- Install Docker on macOS
- Are you already running Docker Toolbox and/or Docker Machine?
- Running Docker Toolbox and Docker for Mac on the same host
- Docker Machine
- Requirements
- Before You Install
- Installation
- Verification
- Welcome to nginx!
- Common Pitfalls
- Operating System
- Shell Scripts
- Multiple Docker Versions
- rstacruz / README.md
- Install Docker Desktop on Mac
- System requirements
- Mac with Intel chip
- Mac with Apple silicon
- Install and run Docker Desktop on Mac
- Quick start guide
- Updates
- Uninstall Docker Desktop
- Docker Desktop for Mac user manual
- Preferences
- General
- Resources
- Advanced
- File sharing
- Proxies
- Network
- Docker Engine
- Command Line
- Kubernetes
- Reset
- Software Updates
- Dashboard
- Add TLS certificates
- Add custom CA certificates (server side)
- Add client certificates
- Directory structures for certificates
Install Docker on macOS
Docker for Mac offers a Mac native application that installs in /Applications . It creates symlinks (symbolic links) in /usr/local/bin for docker and docker-compose to the Mac versions of the commands in the application bundle.
The Docker for Mac bundle installs:
- Docker Engine
- Docker CLI Client
- Docker Compose
- Docker Machine
Are you already running Docker Toolbox and/or Docker Machine?
If so, you need to do a little more work. First, check whether Docker Toolbox environment variables are set:
If you don’t get output, you can go ahead and use Docker for Mac. However, if you do get output (like in the example), you need to unset the Docker variables so the client can talk to the Docker for Mac Engine. Run:
If you use Bash, you can use unset $ to unset all of the Docker environment variables (this does not work in other shells, like zsh or csh ).
When you run env | grep DOCKER now, you should see no output.
Running Docker Toolbox and Docker for Mac on the same host
You can run both Docker Toolbox and Docker for Mac on the same system, but not at the same time.
When you use Docker for Mac, you need to unset all of your environment variables, using one of the methods above. When you want to use a VirtualBox VM you have set up with docker-machine , simply run eval $(docker-machine env default) (assuming you want to target the machine “default”).
Docker Machine
Docker for Mac does not affect previous machines created via Docker Machine, The installation gives you the option to copy containers and images from your local default machine if you have one.
Requirements
You must have a Mac:
- 2010 or newer, with Intel’s hardware Memory Management Unit (MMU).
- OS X 10.10.3 Yosemite or newer (or macOS).
- At least 4 GB of RAM.
- You must not have a VirtualBox installation earlier than version 4.3.30 on your system. If you do, you’ll need to uninstall it.
Before You Install
Take a few minutes to understand some key concepts before you install Docker.
On an “out-of-the-box” Linux installation, the Docker client, daemon, and all containers run directly on localhost, meaning you can access ports on a Docker container using localhost addressing; something like localhost:8080 or 0.0.0.0:8376 .
On macOS, Docker’s daemon runs inside a Linux VM. The macOS Docker client talks to the Docker host VM, and your containers run on the host. You cannot use localhost in this setting; instead, the container’s ports map to the VM’s ports. If your VM has the IP address 10.0.0.5, access the ports like 10.0.0.5:8000 or 10.0.0.5:8376 .
Installation
- Download Docker.
- Double-click the DMG file, and drag-and-drop Docker into your Applications folder.
- You need to authorize the installation with your system password.
- Double-click Docker.app to start Docker.
- The whale in your status bar indicates Docker is running and accessible.
- Docker presents some information on completing common tasks and links to the documentation.
- You can access settings and other options from the whale in the status bar. a. Select About Docker to make sure you have the latest version.
Verification
Check versions of Docker Engine, Compose, and Machine.
Run a Dockerized web server to make sure everything works:
If you do not have the image locally, Docker pulls it from Docker Hub (more on this later). Visit http://localhost to bring up your new homepage; you should see:
Welcome to nginx!
If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.
For online documentation and support please refer to nginx.org. Commercial support is available at nginx.com.
Thank you for using nginx.
Common Pitfalls
Operating System
Unfortunately, if you do not run “Mountain Lion” or later, you cannot run Docker for Mac. You can upgrade your OS to the most recent viable version, provided your system supports it.
Shell Scripts
If you use a shell script to set the Docker environment variables every time you open a command window (Terminal), you need to unset the variables every time you use Docker for Mac (alternately, you can write a shell script to follow behind and unset the variables).
Multiple Docker Versions
Docker for Mac replaces docker and docker-compose with its own versions; if you already have Docker Toolbox on your Mac, Docker for Mac still replaces the binaries. You want the Docker client and Engine to match versions; mismatches can cause problems where the client and host cannot communicate. If you already have Docker Toolbox, and then you install Docker for Mac, you may get a newer version of the Docker client. Running docker version in a command shell displays the version of the client and server you have on your system.
This may also happen if you use Docker Universal Control Plane (UCP).
If you want to support both Docker Toolbox and Docker for Mac, check out the Docker Version Manager (DVM).
Next: Install Docker on Windows 10
Requirements and things to know before installing Docker for Win 10.
By Runnable: The service that speeds up development by providing full-stack environments for every code branch.
Источник
rstacruz / README.md
Docker is available for Linux, MacOS, and Windows.
Docker for Mac is best installed with Homebrew and Homebrew Cask. For other ways to install on MacOS, see Install Docker for Mac in Docker’s docs.
💡 Tip: Avoid Docker Toolbox and boot2docker. These are older packages that have been ceded by Docker for Mac.
Docker is available in Arch Linux’s repositories. Also see Docker in ArchWiki.
docker.io is available from the Ubuntu repositories (as of Xenial).
💡 Tip: If the docker.io package isn’t available for you, see Get Docker CE for Ubuntu for an alternative.
Install Windows Subsystem for Linux and choose Ubuntu as your guest OS. Install Docker as you normally would on Ubuntu (see above). After that, see these instructions for info on how to get it running.
💡 Tip: Avoid Docker for Windows. While it works in most cases, you’ll still face NTFS limitations without WSL (eg, lack of symlinks, which is needed for Yarn/npm to work).
Verifying if it works
If everything works, you should have the following commands available:
If you get an error like the one below, you might need to start the Docker daemon.
To start the Docker daemon, it probably needs one of these commands
Enabling on startup
For Arch Linux, Ubuntu and CentOS, this will enable auto-starting of the Docker service:
Источник
Install Docker Desktop on Mac
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Welcome to Docker Desktop for Mac. This page contains information about Docker Desktop for Mac system requirements, download URLs, instructions to install and update Docker Desktop for Mac.
Download Docker Desktop for Mac
System requirements
Your Mac must meet the following requirements to install Docker Desktop successfully.
Mac with Intel chip
macOS must be version 10.14 or newer. That is, Mojave, Catalina, or Big Sur. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of macOS.
If you experience any issues after upgrading your macOS to version 10.15, you must install the latest version of Docker Desktop to be compatible with this version of macOS.
Docker supports Docker Desktop on the most recent versions of macOS. That is, the current release of macOS and the previous two releases. As new major versions of macOS are made generally available, Docker stops supporting the oldest version and supports the newest version of macOS (in addition to the previous two releases). Docker Desktop currently supports macOS Mojave, macOS Catalina, and macOS Big Sur.
At least 4 GB of RAM.
VirtualBox prior to version 4.3.30 must not be installed as it is not compatible with Docker Desktop.
Mac with Apple silicon
You must install Rosetta 2 as some binaries are still Darwin/AMD64. To install Rosetta 2 manually from the command line, run the following command:
Install and run Docker Desktop on Mac
Double-click Docker.dmg to open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder.
Double-click Docker.app in the Applications folder to start Docker. In the example below, the Applications folder is in “grid” view mode.
The Docker menu (
Here’s a summary of the key changes:
- Our Docker Subscription Service Agreement includes a change to the terms of use for Docker Desktop
- It remains free for small businesses (fewer than 250 employees AND less than $10 million in revenue), personal use, education, and non-commercial open source projects.
- It requires a paid subscription for professional use in larger enterprises.
- The effective date of these terms is August 31, 2021. There is a grace period until January 31, 2022 for those that will require a paid subscription to use Docker Desktop.
- The existing Docker Free subscription has been renamed Docker Personal and we have introduced a Docker Business subscription .
- The Docker Pro, Team, and Business subscriptions include commercial use of Docker Desktop.
Click the checkbox to indicate that you accept the updated terms and then click Accept to continue. Docker Desktop starts after you accept the terms.
If you do not agree to the terms, the Docker Desktop application will close and you can no longer run Docker Desktop on your machine. You can choose to accept the terms at a later date by opening Docker Desktop.
For more information, see Docker Desktop License Agreement. We recommend that you also read the Blog and FAQs to learn how companies using Docker Desktop may be affected.
Quick start guide
If you’ve just installed the app, Docker Desktop launches the Quick Start Guide. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it is a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop. Click the Docker menu (
Updates
When an update is available, Docker Desktop displays an icon to indicate the availability of a newer version.
Starting with Docker Desktop 4.1.0, the Software Updates section in the General tab also notifies you of any updates available to Docker Desktop. You can choose to download the update right away, or click the Release Notes option to learn what’s included in the updated version. If you are on a Docker Team or a Business subscription, you can turn off the check for updates by clearing the Automatically Check for Updates checkbox in the General settings. This will also disable the notification badge that appears on the Docker Dashboard.
To encourage developers to stay up to date, Docker Desktop displays a reminder two weeks after an update becomes available. You can dismiss this daily reminder by clicking Snooze. You can skip an update when a reminder appears by clicking the Skip this update option.
Docker Subscription Service Agreement
Beginning on August 31, 2021, you must agree to the Docker Subscription Service Agreement to continue using Docker Desktop. Read the Blog and the Docker subscription FAQs to learn more about the changes.
Click Download update When you are ready to download the update. This downloads the update in the background. After downloading the update, click Update and restart from the Docker menu. This installs the latest update and restarts Docker Desktop for the changes to take effect.
When Docker Desktop starts, it displays the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window. Read the information presented on the screen to understand how the changes impact you. Click the checkbox to indicate that you accept the updated terms and then click Accept to continue.
If you do not agree to the terms, the Docker Desktop application will close and you can no longer run Docker Desktop on your machine. You can choose to accept the terms at a later date by opening Docker Desktop.
Docker Desktop starts after you accept the terms.
Uninstall Docker Desktop
To uninstall Docker Desktop from your Mac:
- From the Docker menu, select Troubleshoot and then select Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Uninstalling Docker Desktop destroys Docker containers, images, volumes, and other Docker related data local to the machine, and removes the files generated by the application. Refer to the back up and restore data section to learn how to preserve important data before uninstalling.
Источник
Docker Desktop for Mac user manual
Estimated reading time: 16 minutes
Welcome to Docker Desktop! The Docker Desktop for Mac user manual provides information on how to configure and manage your Docker Desktop settings.
For information about Docker Desktop download, system requirements, and installation instructions, see Install Docker Desktop.
Preferences
The Docker Preferences menu allows you to configure your Docker settings such as installation, updates, version channels, Docker Hub login, and more.
Choose the Docker menu 
General
On the General tab, you can configure when to start and update Docker:
Automatically check for updates: By default, Docker Desktop is configured to check for newer versions automatically. If you have installed Docker Desktop as part of an organization, you may not be able to update Docker Desktop yourself. In that case, upgrade your existing organization to a Team plan and clear this checkbox to disable the automatic check for updates.
Start Docker Desktop when you log in: Automatically starts Docker Desktop when you open your session.
Include VM in Time Machine backups: Select this option to back up the Docker Desktop virtual machine. This option is disabled by default.
Use gRPC FUSE for file sharing: Clear this checkbox to use the legacy osxfs file sharing instead.
Send usage statistics: Docker Desktop sends diagnostics, crash reports, and usage data. This information helps Docker improve and troubleshoot the application. Clear the check box to opt out.
Show weekly tips: Displays useful advice and suggestions about using Docker.
Open Docker Desktop dashboard at startup: Automatically opens the dashboard when starting Docker Desktop.
Use Docker Compose V2: Select this option to enable the docker-compose command to use Docker Compose V2. For more information, see Docker Compose V2.
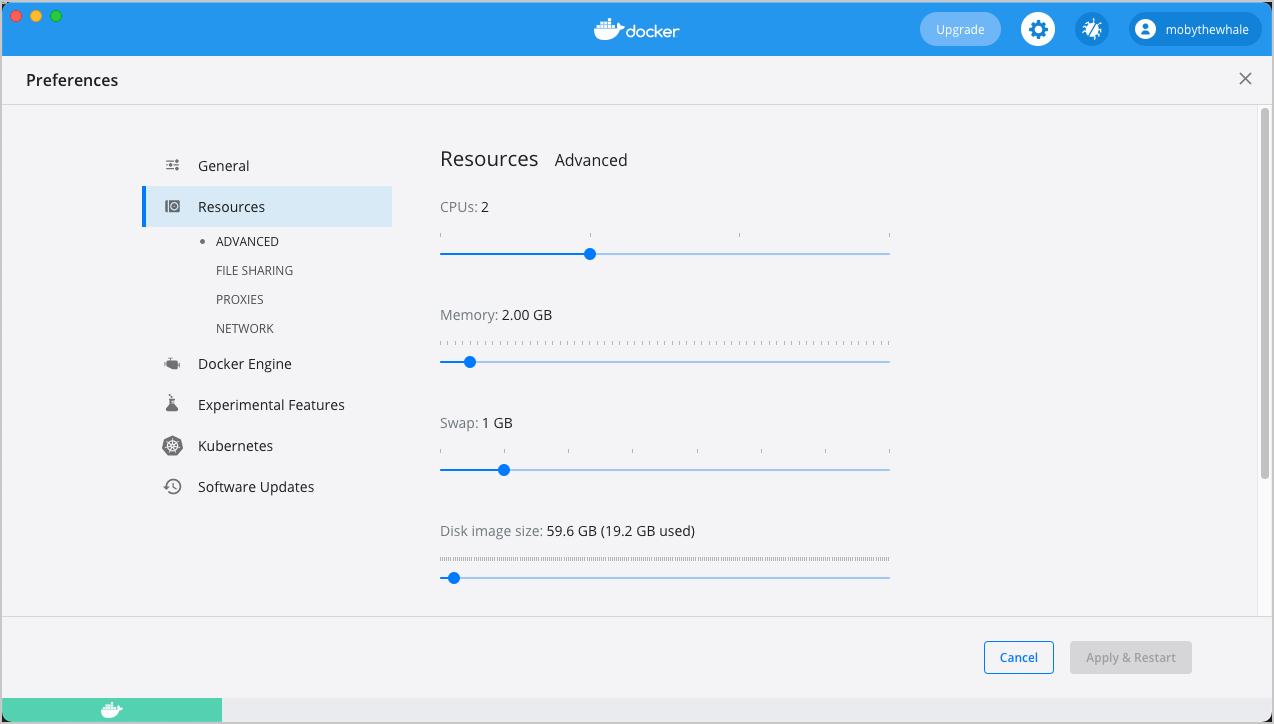
Resources
The Resources tab allows you to configure CPU, memory, disk, proxies, network, and other resources.
Advanced
On the Advanced tab, you can limit resources available to Docker.
Advanced settings are:
CPUs: By default, Docker Desktop is set to use half the number of processors available on the host machine. To increase processing power, set this to a higher number; to decrease, lower the number.
Memory: By default, Docker Desktop is set to use 2 GB runtime memory, allocated from the total available memory on your Mac. To increase the RAM, set this to a higher number. To decrease it, lower the number.
Swap: Configure swap file size as needed. The default is 1 GB.
Disk image size: Specify the size of the disk image.
Disk image location: Specify the location of the Linux volume where containers and images are stored.
You can also move the disk image to a different location. If you attempt to move a disk image to a location that already has one, you get a prompt asking if you want to use the existing image or replace it.
File sharing
Use File sharing to allow local directories on the Mac to be shared with Linux containers. This is especially useful for editing source code in an IDE on the host while running and testing the code in a container. By default the /Users , /Volume , /private , /tmp and /var/folders directory are shared. If your project is outside this directory then it must be added to the list. Otherwise you may get Mounts denied or cannot start service errors at runtime.
File share settings are:
Add a Directory: Click + and navigate to the directory you want to add.
Apply & Restart makes the directory available to containers using Docker’s bind mount ( -v ) feature.
Tips on shared folders, permissions, and volume mounts
Share only the directories that you need with the container. File sharing introduces overhead as any changes to the files on the host need to be notified to the Linux VM. Sharing too many files can lead to high CPU load and slow filesystem performance.
Shared folders are designed to allow application code to be edited on the host while being executed in containers. For non-code items such as cache directories or databases, the performance will be much better if they are stored in the Linux VM, using a data volume (named volume) or data container.
If you share the whole of your home directory into a container, MacOS may prompt you to give Docker access to personal areas of your home directory such as your Reminders or Downloads.
By default, Mac file systems are case-insensitive while Linux is case-sensitive. On Linux, it is possible to create 2 separate files: test and Test , while on Mac these filenames would actually refer to the same underlying file. This can lead to problems where an app works correctly on a Mac (where the file contents are shared) but fails when run in Linux in production (where the file contents are distinct). To avoid this, Docker Desktop insists that all shared files are accessed as their original case. Therefore, if a file is created called test , it must be opened as test . Attempts to open Test will fail with the error No such file or directory . Similarly, once a file called test is created, attempts to create a second file called Test will fail. For more information, see Volume mounting requires file sharing for any project directories outside of /Users .)
Proxies
Docker Desktop detects HTTP/HTTPS Proxy Settings from macOS and automatically propagates these to Docker. For example, if you set your proxy settings to http://proxy.example.com , Docker uses this proxy when pulling containers.
Your proxy settings, however, will not be propagated into the containers you start. If you wish to set the proxy settings for your containers, you need to define environment variables for them, just like you would do on Linux, for example:
For more information on setting environment variables for running containers, see Set environment variables.
Network
You can configure Docker Desktop networking to work on a virtual private network (VPN). Specify a network address translation (NAT) prefix and subnet mask to enable Internet connectivity.
Docker Engine
The Docker Engine page allows you to configure the Docker daemon to determine how your containers run.
Type a JSON configuration file in the box to configure the daemon settings. For a full list of options, see the Docker Engine dockerd commandline reference.
Click Apply & Restart to save your settings and restart Docker Desktop.
Command Line
On the Command Line page, you can specify whether or not to enable experimental features.
Experimental features provide early access to future product functionality. These features are intended for testing and feedback only as they may change between releases without warning or can be removed entirely from a future release. Experimental features must not be used in production environments. Docker does not offer support for experimental features.
For a list of current experimental features in the Docker CLI, see Docker CLI Experimental features.
You can toggle the experimental features on and off in Docker Desktop. If you toggle the experimental features off, Docker Desktop uses the current generally available release of Docker Engine.
You can see whether you are running experimental mode at the command line. If Experimental is true , then Docker is running in experimental mode, as shown here. (If false , Experimental mode is off.)
Kubernetes
Docker Desktop includes a standalone Kubernetes server that runs on your Mac, so that you can test deploying your Docker workloads on Kubernetes. To enable Kubernetes support and install a standalone instance of Kubernetes running as a Docker container, select Enable Kubernetes.
For more information about using the Kubernetes integration with Docker Desktop, see Deploy on Kubernetes.
Reset
On Docker Desktop Mac, the Restart Docker Desktop, Reset to factory defaults, and other reset options are available from the Troubleshoot menu.
For information about the reset options, see Logs and Troubleshooting.
Software Updates
The Software Updates section notifies you of any updates available to Docker Desktop. You can choose to download the update right away, or click the Release Notes option to learn what’s included in the updated version.
If you are on a Docker Team or a Business subscription, you can turn off the check for updates by clearing the Automatically Check for Updates checkbox in the General settings. This will also disable the notification badge that appears on the Docker Dashboard.
Dashboard
The Docker Desktop Dashboard enables you to interact with containers and applications and manage the lifecycle of your applications directly from your machine. The Dashboard UI shows all running, stopped, and started containers with their state. It provides an intuitive interface to perform common actions to inspect and manage containers and existing Docker Compose applications. For more information, see Docker Desktop Dashboard.
Add TLS certificates
You can add trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) (used to verify registry server certificates) and client certificates (used to authenticate to registries) to your Docker daemon.
Add custom CA certificates (server side)
All trusted CAs (root or intermediate) are supported. Docker Desktop creates a certificate bundle of all user-trusted CAs based on the Mac Keychain, and appends it to Moby trusted certificates. So if an enterprise SSL certificate is trusted by the user on the host, it is trusted by Docker Desktop.
To manually add a custom, self-signed certificate, start by adding the certificate to the macOS keychain, which is picked up by Docker Desktop. Here is an example:
Or, if you prefer to add the certificate to your own local keychain only (rather than for all users), run this command instead:
Note: You need to restart Docker Desktop after making any changes to the keychain or to the
/.docker/certs.d directory in order for the changes to take effect.
For a complete explanation of how to do this, see the blog post Adding Self-signed Registry Certs to Docker & Docker Desktop for Mac.
Add client certificates
You can put your client certificates in
When the Docker Desktop application starts, it copies the
/.docker/certs.d folder on your Mac to the /etc/docker/certs.d directory on Moby (the Docker Desktop xhyve virtual machine).
You need to restart Docker Desktop after making any changes to the keychain or to the
/.docker/certs.d directory in order for the changes to take effect.
The registry cannot be listed as an insecure registry (see Docker Engine. Docker Desktop ignores certificates listed under insecure registries, and does not send client certificates. Commands like docker run that attempt to pull from the registry produce error messages on the command line, as well as on the registry.
Directory structures for certificates
If you have this directory structure, you do not need to manually add the CA certificate to your Mac OS system login:
The following further illustrates and explains a configuration with custom certificates:
You can also have this directory structure, as long as the CA certificate is also in your keychain.
To learn more about how to install a CA root certificate for the registry and how to set the client TLS certificate for verification, see Verify repository client with certificates in the Docker Engine topics.
Источник