- Поиск ключа восстановления BitLocker в Windows 10
- Где найти ключ восстановления BitLocker?
- Что такое ключ восстановления BitLocker?
- Почему система Windows запрашивает ключ восстановления BitLocker?
- Как функция BitLocker активируется на моем устройстве?
- Finding your BitLocker recovery key in Windows 10
- Where can I find my BitLocker recovery key?
- What is my BitLocker recovery key?
- Why is Windows asking for my BitLocker recovery key?
- How was BitLocker activated on my device?
- Как разблокировать BitLocker Windows 10
- Что такое BitLocker Windows 10
- Как отключить BitLocker в Windows 10
- BitLocker recovery guide
- What is BitLocker recovery?
- What causes BitLocker recovery?
- Testing recovery
- Planning your recovery process
- Self-recovery
- Recovery password retrieval
- Record the name of the user’s computer
- Verify the user’s identity
- Locate the recovery password in ADВ DS
- Multiple recovery passwords
- Gather information to determine why recovery occurred
- Give the user the recovery password
- Post-recovery analysis
- Determine the root cause of the recovery
- Resolve the root cause
- Unknown PIN
- Lost startup key
- Changes to boot files
- Windows RE and BitLocker Device Encryption
- BitLocker recovery screen
- Custom recovery message
- BitLocker recovery key hints
- Example 1 (single recovery key with single backup)
- Example 2 (single recovery key with single backup)
- Example 3 (single recovery key with multiple backups)
- Example 4 (multiple recovery passwords)
- Example 5 (multiple recovery passwords)
- Using additional recovery information
- BitLocker key package
- Resetting recovery passwords
- Retrieving the BitLocker key package
Поиск ключа восстановления BitLocker в Windows 10
Если система запрашивает у вас ключ восстановления BitLocker, следующие инструкции помогут вам найти его и понять, почему ключ был запрошен.
Где найти ключ восстановления BitLocker?
Перед активацией защиты функция BitLocker обеспечивает безопасное создание резервной копии ключа восстановления. Ключ восстановления может находиться в нескольких местах, в зависимости от того, какой параметр был выбран при активации BitLocker.
В учетной записи Майкрософт выполните Вход в учетную запись Майкрософт на другом устройстве, чтобы найти ключ восстановления.
Если вы используете современное устройство, поддерживающее автоматическое шифрование устройств, ключ восстановления, скорее всего, будет находиться в вашей учетной записи Майкрософт. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Шифрование устройства в Windows 10.
Если устройство настроил другой пользователь или защита BitLocker была активирована другим пользователем, ключ восстановления может находиться в учетной записи Майкрософт этого пользователя.
Для сохраненного распечатки: Ключ восстановления может находиться на распечатке, сохраненном при активации BitLocker. Проверьте свои важные документы, относящиеся к компьютеру.
На USB-накопителе: Подсоедините USB-накопитель к заблокированному компьютеру и следуйте инструкциям. Если ключ сохранен на устройстве флэш-памяти как текстовый файл, прочтите этот файл на другом компьютере.
В учетной записи Azure Active Directory: Если ваше устройство было зарегистрировано в Организации с помощью рабочей или учебной учетной записи электронной почты, ваш ключ восстановления может храниться в учетной записи Azure AD , связанной с вашим устройством. Возможно, вы сможете получить к ключу доступ самостоятельно либо вам может потребоваться обратиться к системному администратору.
Удержание системного администратора. Если устройство подключено к домену (обычно это рабочее или учебное устройство), обратитесь к системному администратору для ключа восстановления.
Что такое ключ восстановления BitLocker?
Ключ восстановления BitLocker — это уникальный 48-значный цифровой пароль, который можно использовать для разблокировки системы, если функция BitLocker не может другим способом точно определить, что попытка доступа к системному диску была санкционированной. Этот ключ может храниться в учетной записи Майкрософт, на распечатке, в сохраненном файле или в организации, управляющей устройством. Запрос ключа восстановления в таких случаях является критически важным условием защиты, при выполнении которого функция BitLocker сможет предоставить вам доступ к вашим данным.
Почему система Windows запрашивает ключ восстановления BitLocker?
BitLocker — это технология шифрования Windows, которая защищает данные от несанкционированного доступа путем шифрования диска и отображения запроса на прохождение одного или нескольких этапов проверки подлинности, прежде чем BitLocker сможет разблокировать устройство. Она включается как при обычном использовании Windows, так и при попытке несанкционированного доступа. При обнаружении небезопасного состояния, которым может быть попытка несанкционированного доступа к данным, система Windows запрашивает ключ восстановления BitLocker. Этот дополнительный шаг представляет собой меру безопасности, призванную обеспечить безопасность ваших данных. Внесение изменений определенного характера в оборудование, встроенное ПО и программное обеспечение может приводить к возникновению состояний, которые функция BitLocker не может отличить от возможной атаки. В таких случаях функция BitLocker может требовать прохождение дополнительной проверки безопасности в виде предоставления ключа восстановления, даже если пользователь является авторизованным владельцем устройства. Это позволяет системе защиты абсолютно точно убедиться в том, что попытка разблокировки устройства выполняется полномочным пользователем.
Как функция BitLocker активируется на моем устройстве?
Есть три стандартных способа активировать защиту BitLocker на вашем устройстве.
Ваше устройство является современным устройством, которое отвечает определенным требованиям для автоматического включения шифрования устройств. В этом случае ключ восстановления BitLocker автоматически сохраняется в учетной записи Майкрософт , прежде чем будет активирована защита.
Владелец или Администратор устройства активировал защиту BitLocker (также называемую шифрованием устройств на некоторых устройствах) с помощью приложения «Параметры» или панели управления: В этом случае пользователь активирует BitLocker либо выберет место для сохранения ключа, либо (в случае шифрования устройства), которое оно автоматически сохранит в учетной записи Майкрософт.
Рабочая или учебная организация, управляющая вашим устройством (в настоящее время или в прошлом), активировала защиту BitLocker на вашем устройстве: В этом случае у Организации может быть ключ восстановления BitLocker.
Защита BitLocker всегда активируется пользователем (или от его имени), у которого есть полные права доступа к вашему устройству на уровне администратора независимо от того, кто является этим пользователем — вы, другой человек или организация, управляющая вашим устройством. В ходе настройки функции BitLocker автоматически создается ключ восстановления во время активации защиты.
Если вам не удается найти запрашиваемый ключ восстановления BitLocker и вы не можете отменить внесенные в конфигурацию изменения, которые могли стать причиной запроса ключа, необходимо выполнить сброс устройства с помощью одного из параметров восстановления Windows 10. Сброс устройства приведет к удалению всех файлов.
Finding your BitLocker recovery key in Windows 10
If your system is asking you for your BitLocker recovery key, the following information may help you locate your recovery key and understand why you may be asked to provide it.
Where can I find my BitLocker recovery key?
BitLocker ensured that a recovery key was safely backed up prior to activating protection. There are several places that your recovery key may be, depending on the choice that was made when activating BitLocker:
In your Microsoft account: Sign in to your Microsoft account on another device to find your recovery key:
If you have a modern device that supports automatic device encryption, the recovery key will most likely be in your Microsoft account. For more, see Device encryption in Windows 10.
If the device was set up or BitLocker protection was activated by another user, the recovery key may be in that user’s Microsoft account.
On a printout you saved: Your recovery key may be on a printout that was saved when BitLocker was activated. Look where you keep important papers related to your computer.
On a USB flash drive: Plug the USB flash drive into your locked PC and follow the instructions. If you saved the key as a text file on the flash drive, use a different computer to read the text file.
In an Azure Active Directory account: If your device was ever signed in to an organization using a work or school email account, your recovery key may be stored in that organization’s Azure AD account associated with your device. You may be able to access it directly or you may need to contact a system administrator to access your recovery key.
Held by your system administrator: If your device is connected to a domain (usually a work or school device), ask a system administrator for your recovery key.
What is my BitLocker recovery key?
Your BitLocker recovery key is a unique 48-digit numerical password that can be used to unlock your system if BitLocker is otherwise unable to confirm for certain that the attempt to access the system drive is authorized. This key may be stored in your Microsoft account, printed or saved as a file, or with an organization that is managing the device. The requirement for a recovery key in these cases is a critical component of the protection that BitLocker provides your data.
Why is Windows asking for my BitLocker recovery key?
BitLocker is the Windows encryption technology that protects your data from unauthorized access by encrypting your drive and requiring one or more factors of authentication before it will unlock it, whether for regular Windows use or an unauthorized access attempt. Windows will require a BitLocker recovery key when it detects an insecure condition that may be an unauthorized attempt to access the data. This extra step is a security precaution intended to keep your data safe and secure. Some changes in hardware, firmware, or software can present conditions which BitLocker cannot distinguish from a possible attack. In these cases, BitLocker may require the extra security of the recovery key even if the user is an authorized owner of the device. This is to be certain sure that it really is an authorized user of the device attempting to unlock it.
How was BitLocker activated on my device?
There are three common ways for BitLocker to start protecting your device:
Your device is a modern device that meets certain requirements to automatically enable device encryption: In this case your BitLocker recovery key is automatically saved to your Microsoft account before protection is activated.
An owner or administrator of your device activated BitLocker protection (also called device encryption on some devices) through the Settings app or Control Panel: In this case the user activating BitLocker either selected where to save the key or (in the case of device encryption) it was automatically saved to their Microsoft account.
A work or school organization that is managing your device (currently or in the past) activated BitLocker protection on your device: In this case the organization may have your BitLocker recovery key.
BitLocker is always activated by or on behalf of a user with full administrative access to your device, whether this is you, another user, or an organization managing your device. The BitLocker setup process enforces the creation of a recovery key at the time of activation.
If you are unable to locate a required BitLocker recovery key and are unable to revert and configuration change that might have cause it to be required, you’ll need to reset your device using one of the Windows 10 recovery options. Resetting your device will remove all of your files.
Как разблокировать BitLocker Windows 10
Шифрование дисков (функция BitLocker) используется для защиты файлов и папок от несанкционированного доступа. Разблокировать и заблокировать можно любой раздел накопителя. Даже после подключения к другому компьютеру BitLocker защищает Ваши данные.
Эта статья расскажет, как разблокировать BitLocker в Windows 10. Вам нужно знать пароль или иметь ключ восстановления. Иначе без его форматирования не обойтись. Для дешифрования используем панель управления и командную строку. Как работает BitLocker, смотрите дальше.
Что такое BitLocker Windows 10
Всё просто. Функция шифрования дисков BitLocker позволяет защитить Ваши данные от несанкционированного доступа. Чтобы получить доступ к накопителю, Вам понадобится ввести пароль. Для обычного пользователя можно спорить о полезности такой функциональности.
- Шифрование только занятого места на диске — если Вы настраиваете шифрование на новом диске или ПК, Вам достаточно зашифровать только ту часть диска, которая сейчас используется. BitLocker зашифровывает новые данные автоматически по мере их добавления.
- Шифрование всего диска — если Вы включаете функцию BitLocker на уже используемом ПК или диске, рекомендуется зашифровать весь диск. Это гарантирует защиту всех данных — даже ранее удалённых, но ещё содержащих извлекаемые сведения. Выполняется медленнее.
После шифрования диска Вас будет спрашивать ранее установленный пароль. И только если Вы его знаете, тогда можно получить доступ (введите пароль для разблокировки этого диска). Если Вы забыли свой пароль, Вы можете использовать ключ восстановления для доступа к диску.
В обновлении Windows 10 (версия 1511) предоставлен новый режим шифрования дисков (XTS-AES). Этот режим обеспечивает дополнительную поддержку целостности, но не совместим с более ранними версиями Windows. Указывается новый режим шифрования или совместимости.
Как отключить BitLocker в Windows 10
В контекстном меню зашифрованного диска выберите Управление BitLocker. В панели управления нажмите Отключить BitLocker (напротив нужного раздела). Нужно обладать правами администратора. Ваш диск будет расшифрован после подтверждения действия.
Можно выполнить команду: manage-bde -off H: в командной строке (от имени администратора).
Или команду: Disable-BitLocker -MountPoint «H:» в обновлённой оболочке Windows PowerShell.
Важно! Процесс шифрования и расшифровки может занимать продолжительное время. В зависимости от Вашего накопителя. Разблокировать получается значительно быстрее, чем его зашифровать. Думаю, не стоит сравнивать скорости HHD старого и даже бюджетного SSD.
Мастер шифрования помогает Вам безопасно защитить свои данные. Вам предложат архивировать свой ключ восстановления. Если Вы забыли свой пароль, можно воспользоваться этим ключом (он сохраняется заранее в файле, на USB-устройстве или в учётке Майкрософт).
Функция BitLocker доступна только в редакциях системы Windows 10 : Professional, Enterprise и Education. Можно с уверенностью сказать обязательно в Home версии её может не хватать. Включить или отключить шифрование диска BitLocker можно средствами самой Windows 10.
Включение шифрования данных может немного снизить производительность ПК. Собственно из-за фонового процесса шифрования, который при необходимости будет продолжать выполняться. Но её рекомендуется использоваться для защиты конфиденциальных данных.
BitLocker recovery guide
Applies to:
This article for IT professionals describes how to recover BitLocker keys from AD DS.
Organizations can use BitLocker recovery information saved in Active Directory Domain Services (ADВ DS) to access BitLocker-protected data. Creating a recovery model for BitLocker while you are planning your BitLocker deployment is recommended.
This article assumes that you understand how to set up ADВ DS to back up BitLocker recovery information automatically, and what types of recovery information are saved to ADВ DS.
This article does not detail how to configure ADВ DS to store the BitLocker recovery information.
What is BitLocker recovery?
BitLocker recovery is the process by which you can restore access to a BitLocker-protected drive in the event that you cannot unlock the drive normally. In a recovery scenario, you have the following options to restore access to the drive:
- The user can supply the recovery password. If your organization allows users to print or store recovery passwords, the user can type in the 48-digit recovery password that they printed or stored on a USB drive or with your Microsoft Account online. (Saving a recovery password with your Microsoft Account online is only allowed when BitLocker is used on a PC that is not a member of a domain).
- A data recovery agent can use their credentials to unlock the drive. If the drive is an operating system drive, the drive must be mounted as a data drive on another computer for the data recovery agent to unlock it.
- A domain administrator can obtain the recovery password from AD DS and use it to unlock the drive. Storing recovery passwords in AD DS is recommended to provide a way for IT professionals to be able to obtain recovery passwords for drives in their organization if needed. This method requires that you have enabled this recovery method in the BitLocker Group Policy setting Choose how BitLocker-protected operating system drives can be recovered located at Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\BitLocker Drive Encryption\Operating System Drives in the Local Group Policy Editor. For more information, see BitLocker Group Policy settings.
What causes BitLocker recovery?
The following list provides examples of specific events that will cause BitLocker to enter recovery mode when attempting to start the operating system drive:
On PCs that use BitLocker Drive Encryption, or on devices such as tablets or phones that use BitLocker Device Encryption only, when an attack is detected, the device will immediately reboot and enter into BitLocker recovery mode. To take advantage of this functionality, administrators can set the Interactive logon: Machine account lockout threshold Group Policy setting located in \Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options in the Local Group Policy Editor. Or they can use the MaxFailedPasswordAttempts policy of Exchange ActiveSync (also configurable through Microsoft Intune), to limit the number of failed password attempts before the device goes into Device Lockout.
On devices with TPM 1.2, changing the BIOS or firmware boot device order causes BitLocker recovery. However, devices with TPM 2.0 do not start BitLocker recovery in this case. TPM 2.0 does not consider a firmware change of boot device order as a security threat because the OS Boot Loader is not compromised.
Having the CD or DVD drive before the hard drive in the BIOS boot order and then inserting or removing a CD or DVD.
Failing to boot from a network drive before booting from the hard drive.
Docking or undocking a portable computer. In some instances (depending on the computer manufacturer and the BIOS), the docking condition of the portable computer is part of the system measurement and must be consistent to validate the system status and unlock BitLocker. So if a portable computer is connected to its docking station when BitLocker is turned on, then it might also need to be connected to the docking station when it is unlocked. Conversely, if a portable computer is not connected to its docking station when BitLocker is turned on, then it might need to be disconnected from the docking station when it is unlocked.
Changes to the NTFS partition table on the disk including creating, deleting, or resizing a primary partition.
Entering the personal identification number (PIN) incorrectly too many times so that the anti-hammering logic of the TPM is activated. Anti-hammering logic is software or hardware methods that increase the difficulty and cost of a brute force attack on a PIN by not accepting PIN entries until after a certain amount of time has passed.
Turning off the support for reading the USB device in the pre-boot environment from the BIOS or UEFI firmware if you are using USB-based keys instead of a TPM.
Turning off, disabling, deactivating, or clearing the TPM.
Upgrading critical early startup components, such as a BIOS or UEFI firmware upgrade, causing the related boot measurements to change.
Forgetting the PIN when PIN authentication has been enabled.
Updating option ROM firmware.
Upgrading TPM firmware.
Adding or removing hardware; for example, inserting a new card in the computer, including some PCMIA wireless cards.
Removing, inserting, or completely depleting the charge on a smart battery on a portable computer.
Changes to the master boot record on the disk.
Changes to the boot manager on the disk.
Hiding the TPM from the operating system. Some BIOS or UEFI settings can be used to prevent the enumeration of the TPM to the operating system. When implemented, this option can make the TPM hidden from the operating system. When the TPM is hidden, BIOS and UEFI secure startup are disabled, and the TPM does not respond to commands from any software.
Using a different keyboard that does not correctly enter the PIN or whose keyboard map does not match the keyboard map assumed by the pre-boot environment. This problem can prevent the entry of enhanced PINs.
Modifying the Platform Configuration Registers (PCRs) used by the TPM validation profile. For example, including PCR[1] would result in BitLocker measuring most changes to BIOS settings, causing BitLocker to enter recovery mode even when non-boot critical BIOS settings change.
Some computers have BIOS settings that skip measurements to certain PCRs, such as PCR[2]. Changing this setting in the BIOS would cause BitLocker to enter recovery mode because the PCR measurement will be different.
Moving the BitLocker-protected drive into a new computer.
Upgrading the motherboard to a new one with a new TPM.
Losing the USB flash drive containing the startup key when startup key authentication has been enabled.
Failing the TPM self-test.
Having a BIOS, UEFI firmware, or an option ROM component that is not compliant with the relevant Trusted Computing Group standards for a client computer. For example, a non-compliant implementation may record volatile data (such as time) in the TPM measurements, causing different measurements on each startup and causing BitLocker to start in recovery mode.
Changing the usage authorization for the storage root key of the TPM to a non-zero value.
The BitLocker TPM initialization process sets the usage authorization value to zero, so another user or process must explicitly have changed this value.
Disabling the code integrity check or enabling test signing on Windows Boot Manager (Bootmgr).
Pressing the F8 or F10 key during the boot process.
Adding or removing add-in cards (such as video or network cards), or upgrading firmware on add-in cards.
Using a BIOS hot key during the boot process to change the boot order to something other than the hard drive.
Before you begin recovery, we recommend that you determine what caused recovery. This might help prevent the problem from occurring again in the future. For instance, if you determine that an attacker has modified your computer by obtaining physical access, you can create new security policies for tracking who has physical presence. After the recovery password has been used to recover access to the PC, BitLocker will reseal the encryption key to the current values of the measured components.
For planned scenarios, such as a known hardware or firmware upgrades, you can avoid initiating recovery by temporarily suspending BitLocker protection. Because suspending BitLocker leaves the drive fully encrypted, the administrator can quickly resume BitLocker protection after the planned task has been completed. Using suspend and resume also reseals the encryption key without requiring the entry of the recovery key.
If suspended BitLocker will automatically resume protection when the PC is rebooted, unless a reboot count is specified using the manage-bde command line tool.
If software maintenance requires the computer to be restarted and you are using two-factor authentication, you can enable BitLocker Network Unlock to provide the secondary authentication factor when the computers do not have an on-premises user to provide the additional authentication method.
Recovery has been described within the context of unplanned or undesired behavior, but you can also cause recovery as an intended production scenario, in order to manage access control. For example, when you redeploy desktop or laptop computers to other departments or employees in your enterprise, you can force BitLocker into recovery before the computer is given to a new user.
Testing recovery
Before you create a thorough BitLocker recovery process, we recommend that you test how the recovery process works for both end users (people who call your helpdesk for the recovery password) and administrators (people who help the end user get the recovery password). The -forcerecovery command of manage-bde is an easy way for you to step through the recovery process before your users encounter a recovery situation.
To force a recovery for the local computer:
- Select the Start button, type cmd in the Start Search box, right-click cmd.exe, and then select Run as administrator.
- At the command prompt, type the following command and then press Enter: manage-bde -forcerecovery
To force recovery for a remote computer:
On the Start screen, typeВ cmd.exe, and then select Run as administrator.
At the command prompt, type the following command and then press ENTER: manage-bde -ComputerName -forcerecovery
Recovery triggered by -forcerecovery persists for multiple restarts until a TPM protector is added or protection is suspended by the user. When using Modern Standby devices (such as Surface devices), the -forcerecovery option is not recommended because BitLocker will have to be unlocked and disabled manually from the WinRE environment before the OS can boot up again. For more information, see BitLocker Troubleshooting: Continuous reboot loop with BitLocker recovery on a slate device.
Planning your recovery process
When planning the BitLocker recovery process, first consult your organization’s current best practices for recovering sensitive information. For example: How does your enterprise handle lost Windows passwords? How does your organization perform smart card PIN resets? You can use these best practices and related resources (people and tools) to help formulate a BitLocker recovery model.
Organizations that rely on BitLocker Drive Encryption and BitLocker To Go to protect data on a large number of computers and removable drives running the WindowsВ 10, Windows 8, or Windows 7 operating systems and Windows to Go should consider using the Microsoft BitLocker Administration and Monitoring (MBAM) Tool version 2.0, which is included in the Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack (MDOP) for Microsoft Software Assurance. MBAM makes BitLocker implementations easier to deploy and manage and allows administrators to provision and monitor encryption for operating system and fixed drives. MBAM prompts the user before encrypting fixed drives. MBAM also manages recovery keys for fixed and removable drives, making recovery easier to manage. MBAM can be used as part of a Microsoft System Center deployment or as a stand-alone solution. For more info, see Microsoft BitLocker Administration and Monitoring.
After a BitLocker recovery has been initiated, users can use a recovery password to unlock access to encrypted data. Consider both self-recovery and recovery password retrieval methods for your organization.
When you determine your recovery process, you should:
Become familiar with how you can retrieve the recovery password. See:
Determine a series of steps for post-recovery, including analyzing why the recovery occurred and resetting the recovery password. See:
Self-recovery
In some cases, users might have the recovery password in a printout or a USB flash drive and can perform self-recovery. We recommend that your organization create a policy for self-recovery. If self-recovery includes using a password or recovery key stored on a USB flash drive, the users should be warned not to store the USB flash drive in the same place as the PC, especially during travel, for example if both the PC and the recovery items are in the same bag, then it’s easy for an unauthorized user to access the PC. Another policy to consider is having users contact the Helpdesk before or after performing self-recovery so that the root cause can be identified.
Recovery password retrieval
If the user does not have a recovery password in a printout or on a USB flash drive, the user will need to be able to retrieve the recovery password from an online source. If the PC is a member of a domain, the recovery password can be backed up to AD DS. However, this does not happen by default. You must have configured the appropriate Group Policy settings before BitLocker was enabled on the PC. BitLocker Group Policy settings can be found in the Local Group Policy Editor or the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) under Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\BitLocker Drive Encryption. The following policy settings define the recovery methods that can be used to restore access to a BitLocker-protected drive if an authentication method fails or is unable to be used.
- Choose how BitLocker-protected operating system drives can be recovered
- Choose how BitLocker-protected fixed drives can be recovered
- Choose how BitLocker-protected removable drives can be recovered
In each of these policies, select Save BitLocker recovery information to Active Directory Domain Services and then choose which BitLocker recovery information to store in Active Directory Domain Services (ADВ DS). Select the Do not enable BitLocker until recovery information is stored in AD DS check box if you want to prevent users from enabling BitLocker unless the computer is connected to the domain and the backup of BitLocker recovery information for the drive to ADВ DS succeeds.
If the PCs are part of a workgroup, users should be advised to save their BitLocker recovery password with their Microsoft Account online. Having an online copy of your BitLocker recovery password is recommended to help ensure that you do not lose access to your data in the event that recovery is required.
The BitLocker Recovery Password Viewer for Active Directory Users and Computers tool allows domain administrators to view BitLocker recovery passwords for specific computer objects in Active Directory.
You can use the following list as a template for creating your own recovery process for recovery password retrieval. This sample process uses the BitLocker Recovery Password Viewer for Active Directory Users and Computers tool.
Record the name of the user’s computer
You can use the name of the user’s computer to locate the recovery password in ADВ DS. If the user does not know the name of the computer, ask the user to read the first word of the Drive Label in the BitLocker Drive Encryption Password Entry user interface. This is the computer name when BitLocker was enabled and is probably the current name of the computer.
Verify the user’s identity
Verify that the person that is asking for the recovery password is truly the authorized user of that computer. You might also want to verify that the computer with the name the user provided belongs to the user.
Locate the recovery password in ADВ DS
Locate the Computer object with the matching name in ADВ DS. Because Computer object names are listed in the ADВ DS global catalog, you should be able to locate the object even if you have a multi-domain forest.
Multiple recovery passwords
If multiple recovery passwords are stored under a computer object in ADВ DS, the name of the BitLocker recovery information object includes the date that the password was created.
If at any time you are unsure what password to provide, or if you think you might be providing the incorrect password, ask the user to read the eight character password ID that is displayed in the recovery console.
Since the password ID is a unique value that is associated with each recovery password stored in ADВ DS, running a query using this ID will find the correct password to unlock the encrypted volume.
Gather information to determine why recovery occurred
Before you give the user the recovery password, you should gather any information that will help determine why the recovery was needed, in order to analyze the root cause during the post-recovery analysis. For more info about post-recovery analysis, see Post-recovery analysis.
Give the user the recovery password
Because the recovery password is 48 digits long, the user might need to record the password by writing it down or typing it on a different computer. If you are using MBAM, the recovery password will be regenerated after it is recovered from the MBAM database to avoid the security risks associated with an uncontrolled password.
Because the 48-digit recovery password is long and contains a combination of digits, the user might mishear or mistype the password. The boot-time recovery console uses built-in checksum numbers to detect input errors in each 6-digit block of the 48-digit recovery password, and offers the user the opportunity to correct such errors.
Post-recovery analysis
When a volume is unlocked using a recovery password, an event is written to the event log and the platform validation measurements are reset in the TPM to match the current configuration. Unlocking the volume means that the encryption key has been released and is ready for on-the-fly encryption when data is written to the volume, and on-the-fly decryption when data is read from the volume. After the volume is unlocked, BitLocker behaves the same way, regardless of how the access was granted.
If you notice that a computer is having repeated recovery password unlocks, you might want to have an administrator perform post-recovery analysis to determine the root cause of the recovery and refresh BitLocker platform validation so that the user no longer needs to enter a recovery password each time that the computer starts up. See:
Determine the root cause of the recovery
If a user needed to recover the drive, it is important to determine the root cause that initiated the recovery as soon as possible. Properly analyzing the state of the computer and detecting tampering may reveal threats that have broader implications for enterprise security.
While an administrator can remotely investigate the cause of recovery in some cases, the end user might need to bring the computer that contains the recovered drive on site to analyze the root cause further.
Review and answer the following questions for your organization:
- What BitLocker protection mode is in effect (TPM, TPM + PIN, TPM + startup key, startup key only)? Which PCR profile is in use on the PC?
- Did the user merely forget the PIN or lose the startup key? If a token was lost, where might the token be?
- If TPM mode was in effect, was recovery caused by a boot file change?
- If recovery was caused by a boot file change, was the change an intended user action (for example, BIOS upgrade), or was it caused by malicious software?
- When was the user last able to start the computer successfully, and what might have happened to the computer since then?
- Might the user have encountered malicious software or left the computer unattended since the last successful startup?
To help you answer these questions, use the BitLocker command-line tool to view the current configuration and protection mode (for example, manage-bde -status). Scan the event log to find events that help indicate why recovery was initiated (for example, if the boot file changed). Both of these capabilities can be performed remotely.
Resolve the root cause
After you have identified what caused recovery, you can reset BitLocker protection and avoid recovery on every startup.
The details of this reset can vary according to the root cause of the recovery. If you cannot determine the root cause, or if malicious software or a rootkit might have infected the computer, Helpdesk should apply best-practice virus policies to react appropriately.
You can perform a BitLocker validation profile reset by suspending and resuming BitLocker.
Unknown PIN
If a user has forgotten the PIN, you must reset the PIN while you are logged on to the computer in order to prevent BitLocker from initiating recovery each time the computer is restarted.
To prevent continued recovery due to an unknown PIN
- Unlock the computer using the recovery password.
- Reset the PIN:
- Right-click the drive and then select Change PIN.
- In the BitLocker Drive Encryption dialog, select Reset a forgotten PIN. If you are not logged in with an administrator account, provide administrative credentials at this time.
- In the PIN reset dialog, provide and confirm the new PIN to use and then select Finish.
- You will use the new PIN the next time you unlock the drive.
Lost startup key
If you have lost the USB flash drive that contains the startup key, then you must unlock the drive by using the recovery key and then create a new startup key.
To prevent continued recovery due to a lost startup key
- Log on as an administrator to the computer that has the lost startup key.
- Open Manage BitLocker.
- Select Duplicate start up key, insert the clean USB drive on which you are going to write the key and then select Save.
Changes to boot files
This error might occur if you updated the firmware. As a best practice, you should suspend BitLocker before making changes to the firmware and then resume protection after the update has completed. This action prevents the computer from going into recovery mode. However if changes were made when BitLocker protection was on, then log on to the computer using the recovery password, and the platform validation profile will be updated so that recovery will not occur the next time.
Windows RE and BitLocker Device Encryption
Windows Recovery Environment (RE) can be used to recover access to a drive protected by BitLocker Device Encryption. If a PC is unable to boot after two failures, Startup Repair will automatically start. When Startup Repair is launched automatically due to boot failures, it will only execute operating system and driver file repairs, provided that the boot logs or any available crash dump point to a specific corrupted file. In Windows 8.1 and later, devices that include firmware to support specific TPM measurements for PCR[7] the TPM can validate that Windows RE is a trusted operating environment and will unlock any BitLocker-protected drives if Windows RE has not been modified. If the Windows RE environment has been modified, for example the TPM has been disabled, the drives will stay locked until the BitLocker recovery key is provided. If Startup Repair can’t run automatically from the PC and instead Windows RE is manually started from a repair disk, then the BitLocker recovery key must be provided to unlock the BitLocker–protected drives.
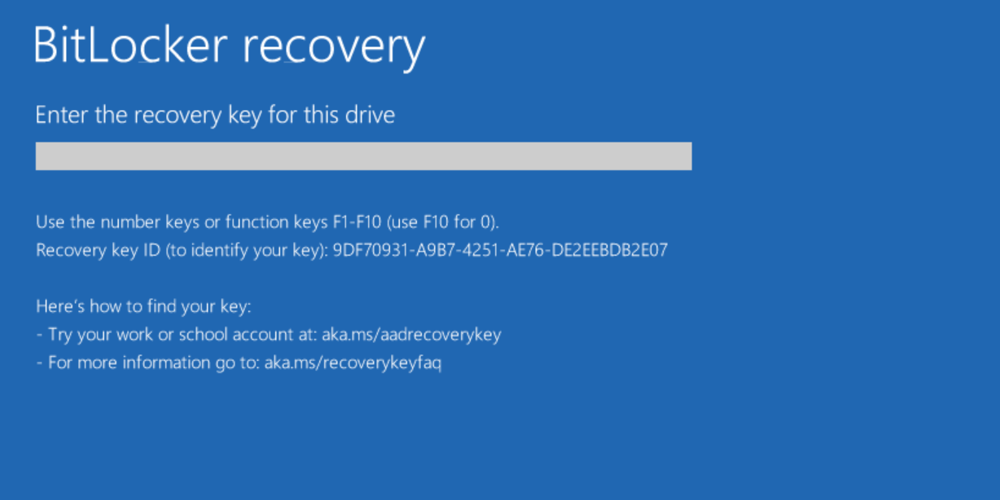
BitLocker recovery screen
During BitLocker recovery, Windows can display a custom recovery message and hints that identify where a key can be retrieved from. These improvements can help a user during BitLocker recovery.
Custom recovery message
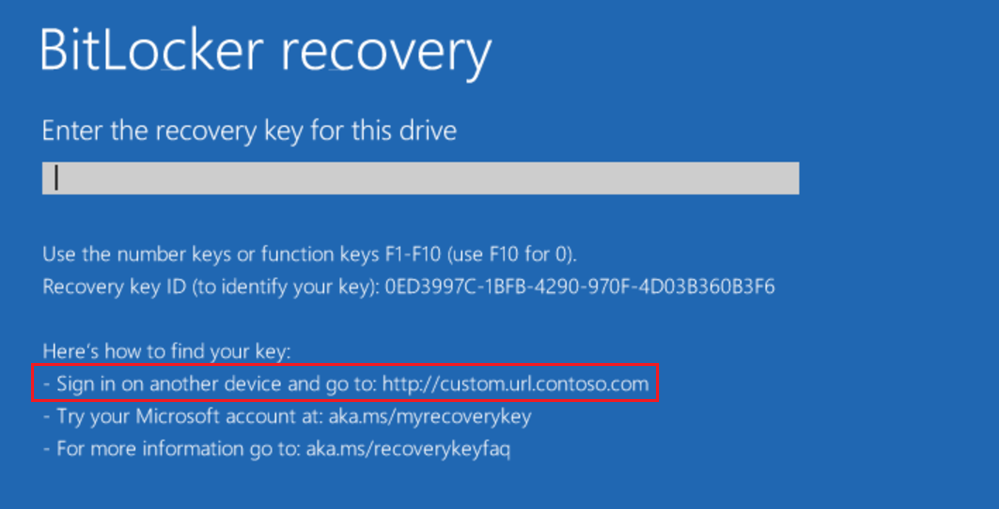
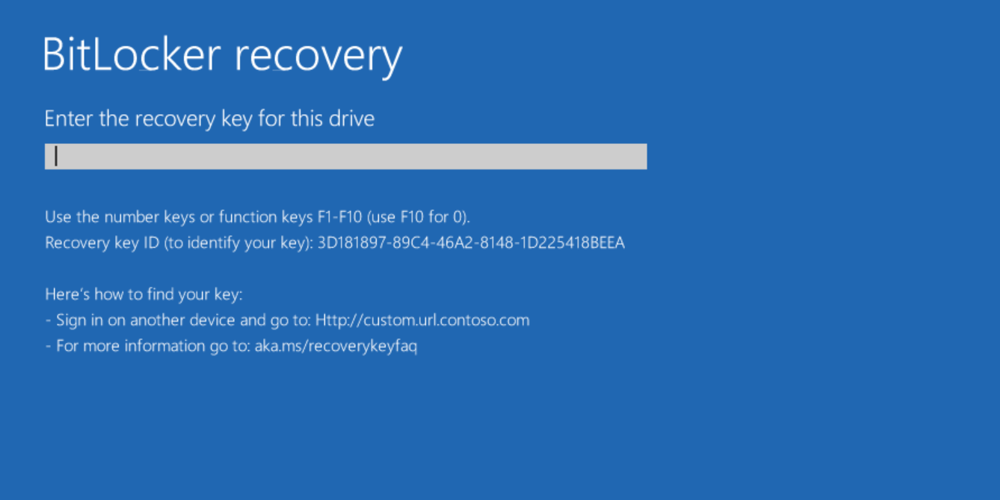
BitLocker Group Policy settings in Windows 10, version 1511, let you configure a custom recovery message and URL on the BitLocker recovery screen, which can include the address of the BitLocker self-service recovery portal, the IT internal website, or a phone number for support.
This policy can be configured using GPO under Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption > Operating System Drives > Configure pre-boot recovery message and URL.
It can also be configured using Intune mobile device management (MDM) in the BitLocker CSP: ./Device/Vendor/MSFT/BitLocker/SystemDrivesRecoveryMessage
Example of customized recovery screen:
BitLocker recovery key hints
BitLocker metadata has been enhanced in Windows 10, version 1903 to include information about when and where the BitLocker recovery key was backed up. This information is not exposed through the UI or any public API. It is used solely by the BitLocker recovery screen in the form of hints to help a user locate a volume’s recovery key. Hints are displayed on the recovery screen and refer to the location where the key has been saved. Hints are displayed on both the modern (blue) and legacy (black) recovery screen. This applies to both the boot manager recovery screen and the WinRE unlock screen.
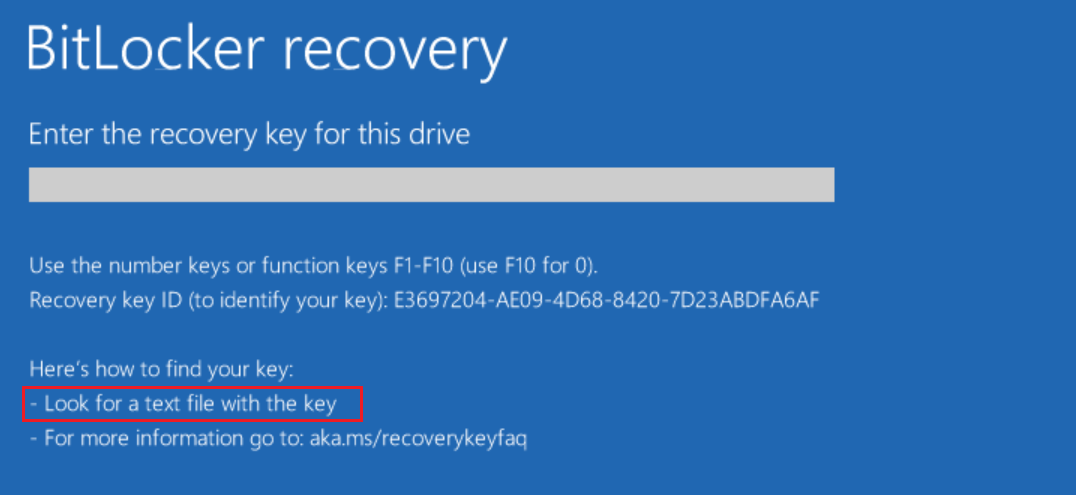
We don’t recommend printing recovery keys or saving them to a file. Instead, use Active Directory backup or a cloud-based backup. Cloud-based backup includes Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and Microsoft Account.
There are rules governing which hint is shown during the recovery (in order of processing):
- Always display custom recovery message if it has been configured (using GPO or MDM).
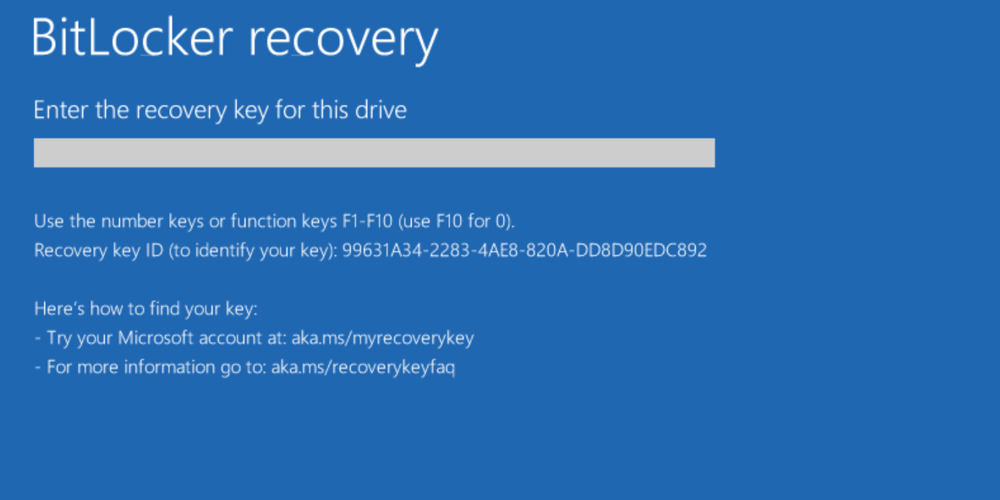
- Always display generic hint: «For more information, go to https://aka.ms/recoverykeyfaq».
- If multiple recovery keys exist on the volume, prioritize the last created (and successfully backed up) recovery key.
- Prioritize keys with successful backup over keys that have never been backed up.
- Prioritize backup hints in the following order for remote backup locations: Microsoft Account > Azure AD > Active Directory.
- If a key has been printed and saved to file, display a combined hint, «Look for a printout or a text file with the key,» instead of two separate hints.
- If multiple backups of the same type (remove vs. local) have been performed for the same recovery key, prioritize backup info with latest backed up date.
- There is no specific hint for keys saved to an on-premises Active Directory. In this case, a custom message (if configured) or a generic message, «Contact your organization’s help desk,» will be displayed.
- If two recovery keys are present on the disk, but only one has been successfully backed up, the system will ask for a key that has been backed up, even if another key is newer.
Example 1 (single recovery key with single backup)
| Custom URL | Yes |
|---|---|
| Saved to Microsoft Account | Yes |
| Saved to Azure AD | No |
| Saved to Active Directory | No |
| Printed | No |
| Saved to file | No |
Result: The hint for the Microsoft Account and the custom URL are displayed.
Example 2 (single recovery key with single backup)
| Custom URL | Yes |
|---|---|
| Saved to Microsoft Account | No |
| Saved to Azure AD | No |
| Saved to Active Directory | Yes |
| Printed | No |
| Saved to file | No |
Result: Only the custom URL is displayed.
Example 3 (single recovery key with multiple backups)
| Custom URL | No |
|---|---|
| Saved to Microsoft Account | Yes |
| Saved to Azure AD | Yes |
| Saved to Active Directory | No |
| Printed | Yes |
| Saved to file | Yes |
Result: Only the Microsoft Account hint is displayed.
Example 4 (multiple recovery passwords)
| Custom URL | No |
|---|---|
| Saved to Microsoft Account | No |
| Saved to Azure AD | No |
| Saved to Active Directory | No |
| Printed | No |
| Saved to file | Yes |
| Creation time | 1PM |
| Key ID | A564F193 |
| Custom URL | No |
|---|---|
| Saved to Microsoft Account | No |
| Saved to Azure AD | No |
| Saved to Active Directory | No |
| Printed | No |
| Saved to file | No |
| Creation time | 3PM |
| Key ID | T4521ER5 |
Result: Only the hint for a successfully backed up key is displayed, even if it isn’t the most recent key.
Example 5 (multiple recovery passwords)
| Custom URL | No |
|---|---|
| Saved to Microsoft Account | Yes |
| Saved to Azure AD | Yes |
| Saved to Active Directory | No |
| Printed | No |
| Saved to file | No |
| Creation time | 1PM |
| Key ID | 99631A34 |
| Custom URL | No |
|---|---|
| Saved to Microsoft Account | No |
| Saved to Azure AD | Yes |
| Saved to Active Directory | No |
| Printed | No |
| Saved to file | No |
| Creation time | 3PM |
| Key ID | 9DF70931 |
Result: The hint for the most recent key is displayed.
Using additional recovery information
Besides the 48-digit BitLocker recovery password, other types of recovery information are stored in Active Directory. This section describes how this additional information can be used.
BitLocker key package
If the recovery methods discussed earlier in this document do not unlock the volume, you can use the BitLocker Repair tool to decrypt the volume at the block level. The tool uses the BitLocker key package to help recover encrypted data from severely damaged drives. You can then use this recovered data to salvage encrypted data, even after the correct recovery password has failed to unlock the damaged volume. We recommend that you still save the recovery password. A key package cannot be used without the corresponding recovery password.
You must use the BitLocker Repair tool repair-bde to use the BitLocker key package.
The BitLocker key package is not saved by default. To save the package along with the recovery password in AD DS, you must select the Backup recovery password and key package option in the Group Policy settings that control the recovery method. You can also export the key package from a working volume. For more details about how to export key packages, see Retrieving the BitLocker Key Package.
Resetting recovery passwords
Invalidate a recovery password after it has been provided and used. It should also be done when you intentionally want to invalidate an existing recovery password for any reason.
You can reset the recovery password in two ways:
- Use manage-bde: You can use manage-bde to remove the old recovery password and add a new recovery password. The procedure identifies the command and the syntax for this method.
- Run a script: You can run a script to reset the password without decrypting the volume. The sample script in the procedure illustrates this functionality. The sample script creates a new recovery password and invalidates all other passwords.
To reset a recovery password using manage-bde:
Remove the previous recovery password
Add the new recovery password
Get the ID of the new recovery password. From the screen, copy the ID of the recovery password.
Back up the new recovery password to AD DS.
You must include the braces in the ID string.
To run the sample recovery password script:
Save the following sample script in a VBScript file. For example: ResetPassword.vbs.
At the command prompt, type a command similar to the following sample script:
cscript ResetPassword.vbs
This sample script is configured to work only for the C volume. You must customize the script to match the volume where you want to test password reset.
To manage a remote computer, you can specify the remote computer name rather than the local computer name.
You can use the following sample script to create a VBScript file to reset the recovery passwords:
Retrieving the BitLocker key package
You can use two methods to retrieve the key package, as described in Using Additional Recovery Information:
- Export a previously saved key package from ADВ DS. You must have Read access to BitLocker recovery passwords that are stored in ADВ DS.
- Export a new key package from an unlocked, BitLocker-protected volume. You must have local administrator access to the working volume, before any damage has occurred.
The following sample script exports all previously saved key packages from ADВ DS.
To run the sample key package retrieval script:
Save the following sample script in a VBScript file. For example: GetBitLockerKeyPackageADDS.vbs.
At the command prompt, type a command similar to the following sample script:
cscript GetBitLockerKeyPackageADDS.vbs -?
You can use the following sample script to create a VBScript file to retrieve the BitLocker key package from ADВ DS:
The following sample script exports a new key package from an unlocked, encrypted volume.
To run the sample key package retrieval script:
Save the following sample script in a VBScript file. For example: GetBitLockerKeyPackage.vbs
Open an administrator command prompt, and then type a command similar to the following sample script: