- How to Download and Install Windows 10 Updates Manually?
- Getting the Last Update Installation Date, Windows Build and Version
- How to Find and Download the Latest Security Updates for Windows 10?
- Manually Install Cumulative Security Updates on Windows 10
- How to download Windows Updates manually in Windows 10
- Download Windows Updates manually
- Installing windows patches manually
- Answered by:
- Question
- Answers
- All replies
- How to patch on Windows?
- 4 Answers 4
- How to manually download and install Windows 10 cumulative updates
- How to download cumulative updates
- How to install cumulative updates
- Wrapping things up
- More Windows 10 resources
- The Dell XPS 15 is our choice for best 15-inch laptop
- Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
- Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
- These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
How to Download and Install Windows 10 Updates Manually?
If you are against of installing Windows updates automatically and disable Windows Update service (wuauserv) completely, then you have to download and install the latest security updates manually once a month. You can also think about manually installing Windows updates in segments of the network isolated from the Internet when testing updates on computers (if you are not using a WSUS server, where you can manage approving of Windows updates manually) and in some other cases. In this article we’ll show you how to manually find, download and install a latest cumulative security update for your Windows 10 build.
Getting the Last Update Installation Date, Windows Build and Version
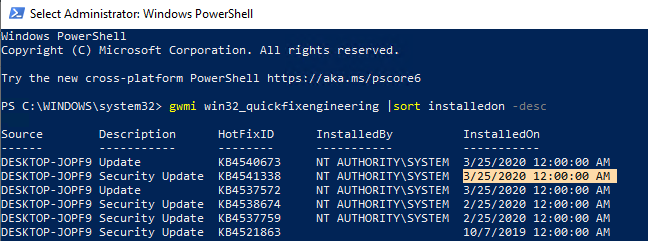
You can check the date of the last updates installation on your computer using the following PowerShell command:
gwmi win32_quickfixengineering |sort installedon -desc
This screenshot shows that the last security update was installed on this computer on March 25, 2020.
Get-WUHistory|Where-Object <$_.Title -like "KB*">|Sort-Object date -desc
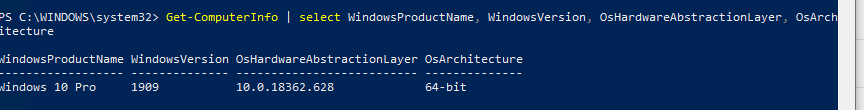
Now you can get the current Windows build and version on your computer. Use the following PowerShell command:
Get-ComputerInfo | select WindowsProductName, WindowsVersion, OsHardwareAbstractionLayer, OsArchitecture
In my case, I need to find the latest security updates for Windows 10 1909 x64.
How to Find and Download the Latest Security Updates for Windows 10?
You can download the latest updates for Microsoft products from the Microsoft Update Catalog — https://www.catalog.update.microsoft.com/Home.aspx. You can find almost any update for all supported Windows versions (the direct import of updates through the WSUS console is also supported). The main problem is that there is no effective search system in the update catalog, so if you do not know the number of the KB you need to install, it is quite difficult to find and download the right update msu package.
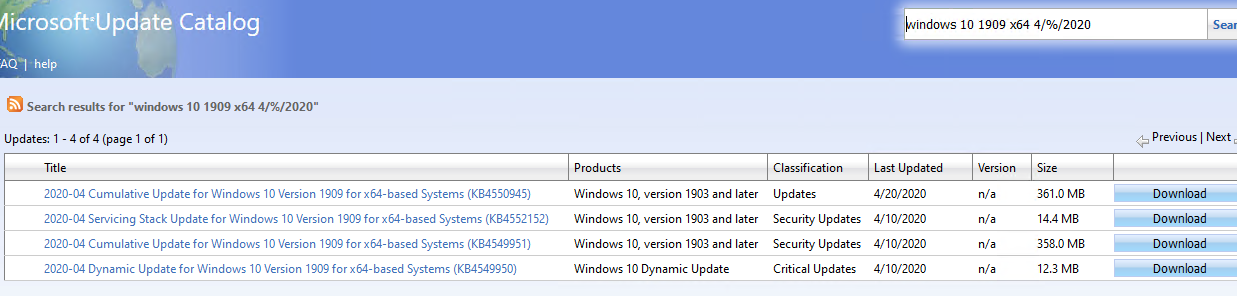
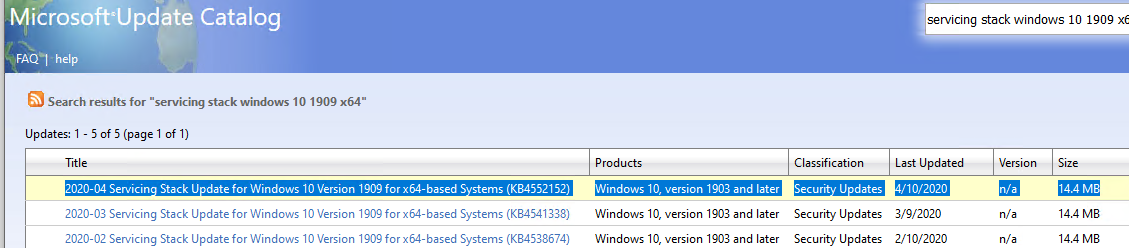
Let’s see how to make a correct search query to find updates for your Windows version and build in Microsoft Update Catalog. This article was written on April 24, 2020, so the latest security updates were released last week. In our case, to search for the security updates for Windows 10 1909 x64 as of April 2020, copy the following search query and paste it into the search field in the right upper corner:
windows 10 1909 x64 4/%/2020
Microsoft Update Catalog has returned the list of 4 updates.
How can you decide, which of these updates you need to download and install? Of course, you can download and install all of them, but you can also save your time. Since Microsoft started using cumulative updates, just download and install the latest cumulative update for your OS version.
There are two large (over 300MB) cumulative updates for Windows 10:
- 2020-04 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1909 for x64-based Systems (KB4550945) 4/20/2020 — 361.0 MB
- 2020-04 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1909 for x64-based Systems (KB4549951) 4/10/2020— 358.0 MB
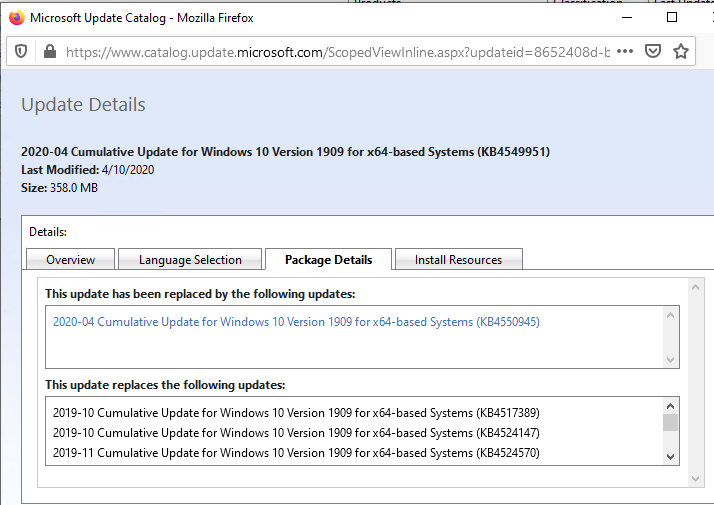
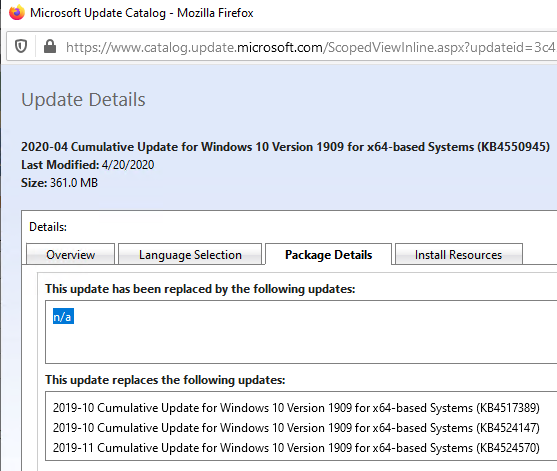
Click on the name of the security update KB4549951. In the next window with update info, go to the Package Details tab. In this tab, you can see, which updates are replaced by this one (This update replaces the following updates:) and which update it replaces in turn (This update has been replaced by the following updates:). The screenshot shows that update KB4549951 is replaced by KB4550945.
Then open the KB4550945 update properties. As you can see, it has no replacement: This update has been replaced by the following updates: n/a. It means that it is the latest cumulative security update for your Windows 10 build.
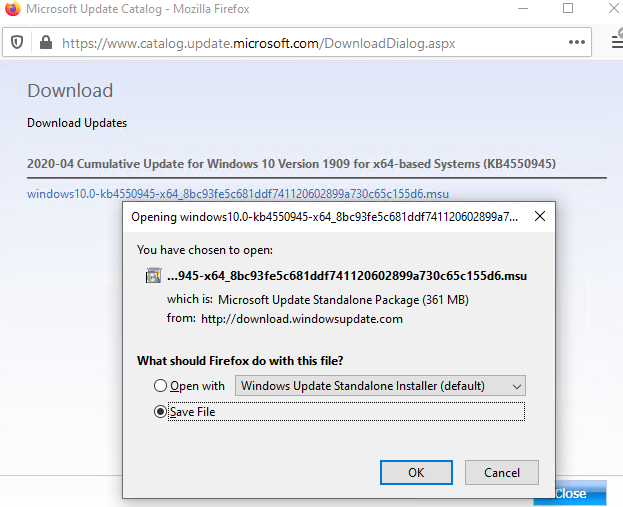
Click Download, and a direct link to download the MSU update file will appear in the next window. Download the file and save it on your local drive.
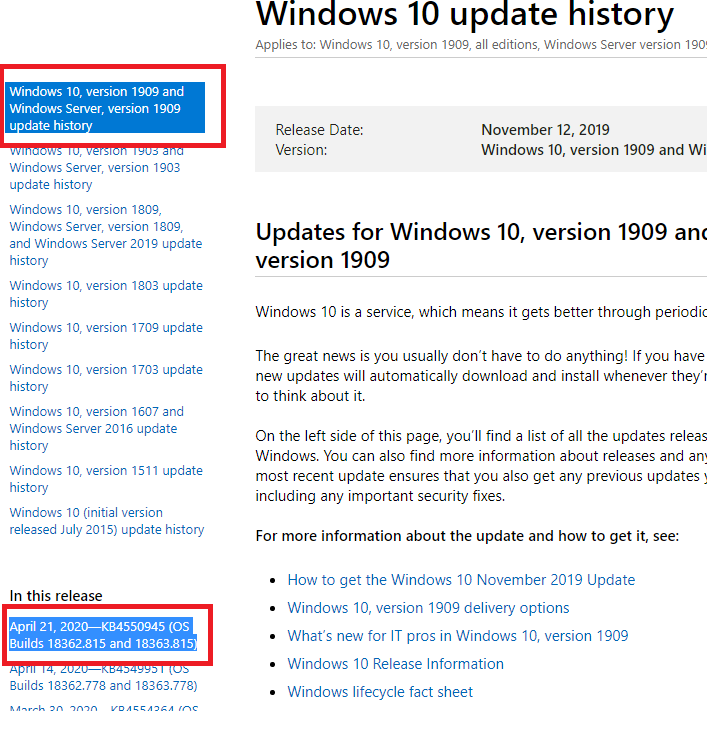
Select your Windows 10 version (in my example, it is Windows 10 1909) from the list on the left, then look at the list called In this release. The first entry refers to a knowledge base (KB) article with the latest cumulative update for the selected Windows version. In our example, it is April 21, 2020—KB4550945 (OS Builds 18362.815 and 18363.815). It is the update we have downloaded using the first method.
Manually Install Cumulative Security Updates on Windows 10
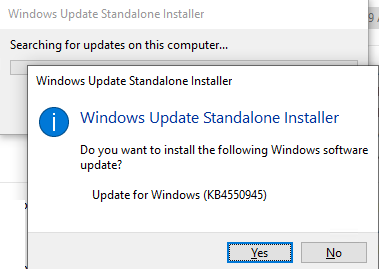
After you have downloaded the MSU file with the latest security update for your Windows 10 version, you can install it. To do it, double click the MSU file and follow the prompts of the Windows Update Standalone Installer.
If the Windows 10 build is correct, but the error still exists, most likely you need to install the latest Windows 10 Servicing Stack Update. Search for it in the Microsoft Update Catalog using the query: servicing stack windows 10 1909 x64 .
After the security update has been installed, restart your computer (if you experience any problems with the OS or apps, you can remove the update according the guide).
You can also install Windows update from the command prompt in the quiet mode using the built-in wusa.exe tool (Windows Update Standalone Installer). The following command will install the specified update in the silent mode and postpone the automatic reboot of the computer after the installation is completed:
wusa C:\updates\windows10.0-kb4550945-x64_8bc93fe5c681ddf741120602899a730c65c155d6 /quiet /norestart
How to download Windows Updates manually in Windows 10
Most of us use Windows Update or Microsoft Update to keep our Windows 10/8/7 operating system and Microsoft software updated. But if you want to, for some, reason, download the updates manually and save it to your computer, this is how you can go about it:
Download Windows Updates manually
On Windows 10, open Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update. Here you can Check for updates.
If any Update has failed to install, you will see it mentioned this.
Note down the KB number of the Windows Update.
On Windows 7, 0pen your Control Panel and navigate to the Windows Update applet. If updates are available, click on the Important updates are available, or the Optional updates are available link. You will be able to see the list along with the KB numbers.
If no updates are available, click on Review your update history link. Here you will see the complete list of Windows Updates including Security Updates and Service Packs, if any, which have been installed on your computer.
Note down the KB number mentioned in the bracket.
Now that you have the KB number, and search for it here on Microsoft.com. If you find no suitable results for Downloads, select All Microsoft. In the results, you will see the Knowledge Base article about the update or hotfix and also the Download page.
If you open its KB article page, you will see the download links for all operating system. Select your operating system and click on the link to be taken to its download page.
Click on the download button to download and save the Windows Update to your computer.
This way, you will be able to install the update manually on any one or more of your computers, as long as it applies to the installed operating system or software.
Downloading, saving, and installing Windows Update manually may be done if you need to save the updates for some reason or if you find that you are unable to update your Windows using Windows Update.
- Microsoft Update Catalog is a service from Microsoft that provides a listing of software updates that can be distributed over a corporate network. Using the Microsoft Update Catalog can prove to be a one-stop location for finding Microsoft software updates, drivers, and hotfixes.
- WSUS Offline Update is a free tool using which, you can update Microsoft Windows or Microsoft Office easily without having an Internet connection.
- Portable Update lets you update Windows 10 offline without an Internet connection.
Date: December 24, 2020 Tags: Windows Updates
Installing windows patches manually
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Answered by:
Question
We do patching using a tool but sometimes patches do not install and we need to RDC to a server then double click the .exe/.msu patch file to get it to install. How can we utilize PowerShell 3.0 to remotely connect to a server then direct it to install a particular .exe/.msu file? I am thinking: enter-pssession -computername %servername% to connect but am not sure how exactly once in to get it via Powershell to run an .exe/.msu file. If there are patch files Q123456.exe and Q654321.msu located in C:\Windows\Patches folder on remote computer how would you use PowerShell 3.0 client to remotely install those patches and save the trouble of having to RDP to the server and manually double click those?
Answers
Thanks for your posting.
In addition, the script below is helpful for you to install an .exe/.msi in a remote computer:
I hope this helps.
All replies
If the name of the server you want to connect to is stored in an environment variable called servername, you will need to switch from the CMD.EXE syntax (%servername%) to the powershell syntax ($env:servername).
Once connected all you need to do is locate the executable you want to run and run it. But note a few caveats:
- it is best to navigate to the folder and run it from there with ./Q123456.exe or run it by specifying its full path C:\windows\patches\Q123456.exe
- executables that pop up any kind of dialog box (i.e. notepad) will NOT result in anyone ever seeing that popup, so avoid them, or run them in such a way as to prevent popups (i.e. an installer that displays a progress bar might accept a -quiet switch).
- if the file is not, strictly speaking, an executable, you might have to run the corresponding executable and pass the filepath as a parameter.
Al Dunbar — remember to ‘mark or propose as answer’ or ‘vote as helpful’ as appropriate.
How to patch on Windows?
Given a (source) patch file, what’s the easiest way to apply this patch on the source files under Windows?
A GUI tool where I can visually compare the unchanged-changed source lines would be great.
4 Answers 4
Patch for Windows is what you’re looking for.
Thanks to Macke, a good way to apply a patch file under Windows OS is using Git. As I understood, Git is a version control solution like SVN.
Here is a guideline to apply a patch :
- First of all, download the latest release of the Windows Git Edition here : GIT
- With the cmd prompt, change directory to the patch file and files to patch
- Now you can use the following command line :
Thank you Macke
Not that since Git 2.3.3 (March 2015), you can use git apply —unsafe-paths to use git apply outside a git repo.
» git apply » was not very careful about reading from, removing, updating and creating paths outside the working tree (under —index / —cached ) or the current directory (when used as a replacement for GNU patch).
The documentation now includes:
By default, a patch that affects outside the working area (either a Git controlled working tree, or the current working directory when » git apply » is used as a replacement of GNU patch) is rejected as a mistake (or a mischief).
When git apply is used as a «better GNU patch», the user can pass the —unsafe-paths option to override this safety check.
This option has no effect when —index or —cached is in use.
So if you have git installed, git apply could help, even outside of any git repo.
How to manually download and install Windows 10 cumulative updates
Microsoft makes available updates for Windows 10 in the regular basis to patch any security hole and to improve the functionality of the operating system. However, even now that updates are mandatory to keep devices always up to date, sometimes updates may not appear for download on your computer for a long time.
Although Windows Update is the preferred method to get updates, Microsoft also allows users to manually download new patches as they become available through the «Microsoft Update Catalog» website. While mainly a resource for IT administrators who need to test updates before pushing them to devices in their network, you can use the Update Catalog to quickly download a new update if it’s not showing for you in Windows Update as an alternative option.
In this Windows 10 guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to find, download, and install updates manually on your device.
How to download cumulative updates
It’s important to note that the Microsoft Update Catalog doesn’t list anything, instead it’s a search page, where you must know exactly the update you want to download.
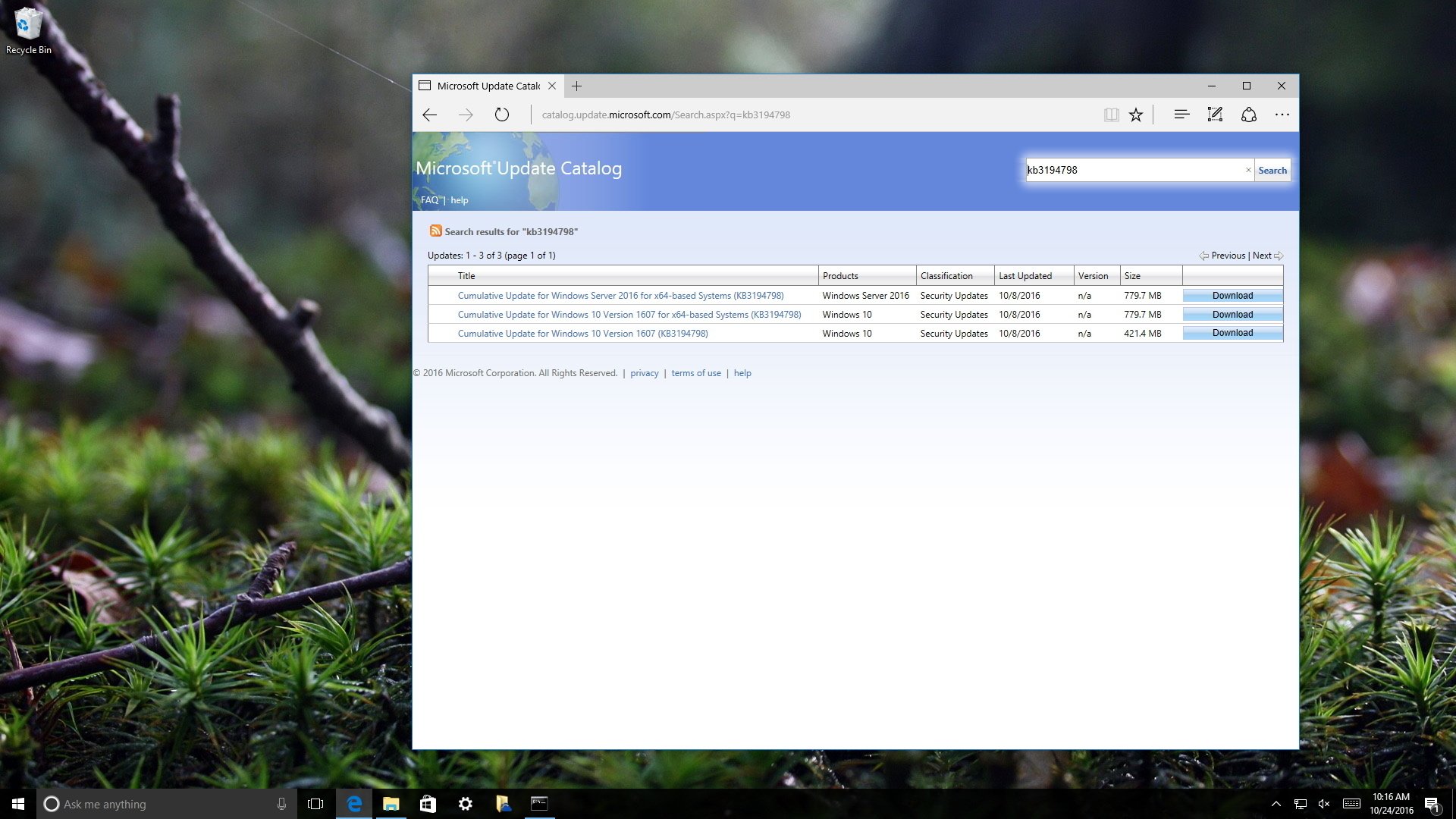
The easiest way to find an update is knowing its Knowledge Base reference number. For example, on October 11th, Microsoft released Windows 10 build 14393.321, which Knowledge Base reference was KB3194798. You can find the references when we publish a new article about a new update, or when you visit the Windows 10 Update History website. Then do the following:
Quick Tip: If you can’t access the site using Microsoft Edge, you can also try opening a new InPrivate window, which should let you get through.
Do a search for the update using the KB number for the update you want. For example, KB3194798.
Click the Download button for the 64-bit or 32-bit version of the update. If you don’t know your system type, do the following:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click on About.
See System type.
A pop-up window will appear with a direct download link, click it to download the .msu file.
How to install cumulative updates
While you can simply double-click the .msu file to install a new update for Windows 10, you may prefer to include options, such as to prevent the operating system from restarting to finish applying the update, which is something you can do using Command Prompt.
- Use the Windows key + I keyboard shortcut to open the Power User menu and select Command Prompt (admin).
Type the following command and press Enter:
wusa C:\PATH-TO-UPDATE\NAME-OF-UPDATE.msu /quiet /norestart
Note: We’re adding the /quiet /norestart switches to prevent the operating system from restarting your computer after installing the update, but later on, you must manually reboot your device to finish applying the update.
Quick Tip: If the name of the update turns to be very long, simply begin typing «Windows10.0-kb» and the hit the Tab key to autocomplete the name.
Wrapping things up
The Microsoft Update Catalog website works best using Internet Explorer, but recent changes that removes ActiveX requirement now allows users to access the site using Chrome and Microsoft Edge. Additionally, alongside cumulative updates, you can also download the latest updates for certain device drivers, and Surface updates.
It’s worth pointing out that even though sometimes updates won’t get through because of a problem on your computer, there will be other times when an update won’t show up because it’s not compatible with your system. If you install a patch that is not working correctly, you can always use our guide to uninstall a problematic update.
While we’re focusing this guide on Windows 10, the same concept shown here works to download and install updates on previous versions of the operating system, including Windows 8.1 and Windows 7.
More Windows 10 resources
For more help articles, coverage, and answers on Windows 10, you can visit the following resources:
We may earn a commission for purchases using our links. Learn more.
The Dell XPS 15 is our choice for best 15-inch laptop
For a lot of people, a 15-inch laptop is a perfect size that offers enough screen for multitasking, and in a lot of cases, some extra performance from powerful hardware. We’ve rounded up the best of the best at this size.
Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
Halo: The Master Chief Collection is more popular than ever, but some fans don’t agree with the live service approach 343 Industries has taken with it. Here’s why those elements are, at the end of the day, great for the game and for Halo overall.
Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
Microsoft announced this week that it was expanding Surface Duo availability to nine new commercial markets. While Surface Duo is undoubtedly a work in progress, this is not a sign of a disaster. It’s also doesn’t mean that Surface Duo is selling a ton either. Instead, the reason for the expansion is a lot more straightforward.
These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
Instant computer — just add a screen. That’s the general idea behind the ultra-portable PC, but it can be hard to know which one you want. Relax, we have you covered!