- Как установить заголовочные файлы ядра в Linux
- Установка заголовочных файлов ядра в Debian, Ubuntu или Linux Mint
- Установка заголовочных файлов ядра в Fedora, CentOS или RHEL
- Правильная инструкция по установке linux-headers в Debian Stretch. uname -r|sed ‘s/[^-]*-[^-]*-//’ — работает неправильно?
- How to Install Kernel Headers in CentOS 7
- Install Kernel Headers in CentOS 7
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- How to Install Kernel Headers in Ubuntu and Debian
- Install Kernel Headers in Ubuntu and Debian
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Fedora Linux Install Linux Kernel Headers And Developer Files
Как установить заголовочные файлы ядра в Linux
Когда вы компилируете драйвер устройства как модуль ядра, вам необходимы установленные заголовочные файлы ядра. Также они требуются, если вы собираете пользовательское приложение, которое взаимодействует напрямую с ядром. При установке заголовочных файлов ядра, необходимо убедиться, что их версия совпадает с версией ядра установленного в системе.
Если версия вашего ядра не менялась после установки дистрибутива, или вы обновляли его с использованием системного менеджера пакетов (то есть apt-get, aptitude или yum) из системных репозиториев, то заголовочные файлы вы также можете установить с помощью пакетного менеджера. Однако если вы скачивали исходный код ядра и компилировали его самостоятельно, то заголовочные файлы необходимо устанавливать с помощью команды make.
Здесь мы предполагаем, что ваше ядро установлено из основного системного репозитория вашего дистрибутива, и вы хотите установить соответствующие заголовочные файлы ядра.
Установка заголовочных файлов ядра в Debian, Ubuntu или Linux Mint
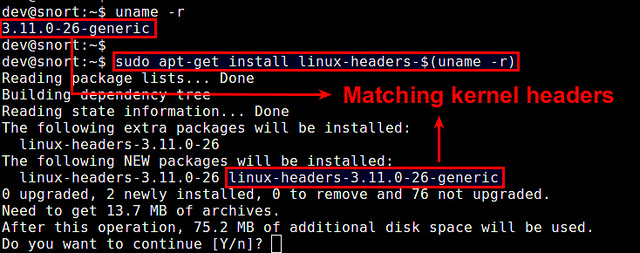
Если вы не компилировали ядро вручную, то можете установить соответствующие заголовочные файлы ядра с помощью команды apt-get.
Сначала проверьте, не установлены ли уже требуемые заголовочные файлы с помощью команды:
Теперь установите заголовочные файлы, как показано ниже.
Проверьте, что установка прошла успешно.
По умолчанию в Debian, Ubuntu или Linux Mint заголовочные файлы находятся в /usr/src.
Установка заголовочных файлов ядра в Fedora, CentOS или RHEL
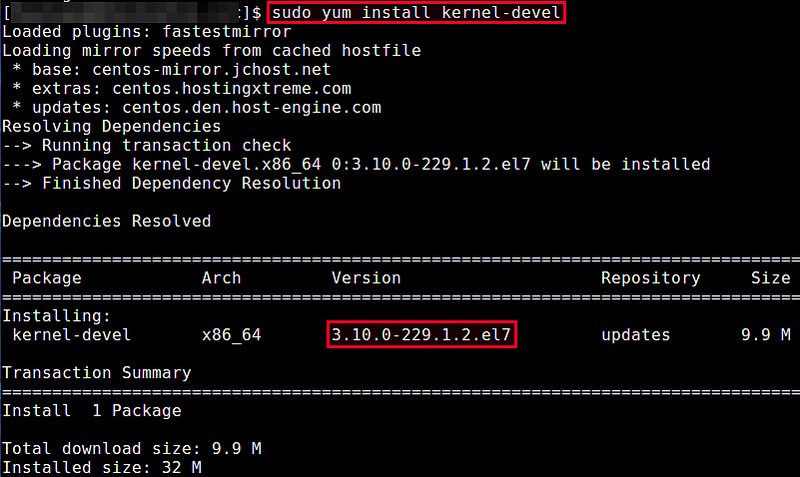
Если вы не обновляли ядро вручную, то можете установить соответствующие заголовочные файлы ядра с помощью команды yum.
Сначала проверьте, не установлены ли уже требуемые заголовочные файлы. По умолчанию заголовочные файлы ядра расположены в /usr/src/kernels/.
Если подходящих заголовочных файлов не установлено, вы можете установить их с помощью команды yum. Она автоматически найдет подходящий пакет.
Если заголовочные файлы ядра, установленные с помощью вышеприведенной команды, не соответствуют установленному в системе ядре, значит оно устарело. В этом случае обновите ядро системы до последней версии с помощью приведенной ниже команды. После обновления необходимо перезагрузить систему.
Теперь проверьте, что установлены заголовочные файлы соответствующей версии с помощью команды:
Источник
Правильная инструкция по установке linux-headers в Debian Stretch. uname -r|sed ‘s/[^-]*-[^-]*-//’ — работает неправильно?
(uname -r|sed ‘s/[^-]*-[^-]*-//’) — что вот это вот делает?
Но почему apt-get устанавливает linux-headers откуда-то отсюда:
Или нужно при установке обязательно указывать часть backports?
apt-get install -t stretch-backports linux-headers-`uname -r`
Я читал это, но не понял что вот это делает: (uname -r|sed ‘s/[^-]*-[^-]*-//’)? uname -r — понятно, но sed.. ‘s/[^-]*-[^-]*-//’)?!
Заменяет последовательность «[не минусы]минус[не минусы]минус» на пустую строку
Кстати, можно было написать uname -r | cut -d- -f3 , но люди почему-то любят использовать sed для всего.
Можно, но пока нет
А как желательно писать при установку пакетов для архитектуры процессора amd64?
apt-get install linux-image-amd64
apt-get install linux-image-$(uname -r|sed ‘s/[^-]*-[^-]*-//’)
Зачем это всё, когда есть мета-пакеты? Поставил мета-пакет и у тебя всегда будет актуальная версия ядра и хедеров после обновления.
для amd64 одинаково, но это-то заклинание именно такое, чтобы не задавать новичку лишний раз вопрос об архитектуре системы, чтобы работало везде.
замудрено больно, мне проще посмотреть что там есть вкусного
и потом полностью указать желаемое
Зачем это всё, когда есть мета-пакеты?
И какой мета-пакет нужен мне?
мне проще посмотреть что там есть вкусного
Ещё есть apt-cache policy
uname -r | cut -d- -f3-
linux-image-amd64 linux-headers-amd64 — если для обоих указать backports, то так и поставятся.
Вместо того, чтобы в гугле на первой странице найти ответ на вопрос, ты лезешь на форум спрашивать. Нет предела тупости.
А ну я уже поставил этот мета-пакет. Осталось только найти 5 пакетов для 390 драйвера. А эта установка мета-пакетов тоже нужна из backpor’ов насколько я понял.
Такой подход не всегда нужен. Иногда надо установить определённую версию, а не последнюю в случае указания мета-пакета.
Так для меня актуально ядро 4.17, а не 4.18, на который указывает мета-пакет.
в таком случае проще поставить нужную версию, чем колупать sed.
Правильная инструкция по установке linux-headers
Источник
How to Install Kernel Headers in CentOS 7
When you compile a custom kernel module such as a device driver on a CentOS system, you need to have kernel header files installed on the system, which include the C header files for the Linux kernel. Kernel header files provide different kinds of function and structure definitions required when installing or compiling any code that interfaces with the kernel.
When you install Kernel Headers, make sure it matches with the currently installed kernel version on the system. If your Kernel version comes with the default distribution installation or you have upgraded your Kernel using yum package manager from system base repositories, then you must install matching kernel headers using package manager only. If you’ve compiled Kernel from sources, you can install kernel headers from sources only.
In this article, we will explain how to install Kernel Headers in CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora distributions using default package manager.
Install Kernel Headers in CentOS 7
First confirm that the matching kernel headers are already installed under /usr/src/kernels/ location on your system using following commands.

If no matching kernel headers are located in the /usr/src/kernels/ directory, go ahead and install kernel headers, which is provided by the kernel-devel package that can be installed using default package manager as shown.

After installing the kernel-devel package, you can find all the kernel headers files in /usr/src/kernels directory using following command.
Note on a VPS (for instance a Linode VPS), a kernel may have a customized version name, in such scenario, you have to identify the kernel version manually and check the installed kernel header files using following commands.

Sample Output
In addition, if you need header files for the Linux kernel for use by glibc, install the kernel-header package using following command.
Now you are good to go with compiling your own or existing kernel modules for software such as VirtualBox and many more.
That’s it! In this article, we have explained how to install kernel-devel and kernel-header packages in CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora systems. Remember that before you can compile kernel modules such as device driver on a Linux system, you should have necessary kernel header files installed. If you have queries, please use the comment form below to reach us.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
How to Install Kernel Headers in Ubuntu and Debian
In our last article, we have explained how to install kernel headers in CentOS 7. Kernel Headers contain the C header files for the Linux kernel, which offers the various function and structure definitions required when compiling any code that interfaces with the kernel, such as kernel modules or device drivers and some user programs.
It is very important to note that the kernel headers package you install should match with the currently installed kernel version on your system. If your kernel version ships with the default distribution installation or you have upgraded your Kernel using dpkg or apt package manager from the Ubuntu or Debian base repositories, then you must install matching kernel headers using package manager only. And if you’ve compiled kernel from sources, you must also install kernel headers from sources.
In this article, we will explain how to install Kernel Headers in Ubuntu and Debian Linux distributions using default package manager.
Install Kernel Headers in Ubuntu and Debian
First check your installed kernel version as well as kernel header package that matches your kernel version using following commands.

On Debian, Ubuntu and their derivatives, all kernel header files can be found under /usr/src directory. You can check if the matching kernel headers for your kernel version are already installed on your system using the following command.

From the above output, it’s clear that the matching kernel header directory doesn’t exist, meaning the package is not yet installed.
Before you can install the appropriate kernel headers, update your packages index, in order to grab information about the latest package releases, using the following command.
Then run the following command that follows to install the Linux Kernel headers package for your kernel version.

Next, check if the matching kernel headers have been installed on your system using the following command

That’s all! In this article, we have explained how to install kernel headers in Ubuntu and Debian Linux and other distributions in the Debian family tree.
Always keep in mind that to compile a kernel module, you will need the Linux kernel headers. If you have any quires, or thoughts to share, use the comment form below to reach us.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Fedora Linux Install Linux Kernel Headers And Developer Files
I ‘m trying to install vmware-tools but Fedora Linux v12 prompting for kernel headers. How do I install kernel headers under Fedora Linux?
You need to install the following two packages:
- kernel-devel : Development package for building kernel modules to match the kernel.
- kernel-headers : Header files for the Linux kernel for use by glibc.
Type the following command as root user to install required packages:
# yum -y install kernel-devel kernel-headers
Once installed type the following command to configure vmware-tools client package:
# vmware-config-tools.pl
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник