- Проверка образа ISO¶
- Загрузите контрольные суммы SHA256, предоставленные Linux Mint¶
- Проверка целостности¶
- Проверка подлинности¶
- Импортируйте ключ подписи Linux Mint:¶
- Проверьте подлинность sha256sum.txt:¶
- Проверка контрольной суммы Linux
- Что такое MD5?
- Проверка контрольных сумм в Linux
- Выводы
- Ubuntu Documentation
- sha256
- sha256sum on Linux
- Check the iso file
- Manual method
- Semi-automatic method
- Success
- Check the CD
- Manual method
- Success?
- MD5SUM on Mac OS X
- digest(1) on Solaris
- SHA256SUM on Windows
- MD5SUM with «Checksums calculator»
- SHA256SUM on CD
- SHA256SUM of burnt media
- External Links
Проверка образа ISO¶
Важно убедиться в целостности и подлинности вашего образа ISO.
Проверка целостности подтверждает, что образ ISO был скачан правильно, и ваш локальный файл является точной копией файла на серверах загрузки. Ошибка во время скачивания может привести к повреждению файла и вызвать различные ошибки во время установки системы.
Проверка подлинности (аутентичности) подтверждает, что скачанный образ ISO был действительно подписан Linux Mint, то есть это не какая-то модифицированная или вредоносная копия, сделанная кем-то другим.
Загрузите контрольные суммы SHA256, предоставленные Linux Mint¶
Все зеркала загрузки предоставляют образы ISO, файл sha256sum.txt и файл sha256sum.txt.gpg . Эти файлы можно найти в том же месте, откуда вы загружаете образ ISO.
Если вы не можете найти их, перейдите на зеркало загрузки Heanet и щёлкните на версии выпуска Linux Mint, который вы загрузили.
Загрузите sha256sum.txt и sha256sum.txt.gpg .
Do not copy their content, use «right-click->Save Link As…» to download the files themselves and do not modify them in any way.
Проверка целостности¶
Для проверки целостности вашего ISO-файла сгенерируйте его контрольную сумму SHA256 и сравните её с контрольной суммой в файле sha256sum.txt .
If you are using Windows follow the tutorial How to verify the ISO image on Windows.
Если суммы совпадают, значит образ ISO был загружен успешно. Если не совпадают, попробуйте загрузить его снова.
Проверка подлинности¶
Для проверки подлинности sha256sum.txt проверьте подпись sha256sum.txt.gpg , как описано ниже.
Импортируйте ключ подписи Linux Mint:¶
Если gpg жалуется на идентификатор ключа, попробуйте следующие команды:
Check the output of the last command, to make sure the fingerprint is 27DE B156 44C6 B3CF 3BD7 D291 300F 846B A25B AE09 (with or without spaces).
Проверьте подлинность sha256sum.txt:¶
Вывод последней команды должен сказать Вам, что файл подписи хороший и что он был подписан с помощью ключа A25BAE09 .
GPG может предупредить Вас, что подпись Linux Mint не является доверенной для Вашего компьютера. Это ожидаемо и вполне нормально.
Для получения дополнительной информации о проверке ISO, или для проверки BETA, LMDE или старых версий, прочитайте Как проверить ISO образы.
© Copyright 2017, Linux Mint Revision 11740971 .
Источник
Проверка контрольной суммы Linux
Контрольная сумма — это цифра или строка, которая вычисляется путем суммирования всех цифр нужных данных. Ее можно использовать в дальнейшем для обнаружения ошибок в проверяемых данных при хранении или передаче. Тогда контрольная сумма пересчитывается еще раз и полученное значение сверяется с предыдущим.
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим что такое контрольная сумма Linux, а также как выполнять проверку целостности файлов с помощью контрольных сумм md5.
Что такое MD5?
Контрольные суммы Linux с вычисляемые по алгоритму MD5 (Message Digest 5) могут быть использованы для проверки целостности строк или файлов. MD5 сумма — это 128 битная строка, которая состоит из букв и цифр. Суть алгоритма MD5 в том, что для конкретного файла или строки будет генерироваться 128 битный хэш, и он будет одинаковым на всех машинах, если файлы идентичны. Трудно найти два разных файла, которые бы выдали одинаковые хэши.
В Linux для подсчета контрольных сумм по алгоритму md5 используется утилита md5sum. Вы можете применять ее для проверки целостности загруженных из интернета iso образов или других файлов.
Эта утилита позволяет не только подсчитывать контрольные суммы linux, но и проверять соответствие. Она поставляется в качестве стандартной утилиты из набора GNU, поэтому вам не нужно ничего устанавливать.
Проверка контрольных сумм в Linux
Синтаксис команды md5sum очень прост:
$ md5sum опции файл
Опций всего несколько и, учитывая задачи утилиты, их вполне хватает:
- -c — выполнить проверку по файлу контрольных сумм;
- -b — работать в двоичном формате;
- -t — работать в текстовом формате;
- -w — выводить предупреждения о неверно отформатированном файле сумм;
- —quiet — не выводить сообщения об успешных проверках.
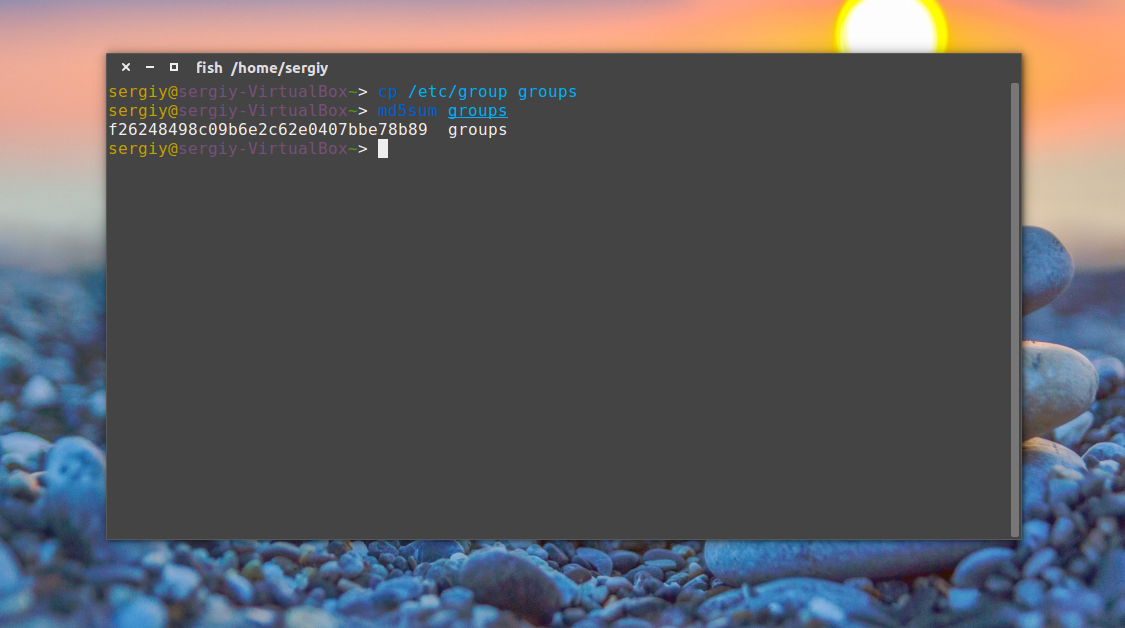
Сначала скопируйте файл /etc/group в домашнюю папку чтобы на нем немного поэкспериментировать:
cp /etc/group groups
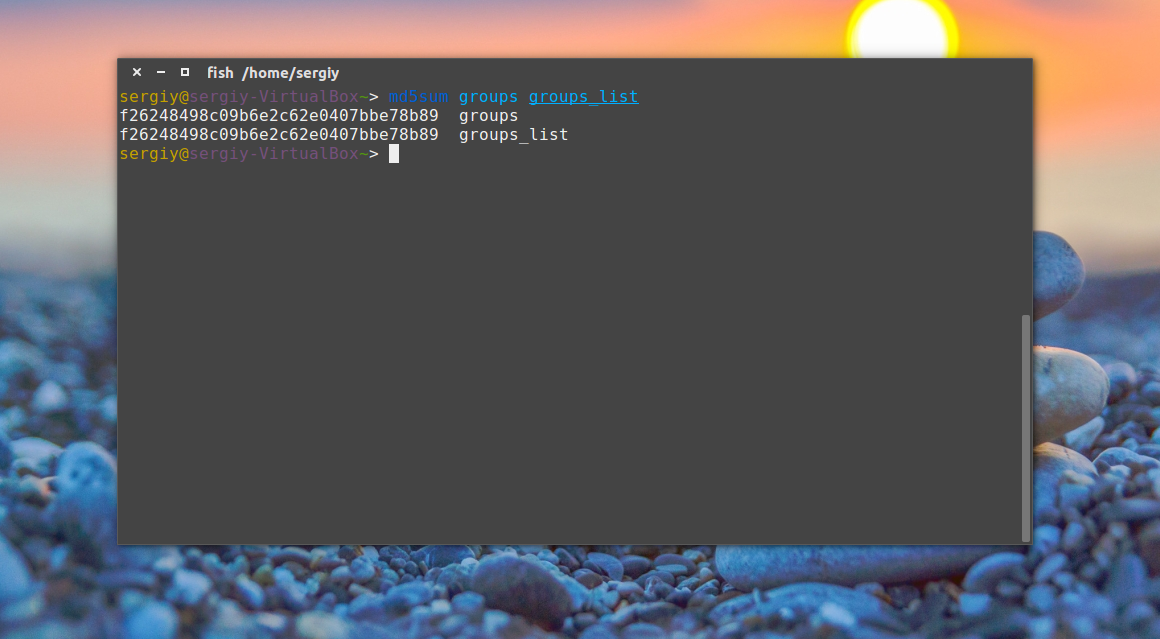
Например, давайте подсчитаем контрольную сумму для файла /etc/group:
Или вы можете сохранить сразу эту сумму в файл для последующей проверки:
md5sum groups > groups.md5
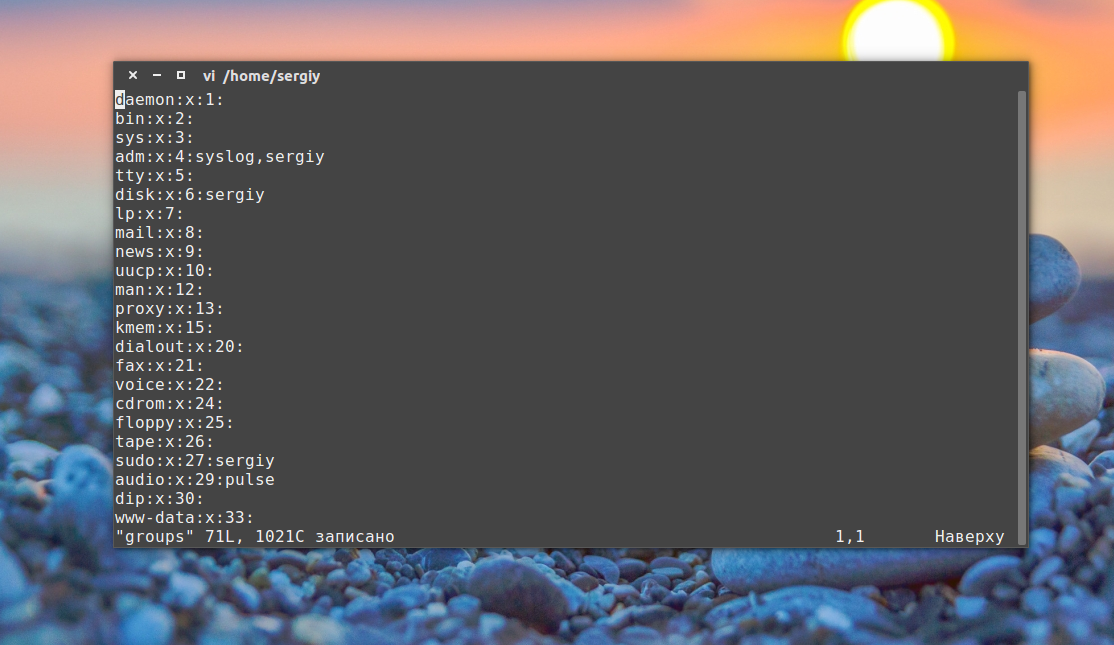
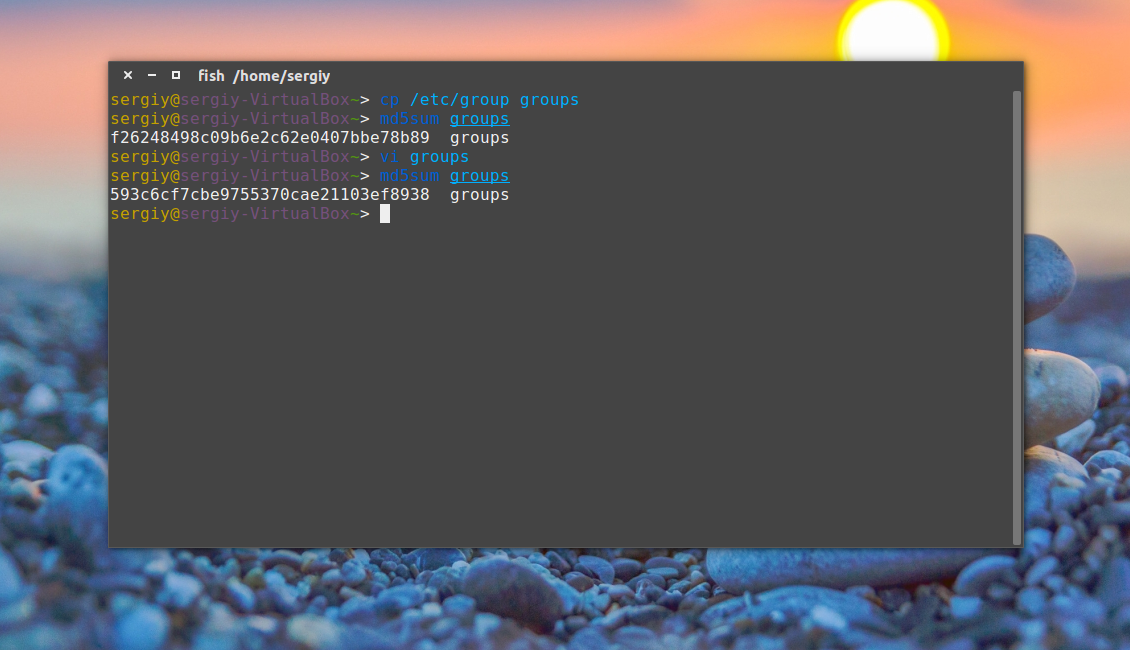
Затем каким-либо образом измените этот файл, например, удалите первую строчку и снова подсчитайте контрольные суммы:
Как видите, теперь значение отличается, а это значит, что содержимое файла тоже изменилось. Дальше верните обратно первую строчку root:x:0: и скопируйте этот файл в groups_list и
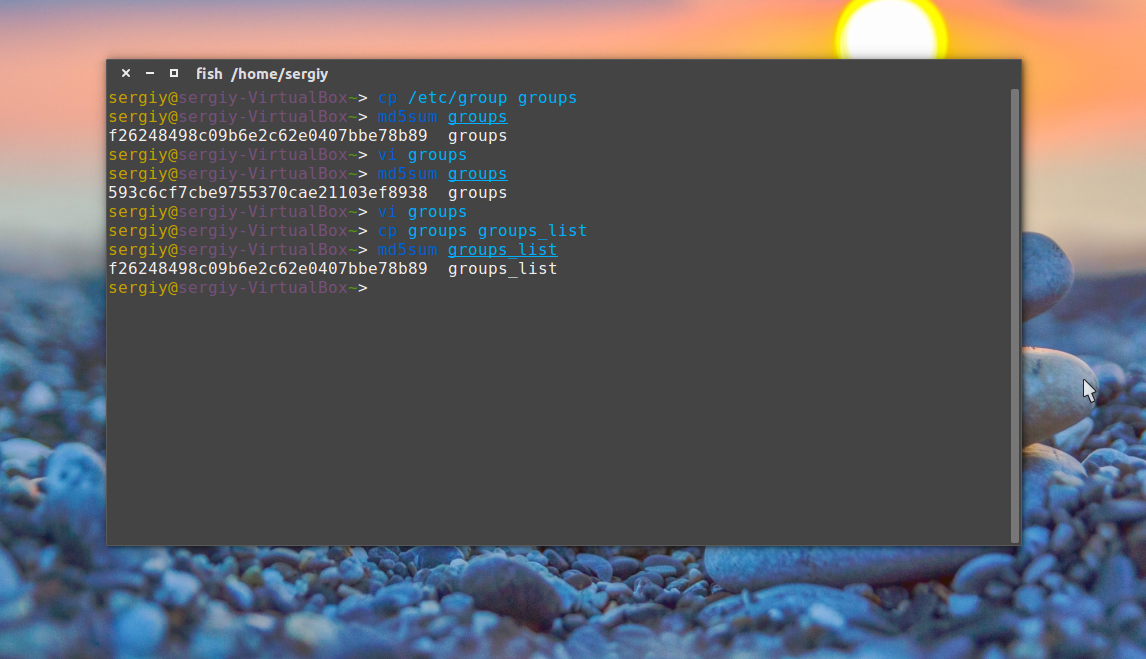
cp groups groups_list
Затем опять должна быть выполнена проверка контрольной суммы linux:
Сумма соответствует первому варианту, даже несмотря на то, что файл был переименован. Обратите внимание, что md5sum работает только с содержимым файлов, ее не интересует ни его имя, ни его атрибуты. Вы можете убедиться, что оба файла имеют одинаковые суммы:
md5sum groups groups_list
Вы можете перенаправить вывод этой команды в файл, чтобы потом иметь возможность проверить контрольные суммы:
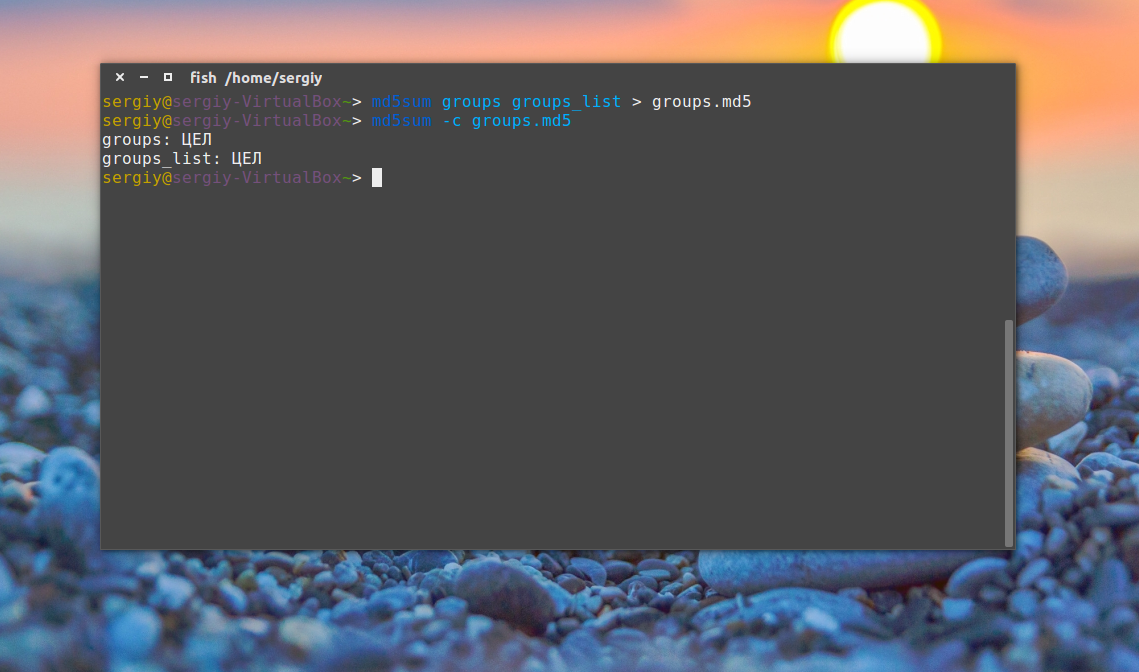
md5sum groups groups_list > groups.md5
Чтобы проверить, не были ли файлы изменены с момента создания контрольной суммы используйте опцию -c или —check. Если все хорошо, то около каждого имени файла появится слово OK или ЦЕЛ:
md5sum -c groups.md5
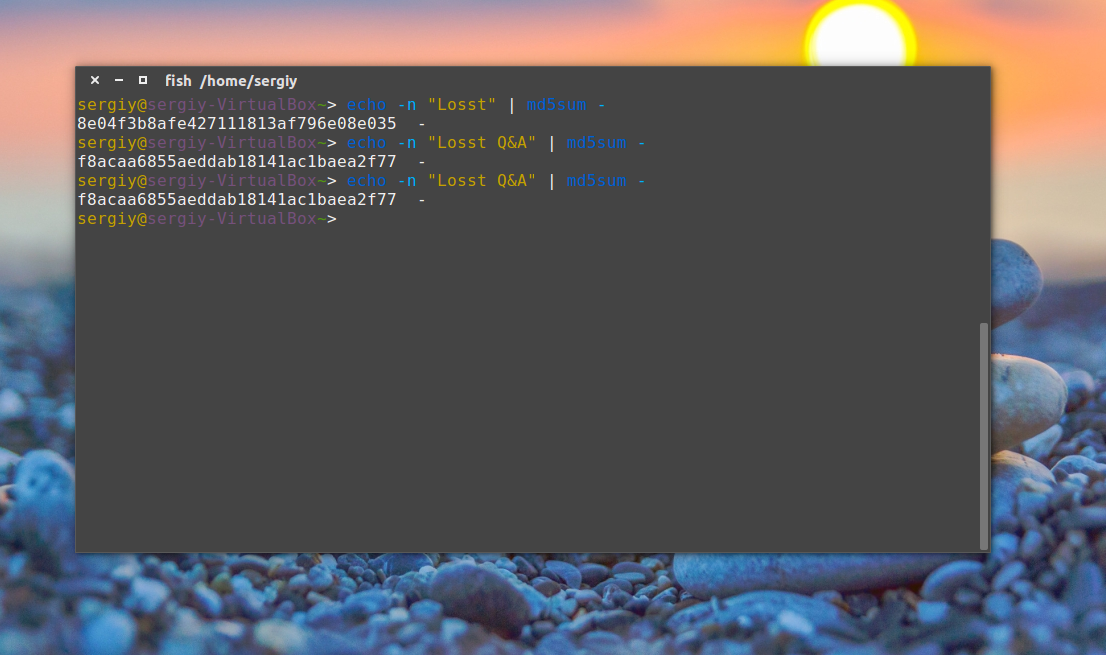
Но теперь вы не можете переименовывать файлы, потому что при проверке утилита будет пытаться открыть их по имени и, естественно, вы получите ошибку. Точно так же все работает для строк:
echo -n «Losst» | md5sum —
$ echo -n «Losst Q&A» | md5sum —
Выводы
Из этой статьи вы узнали как выполняется получение и проверка контрольной суммы linux для файлов и строк. Хотя в алгоритме MD5 были обнаружены уязвимости, он все еще остается полезным, особенно если вы доверяете инструменту, который будет создавать хэши.
Проверка целостности файлов Linux — это очень важный аспект использования системы. Контрольная сумма файла Linux используется не только вручную при проверке загруженных файлов, но и во множестве системных программ, например, в менеджере пакетов. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
На завершение небольшое видео по теме:
Источник
Ubuntu Documentation
The program sha256sum is designed to verify data integrity using the SHA-256 (SHA-2 family with a digest length of 256 bits). SHA-256 hashes used properly can confirm both file integrity and authenticity. SHA-256 serves a similar purpose to a prior algorithm recommended by Ubuntu, MD5, but is less vulnerable to attack.
Comparing hashes makes it possible to detect changes in files that would cause errors. The possibility of changes (errors) is proportional to the size of the file; the possibility of errors increase as the file becomes larger. It is a very good idea to run an SHA-256 hash comparison check when you have a file like an operating system install CD that has to be 100% correct.
In terms of security, cryptographic hashes such as SHA-256 allow for authentication of data obtained from insecure mirrors. The SHA-256 hash must be signed or come from a secure source (such as a HTTPS page or a GPG-signed file) of an organization you trust. See the SHA-256 checksum file for the release you’re using under http://releases.ubuntu.com, such as http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/SHA256SUMS . You should verify this file using the PGP signature, SHA256SUMS.gpg (such as http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/SHA256SUMS.gpg ) as described in VerifyIsoHowto.
sha256
sha256sum on Linux
Most Linux distributions come with the sha256sum utility (on Ubuntu it is part of the coreutils package). We are going to use the Ubuntu 9.10 LiveDVD for the following example:
Check the iso file
Ubuntu distributes the SHA-256 checksum hashes in a file called SHA256SUMS in the same directory listing as the download page for your release http://releases.ubuntu.com.
Manual method
First open a terminal and go to the correct directory to check a downloaded iso file:
Then run the following command from within the download directory.
sha256sum should then print out a single line after calculating the hash:
Compare the hash (the alphanumeric string on left) that your machine calculated with the corresponding hash in the SHA256SUMS file.
When both hashes match exactly then the downloaded file is almost certainly intact. If the hashes do not match, then there was a problem with either the download or a problem with the server. You should download the file again from either the same mirror, or from a different mirror if you suspect a server error. If you continuously receive an erroneous file from a server, please be kind and notify the web-master of that mirror so they can investigate the issue.
Semi-automatic method
First download the SHA256SUMS and SHA256SUMS.gpg files to the same directory as the iso. Then run the following commands in a terminal.
The sha256sum line should output a line such as:
If the OK for your file appears, that indicates the hash matches.
Success
Once you have verified the sha256 hash, go ahead and burn the CD. You may want to refer to the BurningIsoHowto page.
Check the CD
So far so good, you have downloaded an iso and verified its integrity. When you boot from the CD you will be given the option to test its integrity. Great, but if the CD is corrupt then you have already wasted time rebooting. You can check the integrity of the CD without rebooting as follows.
Manual method
Check the calculated hash against UbuntuHashes as shown for the iso file above. Depending on your system, you may need to change cdrom to cdrom0 (or even cdrom1 if you have two CD drives).
Success?
Congratulations, you now have a verified Ubuntu CD. Go ahead and use it (or play frisbee with it if you want).
MD5SUM on Mac OS X
This should be updated by someone with access to a Mac.
There are three methods of using md5sumsum on an OS X machine.
Method 1 — The easiest (if MD5 is available) is using the Disk Utility program (Applications > Utilities, or by choosing «Utilities» from the Finder’s «Go» menu). Open Disk Utility and wait for it to gather information about your disks. Go to the directory where you downloaded the Ubuntu disk image, and drag it to Disk Utility’s dock icon (displays on the left-hand side of Disk Utility, underneath your physical drives). Select the iso file. Go to the «Images» menu and select Checksum > MD5. Be sure to choose «MD5» and NOT «MD5 image checksum» or «CRC-32 image checksum», as they are not the same and will give you different results.
Method 2 — If MD5 is not available in the Images > Checksum menu, open a terminal window (Applications > Utilities > Terminal.app). Type «md5», type a space, drag the iso file into the terminal window (appends command with iso file path), and press Enter. The command line returns the hash number.
Method 3 — You can use the Terminal.app and follow the instructions for SHA256SUM on Linux, except use the command «openssl md5» instead of «sha256sum».
Each method returns a hash number. Compare the hash number with the corresponding hash on the UbuntuHashes page. When both hashes match exactly, then the downloaded file is almost certainly intact.
If the hashes do not match, then there was a problem with either the download or a problem with the server. You should download the file again from either the same mirror, or from a different mirror if you suspect a server error. If you continuously receive an erroneous file from a server, please notify the web-master of that mirror so they can investigate the issue.
digest(1) on Solaris
Use the Solaris digest(1) command, specifying the sha256 algorithm with the -a flag. For instance:
SHA256SUM on Windows
This section also needs to be updated. Is there a sha256sum.exe file distributed by a reliable source? Is there a good GUI?
Windows does not come with sha256sum. You must download one from another location, preferably one that you trust. There are command line utilities that work similarly to the Unix utility; one public domain version with source is available from Fourmilab, but the version available from Cygwin is probably easier to install and update, and Cygwin is also recommended and trusted as the source for many more Unixy utilities. Once installed, Cygwin’s sha256sum behaves exactly as described in SHA256SUM on Linux above.
There are also graphical tools such as the one used in the walk-through provided below.
Download and install winSha256sum, a free and open source hash verification program.
Right-click the ISO file.
Click Send To, then winSha256sum.
Wait for winSha256sum to load and finish the checksum (this may take a significant amount of time depending on your computer’s performance).
Copy the corresponding hash from UbuntuHashes into the bottom text box.
MD5SUM with «Checksums calculator»
«Checksums calculator” is an open source GUI application that has been developed to run on Windows, MacOS X and Linux operating systems on 32bit and 64bit architectures while is translated into 19 languages. It gives you the ability to calculate checksums of functions: md5, sha1, sha256, sha384 and sha512. It is very simple to use, after downloaded the zip file with the version that fits on your computer, doesn’t require any installation, just unzip it to any folder of your choice. Once you run it, select the file you want to calculate the checksum, then select the function and click the «Calculate» button. If you want to compare the result, in the field «Original checksum» give the checksum that you downloaded and click the «Compare» button. You can download the application here.
The program while is running under Windows 7 64bit.
The program while is running under Snow Leopard 10.6 32bit.
The program while is running under Ubuntu 10.04 64bit.
SHA256SUM on CD
I don’t know if there is now a sha256sum.txt file on the CD.
To see if your Ubuntu CD was corrupted when burned to the disk, see the CDIntegrityCheck page, or follow the instructions below.
First mount the CD, if not already mounted:
Then use the supplied sha256sum file on the CD:
Be patient, it takes some time. If the command outputs any errors, you’ll know that either the burn was bad or the .iso is corrupt. Please note that this method does not verify authenticity unless the hash of the iso file is compared to the hash at the secure UbuntuHashes page.
Finally, you can unmount the CD after leaving the folder:
SHA256SUM of burnt media
Depending on how you burn your ISOs you can check the burnt media directly. Start by checking that the ISO file is correct:
Now burn it from Nautilus (right-click, «Write to Disc . «). To check the media directly:
where «/dev/cdrom» is typically a soft-link to your CD/DVD reader/burner. Note that the checksum matches.
External Links
HowToSHA256SUM (последним исправлял пользователь anthony-geoghegan 2015-12-14 23:05:24)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details
Источник