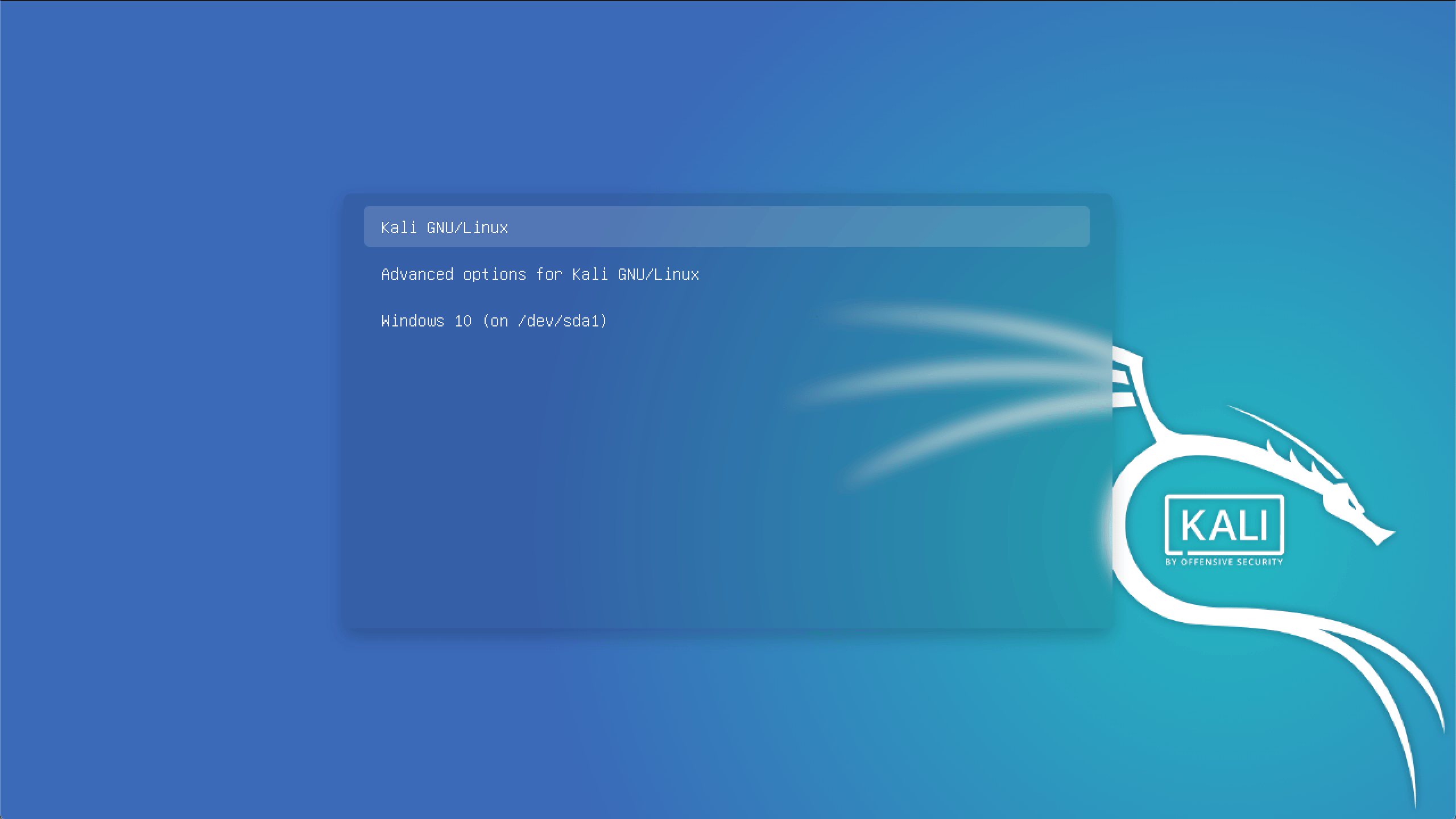
- Installing linux alongside windows
- Installation Prerequisites
- Resize Windows Procedure
- Kali Linux Installation Procedure
- Post Installation
- Time/System Clock
- How to Install Ubuntu Alongside With Windows in Dual-Boot
- Requirements
- Step 1: Prepare Windows Machine for Dual-Boot
- Step 2: Install Ubuntu with Windows Dual-Boot
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
Installing linux alongside windows
Installing Kali Linux next to a Windows installation has its benefits. However, you need to exercise caution during the setup process. First, make sure that you’ve backed up any important data on your Windows installation. Since you’ll be modifying your hard drive, you’ll want to store this backup on external media. Once you’ve completed the backup, we recommend you peruse our Kali Linux Hard Disk install guide, which explains the normal procedure for a basic Kali Linux install.
In our example, we will be installing Kali Linux alongside an installation of Windows (10), which is currently taking up 100% of the disk space in our computer. We will start by resizing our current Windows partition to occupy less space and then proceed to install Kali Linux in the newly-created empty partition.
Installation Prerequisites
This guide will make the following assumptions:
- You have read our single boot Kali Linux install guide, as this has the same Installation Prerequisites (System requirements & setup assumptions).
- When downloading Kali Linux, pick the live image, rather than the installer option.
- A single disk to install to (rather than a dedicated disk per operating system).
We need to use a different image from the single boot Kali Linux install guide, as we need the live image. This is because we need to edit the disk structure without mounting any partitions (otherwise they would be in-use). After we have finished altering the disk layout, we can still install Kali Linux using the live image, but there will be a few differences such as:
Both of these can be addressed post installation, as it saves swapping to the installer image (as you will need either multiple CD/DVD/USBs or to re-image half way though).
This installation has the potential to go wrong very easily as it involves editing existing partitions. Be aware of what partitions you are modifying and where you are installing Kali Linux to.
Having a backup of your Linux files available is a good idea in the event something goes wrong.
Resize Windows Procedure
Before we can install Kali Linux, there needs to be room on the hard disk. By booting into a live Kali Linux session with your chosen installation medium, we can resize the partition to our desired size, as the disk will not be in use because Kali Linux will all be in memory.
To start resizing, make sure you insert your Kali Linux installation medium and power on the device. If needed, press any keyboard shortcuts for a “boot order menu” (depends on each manufacture) or boot into BIOS/UEFI and change the boot order to point to the installation medium first.
When the boot menu/options appears, you should see at least one new option. Depending on the manufacture, hardware, how the system is configured and install medium, you may see more options (e.g. Can you boot into non-UEFI?).
You may need to try a few different options in order to find success.
You may need to disable secure boot
- You should be greeted with the Kali Linux boot screen. Select Live, and you should be booted into the Kali Linux default desktop.
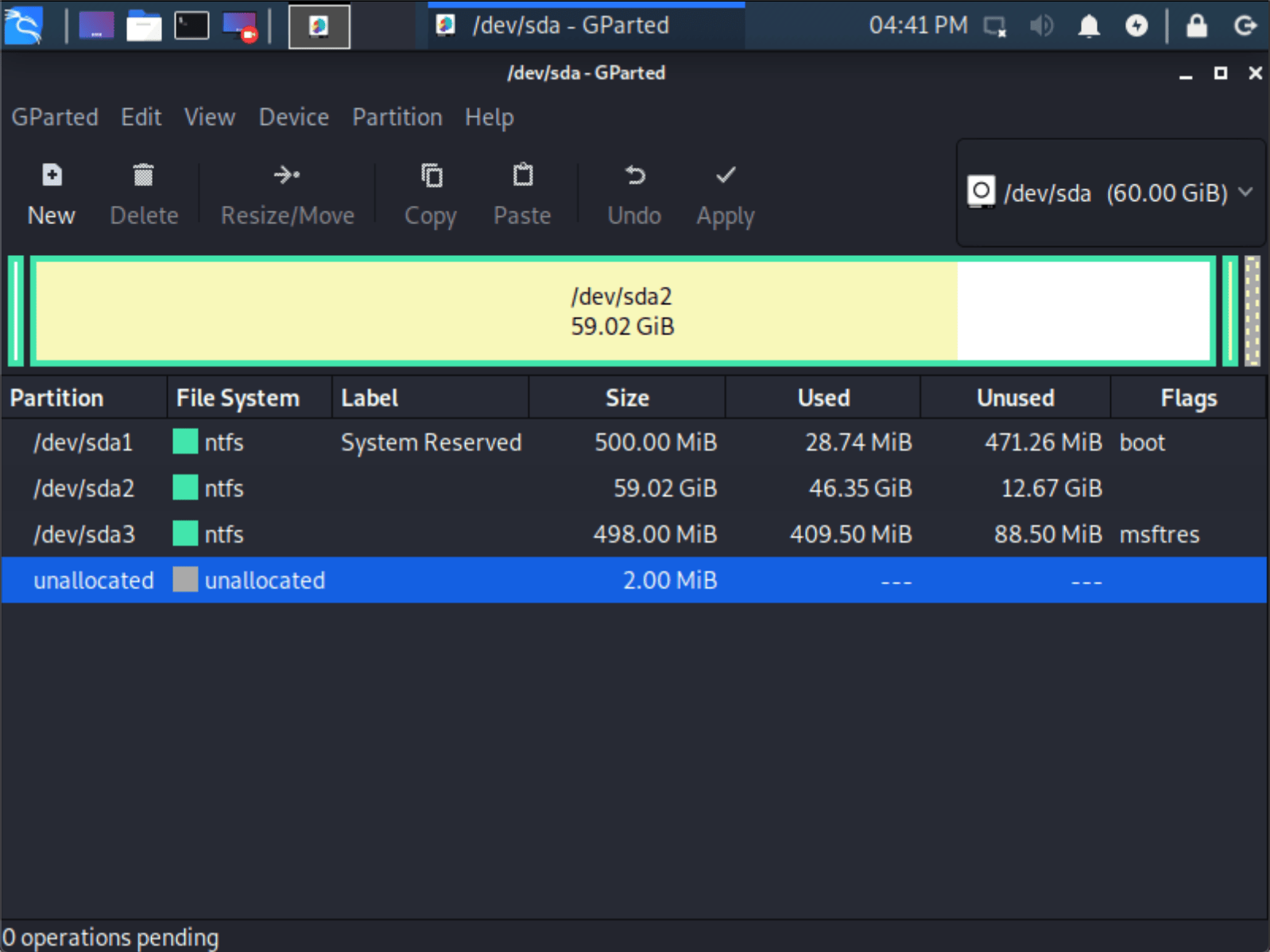
- Now launch GParted, which we’ll use to shrink the existing Windows partition to give us enough room to install Kali Linux in the free space.
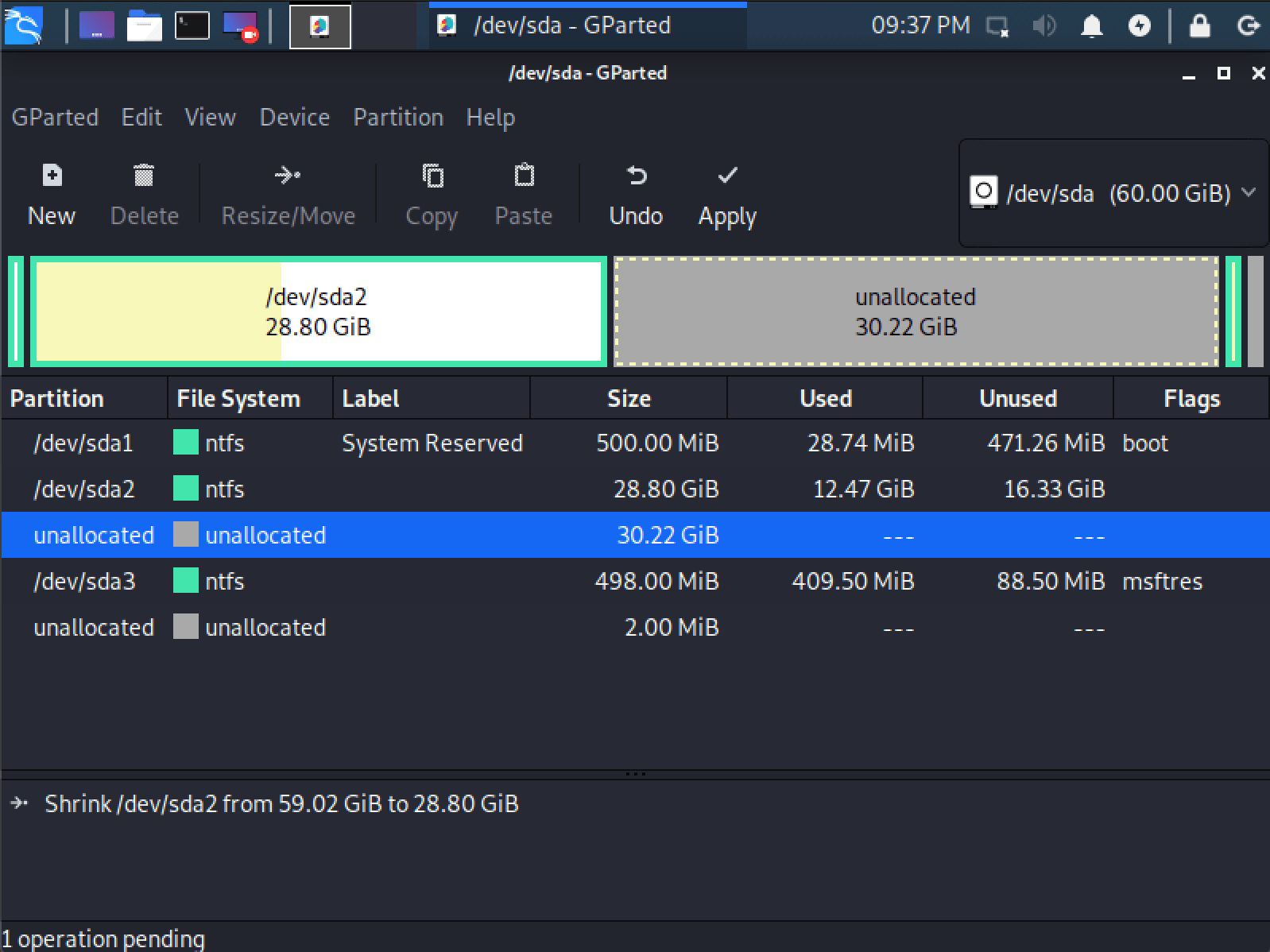
- Once GParted has opened, select your Windows partition ( /dev/sda2 ) & resize it leaving enough space (we recommend at least 20 GB) for the Kali Linux installation.
Depending on your setup, it is often the second option (the largest partition). In our example, there are three partitions:
- Window’s boot partition ( /dev/sda1 )
- Window’s main operating system itself ( /dev/sda2 )
- Window’s System Recovery partition ( /dev/sda3 )
If you are moving past into any non-white in the partition then you are editing a section that is in use.
Only remove from the area of the partition that is not in use.
It is normal to leave the third partition ( /dev/sda3 ), and only shrink the actual install ( /dev/sda2 ).
If you wish to organize the partition to group all the Windows partitions together, placing the free space at the end, you may do so.
- Once you have resized your Windows partition, ensure you “Apply All Operations” on the hard disk. Exit gparted and reboot.
Kali Linux Installation Procedure
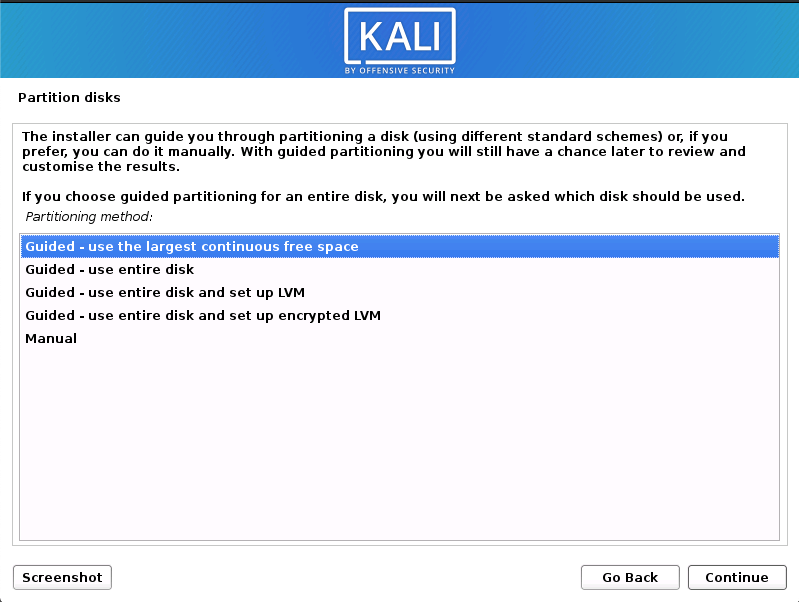
- The installation procedure from this point onwards is similar to a Kali Linux Hard Disk install, until the point of the partitioning. At this point, you need to select “Guided — use the largest continuous free space” (rather than “Guided — the entire disk”) which got created earlier with gparted.
- You can carry on following the single boot Kali Linux install guide, except you will not have the option to select desktop environment or metapackages as you are using the live image. Once the installation is done, reboot.
You should be greeted with a GRUB boot menu, which will allow you to boot either into Kali Linux or Windows.
Post Installation
Now that you’ve completed installing Kali Linux, it’s time to customize your system.
The General Use section has more information and you can also find tips on how to get the most out of Kali Linux in our User Forums.
Time/System Clock
One thing that may be worth knowing about is that occasionally the time will get changed between the Windows and the Linux system. To fix this, we can do the following:
To undo this we can simply do:
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: g0tmi1k
Источник
How to Install Ubuntu Alongside With Windows in Dual-Boot
This tutorial will guide you on how you can perform the installation of Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 19.04, Ubuntu 18.10, or Ubuntu 18.04 in dual-boot with a Microsoft Operating System on machines that come pre-installed with Windows 10.
This guide assumes that your machine comes pre-installed with Windows 10 OS or an older version of Microsoft Windows, such as Windows 8.1 or 8.
In case your hardware uses UEFI then you should modify the EFI settings and disable the Secure Boot feature.
If your computer has no other Operating System already installed and you plan to use a Windows variant alongside Ubuntu, you should first install Microsoft Windows and then proceed with Ubuntu installation.
In this particular case, on Windows installation steps, when formatting the hard disk, you should allocate a free space on the disk with at least 20 GB in size in order to use it later as a partition for Ubuntu installation.
Requirements
Download Ubuntu ISO Image as per your system architecture using the following link:
Step 1: Prepare Windows Machine for Dual-Boot
1. The first thing you need to take care of is to create free space on the computer hard disk in case the system is installed on a single partition.
Log in to your Windows machine with an administrative account and right-click on the Start Menu -> Command Prompt (Admin) in order to enter Windows Command-Line.

2. Once in CLI, type diskmgmt.msc on prompt, and the Disk Management utility should open. From here, right-click on C: the partition and select Shrink Volume in order to resize the partition.

3. On Shrink C: enter a value on space to shrink in MB (use at least 20000 MB depending on the C: partition size) and hit Shrink to start partition resize as illustrated below (the value of space shrink from below image is lower and only used for demonstration purposes).
Once space has been resized you will see a new unallocated space on the hard drive. Leave it as default and reboot the computer in order to proceed with the Ubuntu installation.


Step 2: Install Ubuntu with Windows Dual-Boot
4. For the purpose of this article, We will be installing Ubuntu 20.04 alongside Windows dual boot (you can use any Ubuntu release for installation). Go to the download link from the topic description and grab the Ubuntu Desktop 20.04 ISO image.
Burn the image to a DVD or create a bootable USB stick using a utility such as Universal USB Installer (BIOS compatible) or Rufus (UEFI compatible).
Place the USB stick or DVD in the appropriate drive, reboot the machine, and instruct the BIOS/UEFI to boot up from the DVD/USB by pressing a special function key (usually F12, F10 or F2 depending on the vendor specifications).
Once the media boot-up a new grub screen should appear on your monitor. From the menu select Install Ubuntu and hit Enter to continue.

5. After the boot media finishes loading into RAM you will end up with a completely functional Ubuntu system running in live mode.
On the Launcher choose Install Ubuntu, and the installer utility will start. Choose the keyboard layout you wish to perform the installation and click on the Continue button to proceed further.


6. Next, choose the first option “Normal Installation” and hit on the Continue button again.

7. Now it’s time to select an Installation Type. You can choose to Install Ubuntu alongside Windows Boot Manager, an option that will automatically take care of all the partition steps. Use this option if you don’t require a personalized partition scheme.
In case you want a custom partition layout, check the Something else option and hit on the Continue button to proceed further.
The option Erase disk and install Ubuntu should be avoided on dual-boot because is potentially dangerous and will wipe out your disk.

8. In this step, we’ll create our custom partition layout for Ubuntu. This guide will recommend that you create two partitions, one for root and the other for home accounts data, and no partition for swap (use a swap partition only if you have limited RAM resources or you use a fast SSD).
To create the first partition, the root partition, select the free space (the shrinking space from Windows created earlier), and hit on the + icon below. On partition settings use the following configurations and hit OK to apply changes:
- Size = at least 15000 MB
- Type for the new partition = Primary
- Location for the new partition = Beginning
- Use as = EXT4 journaling file system
- Mount point = /


Create the home partition using the same steps as above. Use all the available free space left for the home partition size. The partition settings should look like this:
- Size = all remaining free space
- Type for the new partition = Primary
- Location for the new partition = Beginning
- Use as = EXT4 journaling file system
- Mount point = /home

9. When finished, hit the Install Now button in order to apply changes to the disk and start the installation process.
A pop-up window should appear to inform you about swap space. Ignore the alert by pressing the Continue button.
Next, a new pop-up window will ask you if you agree with committing changes to the disk. Hit Continue to write changes to disk and the installation process will now start.

10. On the next screen adjust your machine’s physical location by selecting a city nearby from the map. When done hit Continue to move ahead.

11. Pick up a username and password for your administrative sudo account, enter a descriptive name for your computer and hit Continue to finalize the installation.
These are all the settings required for customizing the Ubuntu installation. From here on the installation process will run automatically until it reaches the end.


12. After the installation process reaches its end hit on the Restart Now button in order to complete the installation.
The machine will reboot into the Grub menu, where for ten seconds, you will be presented to choose what OS you wish to use further: Ubuntu 20.04 or Microsoft Windows.
Ubuntu is designated as the default OS to boot from. Thus, just press Enter key or wait for those 10 seconds timeout to drain.


13. After Ubuntu finishes loading, log in with the credentials created during the installation process, and enjoy it. Ubuntu provides NTFS file system support automatically so you can access the files from Windows partitions just by clicking on the Windows volume.


That’s it! In case you need to switch back to Windows, just reboot the computer and select Windows from the Grub menu.
If you want to install some additional software packages and customize Ubuntu, then read our article Top 20 Things to Do After Ubuntu Installation.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник