- Kali Linux Metapackages – Getting the missing tools properly.
- Kali Linux ARM images.
- What are Metapackages!
- Links to Metapackages
- Special Kali Metapackages
- Uninstall Kali Metapackages.
- Coming up next!
- Major Metapackage Makeover
- Systems
- Kali Menu
- Tools
- Courses
- Desktop Managers
- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- Kali Linux Meta-packages
- What are meta-packages in Kali Linux for?
- Meta-packages and Virtual Package
- List of Kali Linux Metapackages
- System
- Desktop environments/window managers
- Tools
- Menu-based tool sets
- Others
- Meta-packages for courses
- Meta-packages kali-linux, kali-desktop-common and kali-linux-*
- How to install a meta-package
- How to see which programs are included in the meta-package
- Meta-packages for WSL (Windows Subsystems for Linux)
- Making your own Kali Linux Metapackages
- Sources:
- Related articles:
- Recommended for you:
- 4 Comments to Kali Linux Meta-packages
Kali Linux Metapackages – Getting the missing tools properly.
Kali Linux ARM images.
When the developers of Kali Linux approached porting the OS to the Raspberry Pi 2 they came up with a unique strategy of offering a base system and then creating an apt-get process to download bundled and preconfigured tool sets. Most researchers won’t fully use the Raspberry Pi as sole Kali product but researchers will use the Raspberry Pi version of Kali as an extension of their own shell, such as a remote wireless auditor. So once we download the base OS you will immediately notice how streamline and easy it is to add the Kali tools and removing them as bundles using the same method.
What are Metapackages!
As mentioned in our quick video, Metapackages are repository packages of tools packed together, with the same kind or likeness, for easy installation. These Metapackages can be used not just for the Raspberry Pi but most ARM or Slim versions of Kali Linux, also another trick you can do is add the Kali Linux distro repository links to say another Debian based Linux and add the same packages, like adding wireless hacks to Ubuntu, it can be done but that requires a bit of Linux skill and more time to explain. Anyway… on to our Raspberry Pi example.
New installations of Kali OS Images on ARM chipsets will only have the basic top 10 Kali tools installed. You should research and configure your new installation to add the Metapackages of attack tools you will be using. Not all tools will be available but most of them are there. Tools that are not available are only missing due to the compatibility of the tool and the ARM chipset architecture. The installation is SUPER easy by using the apt-get method. For instance the command to install all wireless hacking tools is just:
apt-get install kali-linux-wireless
Links to Metapackages 
Please check out all the Kali Metapackages:
Kali Metapackages – Link includes basic name and installation size in GB.
Kali Metapackages detailed description – Basic name and detailed package content.
So you have to calculate the base image size with the add on Metapackages. In my case the uncompressed Kali image was just over 3GB and the wireless hacking tools Metapackage was 6.6GB thus totaling just under 10GB. So you will want a nice big MicroSD card to store your various Metapackages on Kali.
Special Kali Metapackages
apt-get install kali-linux-full – 9 GB
apt-get install kali-linux-all – 15GB
There are full and All versions of Metapackages, if you want to strip and slim down your Kali system and then reinstall you can. This is helpful in some instances where you want to refresh a Kali desktop environment (Yes, these same Metapackages can be installed on Kali desktop :-))
Now it’s incredibly important that I let you know if you decide to go with a full install it may take over several hours. I did manage to install the full and it took over 3 hrs, It took 40 min alone to download the packages and the a few hours to unpack and install them and after the install the OS was kind of funky.
Uninstall Kali Metapackages.
You can also uninstall packages in this method. Say you just want the wireless auditing Metapackage but you have decided not to use the SDR-RTL Metapackage. Well all you have to do is uninstall that Metapackage group something like this:
apt-get remove kali-linux-sdr or apt-get purge kali-linux-sdr
Coming up next!
Please tune in to our YouTube channel series on installing the Kali Linux OS on the Raspberry Pi. We understand that there are many tutorials out there in the hacking community but we feel we can bring a simple common sense approach to installing. Subscribe to our channel and like our vids!
Источник
Major Metapackage Makeover
With our 2019.3 Kali release imminent, we wanted to take a quick moment to discuss one of our more significant upcoming changes: our selection of metapackages. These alterations are designed to optimize Kali, reduce ISO size, and better organize metapackages as we continue to grow.
Before we get into what’s new, let’s briefly recap what a metapackage is. A metapackage is a package that does not contain any tools itself, but rather is a dependency list of normal packages (or other metapackages). This allows us to group related tools together. For instance, if you want to be able to access every wireless tool, simply install the kali-tools-wireless metapackage. This will obtain all wireless tools in one download. As always, you can access the full list of metapackages available in Kali on kali.org/docs/general-use/metapackages/. If you prefer to use the command line, the following command will list out the packages that will be installed via a specific metapackage:
We took the time to create new metapackages and rename existing ones, and we did the same with the tools listed inside of them. As a result of these changes, we’ve implemented a new naming convention for simplicity and improved granular control. At the end of the post there is a table displaying the relationships between previous and new names moving forward, along with a description of the metapackage purpose.
If you have made it this far, you are likely wondering “how does this affect me”?
- If you are using a version of Kali older than 2019.3, if and when you upgrade, you will still have the same set of tools (just newer)!
- However, if you do a fresh install of Kali with a version higher than either weekly W34 or 2019.3 ISO, you will notice some of the tools that get installed by DEFAULT have changed(we have put Kali on a diet!)
Previously, kali-linux-full was the default metapackage, which has been renamed to kali-linux-large with a redirect put in place. We have introduced a new default metapackage called kali-linux-default , which serves as a slimmed-down version of the tools from kali-linux-large .
Depending on how you use Kali will determine which metapackage would suit you best. This is the power of metapackages. For example:
- If you want a core set of tools, stick with kali-linux-default (designed for assessments that are straightforward ).
- If you want a more general and wider range of tools, select kali-linux-large (useful if Internet access is permitted but slow).
- If you want to be prepared for anything, go with kali-linux-everything (great if you are going to be doing air-gap/offline work)
Note: You can install multiple metapackages at once and are not limited to just one, so mix and match!
Each of these metapackages depends on the one above. That means, when we add a new essential tool to kali-linux-default , it is automatically part of kali-linux-large and thus kali-linux-everything . Otherwise, when we add a new tool that may not be useful to everyone, it will be placed into either kali-linux-large or kali-linux-everything — depending on our tool policy. More information about the new tool policy will be made public towards the end of the year. Stay tuned for some very exciting news!
How Kali is being used today has changed since when Kali (and even BackTrack) was first born. Not everyone needs all the tools at once — but they are still available when required. We have opted for a new default set of tools to match the majority of today’s current network environments, by removing edge cases and legacy tools which are rarely used.
Upon doing a system upgrade ( apt -y full-upgrade ) on a version of Kali older than 2019.3, you will see the old metapackage name being removed. This is safe. If you have tried to remove a tool before, you may have run into this (when the tool is part of a metapackage). This is also safe to remove, as it doesn’t remove any other tools. It simply means that when a new tool is added into that metapackage, you won’t receive it.
If you are running 2019.3 and want the old default set of tools, you can do either apt -y install for a one-off package installation or apt -y install kali-linux-large to get the old tool set back. For the 2019.3 release, we will be doing a one-off extra image, which is based on kali-linux-large to help with the transition.
Below are the tables with a complete breakdown of previous metapackages names, along with their new respective names:
Systems
These metapackages are used when generating our images
| Old | New | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| kali-linux | kali-linux-core | Base Kali Linux System — core items that are always included |
| new | kali-linux-default | “Default” desktop (amd64/i386) images include these tools |
| new | kali-linux-light | Kali-Light images use this to be generated |
| new | kali-linux-arm | All tools suitable for ARM devices |
| kali-linux-nethunter | kali-linux-nethunter (same) | Tools used as part of Kali NetHunter |
Kali Menu
These entries are based around the Kali menu
| Old | New | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| new | kali-tools-information-gathering | Used for Open-source Intelligence (OSINT) & information gathering |
| new | kali-tools-vulnerability | Vulnerability assessments tools |
| kali-linux-web | kali-tools-web | Designed doing web applications attacks |
| new | kali-tools-database | Based around any database attacks |
| kali-linux-pwtools | kali-tools-passwords | Helpful for password cracking attacks — Online & offline |
| kali-linux-wireless | kali-tools-wireless | All tools based around Wireless protocols — 802.11, Bluetooth, RFID & SDR |
| new | kali-tools-reverse-engineering | For reverse engineering binaries |
| new | kali-tools-exploitation | Commonly used for doing exploitation |
| new | kali-tools-social-engineering | Aimed for doing social engineering techniques |
| new | kali-tools-sniffing-spoofing | Any tools meant for sniffing & spoofing |
| new | kali-tools-post-exploitation | Techniques for post exploitation stage |
| kali-linux-forensics | kali-tools-forensics | Forensic tools — Live & Offline |
| new | kali-tools-reporting | Reporting tools |
Tools
These are tool listing based on the category and type
| Old | New | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| kali-linux-gpu | kali-tools-gpu | Tools which benefit from having access to GPU hardware |
| new | kali-tools-hardware | Hardware hacking tools |
| new | kali-tools-crypto-stego | Tools based around Cryptography & Steganography |
| new | kali-tools-fuzzing | For fuzzing protocols |
| new | kali-tools-802-11 | 802.11 (Commonly known as “Wi-Fi”) |
| new | kali-tools-bluetooth | For targeting Bluetooth devices |
| kali-linux-rfid | kali-tools-rfid | Radio-Frequency IDentification tools |
| kali-linux-sdr | kali-tools-sdr | Software-Defined Radio tools |
| kali-linux-voip | kali-tools-voip | Voice over IP tools |
| new | kali-tools-windows-resources | Any resources which can be executed on a Windows hosts |
Useful metapackages which are “one off” groupings
| Old | New | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| kali-linux-full | kali-linux-large | Our previous default tools for amd64/i386 images |
| kali-linux-all | kali-linux-everything | Every metapackage and tool listed here |
| kali-linux-top10 | kali-tools-top10 | The most commonly used tools |
| kali-desktop-live | kali-desktop-live (same) | Used during a live session when booted from the image |
| new | kali-tools-headless | Tools which do not require a GUI in order to access them |
Courses
Tools used for Offensive Security’s courses
| Old | New | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| new | offsec-awae | Advanced Web Attacks and Exploitation |
| new | offsec-pwk | Penetration Testing with Kali |
Desktop Managers
Desktop Environment (DE) & Window Manager (WM)
| Old | New | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| kali-desktop-common | kali-desktop-core | Any key tools required for a GUI image |
| new | kali-desktop-e17 | Enlightenment (WM) |
| kali-desktop-gnome | kali-desktop-gnome (same) | GNOME (DE) |
| new | kali-desktop-i3 | i3 (WM) |
| kali-desktop-kde | kali-desktop-kde (same) | KDE (DE) |
| kali-desktop-lxde | kali-desktop-lxde (same) | LXDE (WM) |
| new | kali-desktop-mate | MATE (DE) |
| new | kali-desktop-pantheon | Pantheon (DE) |
| kali-desktop-xfce | kali-desktop-xfce (same) | XFCE (WM) |
If you wish to create your own metapackage, see how we do it here, before you create your own package.
Источник
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
Kali Linux Meta-packages
What are meta-packages in Kali Linux for?
Meta-packages are empty packages that only describe dependencies. They facilitate the installation of a collaborative group of programs previously selected by the maintainer of the meta-package; thus the command
will automatically install all of these programs using the META-PACKAGE dependencies. The kali-desktop-gnome, kali-desktop-kde, and kali-linux-default packages are examples of meta-packages.
Meta-packages are used to install multiple packages at the same time, created as a list of dependencies on other packages. Kali Linux uses them in several ways. One way is to let users decide how many packages from the general Kali list they would like to install. Need to install packages just to run Linux itself? Do you want packages that are enough to run a penetration test in a specific area? Perhaps you want to install all the packages that Kali comes with? Meta-packages can help you with any of these tasks.
Meta-packages and Virtual Package
It is important to clearly distinguish between metapackages and virtual packages. The former are real packages (including real .deb files) whose sole purpose is to express dependencies.
Virtual packages, however, do not physically exist; they are only a means of identifying real packages based on common logical criteria (for example, services provided or compatibility with a standard program or an existing package). Sometimes virtual packages are used as short, handy, or commonly used aliases for real packages.
List of Kali Linux Metapackages
System
- kali-linux-core: A basic Kali Linux system – basic elements that are always present in any installation
- kali-linux-default: The “standard” system images that you can download from the download page (AMD64/i386) include the tools of these images
- kali-linux-light: Used to create an image of Kali-Light, a light version of the system
- kali-linux-arm: All tools suitable for ARM devices
- kali-linux-nethunter: Tools used as part of Kali NetHunter
Desktop environments/window managers
Desktop environments are full-fledged graphical shells like GNOME, Cinnamon, KDE, XFCE and others.
Window managers perform only some functions of the graphical interface, in fact, they only allow you to open several windows, add a desktop background, and can have a simple menu. Due to this simplicity, window managers consume a minimum of resources. But from the point of view of user convenience, they are inferior to a full-fledged desktop environment
- kali-desktop-core: Any key tools needed to display the GUI.
- kali-desktop-e17: Enlightenment (window manager)
- kali-desktop-gnome: GNOME (desktop environment)
- kali-desktop-i3: i3 (window manager)
- kali-desktop-kde: KDE (desktop environment)
- kali-desktop-lxde: LXDE (window manager)
- kali-desktop-mate: MATE (desktop environment)
- kali-desktop-xfce: XFCE (window manager)
Tools
- kali-tools-gpu: Tools that work best when you have access to GPU computing
- kali-tools-hardware: Hardware Hacking Tools
- kali-tools-crypto-stego: Tools based on cryptography and steganography
- kali-tools-fuzzing: For fuzzing protocols
- kali-tools-802-11: 802.11 (commonly known as “Wi-Fi”)
- kali-tools-bluetooth: For targeting Bluetooth devices.
- kali-tools-rfid: RFID tools
- kali-tools-sdr: Software-Defined Radio Tools
- kali-tools-voip: Voice over IP tools
- kali-tools-windows-resources: Any programs that can run on Windows hosts.
Menu-based tool sets
All tools in Kali Linux are structured in menus and sub-menus. Menus are a convenient way to learn about a new tool, but practically useless from the point of view of running utilities, since most of them have a command line interface.
Meta-packages are also generated from these carefully sorted lists.
When installing a meta-package, the corresponding menu item will be created automatically, and relevant programs will also be automatically placed in it.
- kali-tools-information-gathering: Used for open source intelligence (OSINT) and information gathering
- kali-tools-vulnerability: Tools for finding vulnerability
- kali-tools-web: Designed to attack web applications
- kali-tools-database: Selected tools for any database attacks
- kali-tools-passwords: Useful for password cracking attacks – online and offline brute force
- kali-tools-wireless: all tools based on wireless protocols – 802.11, Bluetooth, RFID and SDR
- kali-tools-reverse-engineering: To reverse engineer binaries
- kali-tools-exploitation: Typically used to exploit found vulnerabilities
- kali-tools-social-engineering: Designed to perform social engineering techniques
- kali-tools-sniffing-spoofing: Any tools designed for sniffing and spoofing (man-in-the-middle attack).
- kali-tools-post-exploitation: Post-exploitation tools (backdoors, stealth shells, etc.)
- kali-tools-forensics: Digital Forensics Tools – Real Time and Offline
- kali-tools-reporting: Reporting tools
Others
- kali-linux-large: Previous default tools for AMD64/i386 images
- kali-linux-everything: All the meta-packages and tools listed here
- kali-tools-top10: Most used tools (10 tools in total)
- kali-desktop-live: Used during live session when booting from image
Meta-packages for courses
Tools used for Offensive Security courses,
- offsec-awae: Advanced Web Attacks and Exploitation
- offsec-pwk: Penetration Testing with Kali
Meta-packages kali-linux, kali-desktop-common and kali-linux-*
The meta-packages kali-linux, kali-desktop-common, as well as all metapackages of the form kali-linux-* have been renamed and the old names are no longer used. If you come across them, then you are reading an outdated source.
How to install a meta-package
To install any meta-package, use a command like this:
One or more meta-packages can be installed at a time.
How to see which programs are included in the meta-package
To find out which programs are included in the meta-package, use a command like:
Be aware that other meta-packages may be present in the output of this command!
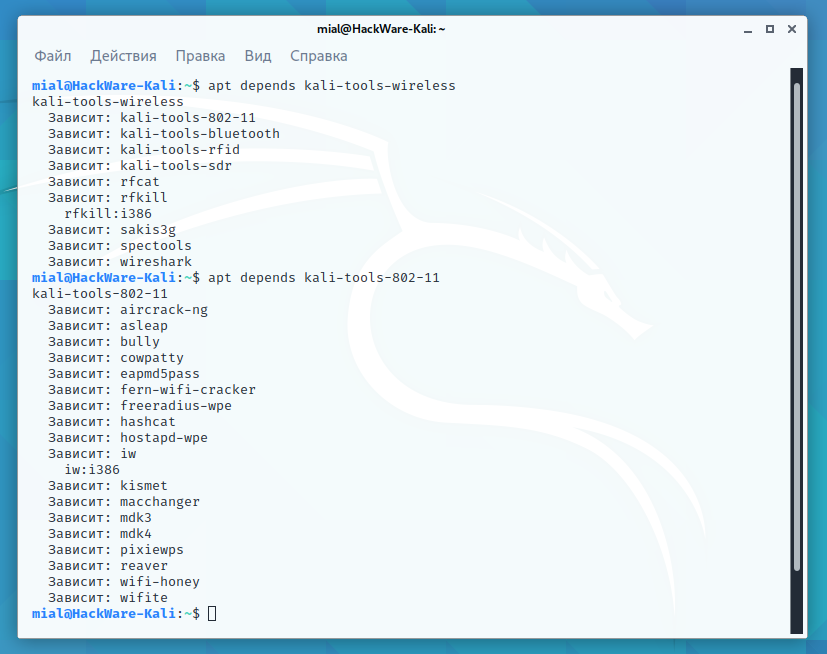
Another way to check which programs make up the meta-package is to visit https://tools.kali.org/kali-metapackages, which lists the available meta-packages and shows the programs included in them.
Meta-packages for WSL (Windows Subsystems for Linux)
By default, no Kali Linux tools are included in the WSL image. This is done to keep the image as small as possible. Optionally, you can install any tool from the Kali Linux repository or use the meta-packages.
You can set the tool categories you need using the meta-packages described above.
For example, a set with the most popular tools for most users
The easiest way to get most of the tools is to install the kali-linux-large metapackage with the following command:
In WSL, you don’t need tools from the following meta-packages (due to lack of access to hardware):
- kali-tools-wireless (all wireless attacks)
- kali-tools-802-11 (Wi-Fi attacks)
- kali-tools-bluetooth (Bluetooth attacks)
- kali-tools-rfid
- kali-tools-sdr
- kali-tools-gpu (currently there is no access to compluting using a video card, but they promise to add it)
- kali-tools-hardware
- kali-tools-sniffing-spoofing (sniffing and spoofing is also not possible due to the fact that the WSL Linux images run on their own virtual network).
Making your own Kali Linux Metapackages

You can create and use your own metapackages to deploy the right environment for you. See “Making your own Kali Linux Metapackages” for details.
Sources:
Related articles:
- How to install a package for which there is no dependency of the required version (in Kali Linux, Debian) (81.1%)
- Package management in Kali Linux and other Debian-based distributions (searching, installing and removing programs, troubleshooting) (69.4%)
- How to change the desktop environment in Kali Linux without reinstalling the operating system (63.8%)
- Error «E: Could not access the lock file /var/lib/dpkg/lock» in Kali Linux (SOLVED) (60.4%)
- Kali Linux updating troubleshooting (60.4%)
- How to find out the exact model of a router (wireless access point) (RANDOM — 0.5%)
Recommended for you:
4 Comments to Kali Linux Meta-packages
└─# apt install kali-tools-exploitation
Reading package lists… Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information… Done
kali-tools-exploitation is already the newest version (2020.4.8).
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 12 not upgraded.
2 not fully installed or removed.
After this operation, 0 B of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y
Setting up set (8.0.3+git20200609-0kali2) …
[Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘/usr/share/set/src/payloads/set_payloads/multi_pyinjector.py’
[Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘/usr/share/set/src/payloads/set_payloads/pyinjector_args.py’
[Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘/usr/share/set/src/payloads/set_payloads/shell.py’
dpkg: error processing package set (—configure):
installed set package post-installation script subprocess returned error exit status 1
dpkg: dependency problems prevent configuration of kali-tools-exploitation:
kali-tools-exploitation depends on set; however:
Package set is not configured yet.
dpkg: error processing package kali-tools-exploitation (—configure):
dependency problems — leaving unconfigured
Errors were encountered while processing:
set
kali-tools-exploitation
E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)
┌──(root💀DESKTOP-NF4O0MG)-[
]
└─# apt depends kali-tools-exploitation
kali-tools-exploitation
Depends: armitage
Depends: beef-xss
Depends: exploitdb
Depends: metasploit-framework
Depends: msfpc
Depends: set
Depends: shellnoob
Depends: sqlmap
Depends: termineter
┌──(root💀DESKTOP-NF4O0MG)-[
]
└─# apt-cache showpkg set
Package: set
Versions:
8.0.3+git20200609-0kali2 (/var/lib/apt/lists/http.kali.org_kali_dists_kali-rolling_main_binary-amd64_Packages) (/var/lib/dpkg/status)
Description Language:
File: /var/lib/apt/lists/http.kali.org_kali_dists_kali-rolling_main_binary-amd64_Packages
MD5: ac8f70cda2355ffa34eda5f489af1096
Reverse Depends:
kali-linux-headless,set
kali-tools-social-engineering,set
kali-tools-exploitation,set
Dependencies:
8.0.3+git20200609-0kali2 — aircrack-ng (0 (null)) ettercap-common (0 (null)) libapache2-mod-php (0 (null)) metasploit-framework (0 (null)) nginx (0 (null)) openssl (0 (null)) python3-impacket (0 (null)) python3-openssl (0 (null)) python3-paramiko (0 (null)) python3-pefile (0 (null)) python3-pexpect (0 (null)) python3-pil (0 (null)) python3-pycryptodome (0 (null)) python3-pymssql (0 (null)) python3-qrcode (0 (null)) python3-requests (0 (null)) upx-ucl (0 (null)) python3:any (0 (null)) apache2 (0 (null)) sendmail-bin (0 (null))
Provides:
8.0.3+git20200609-0kali2 —
Reverse Provides:
┌──(root💀DESKTOP-NF4O0MG)-[
]
└─# uname -a
Linux DESKTOP-NF4O0MG 4.4.0-19041-Microsoft #488-Microsoft Mon Sep 01 13:43:00 PST 2020 x86_64 GNU/Linux
┌──(root💀DESKTOP-NF4O0MG)-[
]
└─# cat /etc/issue
Kali GNU/Linux Rolling \n \l
The package installation fails with same error for set package. I had the same error ealier which was solved by purging python3.9. Do I need to do the same.
Even before you run any of the shown commands, your system is already sick.
If you really want the ‘set’ package you can try installing it later. If the problem persists, you can download ‘set’ source code from GitHub and use it instead of buggy package.
Also remove the second package causing the problem.
Источник




