- Kali linux virtualbox guest additions
- Kali Linux & VirtualBox Guest Addition (Legacy)
- Preparing
- Installing
- Creating Shared Folders with the Host System
- Установка VirtualBox Guest Additions на Kali Linux 1.1.0 (Debian, Ubuntu)
- 11 thoughts to “Установка VirtualBox Guest Additions на Kali Linux 1.1.0 (Debian, Ubuntu)”
- Kali linux virtualbox guest additions
- Wizard
Kali linux virtualbox guest additions
This will NOT show up in the index or search.
It is kept around for historical reasons and may no longer be accurate.
Kali Linux & VirtualBox Guest Addition (Legacy)
This page is dated. You can find the latest version here: Install VirtualBox Guest Additions.
If you run Kali Linux as a “guest” within VirtualBox, this article will help you to successfully install the “Guest Addition” tools.
You must use VirtualBox 4.2.xx or higher in order to take advantage of the improvements, including compatibility updates, and enhanced stability of both the core application and the Guest Additions.
Preparing
Start up your Kali Linux virtual machine, open a terminal window and issue the following command to install the Linux kernel headers.
Once this is complete you can now attach the Guest Additions CD-ROM image. This can be done by selecting Devices from the VirtualBox menu and then select Install Guest Additions.
This will mount the Guest Additions ISO in the virtual CD drive in your Kali Linux virtual machine. When prompted to autorun the CD, click the Cancel button.
Installing
From a terminal window, copy the VboxLinuxAdditions.run file from the Guest Additions CD-ROM to a path on your local system. Ensure it is executable and run the file to begin the installation.
Reboot the Kali Linux VM to complete the Guest Additions installation. You should now have full mouse and screen integration as well as the ability to share folders with the host system.
Creating Shared Folders with the Host System
This section explains how to share folders on your host system with your Kali Linux VirtualBox “guest”.
From the VirtualBox Manager, select your Kali Linux VM instance and click on the Shared Folders link in the right window pane. This will launch a pop up window for adding shared folders. Within this window click the Add Folders icon.
In the Folder Path text box, provide the path to the folder you would like to share, or click the drop-down arrow to browse your host system for the path to the folder. Select the check boxes that allow for Auto-mount and Make Permanent and click the OK button both times when prompted.
Your shared folders will now be available in the media directory. You can create a bookmark or link for easier access to the directory.
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: g0tmi1k
Источник
Установка VirtualBox Guest Additions на Kali Linux 1.1.0 (Debian, Ubuntu)
Возможно вас заинтересует новая актуальная статья «Установка Дополнений гостевой ОС VirtualBox для Kali Linux 2.0».
Здесь описано решение для установки Guest Additions на Kali Linux, но оно в полной мере применима для Debian и любых дистрибутивов основанных на Debian, а также для Ubuntu и любых дистрибутивов основанных на Ubuntu.
После установки операционной системы на VirtualBox первое, что хочется сделать, это установить Guest Additions (VboxGuestAdditions.iso). Ведь эти дополнения дают массу преимуществ, фактически, они выполняют роль драйверов для виртуального компьютера. В некоторые дистрибутивы Linux’а Guest Additions встроен по умолчанию — это очень удобно, не нужно даже думать про его установку. Но с Debian ситуация иная.
Когда я стал устанавливать Guest Additions на Kali Linux 1.1.0, то я столкнулся с рядом проблем. Эти проблемы я разрешил и, чтобы сэкономить ваше время, делюсь своими советами.
Итак, я начал с того, что смонтировал VboxGuestAdditions.iso и стал запускать autorun.sh. Вместо того, чтобы запуститься и выполниться как программа, мне открывалось содержимое этого файла (хотя галочка на запуск как приложение стояла). Эту проблему я решил скопировав все файл VBoxLinuxAdditions.run на жёсткий диск и присвоил емуправо на исполнение как приложения.
Теперь при запуске VBoxLinuxAdditions.run в консоли отображалась информация о том, что удаляется старая версия Guest Additions и пробуется установиться новая, но эта попытка неизменно заканчивалась состоянием ‘fail‘ и советом посмотреть файл var/log/vboxadd-install.log.
Это я и сделал, в этом файле содержалась следующая информация.
Гугл + тематическая ветка форума подсказали ответ. Пометка для новичков: команды набирайте без символов $ и # — эти символы служат только индикатором работы под суперпользователем или под обычным пользователем.
Во-первых, нужно убедиться, что у нас обновлённая версия, в консоли нужно набрать следующую команду:
ИЛИ как рут ввести:
Ищем версию ядра (это опционально), в консоли нужно набрать следующую команду:
Если у вас заголовки не находятся, то, скорее всего, нужно исправить список источников приложений — репозитории. Необходимо восстановить оригинальные записи. Как это сделать описано в этой инструкции.
Установите пакет linux-header для Debina или Ubuntu Linux, в консоли нужно набрать следующую команду:
После этого опять запустил VBoxLinuxAdditions.run с жёсткого диска — и уже никаких фейлов в процессе установки не наблюдалось. После перезагрузки я получил нормальное разрешение гостевой ОС и все другие прелести Guest Additions.
11 thoughts to “Установка VirtualBox Guest Additions на Kali Linux 1.1.0 (Debian, Ubuntu)”
ЗДРАСТВУЙТЕ , ALEXEY ! ВЫ БЫ МОГЛИ ДОБАВИТЬ В ДАННУЮ СТАТЬЮ СКРИПТЫ С ПОШАГОВОЙ ИНСТРУКЦИЕЙ ПО УСТАНОВКИ GUEST ADDITIONS
Здравствуйте, к сожалению, я не понимаю, о чём Вы говорите. Программные скрипты или что-то другое? Guest Additions всегда устанавливается просто — монитруется диск, запускается установочный файл. Просто в некоторых случаях, нужны дополнительные действия. Один из этих случаев здесь и описан — подробнее уже некуда ))
Спасибо за решение! Но не встречалась ли вам такая ситуация на Kali 1.0.9a:
не смотря на то что /etc/apt/sources.list содержит официальные репозитории Кали, после всех
apt-get update, apt-get install, apt-get upgrade и перезагрузок, при попытке обновить хедеры
apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r) отвечает, что Unable to locate linux-headers.3.14-kali-686-pae
и apt-cache search по этим хедерам пуст.
1. Вы не хотите обновиться до Kali Linux 1.1.0? Для этого не нужно ничего переустанавливать, достаточно набрать:
2. Что бросается в глаза в Вашем вопросе, так это неправильное название хэдера
linux-headers.3.14-kali1-686-pae
Поэтому проверьте, действительно ли у Вас источники приложений как здесь http://docs.kali.org/general-use/kali-linux-sources-list-repositories
Даже если у вас стандартные источники + сторонние, это может вызвать проблему. Попробуйте убрать сторонние. Даже если Вы точно знаете, что Вы его не трогали — просто проверьте, был случай, когда список источников оказался пустым.
Т.е. должно быть так (и ничего более):
deb http: // http.kali.org / kali kali main non-free contrib
deb http: // security.kali.org / kali-security kali / updates main contrib non-free
(если будете обновлять список приложений, думаю, знаете и без меня, но на всякий случай напомню — после этого apt-get update)
Проблема практически наверняка в источниках приложений — больше просто не в чем. Следующие советы на случай, если с источниками всё впорядке.
3. Попробуйте установить такой командой:
apt-get install linux-headers-3.14-kali1-686-pae
4. А если поискать так apt-cache search linux-headers что находит?
Если советы не помогли — пишите. Обязательно дожмём проблему.
у меня ноут , соединение с инетом посредствам вай фая , Kali linux установлена на виртулку . в Kali linux инет ЕСТЬ идет по лакалке но НЕТ вай фая . как настроить вай фай . в настройках сетевого соединения Вобще никаких подключений не видно .
WiFite v2 (r85) automated wireless auditor designed for Linux
[+] scanning for wireless devices…
[!] no wireless interfaces were found.
[!] you need to plug in a wifi device or install drivers.
WiFite v2 (r85) automated wireless auditor designed for Linux
[+] scanning for wireless devices…
[!] no wireless interfaces were found.
[!] you need to plug in a wifi device or install drivers.
ААА, понял. Всё нормально, его и не должно быть.
Наличие вай-файя в виртуальной машине можно добиться только одним способом — купить USB Wi-Fi приёмник, и в настройках виртуальной машины подключить это устройство к виртуальной системе — иначе никак.
Ничего кроме USB (никакие там PCI) виртуальная машина использовать не может. Точно также, виртуальная система никогда не сможет напрямую использовать видеокарту.
скажите а дрова ноутбука не будут конфликтовать с дровами usb wi- fi приемника ?
В теории, не должны конфликтовать. Ведь когда виртуальная машина «принимает» USB устройство, то оно перестаёт существовать для реального компьютера (даже пропадает из списка устройств). Как будет на практике — не знаю, может кто-то другой более подробно отпишется.
Не все беспроводные карты одинаково хорошо подходят для анализа Wi-Fi сетей (некоторые вообще ничего не могут). Перед покупкой нужно гуглить, что лучше брать. Вот здесь есть список, но сам я не проверял.
Но хотелось бы в начале статьи или ссылку, или кратенько о прблеме.
В частности, зачем нужны additions?
Хорошее замечание — сделаю краткое описание гостевых дополнений (Guest Additions).
Источник
Kali linux virtualbox guest additions
This guide is about virtualizing Kali Linux inside of VirtualBox, allowing you to have a Kali VM. This is a great way to use Kali, as it is completely separate from the host, allows you to interact with other VMs (as well as the host machine and other machines on the network), and allows you to revert to snapshots.
You may wish to follow our other guide if you are trying to install VirtualBox on Kali Linux (as a host).
The guide below is what we use to generate our pre-made Kali Linux VirtualBox images. You may alter this to your needs. We always generate the images using the latest version of VirtualBox.
You may need to enable virtualization in your BIOS/UEFI for (e.g. Intel VT-x/AMD-V)
Wizard
Upon starting up VirtualBox, select “New” (Machine -> New).
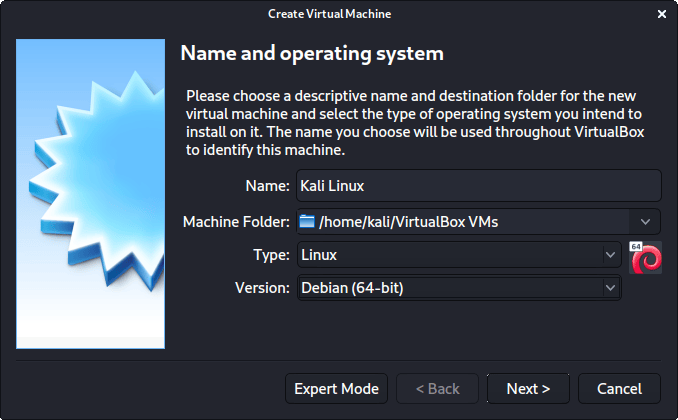
The next screen is “Name and operating system” which is where you name the VM. This name is also used in any filenames (such as the configuration, hard disk and snapshot — which isn’t changed from this point).
We are keeping it generic in this guide (as Kali is a rolling distribution, and we update it), however for our releases, we use the version number in the name as it is a fixed release ( kali-linux-YYYY.N-vbox-ARCH . Example: kali-linux-2021.3-vbox-amd64 ).
For the “Type”, we set it as Linux . For the “Version”, we are going to be using the x64 desktop image, so we are going to select Debian (64-bit) .
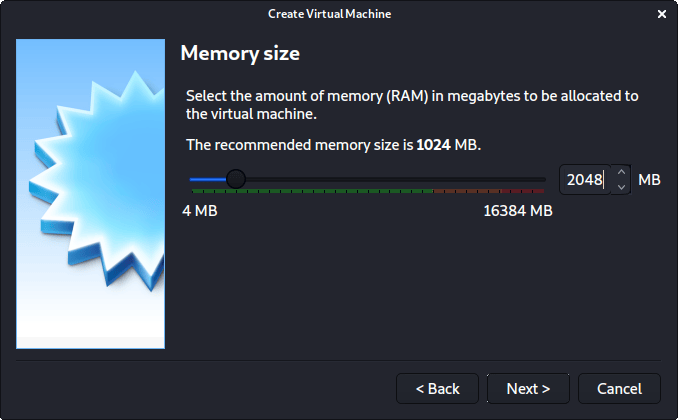
“Memory size” is the next section, where we can define how much RAM to use. Again, the higher the amount of RAM, the more applications can be open and at increased performance. Various tools inside of Kali can be demanding of resources. When we make the general VMs, we select 2048 MB (2GB) for RAM, but we often increase this for our personal machines as we have high-performing devices with spare RAM which Kali can utilize.
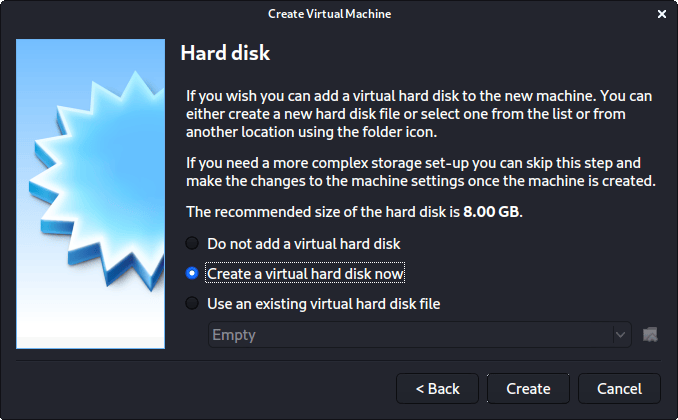
This screen below, “Hard disk”, allows us to Create a new virtual disk now .
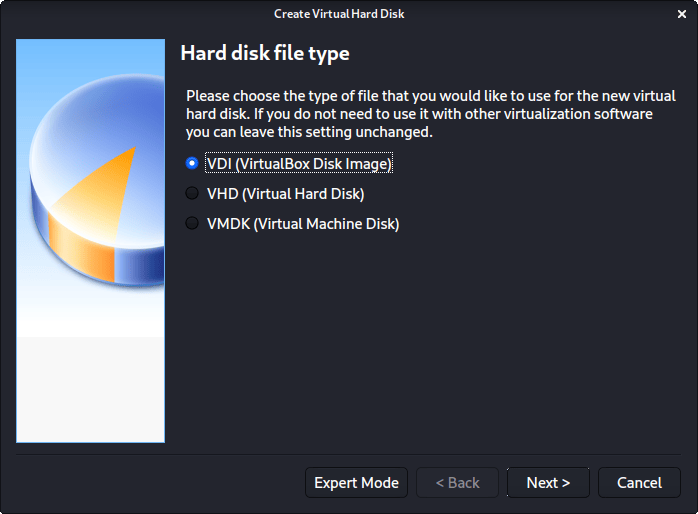
For the “Hard disk file type”, we select VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image) (and its the default option).
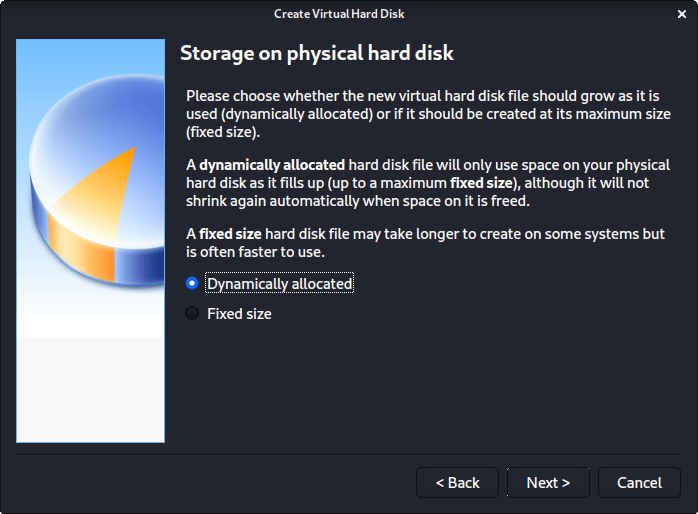
For the following screen, “Storage on physical hard disk”, we go with the default option of Dynamically allocated .
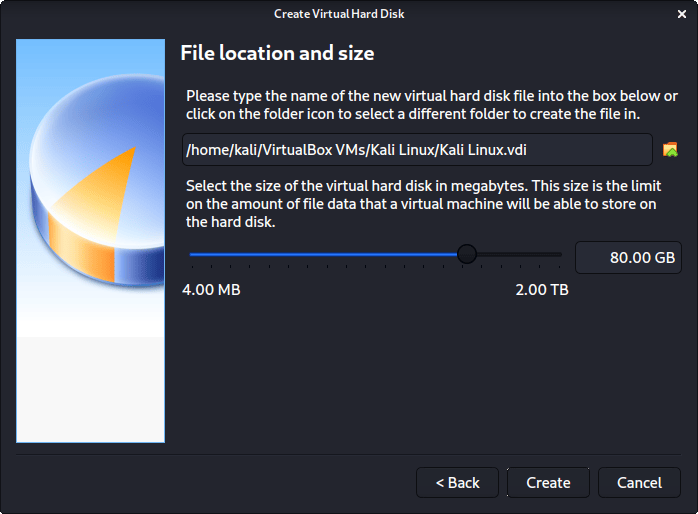
Now with “File location and size”, we can now define how large the virtual hard disk will be. We use 80.00 GB for our VMs.
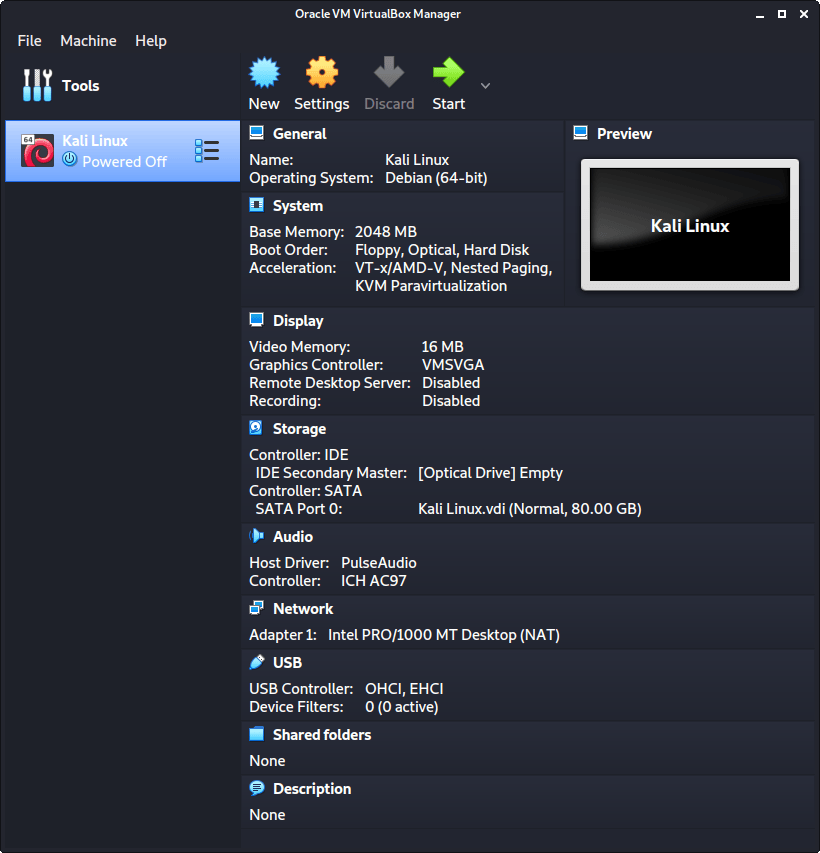
After clicking on “Create”, the wizard is complete.
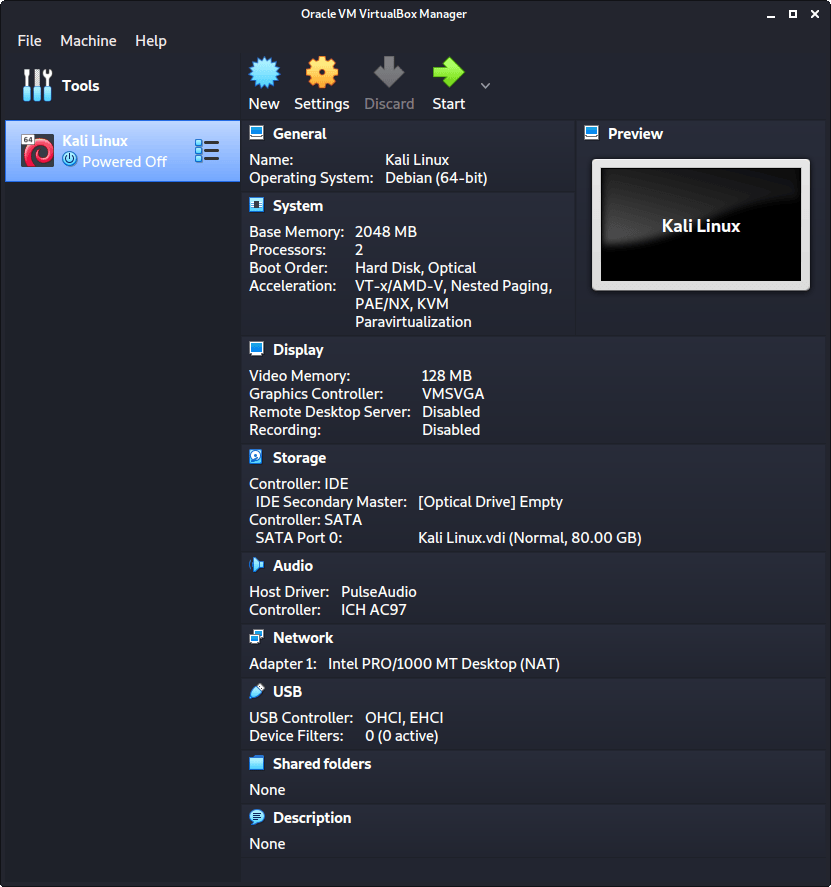
Now we click on “Settings”, to customize the VM further.
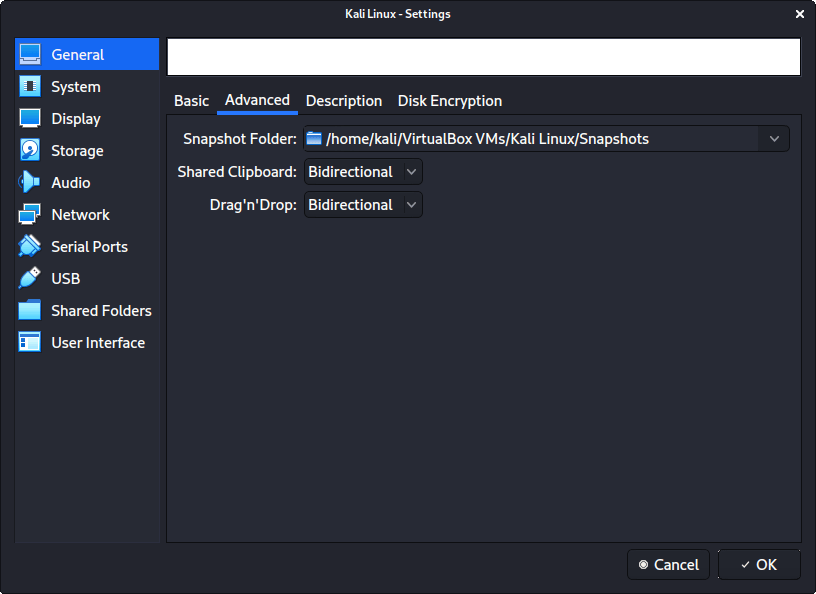
In “General” -> “Advanced”, we make sure to set “Shared Clipboard” to bidirectional , as well as “Drag’n’Drop” to bidirectional
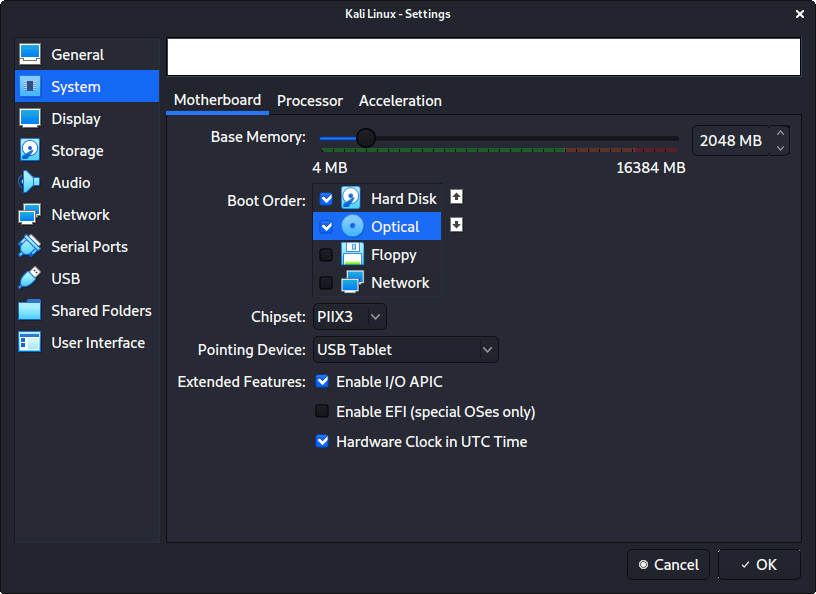
In “System” -> “Motherboard”, we change the “Boot Order” to make sure Hard Disk is top and Optical is the second. Everything else is disabled.
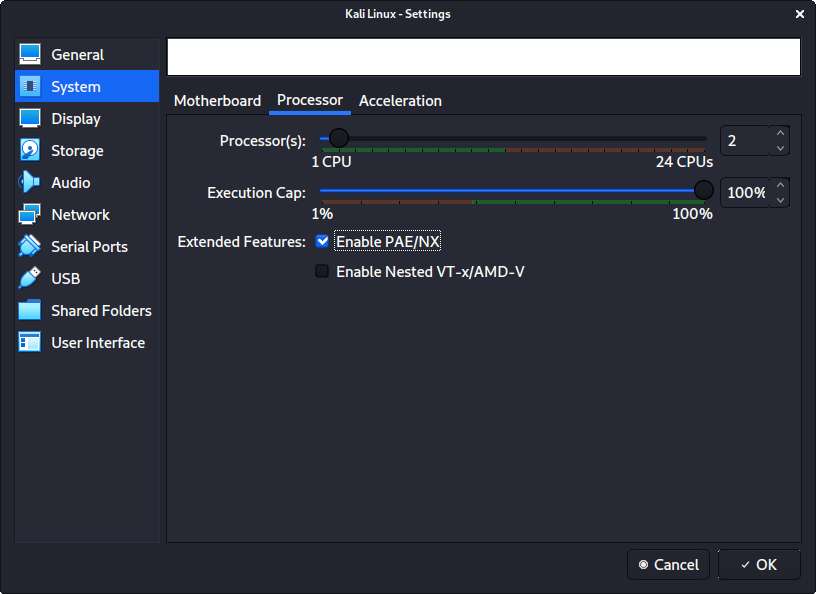
In “System” -> “Processor”, we increase the “Processor(s)” to be 2 .
At the same time, we also enable “Extended Features” for Enable PAE/NX .
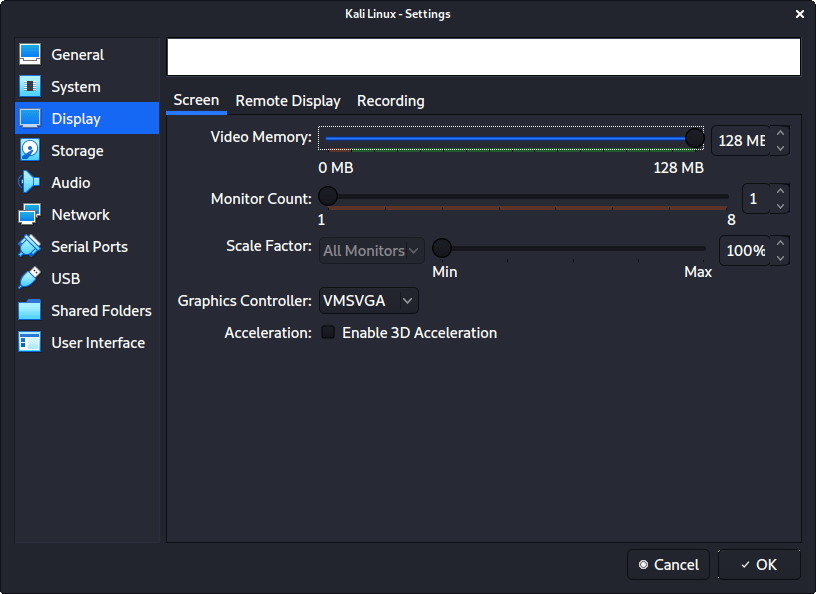
In “Display” -> “Screen”, we make sure to have “Video Memory” set to 128 MB
Another item to point out is to make sure that “Accelerated 3D graphics” is disabled, as people have reported that causes issues.
The final settings view looks like the following:
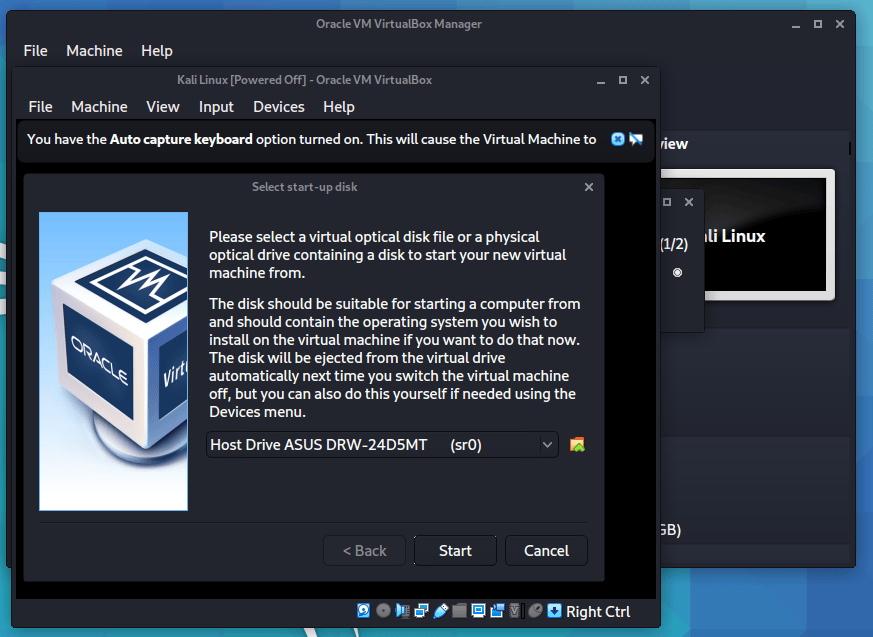
When we are ready to go, press “Start”.
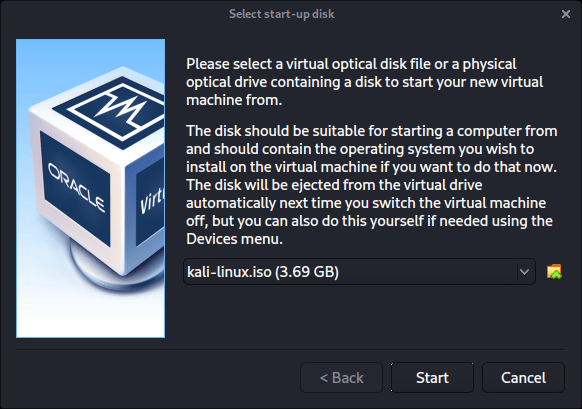
The first time we run it, we will get a prompt saying do we wish to mount an image to use as a “start-up disk”. We want to use our Kali image, rather than a physical drive, so we select the icon to the side of the drop down.
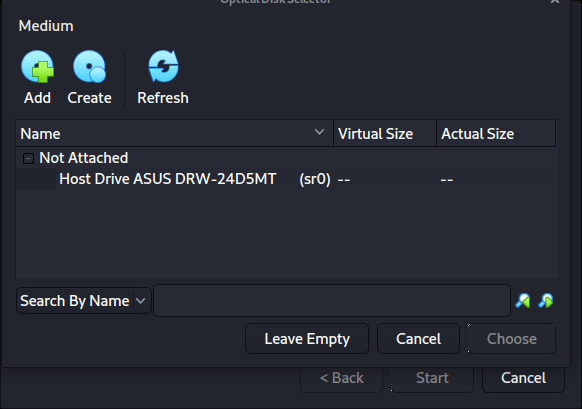
A new pop up will open, “Optical Disk Selector”. We will now press “Add”, then navigate to where our ISO is located.
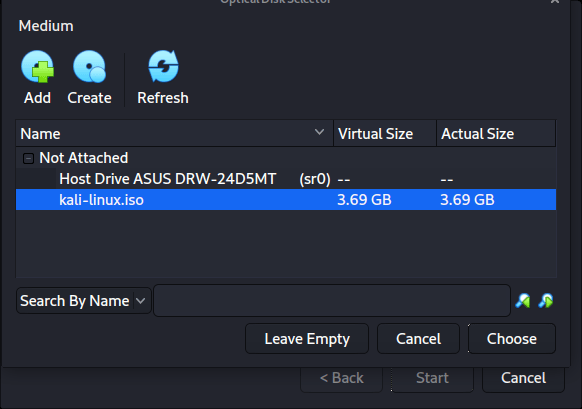
After pressing “Open”, we can see its been added, so we make sure its selected and press “Choose”.
All that is left now to do is press “Start”.
After all this is done, we save, start up the VM, and then continue installing Kali Linux as we normally would for a bare metal install.
During Kali Linux setup process, the install wizard should detect if its inside a VM. If it is, should then automatically install any additional tools (such as virtualbox-guest-x11 ) to give a better user experience. If you want to manually re-install it, you can see our VirtualBox Guest Guide.
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: g0tmi1k
Источник