- Инструменты Kali Linux
- Список инструментов для тестирования на проникновение и их описание
- SMBCrunch
- Описание SMBCrunch
- Справка по SMBHunt
- Справка по SMBList
- Справка по SMBGrab
- Руководство по SMBCrunch
- SMBHunt
- SMBList
- SMBGrab
- Примеры запуска SMBCrunch
- Установка SMBCrunch
- Установка в Kali Linux
- Установка в BlackArch
- Взаимодействие сканеров уязвимостей с Metasploit. Часть 1
- Packages and Binaries:
- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- SMB and Samba Security Audit Tools
- Table of contents
- 1. SMB and network folders discovering. Shares and files enumeration
- smbclient utilities
- SMB discovering via port scanning
- enum4linux
- nullinux
- SMB Spider
- acccheck
- Credninja
- SMBMap
- SPARTA
- SMBCrunch
- 2. Man-in-the-middle attack on SMB. Relays
- Responder
- Inveigh
- Intercepter-ng
- Ettercap. Ettercap Plugins
- MITMf
- Netcreds
- 3. Brute-force attack on Windows user credentials via SMB
- patator
- Hydra
- Medusa
- BruteSpray
- 4. SMB post-exploitation tools
- keimpx
- 5. Nmap scripts for gathering information and auditing SMB
- 6. Other programs
Инструменты Kali Linux
Список инструментов для тестирования на проникновение и их описание
SMBCrunch
Описание SMBCrunch
SMBCrunch представляет собой 3 инструмента, которые работают вместе для сбора информации о файловых шарах (совместных сетевых папках) Windows. Названия инструментов:
Одними из самых затратных по времени задачами ред тимеров (red teamer) является углубление в файловые системы и сетевые папки в попытке идентифицировать любую потенциально чувствительную информацию. SMBCrunch позволяет тестерам на проникновение быстро идентифицировать в сети Windows File Shares (сетевые папки), выполнить рекурсивный листинг директорий указанных шар и может даже собрать файлы с удалённых шар, если они выглядят интересными целями.
Автор: Chris King
Справка по SMBHunt
Аргументы и опции:
Справка по SMBList
Аргументы и опции:
Справка по SMBGrab
Аргументы и опции:
Руководство по SMBCrunch
Страница man отсутствует.
SMBHunt
Для заданного хоста, файла со списками хостов или файла gnmap (с результатами сканирования программой Nmap) находит все сетевые папки Windows данных серверов. Если предоставлен файл gnmap, то скрипт ищет сервера с открытым портом 445. Если для проверки не предоставлены учётные данные, то программа проверит доступность общих папок по нулевой сессии.
Предупреждение: если ваш пользователь имеет доступ к одной совместной папке на сервере, скрипт покажет все шары, размещённые на этом сервере. Если сетевая папка показана в выводе, то это не означает, что у вас есть доступ к этой шаре. Для определения возможности доступа используйте следующий инструмент SMBList.
Этот скрипт предупреждает вас, если предоставленные вами учётные данные не подошли, это сделано для того, чтобы избежать блокировки доменных аккаунтов. Переключатель «-f» отменяет эту защиту.
Этот скрипт проверяет только сервер, используя одну пару учётных данных. Это сделано специально, поскольку сервер ответит полным списком общих ресурсов, даже если пользователь имеет доступ только к одной общей папке в системе.
SMBList
Сохраняет рекурсивный листинг директорий всех обнаруженных сетевых папок. Вы можете указать список учётных данных для тестирования. Затем с помощью программы grep вы можете найти потенциально хорошие файлы на цели.
SMBList принимает файл вывода от «SMBHunt.pl» (или файл содержащий сетевые папки, разделённые переводом новой строки в формате «\server\share») и выполняет рекурсивный листинг этих общих папок используя предоставленные учётные данные. SMBList попытается аутентифицироваться на сетевых папках пока не будут найдены верные учётные данные из предоставленного списка. Затем скрипт сохранит списки файлов директорий в указанной подпапке.
Такой подход делает поиск по списку файлов с помощью команды grep крайне простым!
Самые полные результаты собраны в файле ALL_COMBINED_RESULTS.txt.
SMBGrab
Списки файлов из утилиты SMBList.pl могут быть переданы по трубе (контейнеру) в эту утилиту для скачивания всех нужных файлов с сетевых папок. Исходный список из SMBList.pl следует отфильтровать с помощью grep перед передачей в этот скрипт, в противном случае будут загружены все файлы (что эквивалентно копированию целой сетевой папки, что может быть плохо).
Примеры запуска SMBCrunch
Подключиться к указанному хосту (-i 192.168.0.101), с логином и паролем (-a ‘Alexey:qweqwe123’), найденные сетевые папки записать в файл (-o shares_found.txt):
Программой Nmap просканировать порты (-p 139,445) в подсети (192.168.0.0/24) и собранные данные сохранить в файл, удобный для анализа программой grep (-oG portscan445.gnmap):
Используя файл с результатами сканирования Nmap из предыдущей команды (-i portscan445.gnmap), извлечь хосты с открытым портом 445 и подключиться с указанными учётными данными (-a ‘Alexey:qweqwe123’), сохранить списки сетевых папок в файл (-o shares_found.txt):
Используя файл со списком сетевых папок (-s shares_found.txt) подключиться к ним с указанными учётными данными (-c ‘Alexey:qweqwe123’), составить списки файлов и сохранить их в указанную директорию (-o share_listing) расходуя на каждую шару не более 150 секунд (-m 150):
Из файла share_listing/ALL_COMBINED_RESULTS.txt, содержащего все списки файлов, отфильтровать только удовлетворяющие указанному шаблону (grep -i ‘password.txt’), скачать их и сохранить в директорию (-s savedfiles):
Скачать исполнимые файлы (с расширением .exe) их всех сетевых папок, сохранить их в папку (savedfiles -n) и не добавлять в конец каждого файла информацию о нём (-s):
Установка SMBCrunch
Установка в Kali Linux
Установка в BlackArch
Программа предустановлена в BlackArch.
Информация об установке в другие операционные системы будет добавлена позже.
Источник
Взаимодействие сканеров уязвимостей с Metasploit. Часть 1
Мы начинаем цикл обучающих статей, посвященных взаимодействию сканеров уязвимостей с Метасплоитом.
Требуемое программное обеспечение: Kali Linux.
Необходимые знания: опыт работы с консолью Linux-систем (в частности, дистрибутивом Kali Linux) и консолью Метасплойта.
Большинство атак основано на уязвимостях в программном обеспечении или ошибках конфигурации. В связи с этим рекомендуемыми мерами для обеспечения информационной безопасности организации являются регулярное сканирование системы на наличие уязвимостей и тестирование на проникновение.
Сканирование на наличие уязвимостей позволяет проверить диапазон указанных IP-адресов на возможные проблемы в системе безопасности, предоставляя пентестерам информацию о вероятных векторах атак. При работе со сканерами уязвимостей нужно помнить, что они могут ошибаться и выдавать ложную или неправильную информацию.
Как известно, Metasploit Framework – это инструмент для создания, тестирования и использования эксплойтов. Но, благодаря поддержки модулей и плагинов, он вполне может сгодиться и для поиска уязвимостей.
В первой части мы рассмотрим модули, встроенные в Metasploit, которые позволяют выявить наиболее распространенные бреши в системах безопасности.
SMB Login Check
Модуль SMB Login Check подключается по протоколу SMB к заданному диапазону ip-адресов и определяет, можно ли по связке имя пользователя / пароль получить доступ к цели.
Подгружаем модуль
use auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_login
задаем необходимые настройки и запускаем его
Следует иметь ввиду, что такое сканирование не останется незамеченным, т.к. при каждой неудачной попытке аутентификации создается соответствующая запись в журнале Windows. В дальнейшем успешные результаты сканирования могут быть использованы в модуле эксплойта windows/smb/psexec для создания Meterpreter-сессии.
VNC-аутентификация
VNC-сканер будет искать VNC-сервера без парольной аутентификации. Некоторые сисадмины пренебрегают требованиями по обеспечению информационной безопасности и не устанавливают пароли для установки соединения, что обнаруживается в процессе сканирования. Для использования VNC-сканера сначала нужно выбрать модуль auxiliary/scanner/vnc/vnc_none_auth
задать настройки, а затем его запустить
По окончанию сканирования выведется результат со списком уязвимых VNC-серверов.
Веб-сканер WMAP
WMAP — многофункциональный веб-сканер по поиску уязвимостей, созданный на основе SQLMap. Благодаря взаимодействию с Metasploit, мы можем проводить сканирование веб-приложений прямо из фреймворка.
Для начала воспользуемся встроенным модулем Metasploit Web Crawler – поисковым роботом, который позволяет определить структуру сайта и работает вкупе с wmap’ом.
use auxiliary/scanner/http/crawler
укажем адрес сайта и его стартовую страницу (оставил значение по умолчанию). Теперь модуль готов к работе.
Далее загрузим плагин wmap
load wmap
На этом этапе сканирования у нас уже имеется информация о структуре сайта, которая сохранилась в нашей базе данных. Просмотреть её можно с помощью команды wmap_site –s [id], где id – номер цели в списке wmap_sites –l
wmap_site –s 0
Теперь определимся с целью
wmap_targets -t 192.168.42.129
Здесь можно задать как диапазон ip-адресов, так и указать url, ведущий на определенный раздел сайта.
Автоматический поиск уязвимостей запускается командой wmap_run
Посмотрим список модулей, которые доступны для сканирования нашей цели
wmap_run –t
Можно запустить как конкретный модуль, указав к нему путь, например, wmap_run -e auxiliary/scanner/http/robots_txt, так и запустить все перечисленные модули сразу (что мы и сделаем)
wmap_run -e
После завершения сканирования, информация об обнаруженных уязвимостях сохранятся в базе данных WMAP’а, Посмотрим, что же он там нашел
wmap_vulns –l
Источник
Packages and Binaries:
CTDB is a cluster implementation of the TDB database used by Samba and other projects to store temporary data. If an application is already using TDB for temporary data it is very easy to convert that application to be cluster aware and use CTDB instead.
CTDB provides the same types of functions as TDB but in a clustered fashion, providing a TDB-style database that spans multiple physical hosts in a cluster.
- CTDB provides a TDB that has consistent data and consistent locking across all nodes in a cluster.
- CTDB is very fast.
- In case of node failures, CTDB will automatically recover and repair all TDB databases that it manages.
- CTDB is the core component that provides pCIFS (“parallel CIFS”) with Samba3/4.
- CTDB provides HA features such as node monitoring, node failover, and IP takeover.
- CTDB provides a reliable messaging transport to allow applications linked with CTDB to communicate to other instances of the application running on different nodes in the cluster.
- CTDB has pluggable transport backends. Currently implemented backends are TCP and Infiniband.
- CTDB supports a system of application specific management scripts, allowing applications that depend on network or filesystem resources to be managed in a highly available manner on a cluster.
Installed size: 3.45 MB
How to install: sudo apt install ctdb
- iproute2
- libbsd0
- libc6
- libpopt0
- libtalloc2
- libtdb1
- libtevent0
- libwbclient0
- lsb-base
- psmisc
- samba-libs
- sudo
- tdb-tools
- time
Clustered TDB CTDB management utility
ctdb_diagnostics
Dump diagnostic information about CTDB/Samba installation
Источник
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
SMB and Samba Security Audit Tools
Table of contents
I composed a list of programs that somehow relate to security assessment and hacking of SMB protocol and Windows shares (network folders). A successful attack on SMB network folders can disclose Windows username and password.
I divided the picked up utilities into the following groups:
- SMB and network folders discovering. Shares and files enumeration
- Man-in-the-middle attack on SMB. Relays
- Brute-force attack on Windows user credentials via SMB
- SMB post-exploitation tools
- Nmap scripts for gathering information and auditing SMB
This is a fairly arbitrary division, since some programs can be placed in two groups at once, for example, the program looks for SMB balls on the network and tries different passwords.
1. SMB and network folders discovering. Shares and files enumeration
smbclient utilities
To get these programs, install the smbclient package.
Using the smbtree utility, you can detect Windows computers with shares:
Using the smbclient utility, you can view the network shared folders available on the computer:
In addition with smbclient, using the following command, you can connect to the network folder and perform normal file operations:
The previous two commands use the -N option to log in without a password. If you want to connect to a folder that requires authentication, use the -U option after which specify the username, and remove the -N option.
SMB discovering via port scanning
SMB uses ports 445 and 139, so computers with network shares can be searched using Nmap with a command of the form:

You can add the -oG option to save the results to a file – by the way, we will need such a file with some of the following programs:
enum4linux
The enum4linux program uses the tools from the Samba package to collect information using Windows shared folders.
num4linux is preinstalled on Kali Linux and BlackArch.
Let’s consider the usage of the most interesting options. Firstly, this option is -a, which means to collect all possible information:
Some systems are configured to allow anonymous login, but do not allow login without a password – that is, null sessions are prohibited there. To work around this problem, it is enough to specify any username, you can omit the password. Please note that it is important to specify a username not existing on the system where the share is located, otherwise access will not be allowed due to incorrect credentials. The username can be specified with the -u option:
enum4linux program usually itself correctly defines the workgroup and you do not need to specify it manually. But I was faced with a situation when a host on Linux, where the network folder was configured using Samba, enum4linux could not determine the workgroup and generated a lot of errors. To force a workgroup to be specified, use the -w option:


If you only want to get a list of shared folders, then specify the -S option instead of -a:

If you know the username and password to get access the network folder, then specify the username with the -u option, and the password with the -p option:
To get only a list of users, specify the -U option; for information about the operating system, use the -o option. Note that the -a option enables these options, and in total it activates the -U -S -G -P -r -o -n -i options.

ACB is present in the user profile – this is an account control block.
The following values can be:
The sum of the bits is used to describe the user.
Windows Server:
- 0x00000210 for Administrator (judging by the bits, the password has not expired, normal user)
- 0x00000215 for Guest (judging by the bits, the password has not expired, normal user, locked)
Windows 10:
- 0x00000214 for MiAl (judging by the bits, normal user, no password required – indeed, an account without a password)
- 0x00000214 for Tester (judging by the bits, normal user, no password required – in fact, the password is set)
- 0x00000010 for Administrator (judging by the bits, normal user, standard administrator account)
- 0x00000215 for the Guest (judging by the bits, the password has not expired, normal user, locked)
Values without the two hundredth bit (“Password has not expired”) I have also met in Samba (this is SMB for Linux), for example, 0x00000010.
Apparently 0x00000004 (User password not required) refers to access to a network folder, not an account.
nullinux
Nullinux, using SMB, can list OS information, domain information, network shares, directories, and users. If the username and password are not specified in the command line arguments, then an anonymous login or null session is tried. Nullinux is a wrapper for Samba tools (smbclient and rpcclient) to list hosts using various techniques.
nullinux is preinstalled on BlackArch. To install nullinux on Kali Linux, run the following commands:
By default, nullinux will list users and shared folders for all specified hosts. Using the command line arguments, you can configure the enumeration process.
Perform an anonymous connection, a null session for the host (192.168.0.1) with SMB and get information, including network folders and users:
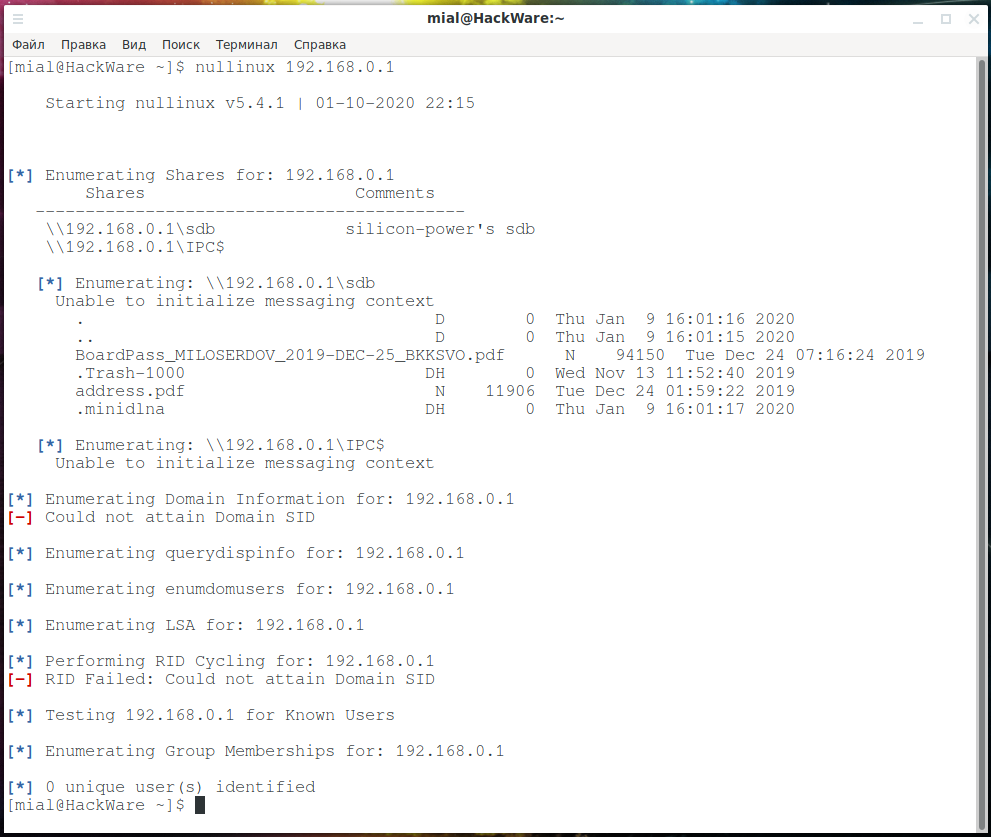
To gather information, connect to a host with a shared folder (192.168.0.101) using the known username (-U ShareOverlord) and password (-P 1234):
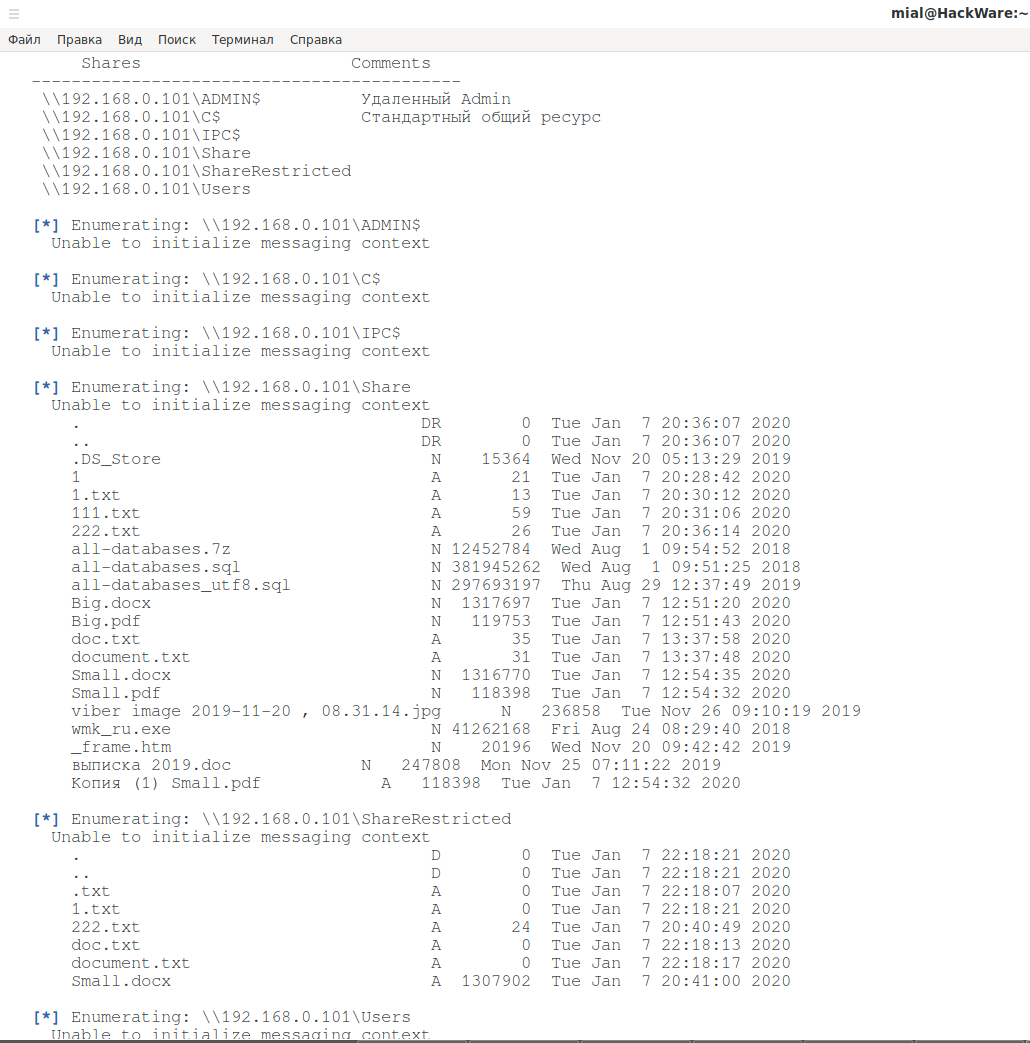
Get a list of shares and their contents (option -shares) for a list of hosts (192.168.0.89,192.168.0.1,192.168.0.101) using a username that does not exist on them (option -p anyuser) for anonymous login to hosts where it is impossible to log in without username:
Let’s look at a few more examples of using nullinux, which are described by the author of this program on wiki page.
Enumerate Multiple Hosts at Once
nullinux provides several options for enumerating users and shares from multiple hosts. Although this can be completed with other tools using a bash loop or Interlace, nullinux simplifies this process.
Creates a nullinux_users.txt File
By using the command line argument “-users”, nullinux will attempt to enumerate users through all available options and display the results on screen. nullinux will compile all users collected during enumeration into a single .txt file, free of duplicates. This nullinux_users.txt file can then be used for password spraying or other internal attacks.
Nullinux can also be set to use non-invasive or lengthy techniques to enumerate users through the «-quick» option. This will perform a quick enumeration of users leaving out brute force options such as known usernames, rid cycling, and enumerating the LSA.
Multi-Threaded RID Cycling
Nullinux will perform RID cycling during the user enumeration process, or as a stand-alone technique, on the target server. This is a multi-threaded process to decrease enumeration time and add functionality to the tool.
SMB Spider
The smbspider program displays the contents of Windows shares. The program works very quickly and, unlike other tools, it does not have problems when entering folders that do not require a password, but require any username. The program can search for files by certain phrases – this is very useful if a large number of shares (network folders) are found and you need to find a file with sensitive data on them, for example, passwords.txt files.
SMB Spider is installed on BlackArch, on Kali Linux it can be installed with the following commands:
To get the contents of a network folder, specify the -s option with the name of the folder, and the host must be specified after the -ip option:
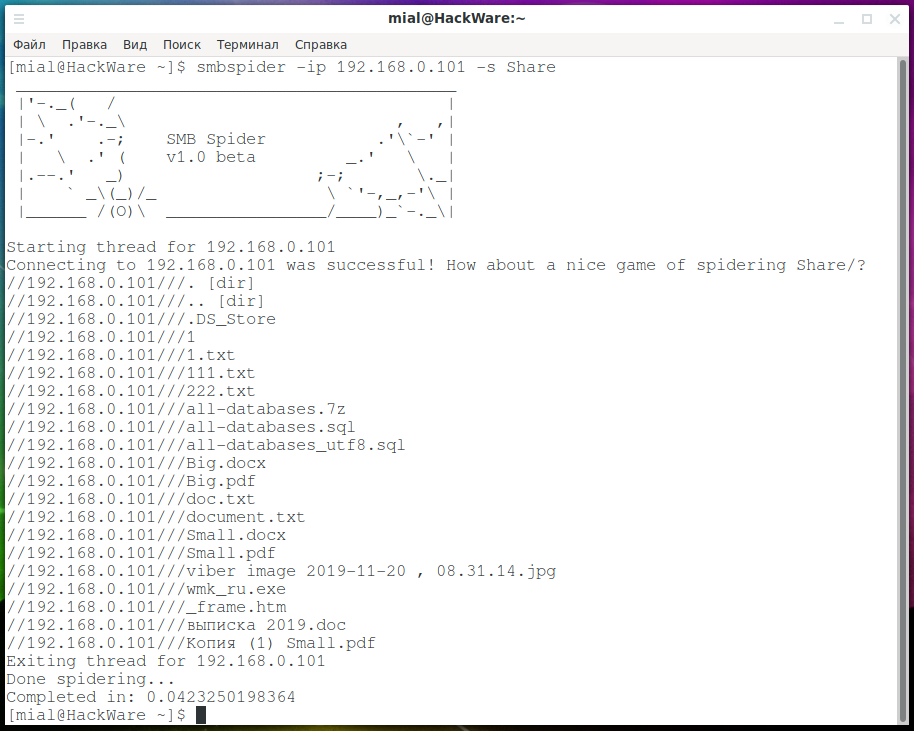
In the previous example, a null session will be used, if you know the username and password, specify the username after the -u option and the password after -p:
acccheck
acccheck can verify the credentials of network folders. The program supports working with lists of usernames and passwords, that is, it can be used for brute-force. Also, the program can work with a list of hosts, but it runs too long during my tests.
Like some other tools, this is wrap for ‘smbclient’ binary.
The acccheck program is available on Kali Linux; it can be installed on any other distribution using the following commands:
Mandatory is one of the following options:
This program can be used both for checking credentials on one host, and for checking many hosts whether the username and password for accessing the network folders are suitable for them.
Example of checking credentials on a single host:
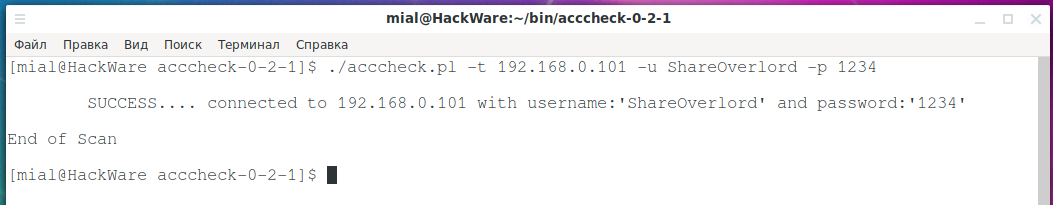
To mass check if the existing SMB credentials are suitable for some host on the network, first create a file with a list of hosts:
And the next command starts scanning the network shares and brute-force credentials for the entire local network:
In Kali Linux, use the acccehck executable name instead of ./acccheck.pl, for example:
If End of Scan is displayed, for example:
So a computer with SMB was found, but valid credentials were not found.
If the credentials is valid, then the output is approximately the following:
Credninja
SMBMap
SMBMap allows users to enumerate samba share drives across an entire domain. List share drives, drive permissions, share contents, upload/download functionality, file name auto-download pattern matching, and even execute remote commands. This tool was designed with pen testing in mind, and is intended to simplify searching for potentially sensitive data across large networks.
SMBMap is preinstalled on Kali Linux and BlackArch.
SMBMap usage example:
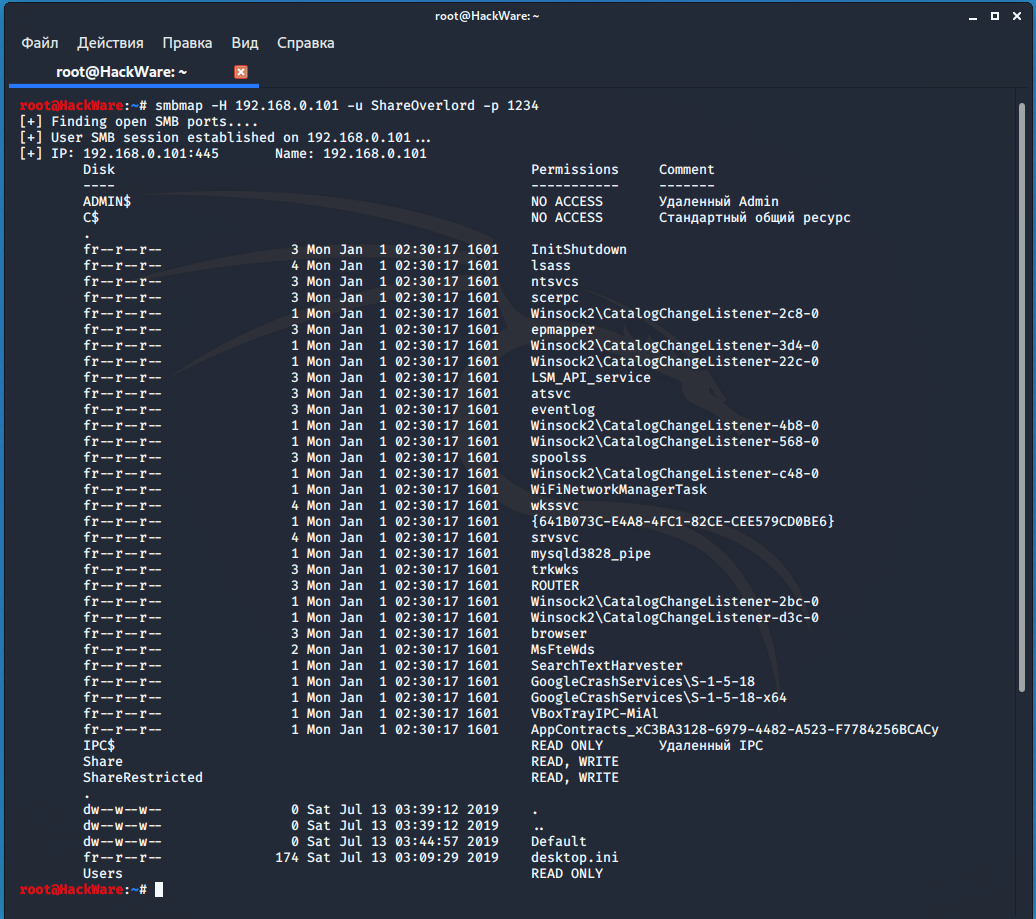
If you specify the -v option, information about the host operating system with a network folder will be displayed:

SPARTA
SPARTA is a Python-based graphical user interface (GUI) application that simplifies penetration testing of network infrastructure, assisting the penetration tester in the scanning and enumeration phase. It allows you to save time for the tester thanks to a simple graphical interface and the output of the received information in a readable form. The less time is spent on typing commands and tuning instruments, the more time can be spent focusing on analyzing the results.
Among others features, the program perform security auditing of SMB and brute-force SMB.
SMBCrunch
SMBCrunch is 3 tools that work together to gather information about Windows file shares (network folders). Tool Names:
- SMBHunt – searches for computers with network folders and lists shares
- SMBList – composes file lists of specified network folders based on the file generated by SMBHunt
- SMBGrab – grabs files from network folders based on the file generated by the SMBList program. Searching and filtering data can be done with grep.
These scripts can be used separately, but it is more convenient to use them one after another, transferring the generated files from one program to another.
SMBCrunch is preinstalled on BlackArch, to install on Kali Linux run:
There are two required options for SMBHunt.pl. The first is -i, after which you need to specify either the host, or the file with the list of hosts, or the file with the Nmap scan results. The second required option is -a, after it you must specify either a file with user credentials, or one pair of credentials. The username and password must be divided by a colon; if they are specified in the file, then one pair per line. After the -o option, you can specify a file to save data:
An example of connecting to a specific host:
And this is an example of preliminary scanning and gathering information from all hosts on which the open port 445 is found:

The program SMBList.pl also has two required options. After the -c option, you need to specify a username and password, or a file with credentials. After the -s option, specify the file that was generated by the previous program. After the -o option, you can specify the name of the directory where the compiled lists of files on network folders will be saved:

A complete list of all files in network folders is collected in the file share_listing/ALL_COMBINED_RESULTS.txt, and separate files for each network folder are compiled.
The SMBGrab.pl script accepts a list of files not through an option, but through standard input. Thanks to this approach, grep can filter the files you need to download.
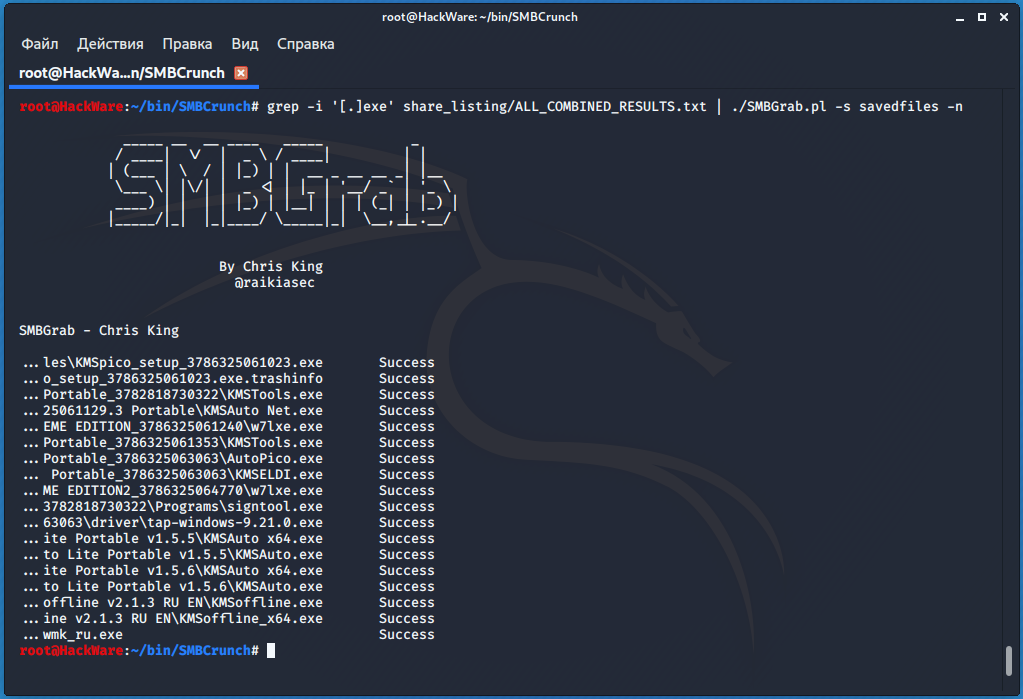
In the following example, only lines containing ‘password.txt‘ will be found in the file share_listing/ALL_COMBINED_RESULTS.txt, these lines will be piped to the SMBGrab.pl program and it will save them to the savedfiles directory:
Please note that by default, SMBGrab.pl adds information about this file (download, creation timestamps, etc.) to each file. And it adds to any files – including binary ones. To keep the files in their original form, specify the -n option. An example of a command in which .exe files are downloaded and saved in their original form:
2. Man-in-the-middle attack on SMB. Relays
Responder
Responder is a tool for performing a man-in-the-middle attack against authentication methods in Windows. This program includes the LLMNR, NBT-NS and MDNS poisoner to redirect requests and authentication hashes traffic. The program also includes HTTP/SMB/MSSQL/FTP/LDAP authentication rogue servers that support authentication methods such as NTLMv1/NTLMv2/LMv2, Extended Security NTLMSSP and basic HTTP authentication, for which the Responder acts as a relay.
That is, the Responder intercepts usernames and authentication hashes on the network with Windows computers. After breaking the hash, the user password is revealed.
To launch an attack, you need to run a command of the form:
Where instead of the word INTERFACE you need to specify the name of the network interface in your system on which you want to carry out the attack.
For more details, as well as a way to crack authentication hashes, see the article “Windows Network Authentication Hacking”.
Inveigh
Intercepter-ng
Intercepter-NG is a multifunctional network toolkit for IT professionals of various types. The main goal is to restore interesting data from the network stream and perform various kinds of man-in-the-middle attacks (MiTM). In addition, the program allows you to detect ARP spoofing (can be used to detect MiTM), identify and exploit some types of vulnerabilities, brute-force login credentials for network services. The program can work both with live traffic flow and analyze files with captured traffic to detect files and credentials.
SMB related features:
- Reconstructing files from SMB
- SMB relay
- SMB Hijack (interception)
Ettercap. Ettercap Plugins
Ettercap is a comprehensive man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attack kit. It is able to sniff live connections, filter on the fly the contents of the transmitted data and many other tricks. It supports active and passive tampering of many protocols and includes many functions for network and host analysis.
Among the Ettercap plugins, there are two plugins aimed at attacking the SMB protocol.
smb_clear
It forces the client to send smb password in clear text distorting protocol negotiations. You must be in the middle of the connection to use it successfully. It hooks the smb dissector, so you will keep it active. If you use it against a Windows client, then the result is unlikely to be successful. Try it against *nix smbclient.
smb_down
It forces the client not to use NTLM2 password exchange during smb authentication. Thus, hashes are obtained that can easily be cracked in LC4. You must be in the middle of the connection to use it successfully. It hooks the smb dissector, so you will keep it active.
MITMf
MITMf is a framework for Man-In-The-Middle attacks. This tool is based on sergio-proxy and is an attempt to revive and update this project.
SMB related modules:
Netcreds
Net-Creds carefully sniffs passwords and hashes from the interface or from the pcap file. Combines fragmented packets and does not rely on ports to identify the service. It supports SMB protocol.
3. Brute-force attack on Windows user credentials via SMB
patator
The patator program is designed for brute-force credentials and is one of the most flexible to configure.
For online brute-force login and user password to access the network shared folder (and therefore the Windows user credentials), run a command of the form:
In this command:
- ./patator.py is the name of the executable file, depending on the installation method it may be patator
- smb_login is SMB brute force module
- host=192.168.0.101 is IP address of the computer with SMB. You can specify a file with hosts (more precisely, the file placeholder number)
- user=FILE0 is username for brute force. Instead of a name, a placeholder with a pointer to file number 0
- password=FILE1 is password for brute force. Instead of a single password, a placeholder is written with a pointer to the file number 1
- 0=/root/logins.txt is path to file number 0
- 1=/root/passwords.txt is path to file number 1
- -x ignore:fgrep=’STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE’ means do not display attempts, in response to which the line STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE was received

That is, two pairs of credentials were found:
Obtained computer name and version of Windows:
- \HACKWARE-MIAL (Windows 10.0 Build 18362)
Another account was found for which the message STATUS_ACCOUNT_RESTRICTION was received:
The message said that there are account restrictions for the mial user. The reason is that the username and password are correct (empty password), but users without a password are not allowed on this computer.
Hydra
The hydra program supports a huge number of services, thanks to its speed and reliability, it has earned well-deserved appreciation among penetration testers.
Example command to start the brute force SMB:
To say true, I did not succeed due to an error:
Medusa
Medusa is a fast, parallel, and modular login brute-forcer. The goal is to support as many services on which remote authentication as possible.
Example command launch:
The reason for it, most likely, is that on the host where I want to brute-force the username and password of Windows users, support for the SMB 1 protocol is disabled. In Medusa, you can specify the authentication method:
In this case, another error occurs:
The essence of the message is that NTLMv2 is disabled, and LMv2 should be enough for us.
APT2 is a suite of tools for automated penetration testing.
Modules for SMB security audit:
BruteSpray
BruteSpray accepts the results of nmap GNMAP/XML scans and, using Medusa, automatically brute-force services using dictionaries with standard logins and passwords. BruteSpray can even find non-standard ports using the -sV option inside Nmap.
4. SMB post-exploitation tools
CrackMapExec is an all-in-one tool for testing the Windows/Active Directory environment. It is inspired/based on previous developments, including, as a submodule, it includes the PowerSploit repository.
The program can enumerate logged-in users and index SMB shared folders, perform psexec-style attacks, automatic Mimikatz/Shellcode/DLL injections into memory using Powershell, dumping NTDS.dit and more!
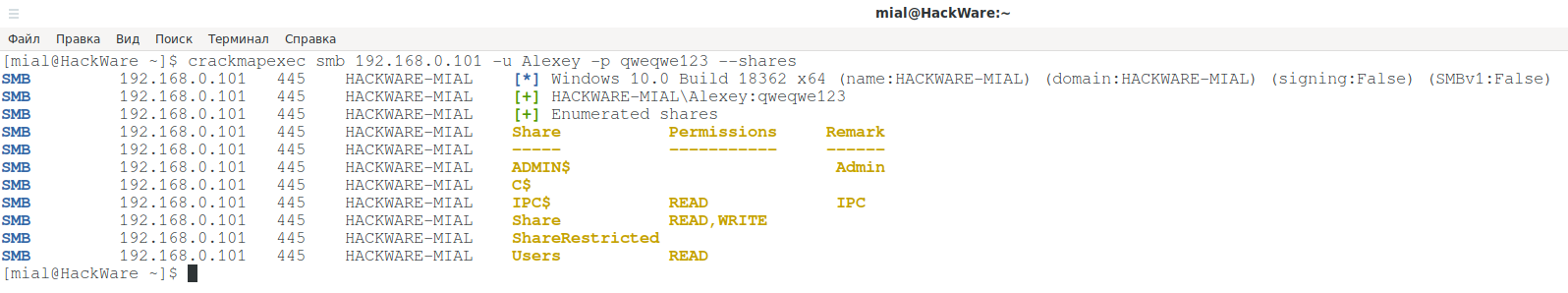
An example of listing shared folders:
keimpx
It can be used to quickly check for valid credentials across a network over SMB. Credentials can be:
- Combination of user / plain-text password.
- Combination of user / NTLM hash.
- Combination of user / NTLM logon session token.
If any valid credentials are discovered across the network after its attack phase, the user is asked to choose which host to connect to and which valid credentials to use. They will then be provided with an interactive SMB shell where the user can:
- Spawn an interactive command prompt.
- Navigate through the remote SMB shares: list, upload, download files, create, remove files, etc.
- Deploy and undeploy their own services, for instance, a backdoor listening on a TCP port for incoming connections.
- List users details, domains and password policy.
Scan the subnet (-t 192.168.0.0/24) by checking the validity of the username (-U Alexey) and password (-P qweqwe123) for all hosts with shares:
Connect to the remote host (-t 192.168.0.101) using the username (-U Alexey) and password (-P qweqwe123):
As a result, the specified credentials will be checked for correctness. If they are correct, you will be prompted to connect and open an interactive shell to interact with the remote system.

Pupy is an open source tool for remote administration and subsequent operation (post-exploitation), working on various platforms (Windows, Linux, OSX, Android).
5. Nmap scripts for gathering information and auditing SMB
There are quite a few Nmap scripts for SMB analysis or information gathering. Usually they are quite specific (for example, checking for a specific vulnerability or for infection with a specific backdoor) and/or outdated. Nevertheless, some scripts provide unique information, for example, versions of SMB dialects supported by a computer with network folders. Another reason to get acquainted with NSE (Nmap scripts) is that among real servers there are quite old ones.
The script name is specified after the —script option. Moreover, you can engage all SMB scripts, because the names support wildcards:
But the completion of the previous command never happened for me… Therefore, I specify one script at a time.
Each time the script is run, Nmap scans the ports: unless otherwise specified by the options, the 1000 most common ports are checked. This can be time consuming, especially when sequentially checking with several scripts. Without port scanning scripts will not work, that is, you cannot specify the -sn option. But the scanning time can be reduced if you specify only one port – TCP port 445, which is bind by SMB.
Examples of gathering information about SMB using Nmap scripts.
I tested on 4 different systems: two Windows 10 computers with different settings (with permission to enter with and without password; with SMB 1 support and without), one Linux system with Samba and one router with Samba. Only a few scripts worked for me – they are all listed below. However, you may be more fortunate and find older machines where scripts come in handy, so the following is a complete table of Nmap scripts related to SMB.
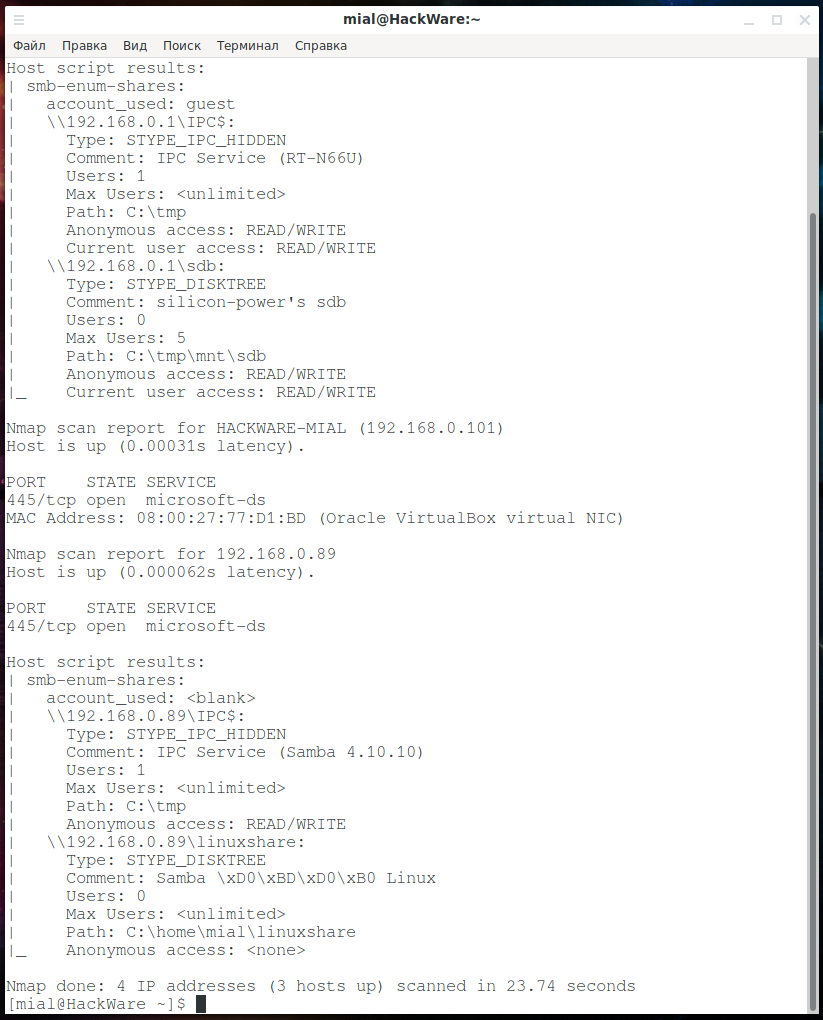
smb-enum-shares. Listing network folders on a host:
smb-protocols. Getting information about supported protocols:

smb2-capabilities. Checking the capabilities of the SMB 2 protocol:

smb2-security-mode. Security Mode Settings:

smb2-time. Getting time via SMB:
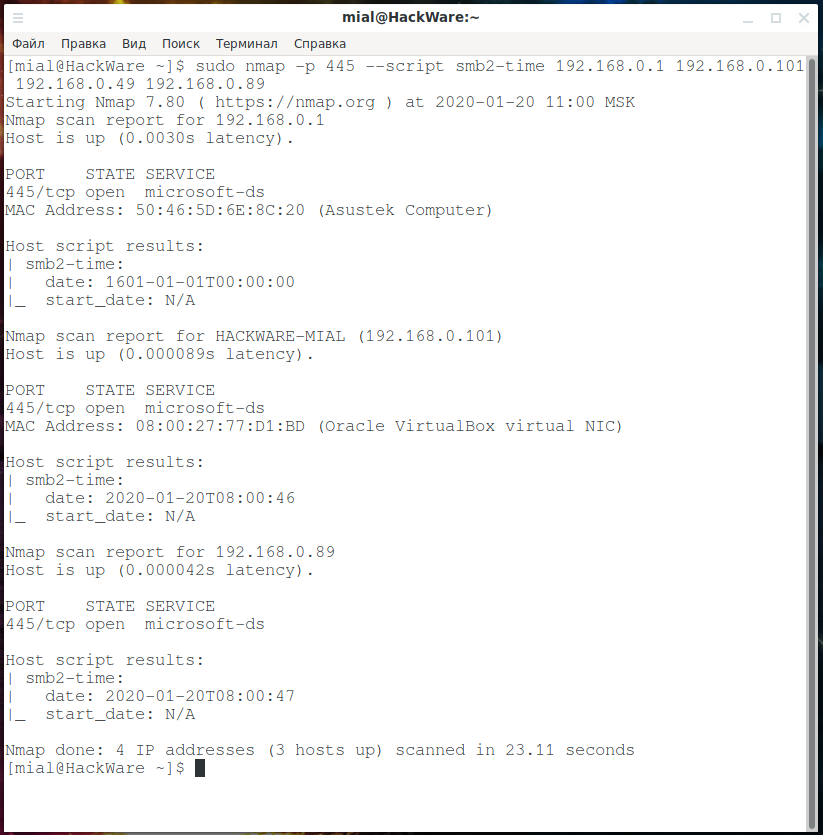
smb-os-discovery. Operating System Information:
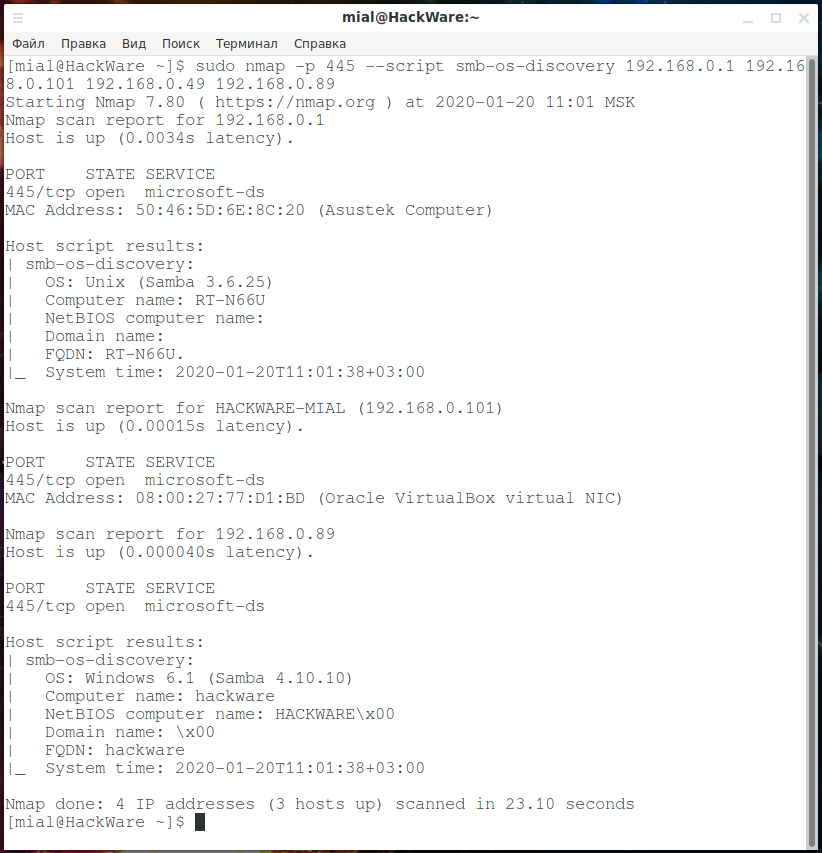
Arguments can be passed to some scripts (see the details for each specific script), the —script-args option is used for this, for example: —script-args=’smbusername=Alexey,smbpassword=qweqwe123′
Below is a table with all Nmap scripts (NSE) for checking or gathering information about SMB.
| Script Name | Description |
|---|---|
| smb-brute |




