- Install IntelliJ IDEA
- System requirements
- Install using the Toolbox App
- Install the Toolbox App
- Install the Toolbox App
- Install the Toolbox App
- Standalone installation
- Silent installation on Windows
- Silent configuration file
- Install as a snap package on Linux
- Advanced configuration
- JVM options
- Configure JVM options
- Common options
- Platform properties
- Path variables
- Create a new path variable
- Ignored path variables
Install IntelliJ IDEA
IntelliJ IDEA is a cross-platform IDE that provides consistent experience on the Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems.
IntelliJ IDEA is available in the following editions:
Community Edition is free and open-source, licensed under Apache 2.0. It provides all the basic features for JVM and Android development.
IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate is commercial, distributed with a 30-day trial period. It provides additional tools and features for web and enterprise development.
For more information, see the comparison matrix.
System requirements
| Requirement | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| RAM | 2 GB of free RAM | 8 GB of total system RAM |
| CPU | Any modern CPU | Multi-core CPU. IntelliJ IDEA supports multithreading for different operations and processes making it faster the more CPU cores it can use. |
| Disk space | 2.5 GB and another 1 GB for caches | SSD drive with at least 5 GB of free space |
| Monitor resolution | 1024×768 | 1920×1080 |
| Operating system | Latest 64-bit version of Windows, macOS, or Linux (for example, Debian, Ubuntu, or RHEL) |
You do not need to install Java to run IntelliJ IDEA because JetBrains Runtime is bundled with the IDE (based on JRE 11). However, to develop Java applications, a standalone JDK is required.
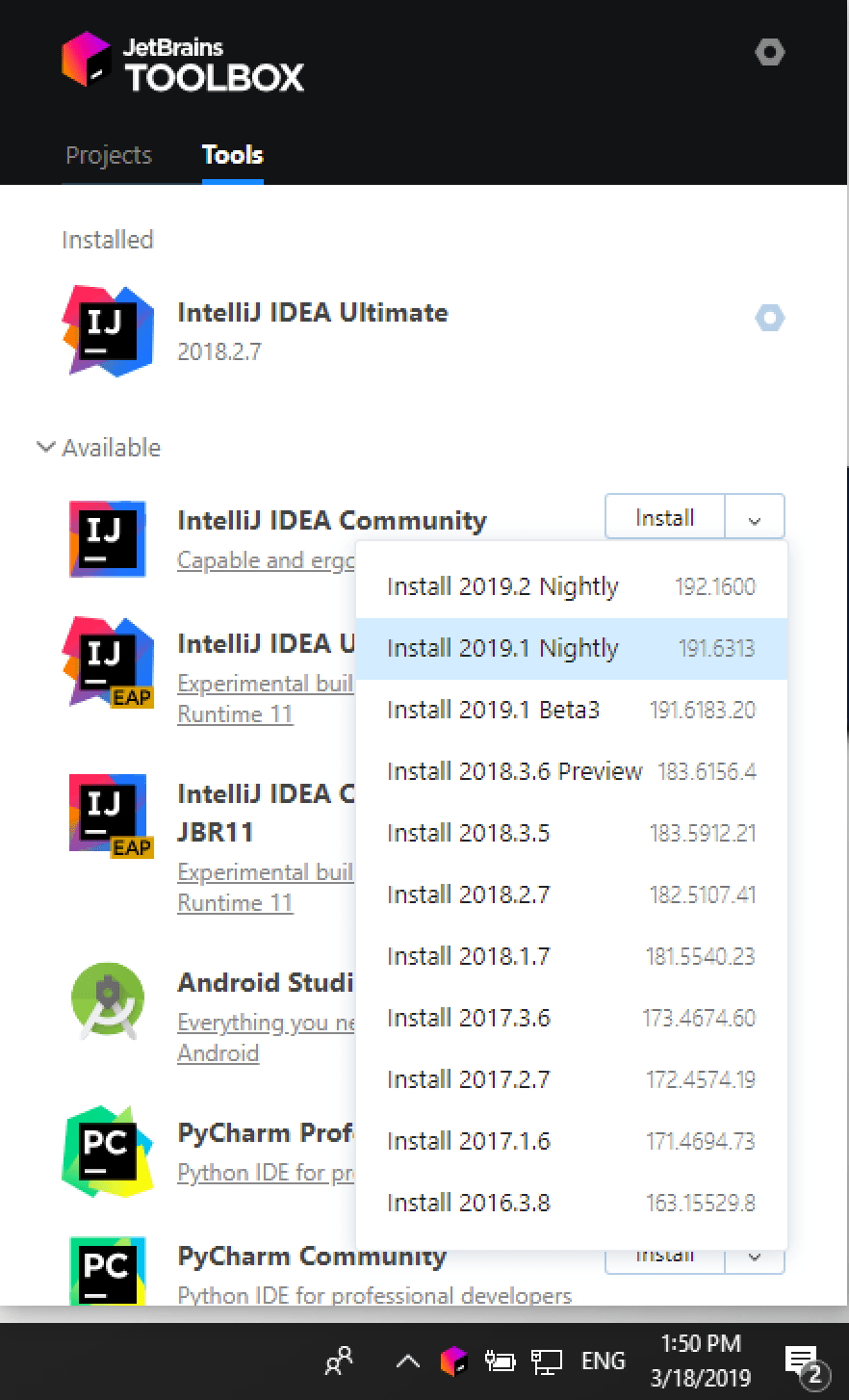
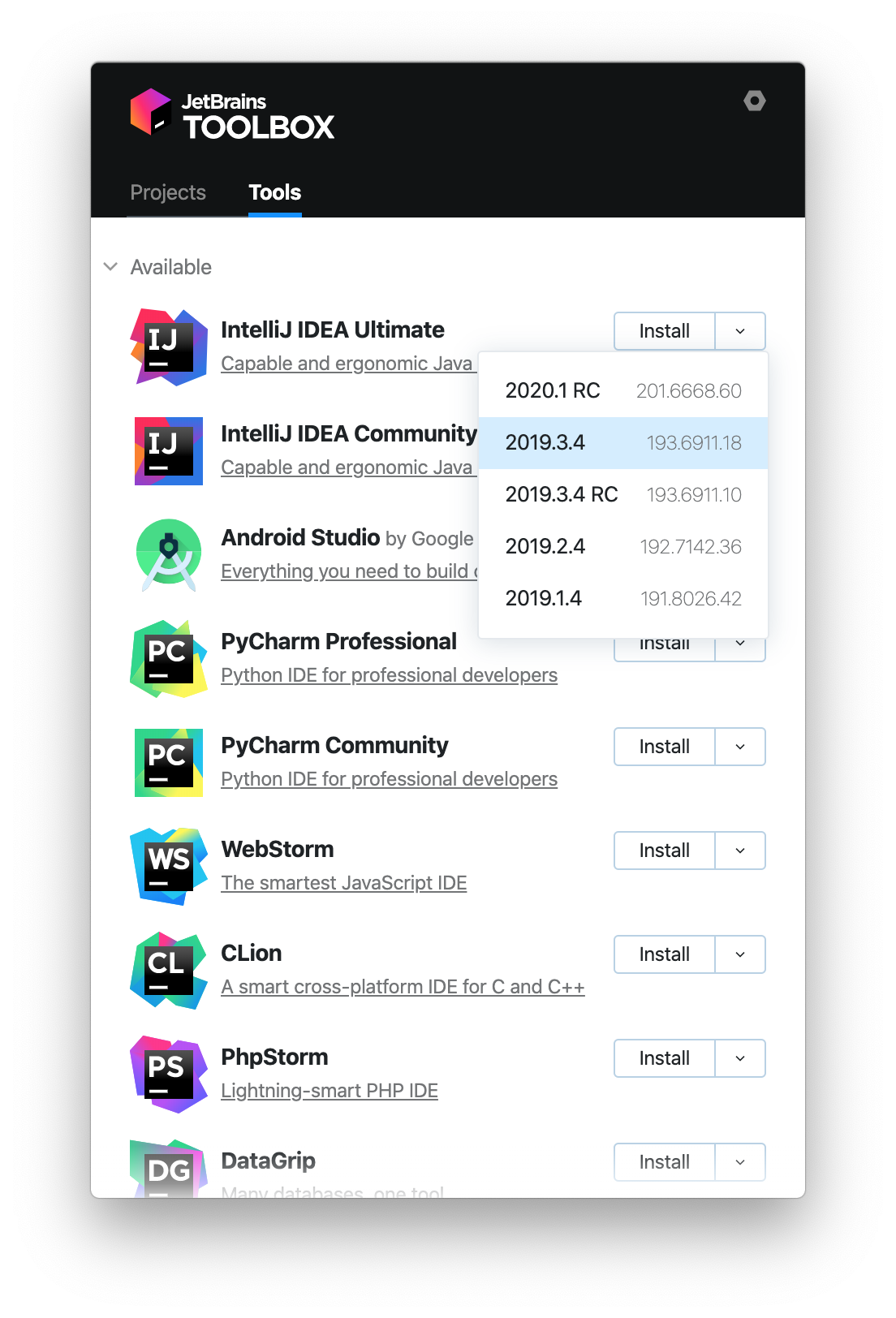
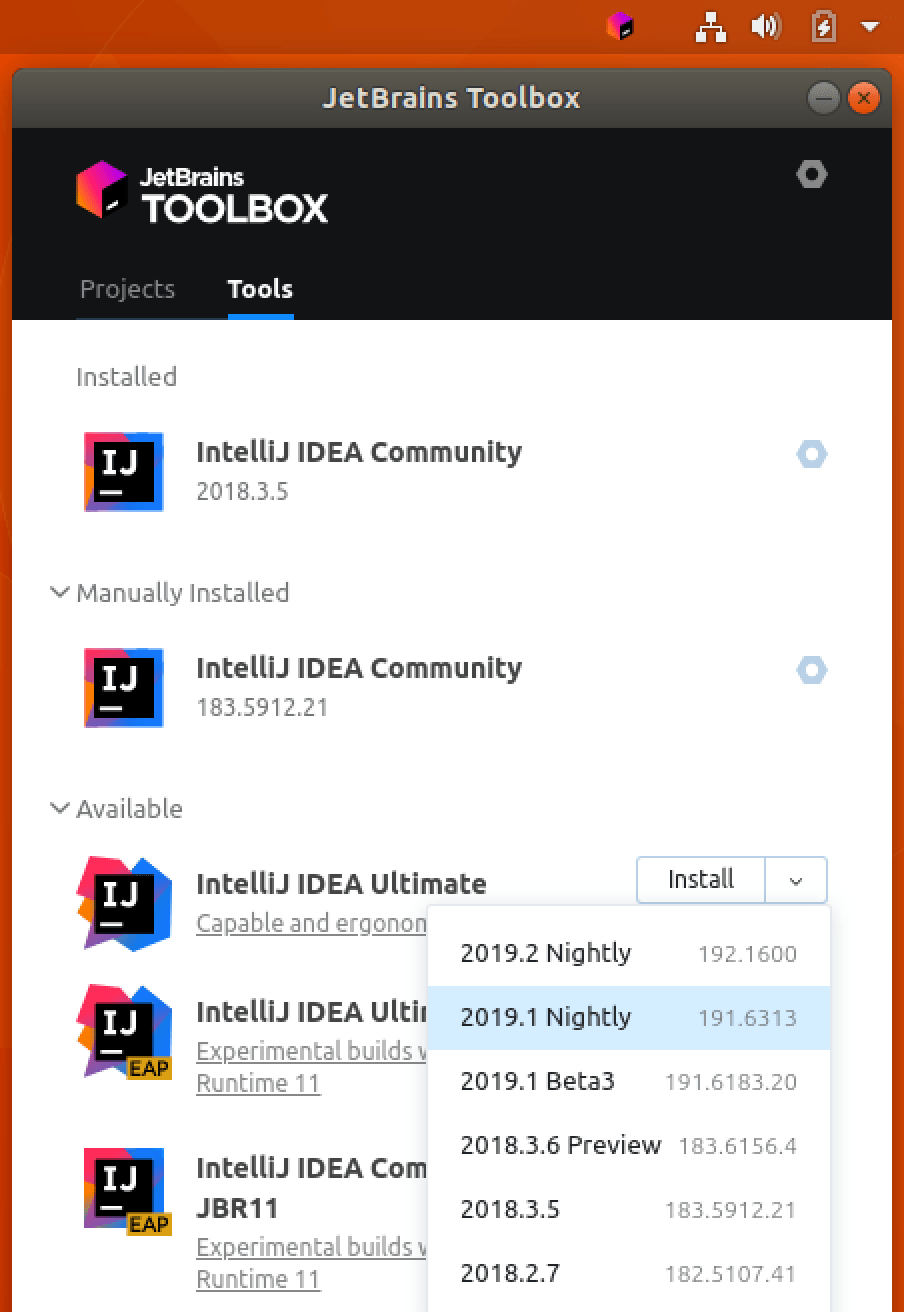
Install using the Toolbox App
The JetBrains Toolbox App is the recommended tool to install JetBrains products. Use it to install and manage different products or several versions of the same product, including Early Access Program (EAP) and Nightly releases, update and roll back when necessary, and easily remove any tool. The Toolbox App maintains a list of all your projects to quickly open any project in the right IDE and version.
Install the Toolbox App
Download the installer .exe from the Toolbox App web page.
Run the installer and follow the wizard steps.
After you run the Toolbox App, click its icon in the notification area and select which product and version you want to install.
Log in to your JetBrains Account from the Toolbox App and it will automatically activate the available licenses for any IDE that you install.
Install the Toolbox App
Download the disk image .dmg from the Toolbox App web page.
There are separate disk images for Intel and Apple Silicon processors.
Mount the image and drag the JetBrains Toolbox app to the Applications folder.
After you run the Toolbox App, click its icon in the main menu and select which product and version you want to install.
Log in to your JetBrains Account from the Toolbox App and it will automatically activate the available licenses for any IDE that you install.
Install the Toolbox App
Download the tarball .tar.gz from the Toolbox App web page.
Extract the tarball to a directory that supports file execution.
For example, if the downloaded version is 1.17.7391, you can extract it to the recommended /opt directory using the following command:
Execute the jetbrains-toolbox binary from the extracted directory to run the Toolbox App and select which product and version you want to install. After you run the Toolbox App for the first time, it will automatically add the Toolbox App icon to the main menu.
Log in to your JetBrains Account from the Toolbox App and it will automatically activate the available licenses for any IDE that you install.
You can use this shell script that automatically downloads the tarball with the latest version of the Toolbox App, extracts it to the recommended /opt directory, and creates a symbolic link in the /usr/local/bin directory.
Standalone installation
Install IntelliJ IDEA manually to manage the location of every instance and all the configuration files. For example, if you have a policy that requires specific install locations.
Run the installer and follow the wizard steps.
On the Installation Options step, you can configure the following:
Create a desktop shortcut for launching IntelliJ IDEA.
Add the directory with IntelliJ IDEA command-line launchers to the PATH environment variable to be able to run them from any working directory in the Command Prompt.
Add the Open Folder as Project action to the system context menu (when you right-click a folder).
Associate specific file extensions with IntelliJ IDEA to open them with a double-click.

To run IntelliJ IDEA, find it in the Windows Start menu or use the desktop shortcut. You can also run the launcher batch script or executable in the installation directory under bin .
Extract the archive to the desired folder.
To run IntelliJ IDEA, use the launcher batch script or executable in the extracted directory under bin .
There are separate disk images for Intel and Apple Silicon processors.
Mount the image and drag the IntelliJ IDEA app to the Applications folder.
Run the IntelliJ IDEA app from the Applications directory, Launchpad, or Spotlight.
Extract the tarball to a directory that supports file execution.
For example, to extract it to the recommended /opt directory, run the following command:
Do not extract the tarball over an existing installation to avoid conflicts. Always extract it to a clean directory.
Execute the idea.sh script from the extracted directory to run IntelliJ IDEA.
To create a desktop entry, do one of the following:
On the Welcome screen, click Configure | Create Desktop Entry
From the main menu, click Tools | Create Desktop Entry
When you run IntelliJ IDEA for the first time, some steps are required to complete the installation, customize your instance, and start working with the IDE.
For information about the location of the default IDE directories with user-specific files, see Directories used by the IDE.
Silent installation on Windows
Silent installation is performed without any user interface. It can be used by network administrators to install IntelliJ IDEA on a number of machines and avoid interrupting other users.
To perform silent install, run the installer with the following switches:
/S : Enable silent install
/CONFIG : Specify the path to the silent configuration file
/D : Specify the path to the installation directory
This parameter must be the last in the command line and it should not contain any quotes even if the path contains blank spaces.
To check for issues during the installation process, add the /LOG switch with the log file path and name between the /S and /D parameters. The installer will generate the specified log file. For example:
Silent configuration file
You can download the default silent configuration file for IntelliJ IDEA at https://download.jetbrains.com/idea/silent.config
The silent configuration file defines the options for installing IntelliJ IDEA. With the default options, silent installation is performed only for the current user: mode=user . If you want to install IntelliJ IDEA for all users, change the value of the installation mode option to mode=admin and run the installer as an administrator.
The default silent configuration file is unique for each JetBrains product. You can modify it to enable or disable various installation options as necessary.
It is possible to perform silent installation without the configuration file. In this case, omit the /CONFIG switch and run the installer as an administrator. Without the silent configuration file, the installer will ignore all additional options: it will not create desktop shortcuts, add associations, or update the PATH variable. However, it will still create a shortcut in the Start menu under JetBrains .
Install as a snap package on Linux
You can install IntelliJ IDEA as a self-contained snap package. Since snaps update automatically, your IntelliJ IDEA installation will always be up to date.
To use snaps, install and run the snapd service as described in the installation guide.
On Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and later, this service is pre-installed.
IntelliJ IDEA is distributed via two channels:
The stable channel includes only stable versions. To install the latest stable release of IntelliJ IDEA, run the following command:
The —classic option is required because the IntelliJ IDEA snap requires full access to the system, like a traditionally packaged application.
The edge channel includes EAP builds. To install the latest EAP build of IntelliJ IDEA, run the following command:
When the snap is installed, you can launch it by running the intellij-idea-community , intellij-idea-ultimate , or intellij-idea-educational command.
To list all installed snaps, you can run sudo snap list . For information about other snap commands, see the Snapcraft documentation.
Источник
Advanced configuration
Besides the standard options available, IntelliJ IDEA enables you to perform low-level configuration of the underlying platform and the Java runtime.
This may lead to unexpected problems and make your IntelliJ IDEA installation inoperable if you are not sure what you are doing. Contact JetBrains Support for instructions regarding the options and values that might help you with whatever issue you are trying to solve.
JVM options
IntelliJ IDEA runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which has various options that control its performance. The default options used to run IntelliJ IDEA are specified in the following file:
Do not change JVM options in the default file, because it is replaced when IntelliJ IDEA is updated. Moreover, in case of macOS, editing this file violates the application signature.
Configure JVM options
Do one of the following to create a copy of the default file with JVM options in the configuration directory that will override the original file:
From the main menu, select Help | Edit Custom VM Options .
If you do not have any project open, on the Welcome screen, click Configure and then Edit Custom VM Options .
If you cannot start IntelliJ IDEA, manually copy the default file with JVM options to the IntelliJ IDEA configuration directory.
If you do not have write access to the IntelliJ IDEA configuration directory, you can add the IDEA_VM_OPTIONS environment variable to specify the location of the file with your preferred JVM options. This file will override both the original default file and the copy located in the IntelliJ IDEA configuration directory.
If you are using the Toolbox App, it manages the installation and configuration directory and lets you configure JVM options for every IDE instance. Open the Toolbox App, click the screw nut icon for the necessary instance, and select Settings .
Common options
The default values of the JVM options should be optimal in most cases. The following are the most commonly modified ones:
Limits the maximum memory heap size that the JVM can allocate for running IntelliJ IDEA. The default value depends on the platform. If you are experiencing slowdowns, you may want to increase this value, for example, to set the value to 2048 megabytes, change this option to -Xmx2048m .
For more information about the available JVM options, see the java reference for Windows or macOS/Linux.
Platform properties
IntelliJ IDEA enables you to customize various platform-specific properties, such as the path to user-installed plugins and the maximum supported file size. The default properties used to run IntelliJ IDEA are specified in the following file:
Источник
Path variables
Path variables are placeholders that stand for absolute paths to resources that are linked to your project but are stored outside it. If you are working in a team, these absolute paths on the computers of your teammates may differ. With path variables, you can flexibly share your code so all the references to the linked resources are resolved properly as the path variables accept the values according to the configuration on each specific computer.
In IntelliJ IDEA, there are some pre-defined variables:
$USER_HOME$ : stands for your home directory.
$PROJECT_DIR$ : stands for the directory where your project is stored.
$MODULE_DIR$ : stands for the directory that keeps module configuration files IML .
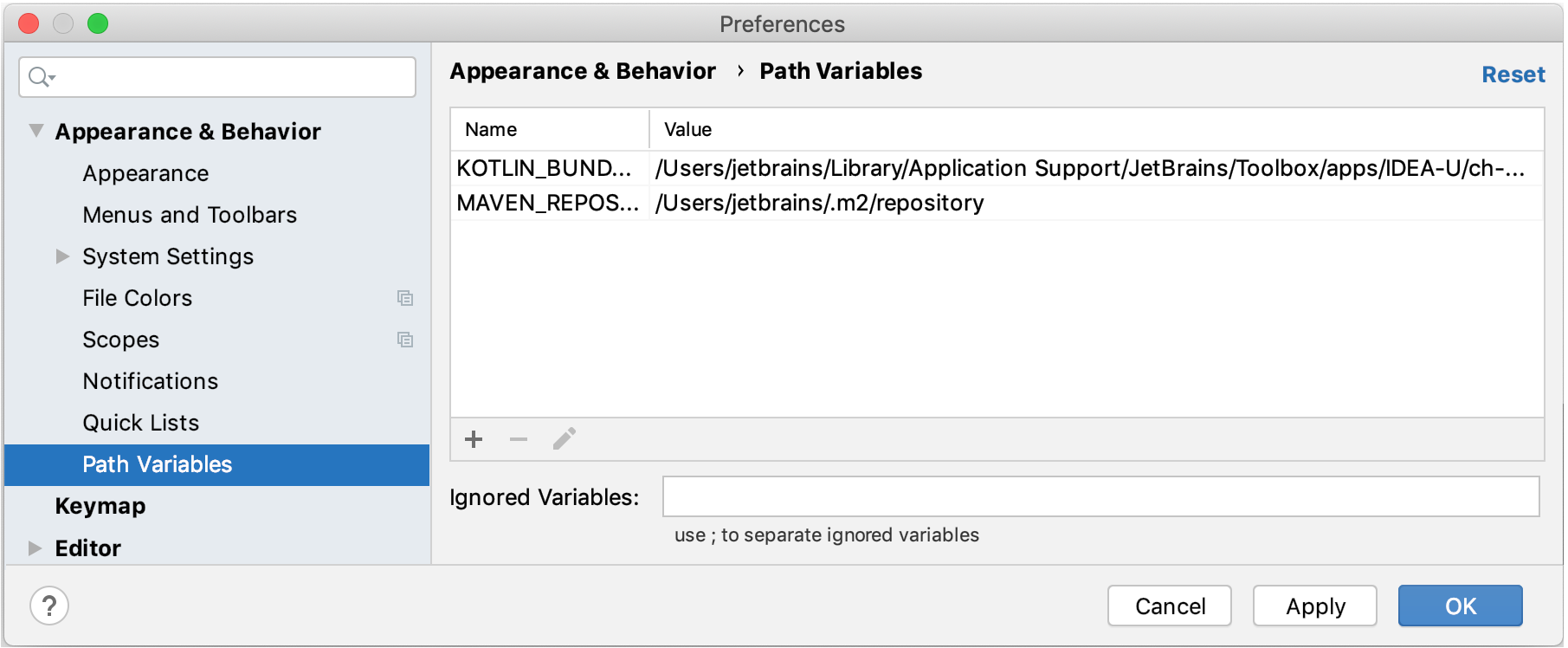
To configure path variables, in the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S , select Appearance & Behavior | Path Variables .
Create a new path variable
For example, you have a third-party library that is not stored in your project directory. If you want to make sure that the path is correct on your teammates’ computers after they update the project from VCS, you can create a new variable.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Appearance & Behavior | Path Variables .
Click and enter the name of the new variable (for example, PATH_TO_LIB ) and its value that points to the library location on your disk.
Share the IML file through your version control system.
After your teammates update their projects from VCS, they will change the PATH_TO_LIB variable value so that it points to the library location on their computers.
Ignored path variables
When you open a project, IntelliJ IDEA checks if there are any unresolved path variables. If the IDE detects any, it will ask you to define values for them. If for some reason you don’t want to do that (for example, if you are not going to use files or directories with the unresolved path variables), you can add them to the list of ignored variables.
You can also use the list of ignored variables if, for example, a program argument passed to the JVM in a run/debug configuration has the same format as an internal ($SOME_STRING$) path variable. In this case, you can add this parameter to the list of ignored variables in order to avoid confusion. Enter SOME_STRING to the Ignored Variables field in the Path Variables dialog.
Источник