- Kali Linux — Website Penetration Testing
- Vega Usage
- ZapProxy
- Database Tools Usage
- sqlmap
- sqlninja
- CMS Scanning Tools
- WPScan
- Joomscan
- SSL Scanning Tools
- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- How to install Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS) on Kali Linux
- OpenVAS is now renamed Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM)
- Errors when installing and starting GVM, OpenVAS
- How to install OpenVAS (GVM)
- Setting up OpenVAS
- Configuring Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM)
- Conclusion
- Related articles:
- Recommended for you:
- 2 Comments to How to install Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS) on Kali Linux
Kali Linux — Website Penetration Testing
In this chapter, we will learn about website penetration testing offered by Kali Linux.
Vega Usage
Vega is a free and open source scanner and testing platform to test the security of web applications. Vega can help you find and validate SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), inadvertently disclosed sensitive information, and other vulnerabilities. It is written in Java, GUI based, and runs on Linux, OS X, and Windows.
Vega includes an automated scanner for quick tests and an intercepting proxy for tactical inspection. Vega can be extended using a powerful API in the language of the web: JavaScript. The official webpage is https://subgraph.com/vega/
Step 1 − To open Vega go to Applications → 03-Web Application Analysis → Vega
Step 2 − If you don’t see an application in the path, type the following command.
Step 3 − To start a scan, click “+” sign.
Step 4 − Enter the webpage URL that will be scanned. In this case, it is metasploitable machine → click “ Next”.
Step 5 − Check all the boxes of the modules you want to be controlled. Then, click “Next”.
Step 6 − Click “Next” again in the following screenshot.
Step 7 − Click “Finish”.
Step 8 − If the following table pops up, click “Yes”.
The scan will continue as shown in the following screenshot.
Step 9 − After the scan is completed, on the left down panel you can see all the findings, that are categorized according to the severity. If you click it, you will see all the details of the vulnerabilities on the right panel such as “Request”, ”Discussion”, ”Impact”, and ”Remediation”.
ZapProxy
ZAP-OWASP Zed Attack Proxy is an easy-to-use integrated penetration testing tool for finding vulnerabilities in web applications. It is a Java interface.
Step 1 − To open ZapProxy, go to Applications → 03-Web Application Analysis → owaspzap.
Step 2 − Click “Accept”.
ZAP will start to load.
Step 3 − Choose one of the Options from as shown in the following screenshot and click “Start”.
Following web is metasploitable with IP :192.168.1.101
Step 4 − Enter URL of the testing web at “URL to attack” → click “Attack”.
After the scan is completed, on the top left panel you will see all the crawled sites.
In the left panel “Alerts”, you will see all the findings along with the description.
Step 5 − Click “Spider” and you will see all the links scanned.
Database Tools Usage
sqlmap
sqlmap is an open source penetration testing tool that automates the process of detecting and exploiting SQL injection flaws and taking over of database servers. It comes with a powerful detection engine, many niche features for the ultimate penetration tester and a broad range of switches lasting from database fingerprinting, over data fetching from the database, to accessing the underlying file system and executing commands on the operating system via out-of-band connections.
Let’s learn how to use sqlmap.
Step 1 − To open sqlmap, go to Applications → 04-Database Assessment → sqlmap.
The webpage having vulnerable parameters to SQL Injection is metasploitable.
Step 2 − To start the sql injection testing, type “sqlmap – u URL of victim”
Step 3 − From the results, you will see that some variable are vulnerable.
sqlninja
sqlninja is a SQL Injection on Microsoft SQL Server to a full GUI access. sqlninja is a tool targeted to exploit SQL Injection vulnerabilities on a web application that uses Microsoft SQL Server as its back-end. Full information regarding this tool can be found on http://sqlninja.sourceforge.net/
Step 1 − To open sqlninja go to Applications → 04-Database Assesment → sqlninja.
CMS Scanning Tools
WPScan
WPScan is a black box WordPress vulnerability scanner that can be used to scan remote WordPress installations to find security issues.
Step 1 − To open WPscan go to Applications → 03-Web Application Analysis → “wpscan”.
The following screenshot pops up.
Step 2 − To scan a website for vulnerabilities, type “wpscan –u URL of webpage”.
If the scanner is not updated, it will ask you to update. I will recommend to do it.
Once the scan starts, you will see the findings. In the following screenshot, vulnerabilities are indicated by a red arrow.
Joomscan
Joomla is probably the most widely-used CMS out there due to its flexibility. For this CMS, it is a Joomla scanner. It will help web developers and web masters to help identify possible security weaknesses on their deployed Joomla sites.
Step 1 − To open it, just click the left panel at the terminal, then “joomscan – parameter”.
Step 2 − To get help for the usage type “joomscan /?”
Step 3 − To start the scan, type “ joomscan –u URL of the victim”.
Results will be displayed as shown in the following screenshot.
SSL Scanning Tools
TLSSLed is a Linux shell script used to evaluate the security of a target SSL/TLS (HTTPS) web server implementation. It is based on sslscan, a thorough SSL/TLS scanner that is based on the openssl library, and on the “openssl s_client” command line tool.
The current tests include checking if the target supports the SSLv2 protocol, the NULL cipher, weak ciphers based on their key length (40 or 56 bits), the availability of strong ciphers (like AES), if the digital certificate is MD5 signed, and the current SSL/TLS renegotiation capabilities.
To start testing, open a terminal and type “tlssled URL port“. It will start to test the certificate to find data.
You can see from the finding that the certificate is valid until 2018 as shown in green in the following screenshot.
w3af is a Web Application Attack and Audit Framework which aims to identify and exploit all web application vulnerabilities. This package provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for the framework. If you want a command-line application only, install w3af-console.
The framework has been called the “metasploit for the web”, but it’s actually much more as it also discovers the web application vulnerabilities using black-box scanning techniques. The w3af core and its plugins are fully written in Python. The project has more than 130 plugins, which identify and exploit SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), remote file inclusion and more.
Step 1 − To open it, go to Applications → 03-Web Application Analysis → Click w3af.
Step 2 − On the “Target” enter the URL of victim which in this case will be metasploitable web address.
Step 3 − Select the profile → Click “Start”.
Step 4 − Go to “Results” and you can see the finding with the details.
Источник
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
How to install Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS) on Kali Linux
OpenVAS is now renamed Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM)
When the OpenVAS project was created, it only consisted of a vulnerability scanning engine. Greenbone Networks received funding shortly thereafter to provide professional vulnerability scanning support. Greenbone took over development leadership, added a few software components, and turned OpenVAS into a multi-pronged vulnerability management solution that still retains the value of open and free software.
Over the years, it became apparent that the use of OpenVAS as a trademark for an open source project and funding for almost all of the project’s development had not been appreciated from outside. Therefore, after the release of the OpenVAS 9 platform, it was renamed Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) and released as Greenbone Source Edition (GSE). Since GVM 10, the term OpenVAS is used only for the scanner component, as it was at the beginning of the project.
Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) packages: https://github.com/greenbone
Errors when installing and starting GVM, OpenVAS
During the installation and launch process, I encountered quite a few errors, which, nevertheless, were resolved. Under the assumption that these errors are common to everyone (not just my particular installation), I described these errors right during the installation process, as a result of which the instructions became cluttered.
If during the installation process you do not encounter the described errors, please write about it in the comments – if the errors do not appear for everyone, then I will put them at the very end of the article, due to which, in general, the instruction will become clearer.
How to install OpenVAS (GVM)
Since the authors renamed openvas to gvm (more precisely, divided it into different packages), now the main package is gvm, when it is installed, all other necessary packages will also be obtained as dependencies.
Installation is done like this:
Setting up OpenVAS
Let’s start by setting up the Open Vulnerability Assessment Scanner (OpenVAS) for Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) solution.
It is used in Greenbone Security Manager and is a full-fledged scan engine that performs constantly updated and expanded submissions of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs).
The scanner needs a running Redis server to temporarily store the collected information on the scanned hosts. Configuring the Redis server is done like this (these commands need to be executed once):
Starting the Redis server (must be done after every computer restart):
Or, if you like, add it to startup:
The Greenbone Vulnerability Management (gvmd) service acts as an OSP client to connect to and manage scanners. openvas does not act as an OSP service – you need the OSPD-OpenVAS module for that. Actual user interfaces (like GSA or GVM-Tools) will only interact with gvmd and/or ospd-openvas, not the scanner. You can run openvas to load plugins in Redis using the following command:
but ospd-openvas will update automatically.
Please note that although you can run openvas as a non-elevated user, it is recommended that you run openvas as root because some network vulnerability tests (NVTs) require root privileges to perform certain operations, such as package spoofing. If you run openvas as a user without permission to perform these operations, the scan results are likely to be incomplete.
Since openvas will be launched from the ospd-openvas process using sudo, the following configuration is required in the sudoers file:
add this line to allow the user running ospd-openvas to run openvas as root
Replace USERNAME with your Linux username.
You can find out the username with the command:
If something does not work, then you can view the log with the command:
Configuring Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM)
Greenbone Vulnerability Manager is the central management service between security scanners and user clients.
It manages the storage of any vulnerability management configuration and scan results. Data, control commands, and workflows are accessed through the XML-based Greenbone Management Protocol (GMP). Scanners such as OpenVAS are controlled through the Open Scanner Protocol (OSP).
Deployment script (instead of openvas-setup):
This script needs to be run only once.
The script ended with an error:
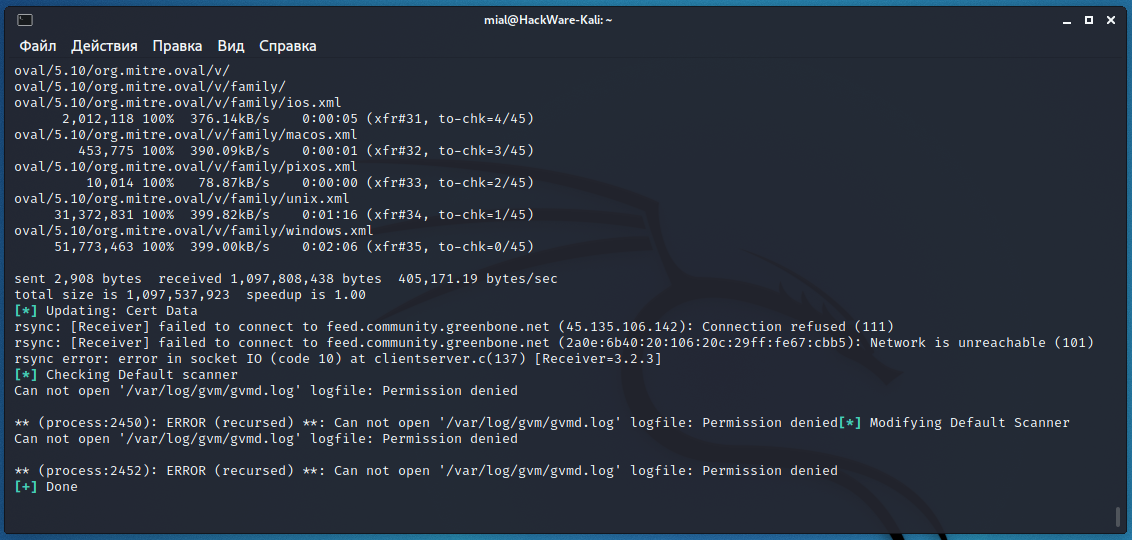
also showed an error in the fourth step:
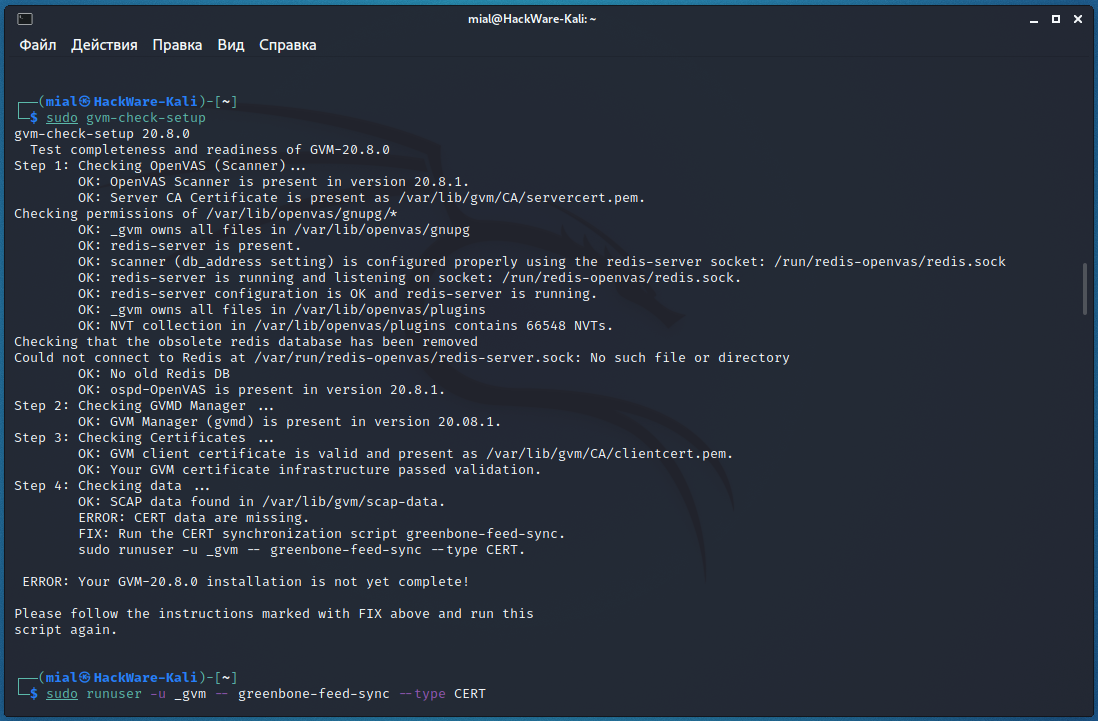
To fix the error “ERROR: CERT data are missing. FIX: Run the CERT synchronization script greenbone-feed-sync” run the following command:
Re-running the check showed an error at the fifth step:

There are several errors at once, but the key one is “ERROR: No users found. You need to create at least one user to log in.”, To fix it, run a command like this:
For example, to create a user named mial and password 2:
The previous command failed:
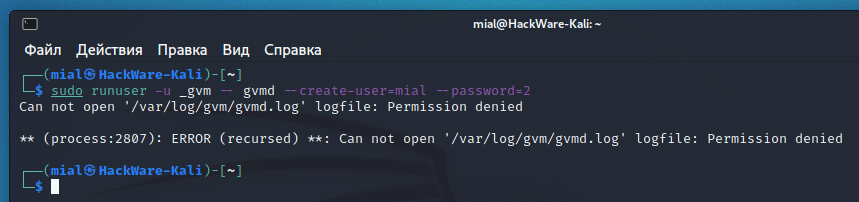
The essence of the error is that the command does not have enough permissions to write to the /var/log/gvm/gvmd.log file, even though the previous command was run with sudo. To fix the error, run the following command:
Then run the new user creation again.
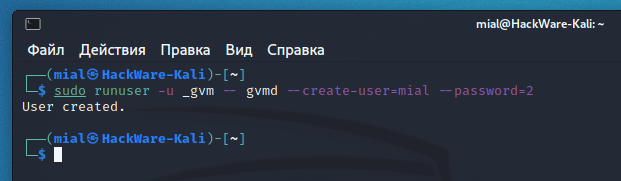
And one more mistake at the seventh step:
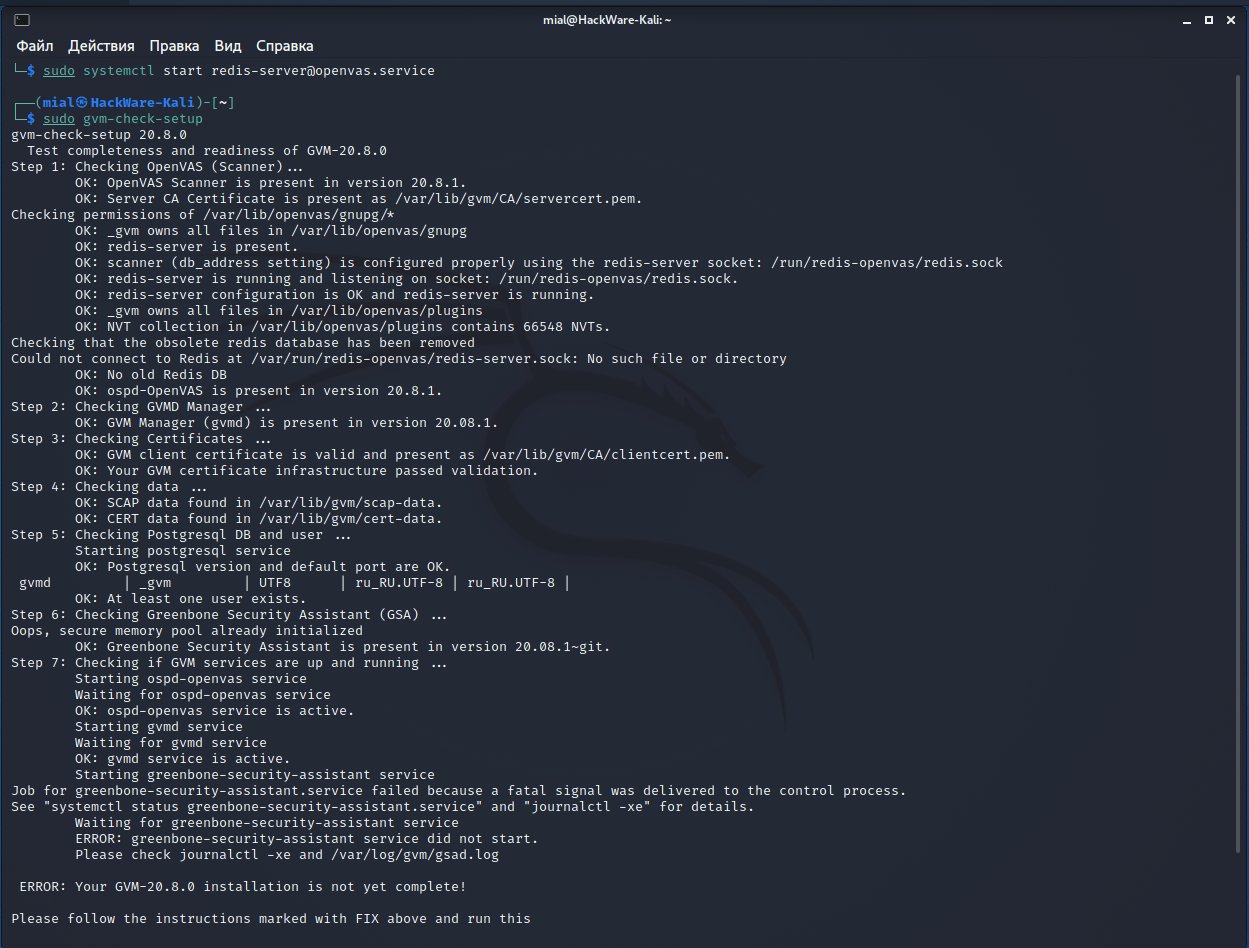
I don’t know how to solve it completely, but I know how to get around it.
Let’s move on to starting the necessary services.
Do not forget that before starting the service you need to start the Redis server, that is, type following before executing the primary command:
Main service start:
And we get the following:

The essence of the messages is that everything started fine, except for the greenbone-security-assistant, that is, gsa, that is, Web UI (Greenbone Security Assistant), that is, the web interface.
You can see the contents of the log file:
https daemon failed to start .
gsad has a —http-only option which only runs HTTP without HTTPS. Let’s use it:
Again, the next message will be displayed that something is wrong:
However, the web interface is now available at http://127.0.0.1:9392 (but not available at https://127.0.0.1:9392!).
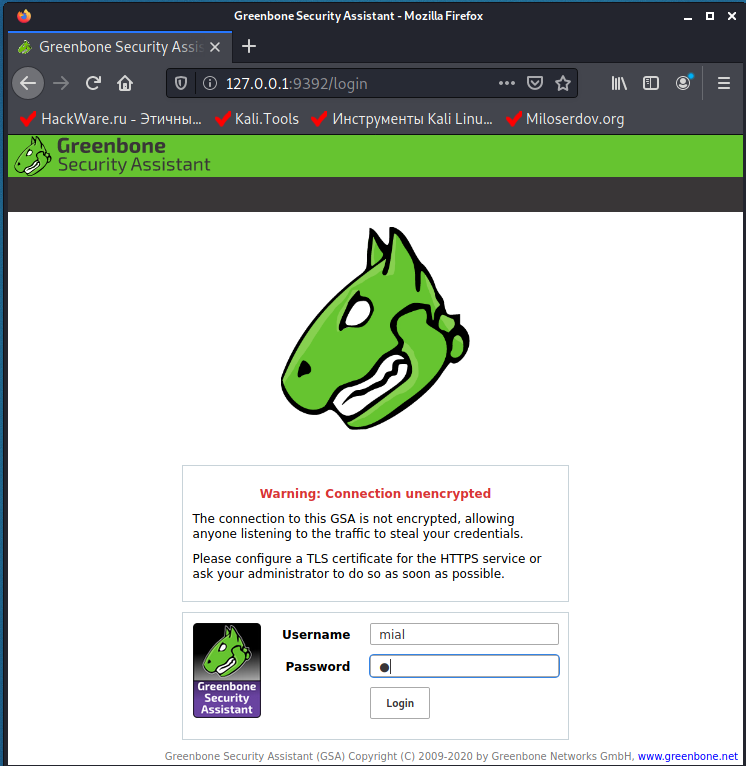
Log in using the credentials that you came up with when creating a new user.
To stop the service:
In the future, sometimes run the command to update signatures:
If something does not work, then you can view the log with the command:
Conclusion
One of the following instructions will be devoted to how to work in Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS).
And do not forget to write – have you encountered the described errors during installation?
Related articles:
- Default passwords in Kali Linux (100%)
- Kali Linux Rolling post install tips (51.2%)
- How to install OWASP Mutillidae II and Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) in Kali Linux (51.2%)
- How to install and run VLC, Google Chrome, and Chromium on Kali Linux (51.2%)
- How to update Kali Linux (51.2%)
- How to install Java (JDK) on Windows and Linux (RANDOM — 50%)
Recommended for you:
2 Comments to How to install Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) (formerly OpenVAS) on Kali Linux
I found feed status are «update in progress» and «scap database is required» on my Open VAS GVM platform.I have tried may option to update feeds but notings works.
This is log OPEN VAS:
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 06h52.30 utc:5664: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 09h04.08 utc:1213: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 09h48.54 utc:1297: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 10h09.17 utc:1168: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 13h05.31 utc:1220: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 13h23.30 utc:1159: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 13h55.51 utc:1148: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 15h45.48 utc:1197: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 17h46.23 utc:1712: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-11 18h09.25 utc:1194: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-13 15h31.07 utc:1204: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109101034
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h31.17 utc:2876: redis_find: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h31.17 utc:2876: get_redis_ctx: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h31.17 utc:2876: get_redis_ctx: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h37.41 utc:3412: redis_find: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h37.41 utc:3412: get_redis_ctx: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:CRITICAL:2021-09-13 15h37.41 utc:3412: get_redis_ctx: redis connection error to /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock: No such file or directory
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-13 16h25.01 utc:3395: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109131026
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2021-09-13 16h34.58 utc:1214: Updated NVT cache from version 0 to 202109131026
Hi! thanks for the tutorial!
on «sudo gvm-setup» i get this:
rsync: [generator] failed to set permissions on «/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2014/gb_fedora_2014_5004_httpd_fc19.nasl»: Function not implemented (38)
rsync: [generator] failed to set permissions on «/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2014/gb_fedora_2014_5006_json-c_fc20.nasl»: Function not implemented (38)
rsync: [generator] failed to set permissions on «/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2014/gb_fedora_2014_5015_elfutils_fc20.nasl»: Function not implemented (38)
Источник







































