to boot from CD/DVD/USB in your BIOS/UEFI.
Kali Linux Installation Procedure
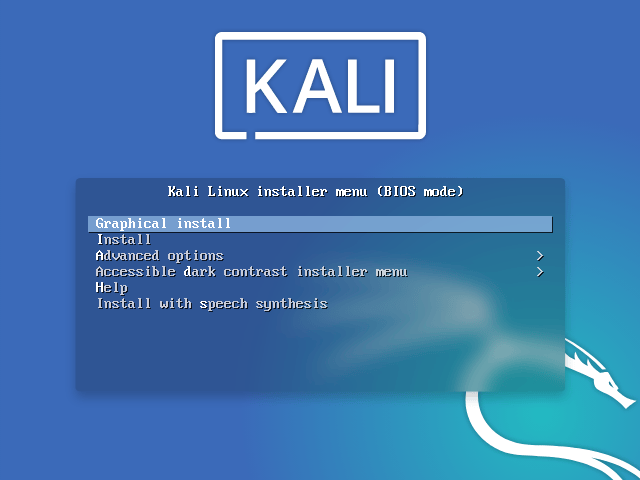
- To start your installation, boot with your chosen installation medium. You should be greeted with the Kali Linux Boot screen. Choose either Graphical install or Install (Text-Mode). In this example, we chose the Graphical install.
If you’re using the live image instead, you will see another mode, Live, which is also the default boot option.
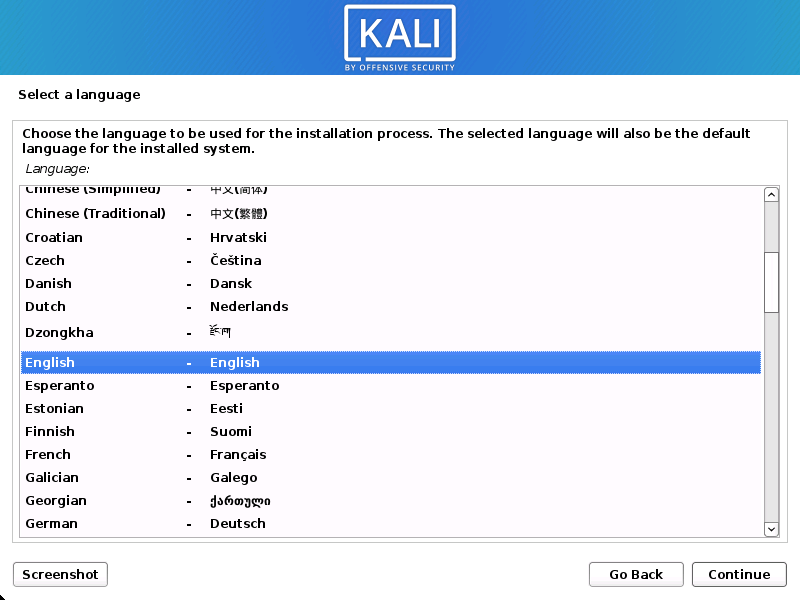
Language
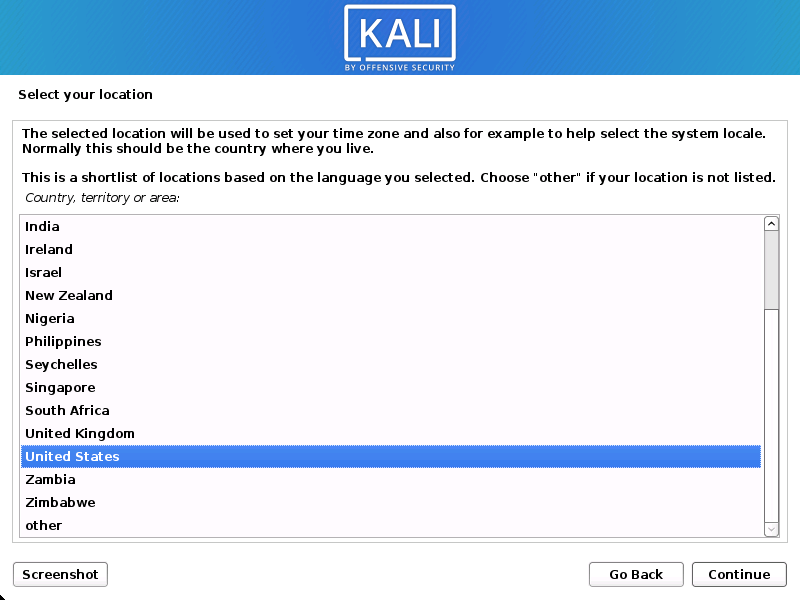
- Select your preferred language. This will be used for both the setup process and once you are using Kali Linux.
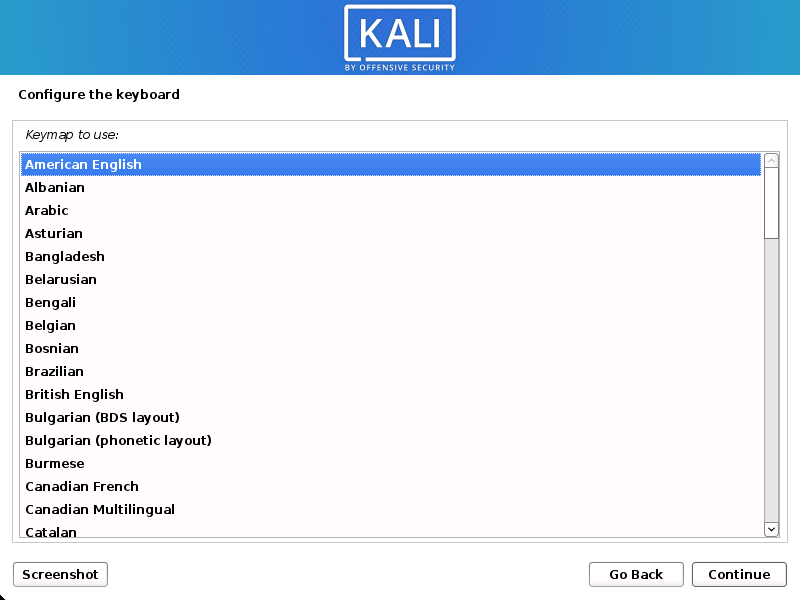
- Specify your geographic location.
- Select your keyboard layout.
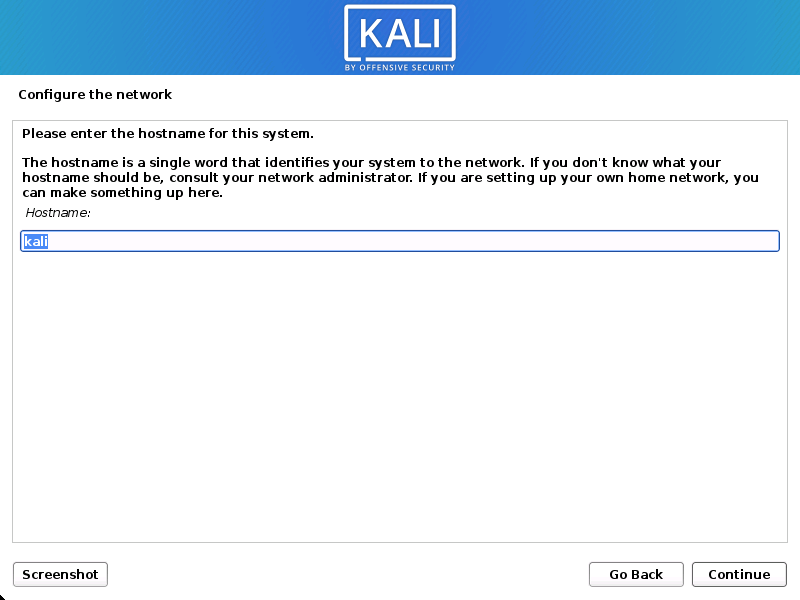
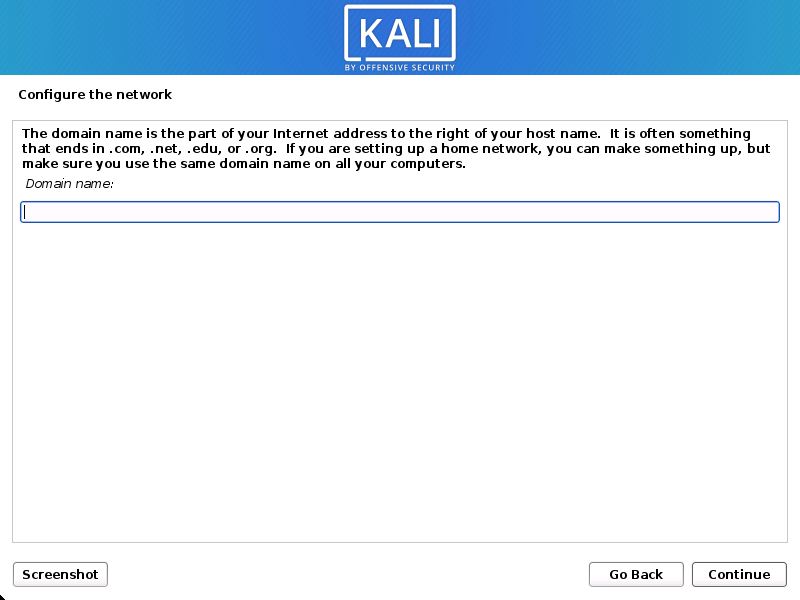
Network
- The setup will now probe your network interfaces, looks for a DHCP service, and then prompt you to enter a hostname for your system. In the example below, we’ve entered kali as our hostname.
If there is no network access with DHCP service detected, you may need to manually configure the network information or do not configure the network at this time.
- If there isn’t a DHCP service running on the network, it will ask you to manually enter the network information after probing for network interfaces, or you can skip.
- If Kali Linux doesn’t detect your NIC, you either need to include the drivers for it when prompted, or generate a custom Kali Linux ISO with them pre-included.
- If the setup detects multiple NICs, it may prompt you which one to use for the install.
- If the chosen NIC is 802.11 based, you will be asked for your wireless network information before being prompted for a hostname.
- You may optionally provide a default domain name for this system to use (values may be pulled in from DHCP or if there is an existing operating systems pre-existing).
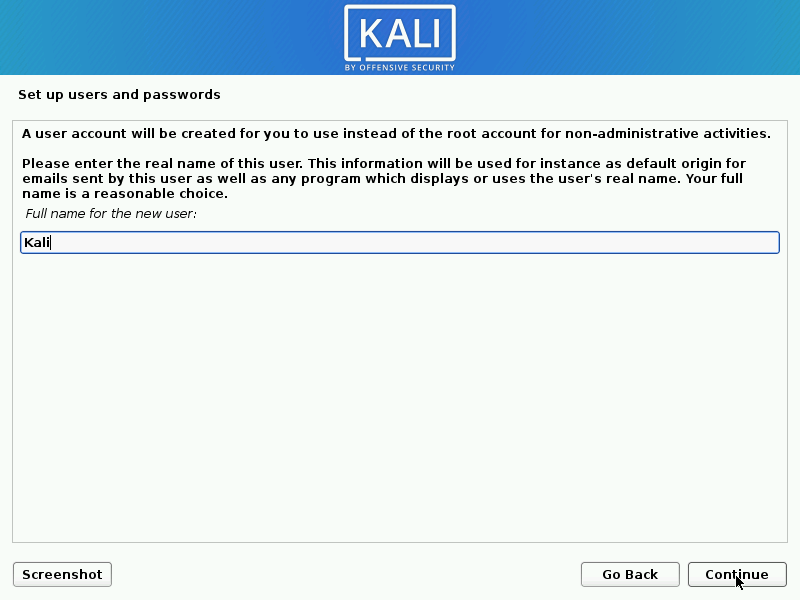
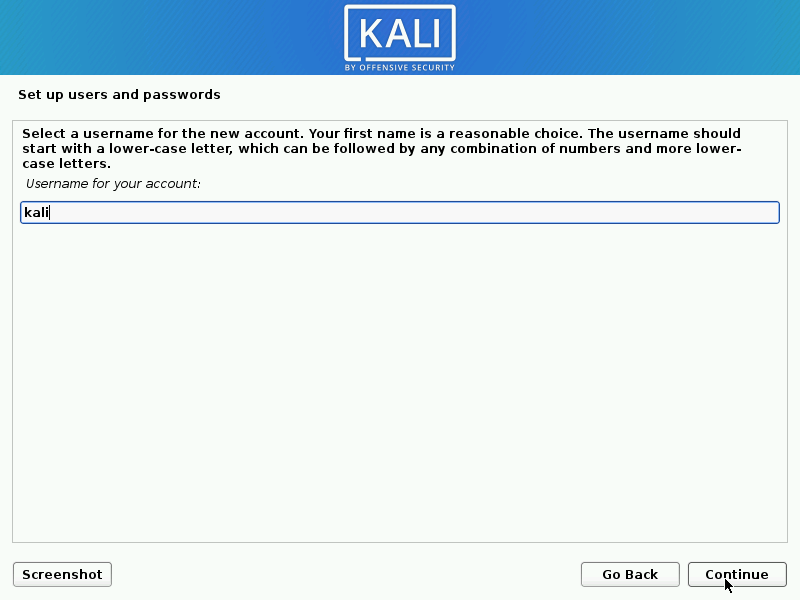
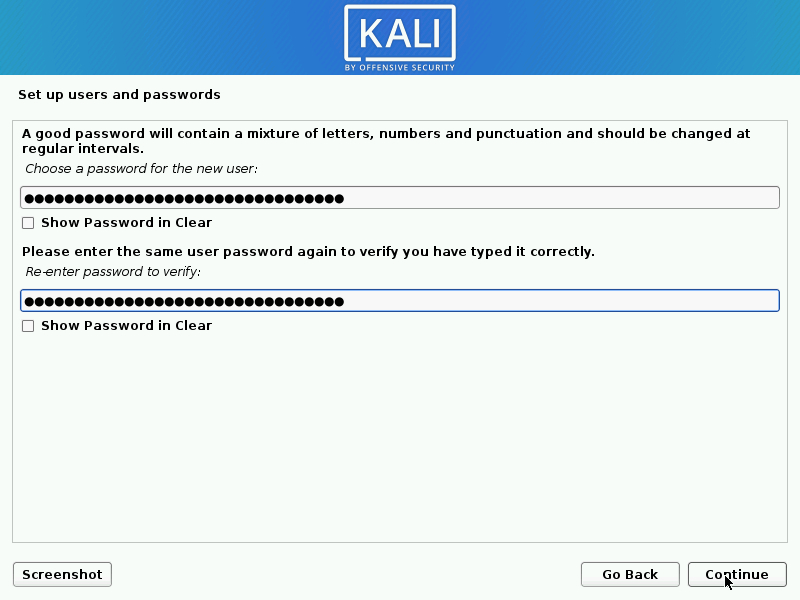
User Accounts
- Next, create the user account for the system (Full name, username and a strong password).
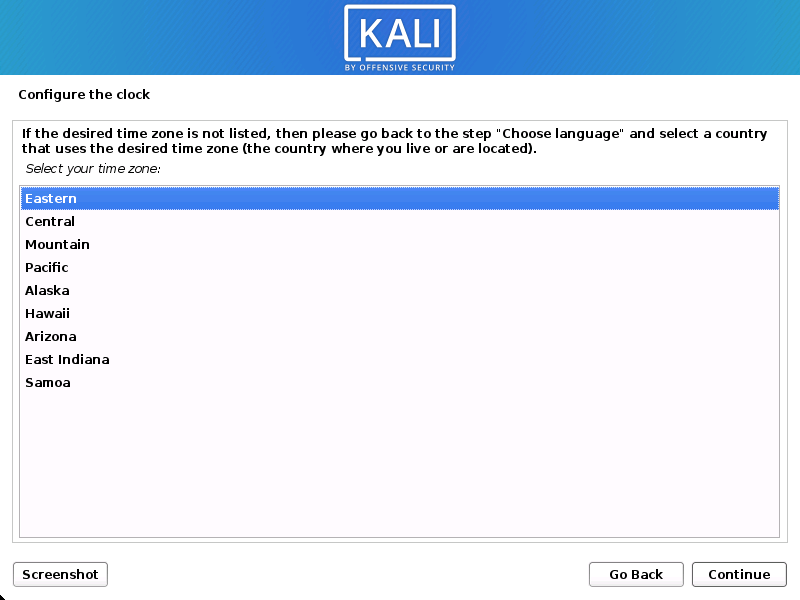
Clock
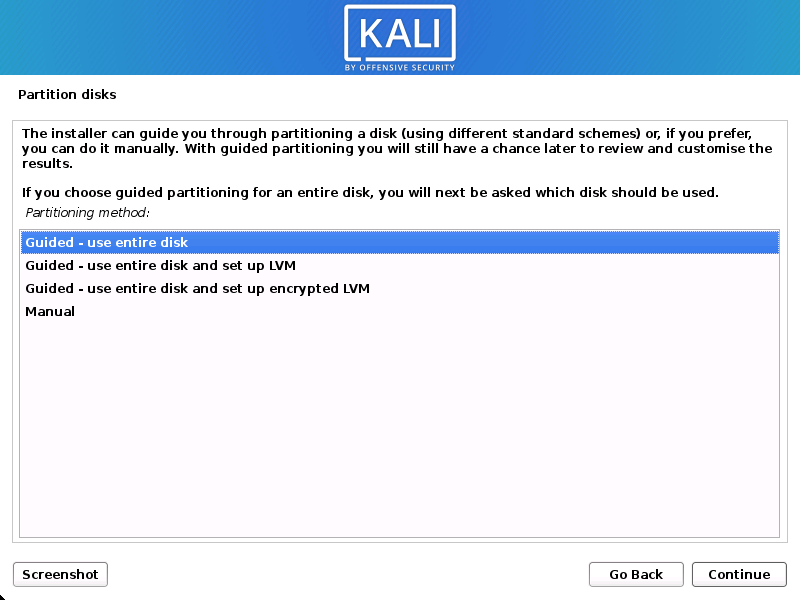
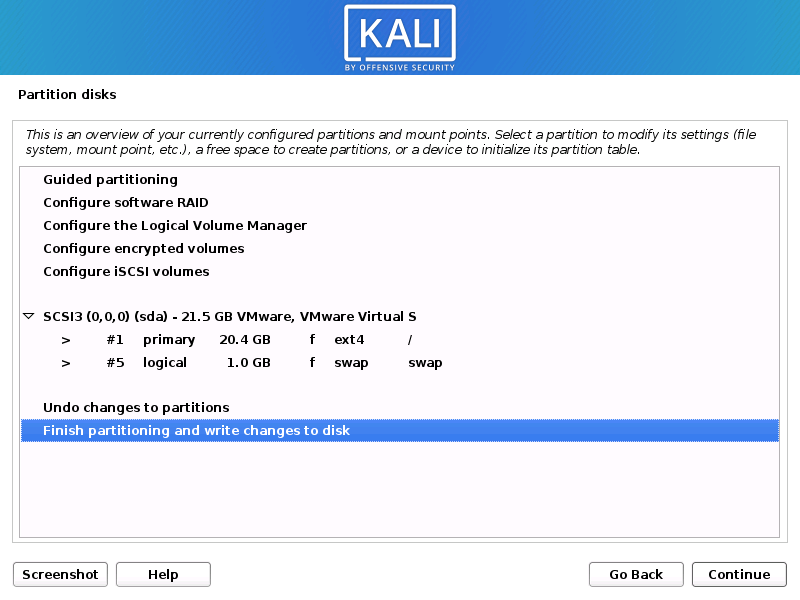
- The installer will now probe your disks and offer you various choices, depending on the setup.
In our guide, we are using a clean disk, so we have four options to pick from. We will select Guided — the entire disk, as this is the single boot installation for Kali Linux, so we do not want any other operating systems installed, so we are happy to wipe the disk.
If there is an pre-existing data on the disk, you will have have an extra option (Guided — use the largest continuous free space) than the example below. This would instruct the setup not to alter any existing data, which is perfect for for dual-booting into another operating system. As this is not the case in this example, it is not visible.
Experienced users can use the “Manual” partitioning method for more granular configuration options, which is covered more in our BTRFS guide.
If you want to encrypt Kali Linux, you can enable Full Disk Encryption (FDE), by selecting Guided — used entire disk and setup encrypted LVM. When selected, later on in the setup (not in this guide) prompt you to enter a password (twice). You will have to enter this password every time you start up Kali Linux.
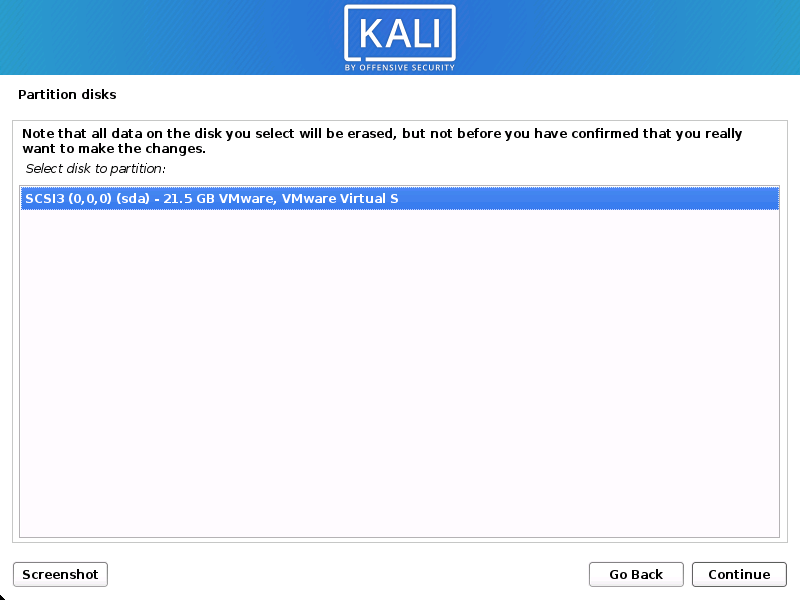
- Select the disk to be partitioned.
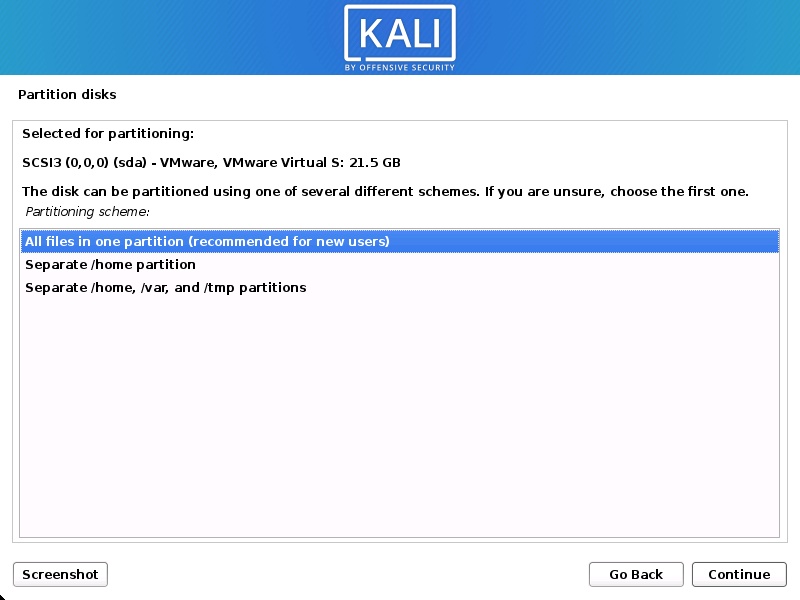
- Depending on your needs, you can choose to keep all your files in a single partition — the default — or to have separate partitions for one or more of the top-level directories.
If you’re not sure which you want, you want “All files in one partition”.
- Next, you’ll have one last chance to review your disk configuration before the installer makes irreversible changes. After you click Continue, the installer will go to work and you’ll have an almost finished installation.
Encrypted LVM
If enabled in the previous step, Kali Linux will now start to perform a secure wipe of the hard disk, before asking you for a LVM password.
Please sure a strong password, else you will have to agree to the warning about a weak passphrase.
This wipe may take “a while” (hours) depending on the size and speed of the drive.
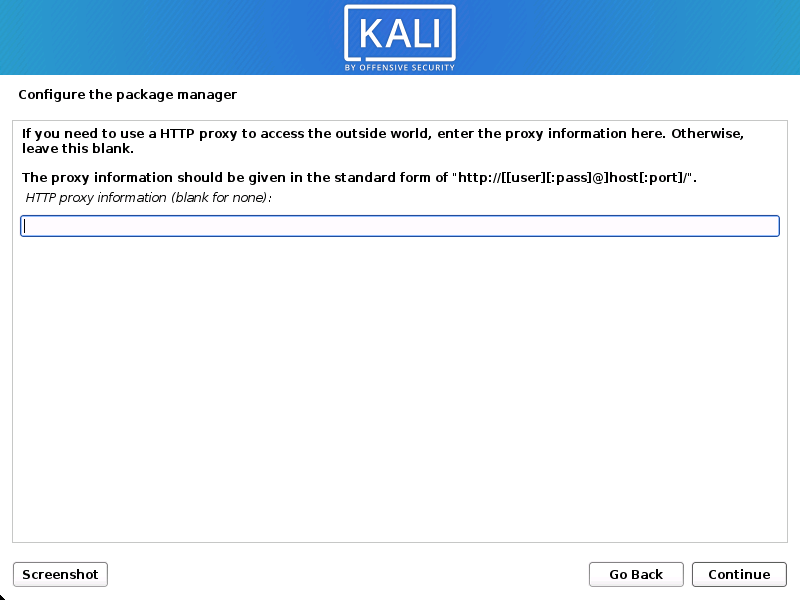
If you wish to risk it, you can skip it.Proxy Information
- Kali Linux uses a central repository to distribute applications. You’ll need to enter any appropriate proxy information as needed.
Metapackages
If network access was not setup, you will want to continue with setup when prompt.
If you are using the Live image, you will not have the following stage.
- Next you can select which metapackages you would like to install. The default selections will install a standard Kali Linux system and you don’t really have to change anything here.
Please refer to this guide if you prefer to change the default selections.
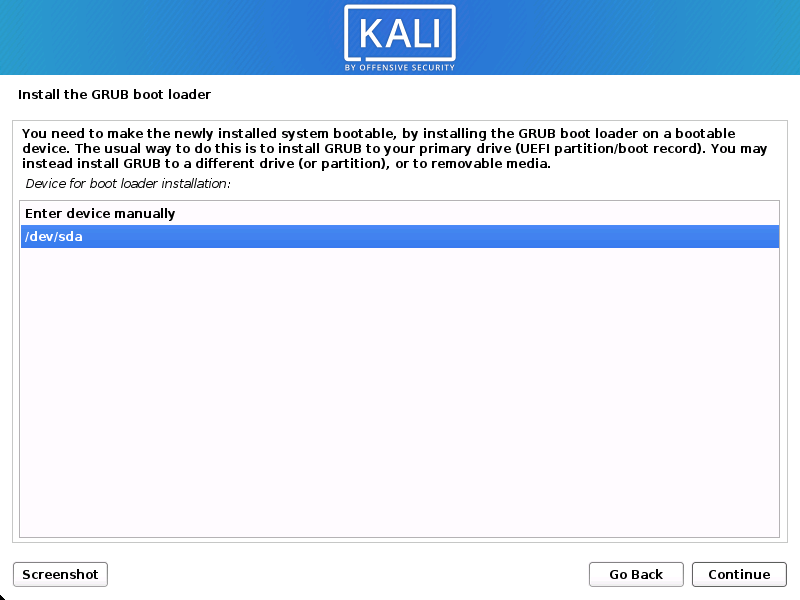
Boot Information
- Next confirm to install the GRUB boot loader.
- Select the hard drive to install the GRUB bootloader in (it does not by default select any drive).
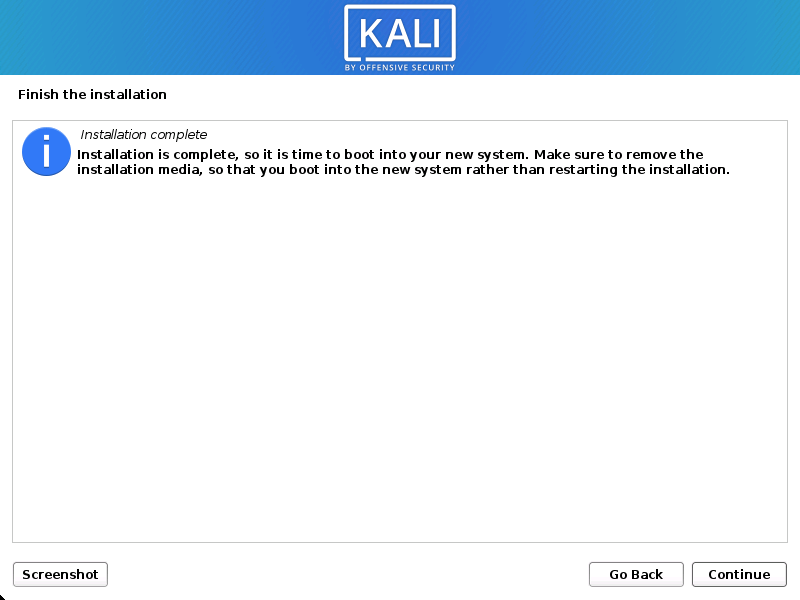
Reboot
- Finally, click Continue to reboot into your new Kali Linux installation.
Post Installation
Now that you’ve completed installing Kali Linux, it’s time to customize your system.
The General Use section has more information and you can also find tips on how to get the most out of Kali Linux in our User Forums.
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: gamb1tИсточник