- Kali linux ssh root
- Enabling the root account
- Enabling root for SSH
- Enabling root for GNOME and KDE login
- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- How to enable SSH in Kali Linux. How to connect to Kali Linux via SSH
- SSH on Kali Linux on ARM computers
- SSH in Kali Linux on desktop computers
- How to connect to Kali Linux via SSH
- Why SSH does not accept root password
- How to configure key authentication in Kali Linux (SSH without password)
- Packages and Binaries:
- openssh-client
- openssh-server
- openssh-sftp-server
- openssh-tests
- ssh-askpass-gnome
- Статья Включение SSH на Kali Linux
- Pirnazar
- The Codeby
Kali linux ssh root
There are some cases where you may need to use superuser, root, for an extended period of time. In these cases we can easily access the root account with a simple sudo su (which will ask for the current user’s password), selecting the root terminal icon in the Kali menu, or alternatively using su — (which will ask for the root user’s password) if you have set a password for the root account that you know of. When finished, exit or CTRL+D will take us out of this elevated shell.
However, there may be other times where you may want to use root across multiple sessions without the hassle of elevating privileges. In these situations we will need to install a package and make a few modifications to fully enable the root account for use due to security reasons of keeping the root account disabled by default.
Enabling the root account
The first thing to do is set a root password, which should be different to the current user’s password (in this case kali ). We can do this by doing the following:
Please note that the password prompt will not display output as you are typing in the password, but it will still register the keystrokes.
The next thing we need to decide is if we are wanting to use root via SSH or through the login prompt on whichever desktop environment is installed.
Enabling root for SSH
If we look at /etc/ssh/sshd_config we will see a PermitRootLogin line. We will want to change this line to match our use case.
If we have set up SSH key based login for the root account, then we can simply uncomment the appropriate line and continue on. Otherwise, we should change PermitRootLogin to be yes which will allow us to input a password.
Enabling root for GNOME and KDE login
We will first install kali-root-login to change multiple configuration files that will permit us to login to the root account through the GNOME GDM3 and the KDE login prompt. This step is not necessary when using other desktop environments.
We can now log out of our non-root user account and login to root using the password that we set earlier.
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: gamb1t
Источник
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
How to enable SSH in Kali Linux. How to connect to Kali Linux via SSH
SSH allows ones to connect to a remote computer and execute commands on it, connecting and transmitting data occurs via an encrypted channel, which is protected from various attacks of interception and data sniffing and spoofing.
SSH includes two programs: a server and a client. The server is installed on a remote machine, to which you need to connect and execute commands on it. The client is designed to connect to a remote machine.
The SSH server acts as a service that listens on port 22 by default. When connecting by default, password authentication is used – you need to enter the user password on the remote Linux system. You can also configure public key based authentication – this option is more convenient (no password is required) and more secure (keys are less prone to brute force).
Speaking about SSH in Kali Linux, you need to consider that this distribution is available in various versions (see details ‘Where to download Kali Linux. What is the difference between Kali Linux versions’): for personal computers, for ARM computers, for mobile phones, for virtual machines. Consider the specific of SSH in Kali Linux for PC and for ARM.
SSH on Kali Linux on ARM computers
Since usually ARM devices are resource-limited computers without a display, you can only manage them by connecting via SSH. For this reason, the SSH service on such devices is already installed and running by default.
In such systems, use a couple as login credentials:
- User: kali
- Password: kali
The problem with ARM devices without a screen may be that their IP address is not known, because in most local networks IP addresses are automatically assigned by the DHCP protocol. Typically, routers allow you to view a list of devices and their IP addresses. If you do not have such an opportunity, then IP can be found by scanning the network, for example, with the command:
Or by the command:

Instead of _gateway, the Linux operating system will substitute the IP address of your router, as a result, you will get _gateway/24, that is, your local network will be scanned, for example, 192.168.1.0/24. Or, explicitly specify the range for scanning.
SSH in Kali Linux on desktop computers
Kali Linux has already installed the SSH package, but its automatic launch is disabled (like all other network services). Therefore, to connect to Kali Linux via SSH, you need to start this service. If desired, it can be added to auto startup.
There are two options for starting the SSH service:
- ssh.service – SSH service will always be running
- ssh.socket – the system will open port 22 for listening and will wait for a connection to it. If connection happened, the system will start the SSH service. For the rest of the time (when there is no SSH connection), the SSH service will be stopped and will not consume system resources.
The second option is more preferred.
To start the SSH service on Kali Linux:
To add a service to startup:
To check the status of a service:

How to connect to Kali Linux via SSH
The command to connect is as follows:
As the IP_ADDRESS of the remote system, you need to specify its IP. You can find out the IP address with the command:
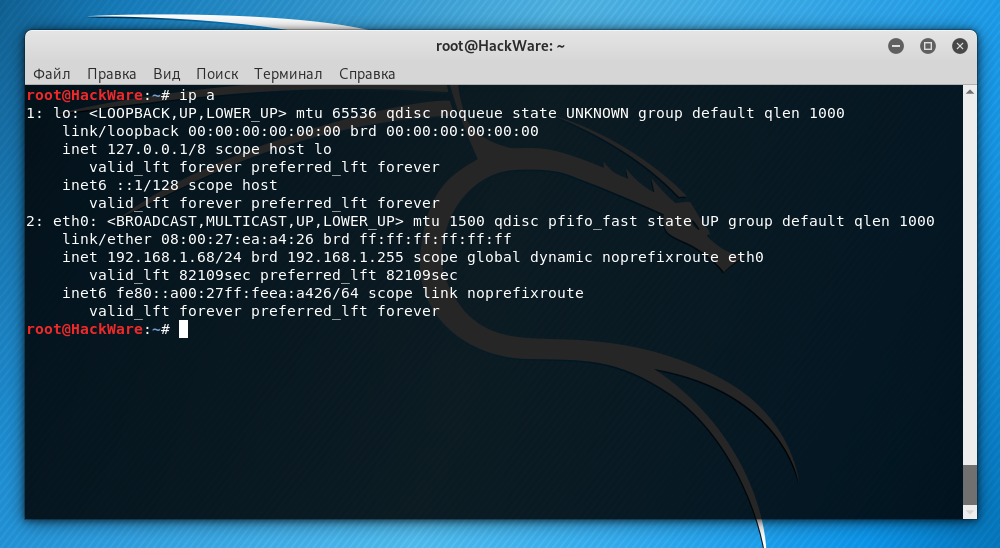
By the way, in order for Kali Linux to always have the same IP address after rebooting, you need to configure a static IP, as described in the article “How to configure Kali Linux to use a static IP address”.
In this case, the Kali Linux IP address is 192.168.1.68. The default user is root. Then the command should be as follows:
But the problem is that in SSH, by default, the authentication via password for the root user is blocked. There are two options to cope the problem:
- authentication via password for root
- configure authentication with keys
We will consider both of them, but I recommend the second option, as safer and more convenient.
Why SSH does not accept root password
SSH service configuration is performed in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file. Let’s open it:
and replace it with:
Save and close the file.
You do NOT need to restart the SSH service, because when you select the ssh.socket option, this service is already stopped and will only be launched the next time you try to connect via SSH.
At the very first connection, the program will display a message:
We type: yes
Then enter the password and we find ourselves in Kali Linux:
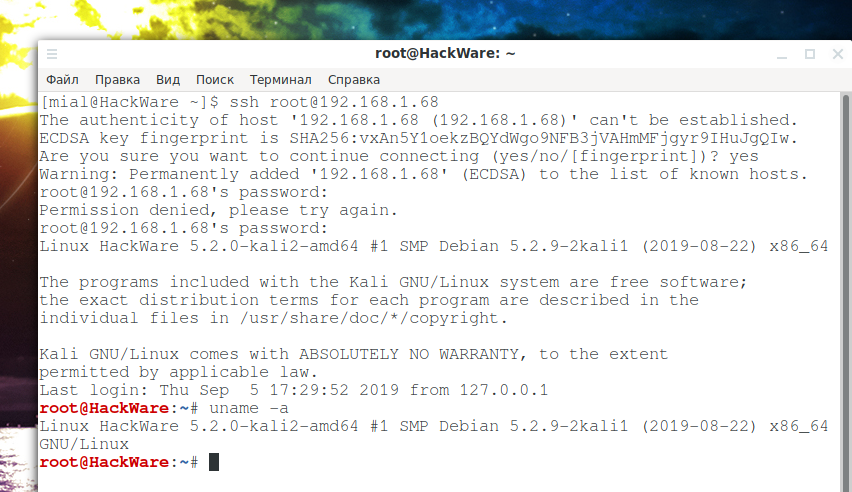
The fact that we are in a different system is indicated by the changed command line prompt – now there is the username and host name of the remote system.
How to configure key authentication in Kali Linux (SSH without password)
Disconnect from the remote machine. And on the local machine, execute the command:
Again, without a preliminary connection, we execute the command on the remote machine (change the IP and username to yours):
Now we need to copy the contents of the id_rsa.pub file to the remote machine. It is very simple to do this (do not forget to change the data to your own):
After that, we connect as usual, but the login will no longer require a password:
Источник
Packages and Binaries:
openssh-client
This is the portable version of OpenSSH, a free implementation of the Secure Shell protocol as specified by the IETF secsh working group.
Ssh (Secure Shell) is a program for logging into a remote machine and for executing commands on a remote machine. It provides secure encrypted communications between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network. X11 connections and arbitrary TCP/IP ports can also be forwarded over the secure channel. It can be used to provide applications with a secure communication channel.
This package provides the ssh, scp and sftp clients, the ssh-agent and ssh-add programs to make public key authentication more convenient, and the ssh-keygen, ssh-keyscan, ssh-copy-id and ssh-argv0 utilities.
In some countries it may be illegal to use any encryption at all without a special permit.
ssh replaces the insecure rsh, rcp and rlogin programs, which are obsolete for most purposes.
Installed size: 4.19 MB
How to install: sudo apt install openssh-client
- adduser
- dpkg
- libc6
- libedit2
- libfido2-1
- libgssapi-krb5-2
- libselinux1
- libssl1.1
- passwd
- zlib1g
OpenSSH secure file copy
OpenSSH secure file transfer
slogin
OpenSSH remote login client
OpenSSH remote login client
ssh-add
Adds private key identities to the OpenSSH authentication agent
ssh-agent
OpenSSH authentication agent
ssh-argv0
Replaces the old ssh command-name as hostname handling
ssh-copy-id
Use locally available keys to authorise logins on a remote machine
ssh-keygen
OpenSSH authentication key utility
ssh-keyscan
Gather SSH public keys from servers
openssh-server
This is the portable version of OpenSSH, a free implementation of the Secure Shell protocol as specified by the IETF secsh working group.
Ssh (Secure Shell) is a program for logging into a remote machine and for executing commands on a remote machine. It provides secure encrypted communications between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network. X11 connections and arbitrary TCP/IP ports can also be forwarded over the secure channel. It can be used to provide applications with a secure communication channel.
This package provides the sshd server.
In some countries it may be illegal to use any encryption at all without a special permit.
sshd replaces the insecure rshd program, which is obsolete for most purposes.
Installed size: 1.52 MB
How to install: sudo apt install openssh-server
- adduser
- debconf | debconf-2.0
- dpkg
- libaudit1
- libc6
- libcom-err2
- libcrypt1
- libgssapi-krb5-2
- libkrb5-3
- libpam-modules
- libpam-runtime
- libpam0g
- libselinux1
- libssl1.1
- libsystemd0
- libwrap0
- lsb-base
- openssh-client
- openssh-sftp-server
- procps
- runit-helper
- ucf
- zlib1g
openssh-sftp-server
This is the portable version of OpenSSH, a free implementation of the Secure Shell protocol as specified by the IETF secsh working group.
Ssh (Secure Shell) is a program for logging into a remote machine and for executing commands on a remote machine. It provides secure encrypted communications between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network. X11 connections and arbitrary TCP/IP ports can also be forwarded over the secure channel. It can be used to provide applications with a secure communication channel.
This package provides the SFTP server module for the SSH server. It is needed if you want to access your SSH server with SFTP. The SFTP server module also works with other SSH daemons like dropbear.
OpenSSH’s sftp and sftp-server implement revision 3 of the SSH filexfer protocol described in:
Newer versions of the draft will not be supported, though some features are individually implemented as extensions.
Installed size: 137 KB
How to install: sudo apt install openssh-sftp-server
openssh-tests
This package provides OpenSSH’s regression test suite. It is mainly intended for use with the autopkgtest system, though can also be run directly using /usr/lib/openssh/regress/run-tests.
Installed size: 5.43 MB
How to install: sudo apt install openssh-tests
- libc6
- libselinux1
- libssl1.1
- openssh-client
- openssh-server
- openssh-sftp-server
- openssl
- putty-tools
- python3-twisted
- zlib1g
This metapackage is a convenient way to install both the OpenSSH client and the OpenSSH server. It provides nothing in and of itself, so you may remove it if nothing depends on it.
Installed size: 262 KB
How to install: sudo apt install ssh
ssh-askpass-gnome
This has been split out of the main openssh-client package so that openssh-client does not need to depend on GTK+.
You probably want the ssh-askpass package instead, but this is provided to add to your choice and/or confusion.
Installed size: 294 KB
How to install: sudo apt install ssh-askpass-gnome
- libc6
- libglib2.0-0
- libgtk-3-0
- libx11-6
- openssh-client | ssh
Источник
Статья Включение SSH на Kali Linux
Kali Linux не поставляется с задействованным SSH. SSH — это предпочитаемый метод удалённого управления для большинства основанных на Linux систем. Безопасная оболочка (SSH) — это криптографический протокол сети для безопасного обмена данными, удалённого входа по командной строке, удалённого выполнения команд и других безопасных сетевых услуг между двумя соединёнными компьютерами. Соединение осуществляется, безопасным каналом в небезопасной сети, между сервером и клиентом, на которых запущен SSH сервер и SSH клиентская программа.
1) Установка сервера OpenSSH
Первый шаг — идём в окно терминала и устанавливаем сервер OpenSSH. Это делается выполнением следующей команды:
У меня выдало вот такое сообщение, в любом случае, продолжаем:
2) Настраиваем SSH для постоянной работы. Другими словами, для сохранения после перезагрузки.
a) Сначала нам нужно удалить уровень выполнения для SSH следующей командой:
3) Меняем дефолтные SSH ключи
Теперь нам нужно заменить дефолтные SSH ключи. Причина этого в том, что каждый Linux и Unix дистрибутив имеют схожие ключи. Потенциально, атакующие могут угадать и взломать ваши SSH ключи и эксплуатировать вашу систему используя техники человека-по-середине.
a) Бэкапим и удаляем дефолтные ключи Kali Linux
b) Создаём новые ключи
Печатаем следующую команду в терминальном окне:
4) MOTD – Message of the Day banner (приветственный баннер)
Вы можете создать приветственный баннер, также известный как Message of the Day (MOTD) на Kali Linux, который показывается когда пользователи входят.
Просто отредактируйте файл /etc/motd (перезапустите ssh после того, как вы завершили редактирование).
Отредактируйте этот файл и вставьте ваш текст.
для графического интерфейса редактирования файла используйте vim -g /etc/motd)
a) MOTD – Сообщение приветственного баннера
Лично мне нравятся делать приветствие из ASCII картинки. Идём сюда для создания вашей собственной картинки ASCII
Мы добавили следующий текст в приветственный баннер:
Видим, что SSH входит в чёрный список. Поэтому открываете этот файл /usr/sbin/update-rc.d
Pirnazar
The Codeby
ООО Кодебай
KREIZ
29.08.2015 в 04:23
не получилось. после установки sshd уже был в системе, только приходилось включать руками. после выполнения п.2 – перестал даже включаться. что делать теперь?
WEBWARE TEAM
29.08.2015 в 18:12
Дополнено для Kali 2.0.
J.D.
07.04.2016 в 14:15
На 2016.1 включается командой update-rc.d -f ssh remove && update-rc.d ssh enable . Для тех, у кого с этим трудности
ALEX1917
06.01.2017 в 03:44
Здравствуйте, помогите решить проблему следующего характера: Поставил Kali LXSD Работала нормально, но потом что-то случилось, и как выключю пк, чтобы снова сесть за компьютер ставлю её заново, т.к. после установки, обновления держу в аптайме по мере возможности, у меня один компьютер сгорел, еле набрал средств на новый, опасаюсь! Ранее включал и выключал и веб-браузеры не исчезали, а так же все приложения исчезают, соответственно терминала тоже нет, а в меню приложений остается 2 пункта. 1) Выйти; 2) Выполнить. Поставил старого гнома 2016(1) Дал команду обновится, но в конце выходит это, чтобы я не делал:
KREIZ
30.08.2015 в 12:02
спасибо, но не помогло. найдется альтернативный вариант – отпишусь.
MADDOG719
02.09.2015 в 12:36
Привет, помоги плиз, одна надежда на Вас)) вообщем не могу запустить ssh на Kali 2.0 все сделал как указано в статье, но не работает. Показывает следующую ошибку:
Очень надеюсь на Вашу помощь. В любом случае большое спасибо)
WEBWARE TEAM
02.09.2015 в 14:39
Ошибку вижу, а что вы делаете чтобы получить эту ошибку? Неужели на чистой системе просто ввели команды из этой статьи и всё сломалось?
Это у вас, наверное, вывод по systemctl status ssh. Выводит ли что-нибудь sshd -t?
Вносились ли изменения в файл /etc/ssh/sshd_config ? Добавляли ли сетевые интерфейсы? Работаете под рутом? Не прослушивает ли другая программа порт 22 или не меняли ли стандартный порт?
В файле /etc/ssh/sshd_config директива ListenAddress у вас закомментирована? Если нет, попробуйте закомментировать и запустить.
MADDOG719
02.09.2015 в 15:19
Огромное спасибо, закоментировал строчку, и врое как запустился.
EMIL
22.09.2015 в 13:27
не помогло. все отлично работает только при рестарте ssh не запускаеться автоматически
сделал ssh enable так как сказано. не помог
EMIL
22.09.2015 в 14:04
все решил. rcconf И там поставил галочку на ssh. дальше reboot и все работает.
ZEMLIA-ZEMLIA
05.12.2015 в 23:13
Не пускало после выполнения данных действий, посмотрел конфиг ssh (а настраиваю kali 2.0 )
там стоит по умолчанию PAM аутентитификация, и к ней включен параметр PermitRootLogin without-password
и закоментирован параметр PasswordAuthentication yes
Поэтому при попытке подключиться пишет пермишен денайт
надо соответствено PermitRootLogin without-password закоментировать
и PasswordAuthentication yes раскоментировать )
COBRA HACKING
01.06.2016 в 13:26
MAdDog719, эту у вас ssh ругается на то что включен без парольный вход под учеткой root
Источник



