- Install Windows from a USB Flash Drive
- What you need
- Step 1 — Format the drive and set the primary partition as active
- Step 2 — Copy Windows Setup to the USB flash drive
- Step 3 — Install Windows to the new PC
- If your Windows image is larger than 4GB
- Share Your Windows Internet With Your Android Phone VIA USB Cable
- Upgrade Via a USB-C Cable
- Perparation
- Upgrade steps
- Preparation
- Download Burning Tool
- Install Burning Tool
- Check The USB Driver
- How to burn an Image on Ubuntu
- WinUSB (Winusb.sys) Installation
- Automatic installation of WinUSB without an INF file
- Installing WinUSB by specifying the system-provided device class
- Writing a custom INF for WinUSB installation
- How to create a driver package that installs Winusb.sys
Install Windows from a USB Flash Drive
Here’s how to create a bootable Windows installation USB drive starting with a Windows .iso file or a Windows Setup DVD.
If you’re looking for an easy way to create a bootable USB Windows installation drive, use the media creation tool.
What you need
- Windows 10 install .iso or DVD
- USB flash drive with at least 5GB free space. This drive will be formatted, so make sure it doesn’t have any important files on it.
- Technician PC — Windows PC that you’ll use to format the USB flash drive
- Destination PC — A PC that you’ll install Windows on
Step 1 — Format the drive and set the primary partition as active
Connect the USB flash drive to your technician PC.
Open Disk Management: Right-click on Start and choose Disk Management.
Format the partition: Right-click the USB drive partition and choose Format. Select the FAT32 file system to be able to boot either BIOS-based or UEFI-based PCs.
Set the partition as active: Right-click the USB drive partition and click Mark Partition as Active.
If Mark Partition as Active isn’t available, you can instead use diskpart to select the partition and mark it active.
Step 2 — Copy Windows Setup to the USB flash drive
Use File Explorer to copy and paste the entire contents of the Windows product DVD or ISO to the USB flash drive.
Optional: add an unattend file to automate the installation process. For more information, see Automate Windows Setup.
Step 3 — Install Windows to the new PC
Connect the USB flash drive to a new PC.
Turn on the PC and press the key that opens the boot-device selection menu for the computer, such as the Esc/F10/F12 keys. Select the option that boots the PC from the USB flash drive.
Windows Setup starts. Follow the instructions to install Windows.
Remove the USB flash drive.
If your Windows image is larger than 4GB
Windows USB install drives are formatted as FAT32, which has a 4GB filesize limit. If your image is larger than the filesize limit:
Copy everything except the Windows image file (sources\install.wim) to the USB drive (either drag and drop, or use this command, where D: is the mounted ISO and E: is the USB flash drive.)
Split the Windows image file into smaller files, and put the smaller files onto the USB drive:
Share Your Windows Internet With Your Android Phone VIA USB Cable
How To Share Your Windows Internet With Your Android Phone VIA USB Cable:- Wondering whether it’s possible to browse through the Internet without WiFi or Mobile data? Yes, it is possible. If your PC has an Internet connection, you can share it with your Android device just by using a USB port and USB cable. Sounds cool? Read on then, this post is for you.
STEP 1
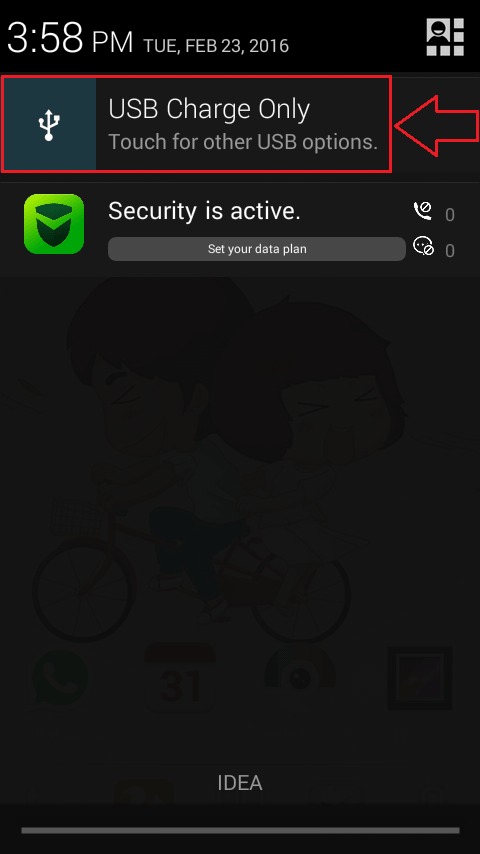
- First of all, connect your Android phone with your PC via the USB port. Your phone will be connected automatically in the USB Charge Only mode. Simply click on the notification as shown in the screenshot. This will open up other options for USB computer connection.
STEP 2
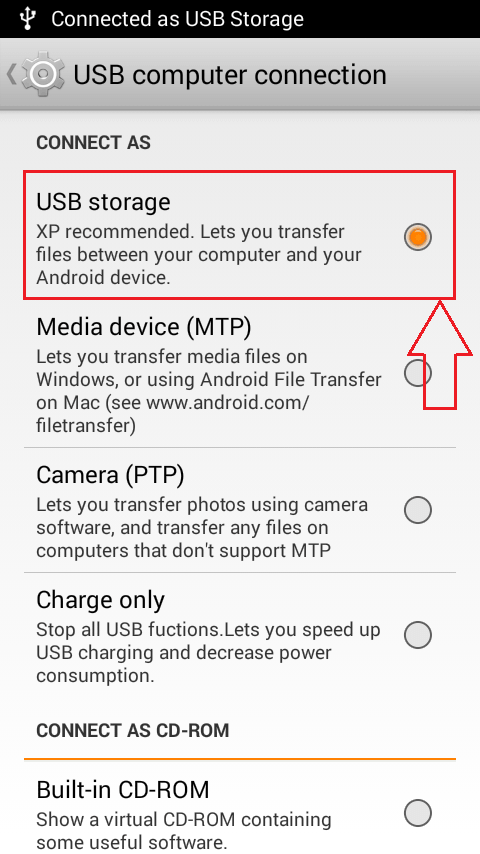
- Find the section named CONNECT AS under USB computer connection. Now check the radio button corresponding to USB storage option as shown in the screenshot.
STEP 3
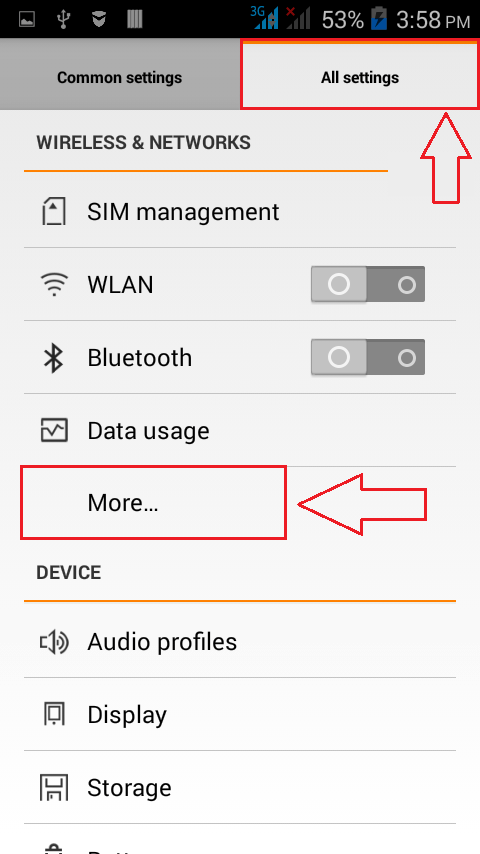
- Once you are done, launch the Settings screen in your Android phone. As next, click on the More option under the section WIRELESS & NETWORKS as shown.
STEP 4
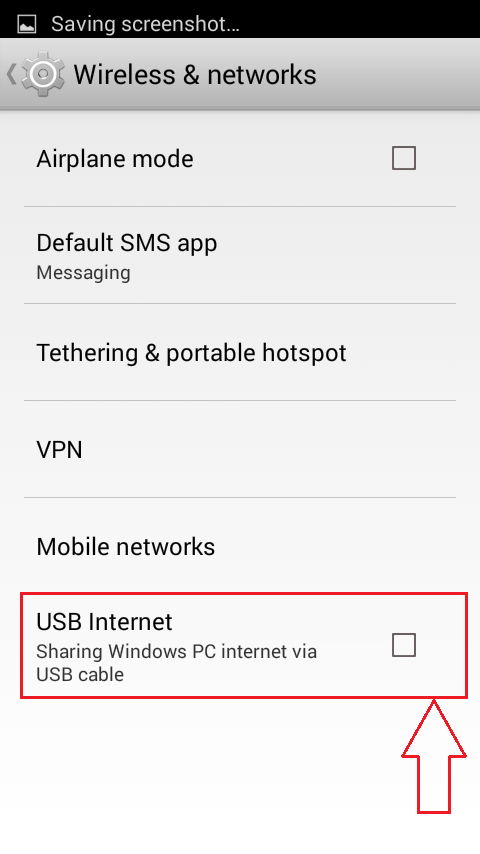
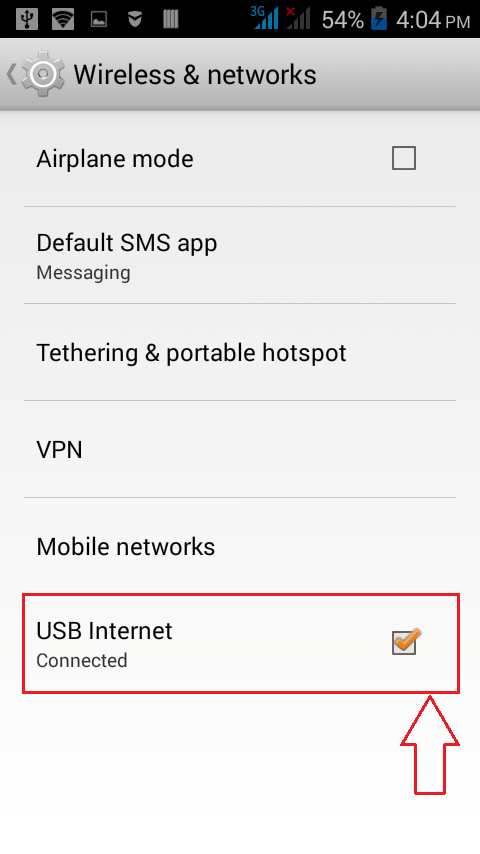
- Now find the option named USB Internet under the Wireless & networks section and click on it.
STEP 5
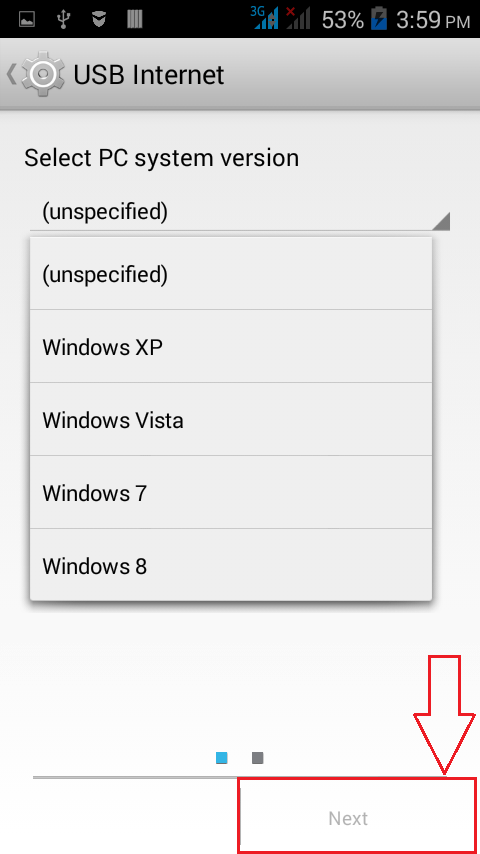
- Select your PC system version from the drop down menu. Once you are done, click on the Next button at the bottom of the screen.
STEP 6
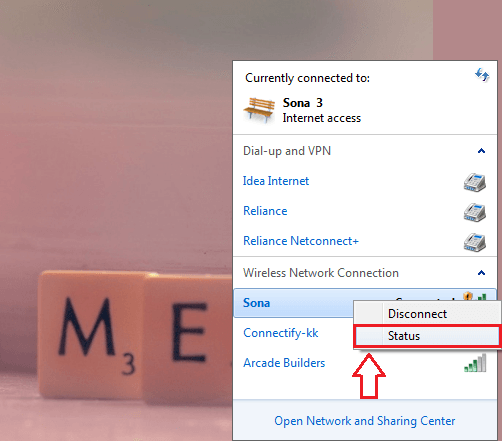
- Now you need to open up the Network center in your PC as shown in the screenshot. Locate and right click on the network that you want to share with your Android device via USB cable. From the options that gets expanded out, click on Status option or Properties option.
STEP 7
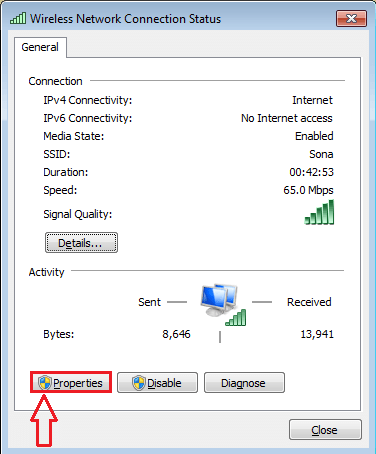
- A new window named Wireless Network Connection Status opens up. You need to locate and click on the button named Properties.
STEP 8
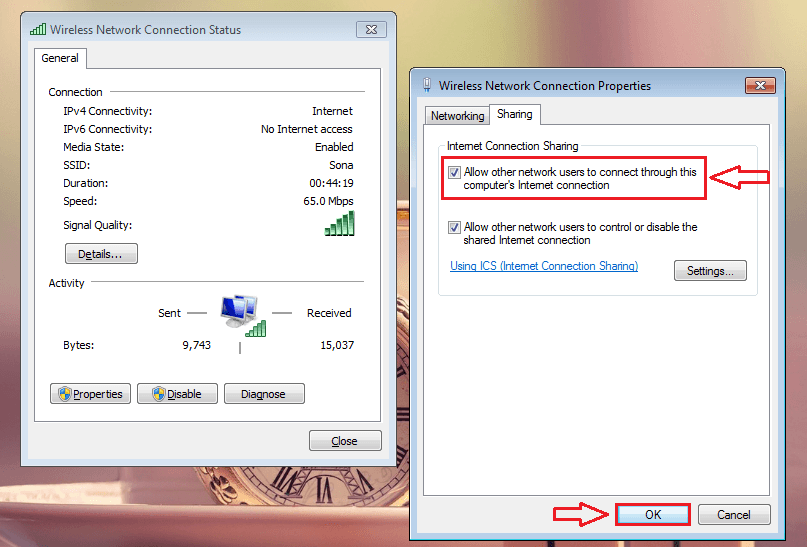
- When the Wireless Network Connection Properties window opens up, click on the Sharing tab and check the checkbox that says Allow other network users to connect through this computer’s Internet connection. Once you are done, simply click on the OK button.
STEP 9
- Now let’s get back to your Android phone from where we left off. Just click on the Done button at the bottom of your phone screen.
STEP 10
- There you are! Your phone is now equipped to browse through the Internet using your PC’s Internet connection.
Try out this trick today itself. Just turn off your WiFi or Mobile data and access any web page via USB cable to amuse your friends. Hope you found the article useful.
Someone who is in love with writing and technical tricks & tips.
Upgrade Via a USB-C Cable
The operation of VIM1, VIM2 and VIM3 is almost the same, so this document will take VIM1 as an example.
Perparation
- Dowload the USB Upgrade Tool and extract it.
- Run setup_v2.x.x.exe to install the tool for upgrading your VIMs:
Upgrade steps
Make soure that you have install the correct USB upgrade Tool, then follow the steps below to upgrade:
Open USB_Burning_tool_v2.x.x.exe , click “File–>Import Image” to choose an image for your VIMs.
Connect your VIMs to your PC with a USB-C data cable (VIMs will power on automatically).
Place your VIMs into “Upgrade Mode”:
- Long press the Power key without releasing it.
- Short press the Reset key and release it.
- Count to 10 seconds and then release the Power key.
If you have performed steps 2 and 3 correctly, your PC will automatically discover your VIMs asa connected USB-device.
Now all you need to do is to click the Start button of the tool and wait for upgrading to complete:
Tips
- To cancel an upgrade, click the Stop button, then close the USB Upgrade Tool. Note that the eMMC might already have been completely erased if you went past the 15% mark.
- Extra power supply(VIM1/VIM2/VIM3) may be required in cases whereby your PC cannot provide enough electrical-current for the upgrade.
Preparation
Download Burning Tool
Image burning tool for Ubuntu is in this repository utils.
Or just pull it (if you have already cloned this repository).
Install Burning Tool
You need to install USB rules and create some links.
You will see this print-out if it was successful.
Root privilege required.
Check The USB Driver
You must now place your VIM board into “Upgrade Mode”.See VIM1/VIM2/VIM3 to enter Upgrade Mode.
Check to see if Ubuntu has detected your VIM1/VIM2 as a connected USB-device.
The message above means that your VIM is connected and recogized by Ubuntu.
How to burn an Image on Ubuntu
There are two commands that be used to burn image: burn-tool and aml-burn-tool .
For example: Burn image for VIM3
- General command burn-tool :
- Amlogic command aml-burn-tool :
For VIM3/VIM3L, you must specify the board with -b VIM3 or it will fail. For VIM1 or VIM2 you can ignore this.
You will see these teminal logs if successful.
WinUSB (Winusb.sys) Installation
For certain Universal Serial Bus (USB) devices, such as devices that are accessed by only a single application, you can install WinUSB (Winusb.sys) in the device’s kernel-mode stack as the USB device’s function driver instead of implementing a driver.
This topic contains these sections:
Automatic installation of WinUSB without an INF file
As an OEM or independent hardware vendor (IHV), you can build your device so that the Winusb.sys gets installed automatically on WindowsВ 8 and later versions of the operating system. Such a device is called a WinUSB device and does not require you to write a custom INF file that references in-box Winusb.inf.
When you connect a WinUSB device, the system reads device information and loads Winusb.sys automatically.
For more information, see WinUSB Device.
Installing WinUSB by specifying the system-provided device class
When you connect your device, you might notice that Windows loads Winusb.sys automatically (if the IHV has defined the device as a WinUSB Device). Otherwise follow these instructions to load the driver:
- Plug in your device to the host system.
- Open Device Manager and locate the device.
- Select and hold (or right-click) the device and select Update driver software. from the context menu.
- In the wizard, select Browse my computer for driver software.
- Select Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer.
- From the list of device classes, select Universal Serial Bus devices.
- The wizard displays WinUsb Device. Select it to load the driver.
If Universal Serial Bus devices does not appear in the list of device classes, then you need to install the driver by using a custom INF. The preceding procedure does not add a device interface GUID for an app (UWP app or Windows desktop app) to access the device. You must add the GUID manually by following this procedure.
Load the driver as described in the preceding procedure.
Generate a device interface GUID for your device, by using a tool such as guidgen.exe.
Find the registry key for the device under this key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\USB\
Under the Device Parameters key, add a String registry entry named DeviceInterfaceGUID or a Multi-String entry named DeviceInterfaceGUIDs. Set the value to the GUID you generated in step 2.
Disconnect the device from the system and reconnect it to the same physical port. NoteВ В If you change the physical port then you must repeat steps 1 through 4.
Writing a custom INF for WinUSB installation
As part of the driver package, you provide an .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the function driver for the USB device.
The following example .inf file shows WinUSB installation for most USB devices with some modifications, such as changing USB_Install in section names to an appropriate DDInstall value. You should also change the version, manufacturer, and model sections as necessary. For example, provide an appropriate manufacture’s name, the name of your signed catalog file, the correct device class, and the vendor identifier (VID) and product identifier (PID) for the device. For info on creating a catalog file, see Creating a Catalog File for Test-Signing a Driver Package.
Also notice that the setup class is set to «USBDevice». Vendors can use the «USBDevice» setup class for devices that do not belong to another class and are not USB host controllers or hubs.
If you are installing WinUSB as the function driver for one of the functions in a USB composite device, you must provide the hardware ID that is associated with the function, in the INF. You can obtain the hardware ID for the function from the properties of the devnode in Device Manager. The hardware ID string format is «USB\VID_vvvv&PID_pppp».
The following INF installs WinUSB as the OSR USB FX2 board’s function driver on a x64-based system.
Starting in Windows 10, version 1709, the Windows Driver Kit provides InfVerif.exe that you can use to test a driver INF file to make sure there are no syntax issues and the INF file is universal. We recommened that you provide a universal INF. For more information, see Using a Universal INF File.
Only include a ClassInstall32 section in a device INF file to install a new custom device setup class. INF files for devices in an installed class, whether a system-supplied device setup class or a custom class, must not include a ClassInstall32 section.
Except for device-specific values and several issues that are noted in the following list, you can use these sections and directives to install WinUSB for any USB device. These list items describe the Includes and Directives in the preceding .inf file.
USB_Install: The Include and Needs directives in the USB_Install section are required for installing WinUSB. You should not modify these directives.
USB_Install.Services: The Include directive in the USB_Install.Services section includes the system-supplied .inf for WinUSB (WinUSB.inf). This .inf file is installed by the WinUSB co-installer if it isn’t already on the target system. The Needs directive specifies the section within WinUSB.inf that contains information required to install Winusb.sys as the device’s function driver. You should not modify these directives. NoteВ В Because WindowsВ XP doesn’t provide WinUSB.inf, the file must either be copied to WindowsВ XP systems by the co-installer, or you should provide a separate decorated section for WindowsВ XP.
USB_Install.HW: This section is the key in the .inf file. It specifies the device interface globally unique identifier (GUID) for your device. The AddReg directive sets the specified interface GUID in a standard registry value. When Winusb.sys is loaded as the device’s function driver, it reads the registry value DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key and uses the specified GUID to represent the device interface. You should replace the GUID in this example with one that you create specifically for your device. If the protocols for the device change, create a new device interface GUID.
NoteВ В User-mode software must call SetupDiGetClassDevs to enumerate the registered device interfaces that are associated with one of the device interface classes specified under the DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key. SetupDiGetClassDevs returns the device handle for the device that the user-mode software must then pass to the WinUsb_Initialize routine to obtain a WinUSB handle for the device interface. For more info about these routines, see How to Access a USB Device by Using WinUSB Functions.
The following INF installs WinUSB as the OSR USB FX2 board’s function driver on a x64-based system. The example shows INF with WDF coinstallers.
USB_Install.CoInstallers: This section, which includes the referenced AddReg and CopyFiles sections, contains data and instructions to install the WinUSB and KMDF co-installers and associate them with the device. Most USB devices can use these sections and directives without modification.
The x86-based and x64-based versions of Windows have separate co-installers.
NoteВ В Each co-installer has free and checked versions. Use the free version to install WinUSB on free builds of Windows, including all retail versions. Use the checked version (with the «_chk» suffix) to install WinUSB on checked builds of Windows.
Each time Winusb.sys loads, it registers a device interface that has the device interface classes that are specified in the registry under the DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key.
NoteВ В If you use the redistributable WinUSB package for WindowsВ XP or Windows ServerВ 2003, make sure that you don’t uninstall WinUSB in your uninstall packages. Other USB devices might be using WinUSB, so its binaries must remain in the shared folder.
How to create a driver package that installs Winusb.sys
To use WinUSB as the device’s function driver, you create a driver package. The driver package must contain these files:
- WinUSB co-installer (Winusbcoinstaller.dll)
- KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll)
- An .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the device’s function driver. For more information, see Writing an .Inf File for WinUSB Installation.
- A signed catalog file for the package. This file is required to install WinUSB on x64 versions of Windows starting withВ Vista.
NoteВ В Make sure that the driver package contents meet these requirements:
- The KMDF and WinUSB co-installer files must be obtained from the same version of the Windows Driver Kit (WDK).
- The co-installer files must be obtained from the latest version of the WDK, so that the driver supports all the latest Windows releases.
- The contents of the driver package must be digitally signed with a Winqual release signature. For more info about how to create and test signed catalog files, see Kernel-Mode Code Signing Walkthrough on the Windows Dev Center — Hardware site.
Create a driver package folder on the machine that the USB device is connected to. For example, c:\UsbDevice.
Copy the WinUSB co-installer (WinusbcoinstallerX.dll) from the WinDDK\BuildNumber\redist\winusb folder to the driver package folder.
The WinUSB co-installer (Winusbcoinstaller.dll) installs WinUSB on the target system, if necessary. The WDK includes three versions of the co-installer depending on the system architecture: x86-based, x64-based, and Itanium-based systems. They are all named WinusbcoinstallerX.dll and are located in the appropriate subdirectory in the WinDDK\BuildNumber\redist\winusb folder.
Copy the KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll) from the WinDDK\BuildNumber\redist\wdf folder to the driver package folder.
The KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll) installs the correct version of KMDF on the target system, if necessary. The version of WinUSB co-installer must match the KMDF co-installer because KMDF-based client drivers, such as Winusb.sys, require the corresponding version of the KMDF framework to be installed properly on the system. For example, Winusbcoinstaller2.dll requires KMDF version 1.9, which is installed by Wdfcoinstaller01009.dll. The x86 and x64 versions of WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll are included with the WDK under the WinDDK\BuildNumber\redist\wdf folder. The following table shows the WinUSB co-installer and the associated KMDF co-installer to use on the target system.
Use this table to determine the WinUSB co-installer and the associated KMDF co-installer.
| WinUSB co-installer | KMDF library version | KMDF co-installer |
|---|---|---|
| Winusbcoinstaller.dll | Requires KMDF version 1.5 or later | |
| Winusbcoinstaller2.dll | Requires KMDF version 1.9 or later | Wdfcoinstaller01009.dll |
| Winusbcoinstaller2.dll | Requires KMDF version 1.11 or later | WdfCoInstaller01011.dll |
Write an .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the function driver for the USB device.
Create a signed catalog file for the package. This file is required to install WinUSB on x64 versions of Windows.
Attach the USB device to your computer.
Open Device Manager to install the driver. Follow the instructions on the Update Driver Software wizard and choose manual installation. You will need to provide the location of the driver package folder to complete the installation.