- Windows
- Editions of Windows
- Windows Home
- Windows Pro
- Business editions
- Why is Microsoft Windows called Windows?
- Microsoft Windows help pages
- Related pages
- What are the features of Microsoft Windows?
- Control Panel
- Cortana
- Desktop
- Device Manager
- Disk Cleanup
- Event Viewer
- File Explorer
- Internet browser
- Microsoft Paint
- Notepad
- Notification area
- Power User Tasks Menu
- Registry Editor
- Settings
- Start and Start menu
- System Information
- Taskbar
- Task Manager
- Windows search box
Windows
Windows may refer to any of the following:
1. Microsoft Windows (also referred to as Windows or Win) is a graphical operating system developed and published by Microsoft. It provides a way to store files, run software, play games, watch videos, and connect to the Internet.
Microsoft Windows was first introduced with version 1.0 on November 10, 1983. Over a dozen versions of Windows were released after that, including the current version, Windows 10.
Editions of Windows
Starting with Windows XP, Microsoft has published various editions of Windows. Each of these Windows editions has the same core operating system, but some editions have additional features, at an additional cost.
The two most common editions of Windows for home computers are Windows Home and Windows Professional.
Windows Home
Windows Home (also called Win Home) is the basic edition of Windows. It provides all the fundamental functions of Windows, such as connecting to the Internet, browsing the web, watching videos, using office software, and playing video games. It is the least expensive edition of Windows, and it comes preinstalled on many new computers.
Windows Pro
Windows Professional (also called Windows Pro, or Win Pro) is an enhanced Windows edition, for power users, and small to medium sized businesses. It includes all the features of Windows Home, plus the following:
- Remote Desktop — allows you to remotely control another Windows computer connected to the Internet.
- Bitlocker — Microsoft’s integrated file encryption.
- Trusted Boot — provides encryption of the boot loader, protecting the computer against rootkits.
- Hyper-V — a Windows hypervisor for running virtual machines, equivalent to third-party software, such as VirtualBox.
- Windows Sandbox — provides a lightweight, sandboxed Windows 10 instance. You can use this isolated «Windows within Windows» environment to safely run suspicious or untrusted software. Windows Sandbox requires a Windows Insider build of Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise.
- Group policy management — Administrators can define group policies, for managing multiple Windows users in a business or organization.
- Support for more than 128 GB of RAM.
- Greater Windows Update installation options, including more flexible scheduling and postponement for up to 35 days.
Business editions
Windows Professional for Workstations and Windows Enterprise provide advanced features for professional studios and large businesses. For more information, refer to the side-by-side comparison in the official Microsoft Windows business edition comparison chart.
Why is Microsoft Windows called Windows?
Before the release of Microsoft Windows, Microsoft users were used to the single task command line operating system MS-DOS. Because Microsoft names most of its products with one word, it needed a word that best described its new GUI operating system. Microsoft chose «Windows» because of the multiple windows that allow different tasks and programs to run at the same time. Because you cannot trademark a common name like «Windows,» it’s officially known as «Microsoft Windows». The first version of Microsoft Windows was version 1.0, released in 1985.
Microsoft Windows help pages
Related pages
2. In general, a window is a fundamental part of a computer GUI (graphical user interface). A window is an area of the display containing a single running application. The window can be moved, resized, hidden, or maximized as desired by the user. The Microsoft Windows operating system is named after this UI element.
3. Regarding Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux or BSD, Windows may refer to the X Window System.
What are the features of Microsoft Windows?
Microsoft Windows includes a wide array of features, tools, and applications to help get the most out of Windows and your computer.
To learn more about the features included in Microsoft Windows, click a link below.
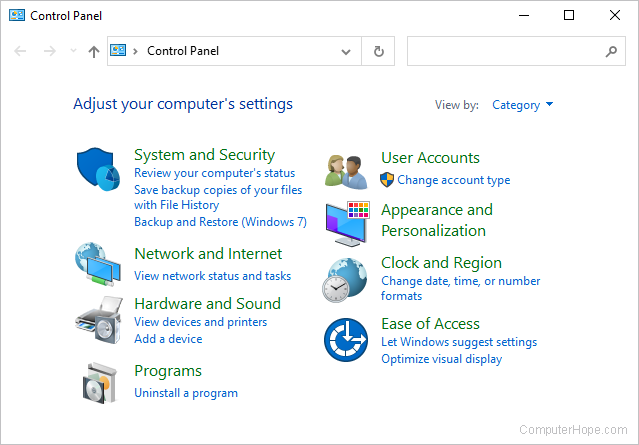
Control Panel
The Control Panel is a collection of tools to help you configure and manage the resources on your computer. You can change settings for printers, video, audio, mouse, keyboard, date and time, user accounts, installed applications, network connections, power saving options, and more.
In Windows 10, the Control Panel is located in the Start menu, under Windows System.
You can also start the Control Panel from the Run box. Press Windows key + R , type control, and press Enter . Or, you may press the Windows key , type Control Panel, and then press Enter .
Many of the Control Panel settings are also accessible in the Windows 10 Settings menu.
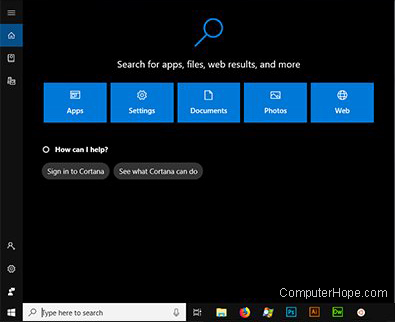
Cortana
Cortana is a virtual assistant introduced in Windows 10 that accepts voice commands. Cortana can answer questions, search your computer or Internet, set appointments and reminders, perform online purchases, and more. Cortana has similarities to other voice-activated services, such as Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant, with the added benefit that it can search the information on your computer.
To access Cortana in Windows 10, press Windows key + S .
Desktop
The desktop is a fundamental part of the default GUI (graphical user interface) in Windows. It is a space where you can organize applications, folders, and documents, which appear as icons. Your desktop is always in the background, behind any other applications you’re running.
When you power on your computer and log in to Windows, the first thing you see is your desktop background, icons, and the taskbar. From here, you can access the installed programs on your computer from the Start menu, or by double-clicking any application shortcuts you may have on your desktop.
You can access your desktop at any time by pressing Windows key + D to minimize any running applications.
With the release of Windows 8 in 2012, the desktop was no longer the default GUI, replaced by the Start Screen. This change was short-lived, and the desktop returned as the default GUI in Windows 10.
Device Manager
The Device Manager lists the hardware devices installed in a computer. It allows users to see what hardware is installed, view and update hardware drivers, and uninstall hardware through the Device Manager.
You can open the Device Manager from the Power User Tasks Menu ( Windows key + X , then press M ).
Disk Cleanup
The Disk Cleanup utility helps increase free disk space on your computer by removing temporary or unnecessary files. Running Disk Cleanup helps improve your computer’s performance, and create additional space to store your downloads, documents, and programs.
You can access Disk Cleanup from the File Explorer.
- Press Windows key + E to open an Explorer window.
- On the left side of the window, find This PC or My Computer, and select it by clicking once.
- Then, on the right side, right-click any disk drive on your computer (C:, for example).
- Select Properties.
- Under the General tab, click Disk Cleanup.
- What is Disk Cleanup?
- My computer is running slow, what steps can I do to fix it?
- How to regain computer hard drive space.
Event Viewer
The Event Viewer is an administrator tool displays errors and important events that happen on your computer. It helps troubleshoot advanced problems in your Windows system.
Event Viewer can be accessed from the Power User Tasks Menu (press Windows key + X , then press V ).
File Explorer
The File Explorer, also called Windows Explorer, provides you with a view of the files and folders on the computer. You can browse the contents of your SSD, hard drive, and attached removable disks. You can search for files and folders, and open, rename, or delete them from the File Explorer.
To open a new File Explorer window, press Windows key + E . You can open more than one Explorer window at the same time, which helps with viewing multiple folders at once, or copying/moving files from one to the other.
Internet browser
Your Internet browser is one of the most important applications on your computer. You can use it to find information on the Internet, view web pages, shop and buy merchandise, watch movies, play games, and more. Microsoft Edge is the default browser in Windows 10. Internet Explorer is included as the default browser in previous versions of Windows, from Windows 95 to Windows 8.1.
To open a new Edge browser window in Windows 10, open the Start menu and scroll down to Microsoft Edge.
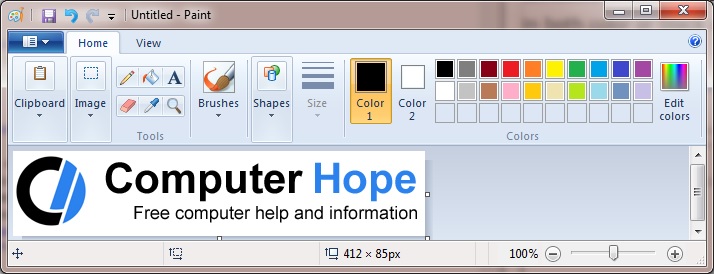
Microsoft Paint
Included in Windows since November 1985, Microsoft Paint is a simple image editor that you can use to create, view, and edit digital images. It provides basic functionality to draw and paint pictures, resize and rotate photographs, and save pictures as different file types.
To open Microsoft Paint in all versions of Windows, press the Windows key , type mspaint, and press Enter . It’s also available in your Start menu: in Windows 10, it’s listed under Windows Accessories, Paint.
Notepad
Notepad is a simple text editor. You can use it to create, view, and edit text files. For instance, you can use Notepad to write a batch file, or a web page written in HTML.
In Windows 10, Notepad is located in your Start menu under Windows accessories. In all versions of Windows, you can start Notepad from the Run box: press Windows key + R , type notepad, and press Enter .
Notification area
The notification area, also known as the system tray, displays the date and time, and shows icons of programs that are started with Windows. It also provides your Internet connection’s status and a speaker icon for adjusting sound volume.
Power User Tasks Menu
Available in Windows 8 and Windows 10, the Power User Tasks Menu provides quick access to helpful and important Windows utilities. From this menu, you can open the Control Panel, Device Manager, File Explorer, Task Manager, and more.
To open the Power User Tasks Menu, press Windows key + X , or right-click the Start menu icon.
Registry Editor
The Registry Editor allows you to view the Windows system registry, and edit registry keys. Computer technicians may use the Registry Editor to fix problems with the Windows operating system or installed software.
In Windows 10, the Registry Editor is located in the Start menu under Windows Administrative Tools. You can also start it by pressing the Windows key , typing regedit, and then pressing Enter .
Making changes to the registry can cause your applications or system to stop functioning correctly. Don’t edit the registry if you’re not sure what your changing and always back up your registry by exporting it to a file before making changes.
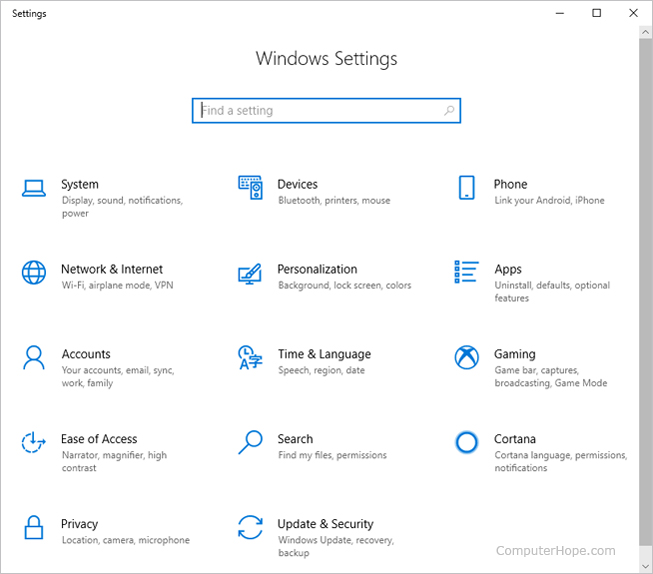
Settings
Available in Windows 8 and Windows 10, Settings allows you to change many aspects of Windows. You can change the desktop background, adjust power settings, review options for external devices, and more.
To open Settings in Windows 10, press Windows key + I . Or, open the Start menu, and click the gear icon (
Start and Start menu
The Start menu is a list of applications and utilities installed on your computer. You can open it by clicking Start on the left side of your taskbar.
Using the keyboard, you can open the Start menu by pressing the Windows key .
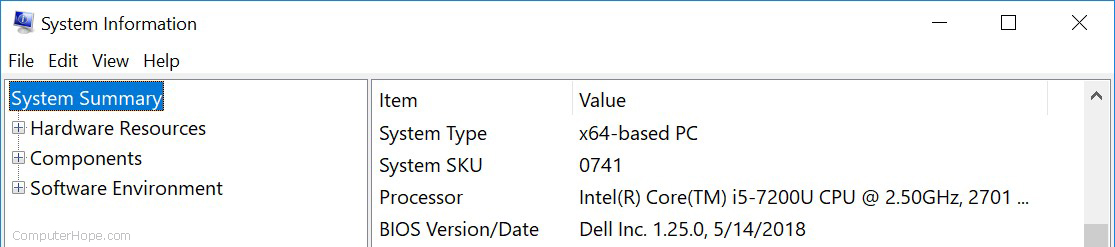
System Information
The System Information utility provides information about the computer, including hardware and Windows details. You can find out details about your computer’s hardware, including processor, memory, video card, and sound card. You can also view and configure environment variables, device drivers, services, and more.
In Windows 10, System Information is located in the Start menu, under Windows Administrative Tools. You can also open it from the Run box: press Windows key + R , type msinfo32, and press Enter .
Taskbar
The Windows taskbar shows programs that are currently open, and a Quick Launch area that allows quick access to launch specific programs. The notification area is on the right side of the taskbar, showing the date and time, and programs running in the background.
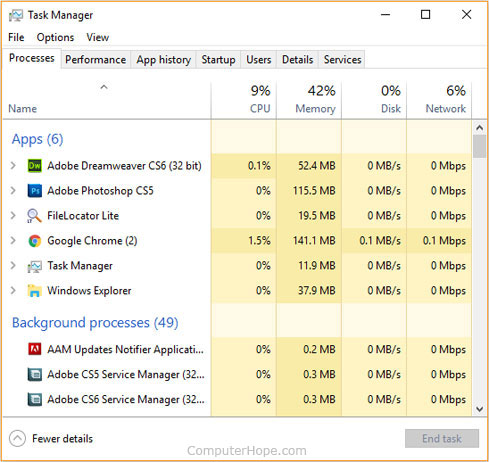
Task Manager
The Task Manager gives you an overview of what’s running on your computer. You can see how much of your system resources is used by each application (task), sorting by CPU, RAM, and disk I/O usage. If a program is frozen or not responding, you can right-click it in Task Manager and end the task, forcing it to quit.
To open the Task Manager at any time, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc .
Windows search box
The Windows search box is a convenient way to search for documents, pictures, videos, applications, and more. In Windows 10, the search box is also integrated with Cortana. The feature first appeared in Windows Vista.
The search box is on your taskbar by default. In Windows 10, if you don’t see the search box, right-click the taskbar and select Taskbar settings. Make sure Use small taskbar buttons is Off. Then, right-click the taskbar again, and select Cortana, Show search box.