- Windows libraries
- Features for Users
- Features for Administrators
- More about Libraries
- Library Contents
- Default Libraries and Known Folders
- Hiding Default Libraries
- Default Save Locations for Libraries
- Indexing Requirements and “Basic” Libraries
- Folder Redirection
- Supported storage locations
- Library Attributes
- DLL DOWNLOADER
- Download Wha library.dll for Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, Vista and XP
- About Wha library.dll link
- Table of Contents
- Operating Systems Compatible with the Wha library.dll File link
- Guide to Download Wha library.dll link
- Methods to Solve the Wha Library.dll Errors link
- Method 1: Solving the DLL Error by Copying the Wha library.dll File to the Windows System Folder link
- Method 2: Copying The Wha library.dll File Into The Software File Folder link
- Method 3: Uninstalling and Reinstalling the Software that Gives You the Wha library.dll Error link
- Method 4: Solving the Wha library.dll Problem by Using the Windows System File Checker (scf scannow) link
- Method 5: Getting Rid of Wha library.dll Errors by Updating the Windows Operating System link
Windows libraries
Applies to: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2
Libraries are virtual containers for users’ content. A library can contain files and folders stored on the local computer or in a remote storage location. In Windows Explorer, users interact with libraries in ways similar to how they would interact with other folders. Libraries are built upon the legacy known folders (such as My Documents, My Pictures, and My Music) that users are familiar with, and these known folders are automatically included in the default libraries and set as the default save location.
Features for Users
Windows libraries are backed by full content search and rich metadata. Libraries offer the following advantages to users:
- Aggregate content from multiple storage locations into a single, unified presentation.
- Enable users to stack and group library contents based on metadata.
- Enable fast, full-text searches across multiple storage locations, from Windows Explorer or from the Start menu.
- Support customized filter search suggestions, based on the types of files contained in the library.
- Enable users to create new libraries and specify which folders they want to include.
Features for Administrators
Administrators can configure and control Windows libraries in the following ways:
- Create custom libraries by creating and deploying Library Description (*.library-ms) files.
- Hide or delete the default libraries. (The Library node itself cannot be hidden or deleted from the Windows Explorer navigation pane.)
- Specify a set of libraries available to Default User, and then deploy those libraries to users that derive from Default User.
- Specify locations to include in a library.
- Remove a default location from a library.
- Remove advanced libraries features, when the environment does not support the local caching of files, by using the Turn off Windows Libraries features that rely on indexed file data Group Policy. This makes all libraries basic (see Indexing Requirements and Basic Libraries), removes libraries from the scope of the Start menu search, and removes other features to avoid confusing users and consuming resources.
More about Libraries
The following is important information about libraries you may need to understand to successfully manage your enterprise.
Library Contents
Including a folder in a library does not physically move or change the storage location of the files or folders; the library is a view into those folders. However, users interacting with files in a library are copying, moving, and deleting the files themselves, not copies of these files.
Default Libraries and Known Folders
The default libraries include:
Libraries are built upon the legacy known folders (such as My Documents, My Pictures, and My Music) that users are familiar with. These known folders are automatically included in the default libraries and set as the default save location. That is, when users drag, copy, or save a file to the Documents library, the file is moved, copied, or saved to the My Documents folder. Administrators and users can change the default save-to location.
Hiding Default Libraries
Users or administrators can hide or delete the default libraries, though the libraries node in the Navigation pane cannot be hidden or deleted. Hiding a default library is preferable to deleting it, as applications like Windows Media Player rely on the default libraries and will re-create them if they do not exist on the computer. See How to Hide Default Libraries for instructions.
Default Save Locations for Libraries
Each library has a default save location. Files are saved or copied to this location if the user chooses to save or copy a file to a library, rather than a specific location within the library. Known folders are the default save locations; however, users can select a different save location. If the user removes the default save location from a library, the next location is automatically selected as the new default save location. If the library is empty of locations or if all included locations cannot be saved to, then the save operation fails.
Indexing Requirements and “Basic” Libraries
Certain library features depend on the contents of the libraries being indexed. Library locations must be available for local indexing or be indexed in a manner conforming to the Windows Indexing Protocol. If indexing is not enabled for one or more locations within a library, the entire library reverts to basic functionality:
- No support for metadata browsing via Arrange By views.
- Grep-only searches.
- Grep-only search suggestions. The only properties available for input suggestions are Date Modified and Size.
- No support for searching from the Start menu. Start menu searches do not return files from basic libraries.
- No previews of file snippets for search results returned in Content mode.
To avoid this limited functionality, all locations within the library must be indexable, either locally or remotely. When users add local folders to libraries, Windows adds the location to the indexing scope and indexes the contents. Remote locations that are not indexed remotely can be added to the local index using Offline File synchronization. This gives the user the benefits of local storage even though the location is remote. Making a folder “Always available offline” creates a local copy of the folder’s files, adds those files to the index, and keeps the local and remote copies in sync. Users can manually sync locations which are not indexed remotely and are not using folder redirection to gain the benefits of being indexed locally.
For instructions on enabling indexing, see How to Enable Indexing of Library Locations.
If your environment does not support caching files locally, you should enable the Turn off Windows Libraries features that rely on indexed file data Group Policy. This makes all libraries basic. For further information, see Group Policy for Windows Search, Browse, and Organize.
Folder Redirection
While library files themselves cannot be redirected, you can redirect known folders included in libraries by using Folder Redirection. For example, you can redirect the “My Documents” folder, which is included in the default Documents library. When redirecting known folders, you should make sure that the destination is either indexed or always available offline in order to maintain full library functionality. In both cases, the files for the destination folder are indexed and supported in libraries. These settings are configured on the server side.
Supported storage locations
The following table show which locations are supported in Windows libraries.
| Supported Locations | Unsupported Locations |
|---|---|
| Fixed local volumes (NTFS/FAT) | Removable drives |
| Shares that are indexed (departmental servers*, WindowsВ home PCs) | Removable media (such as DVDs) Network shares that are accessible through DFS Namespaces or are part of a failover cluster |
| Shares that are available offline (redirected folders that use Offline Files) | Network shares that aren’t available offline or remotely indexed Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices |
| Other data sources: SharePoint, Exchange, etc. |
* For shares that are indexed on a departmental server, Windows Search works well in workgroups or on a domain server that has similar characteristics to a workgroup server. For example, Windows Search works well on a single share departmental server with the following characteristics:
- Expected maximum load is four concurrent query requests.
- Expected indexing corpus is a maximum of one million documents.
- Users directly access the server. That is, the server is not made available through DFS Namespaces.
- Users are not redirected to another server in case of failure. That is, server clusters are not used.
Library Attributes
The following library attributes can be modified within Windows Explorer, the Library Management dialog, or the Library Description file (*.library-ms):
- Name
- Library locations
- Order of library locations
- Default save location
The library icon can be modified by the administrator or user by directly editing the Library Description schema file.
See the Library Description Schema topic on MSDN for information on creating Library Description files.
DLL DOWNLOADER
Download DLL and other System-Files for Windows
Download Wha library.dll for Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, Vista and XP
About Wha library.dll link
The Wha library.dll file is 0.07 MB. The download links have been checked and there are no problems. You can download it without a problem. Currently, it has been downloaded 1056 times and it has received 5.0 out of 5 stars from our users.
Table of Contents
Operating Systems Compatible with the Wha library.dll File link
Guide to Download Wha library.dll link
- First, click the «Download» button with the green background (The button marked in the picture).
Step 1:Download the Wha library.dll file
- «After clicking the Download» button, wait for the download process to begin in the «Downloading» page that opens up. Depending on your Internet speed, the download process will begin in approximately 4 -5 seconds.
Methods to Solve the Wha Library.dll Errors link
ATTENTION! Before beginning the installation of the Wha library.dll file, you must download the file. If you don’t know how to download the file or if you are having a problem while downloading, you can look at our download guide a few lines above.
Method 1: Solving the DLL Error by Copying the Wha library.dll File to the Windows System Folder link
- The file you are going to download is a compressed file with the «.zip» extension. You cannot directly install the «.zip» file. First, you need to extract the dll file from inside it. So, double-click the file with the «.zip» extension that you downloaded and open the file.
- You will see the file named «Wha library.dll» in the window that opens up. This is the file we are going to install. Click the file once with the left mouse button. By doing this you will have chosen the file.
Step 2:Choosing the Wha library.dll file
- Click the «Extract To» symbol marked in the picture. To extract the dll file, it will want you to choose the desired location. Choose the «Desktop» location and click «OK» to extract the file to the desktop. In order to do this, you need to use the Winrar software. If you do not have this software, you can find and download it through a quick search on the Internet.
Step 3:Extracting the Wha library.dll file to the desktop
- Copy the «Wha library.dll» file and paste it into the «C:\Windows\System32» folder.
Step 4:Copying the Wha library.dll file into the Windows/System32 folder
- If you are using a 64 Bit operating system, copy the «Wha library.dll» file and paste it into the «C:\Windows\sysWOW64» as well.
NOTE! On Windows operating systems with 64 Bit architecture, the dll file must be in both the «sysWOW64» folder as well as the «System32» folder. In other words, you must copy the «Wha library.dll» file into both folders.
NOTE! We ran the Command Prompt using Windows 10. If you are using Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista or Windows XP, you can use the same method to run the Command Prompt as administrator.
- Open the Start Menu and before clicking anywhere, type «cmd» on your keyboard. This process will enable you to run a search through the Start Menu. We also typed in «cmd» to bring up the Command Prompt.
- Right-click the «Command Prompt» search result that comes up and click the Run as administrator» option.

%windir%\System32\regsvr32.exe /u Wha library.dll
%windir%\SysWoW64\regsvr32.exe /u Wha library.dll
%windir%\System32\regsvr32.exe /i Wha library.dll
%windir%\SysWoW64\regsvr32.exe /i Wha library.dll
Method 2: Copying The Wha library.dll File Into The Software File Folder link
- First, you must find the installation folder of the software (the software giving the dll error) you are going to install the dll file to. In order to find this folder, «Right-Click > Properties» on the software’s shortcut.
Step 1:Opening the software’s shortcut properties window
- Open the software file folder by clicking the Open File Location button in the «Properties» window that comes up.
Step 2:Finding the software’s file folder
- Copy the Wha library.dll file.
- Paste the dll file you copied into the software’s file folder that we just opened.
Step 3:Pasting the Wha library.dll file into the software’s file folder
- When the dll file is moved to the software file folder, it means that the process is completed. Check to see if the problem was solved by running the software giving the error message again. If you are still receiving the error message, you can complete the 3rd Method as an alternative.
Method 3: Uninstalling and Reinstalling the Software that Gives You the Wha library.dll Error link
- Push the «Windows» + «R» keys at the same time to open the Run window. Type the command below into the Run window that opens up and hit Enter. This process will open the «Programs and Features» window.
Method 4: Solving the Wha library.dll Problem by Using the Windows System File Checker (scf scannow) link
- In order to complete this step, you must run the Command Prompt as administrator. In order to do this, all you have to do is follow the steps below.
NOTE! We ran the Command Prompt using Windows 10. If you are using Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista or Windows XP, you can use the same method to run the Command Prompt as administrator.
- Open the Start Menu and before clicking anywhere, type «cmd» on your keyboard. This process will enable you to run a search through the Start Menu. We also typed in «cmd» to bring up the Command Prompt.
- Right-click the «Command Prompt» search result that comes up and click the Run as administrator» option.

Method 5: Getting Rid of Wha library.dll Errors by Updating the Windows Operating System link
Some softwares need updated dll files. When your operating system is not updated, it cannot fulfill this need. In some situations, updating your operating system can solve the dll errors you are experiencing.
In order to check the update status of your operating system and, if available, to install the latest update packs, we need to begin this process manually.
Depending on which Windows version you use, manual update processes are different. Because of this, we have prepared a special article for each Windows version. You can get our articles relating to the manual update of the Windows version you use from the links below.

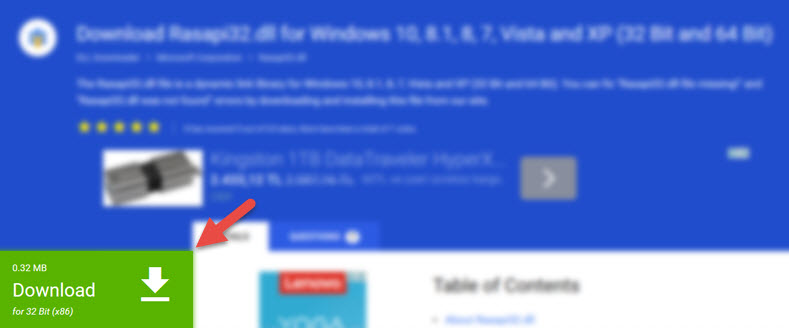 Step 1:Download the Wha library.dll file
Step 1:Download the Wha library.dll file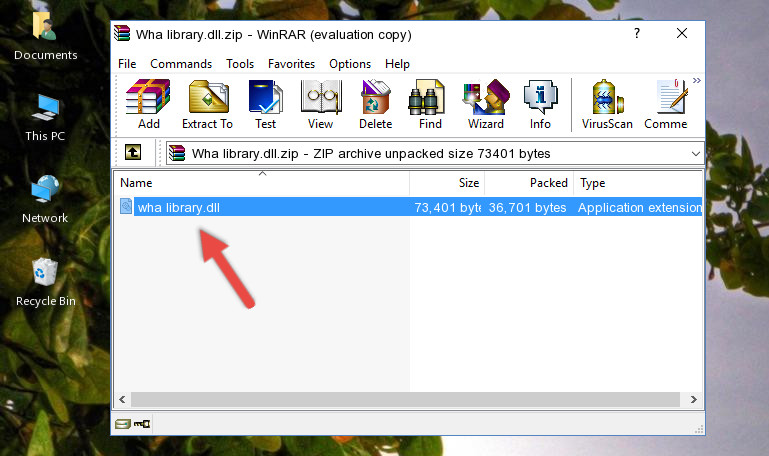 Step 2:Choosing the Wha library.dll file
Step 2:Choosing the Wha library.dll file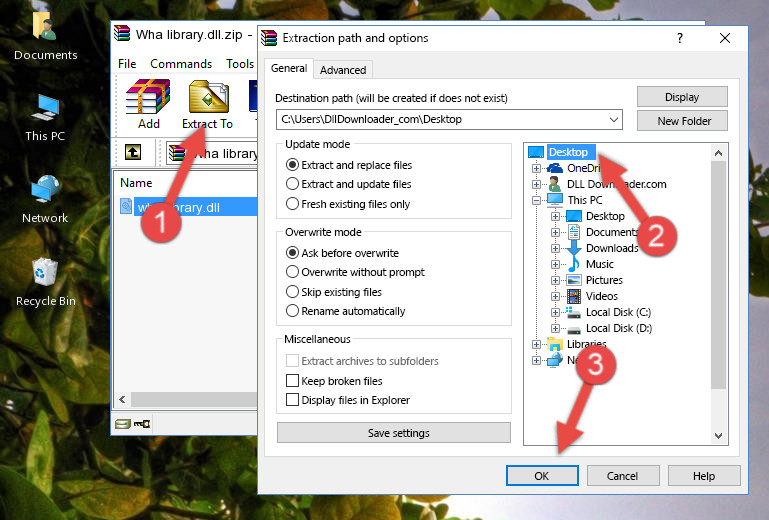 Step 3:Extracting the Wha library.dll file to the desktop
Step 3:Extracting the Wha library.dll file to the desktop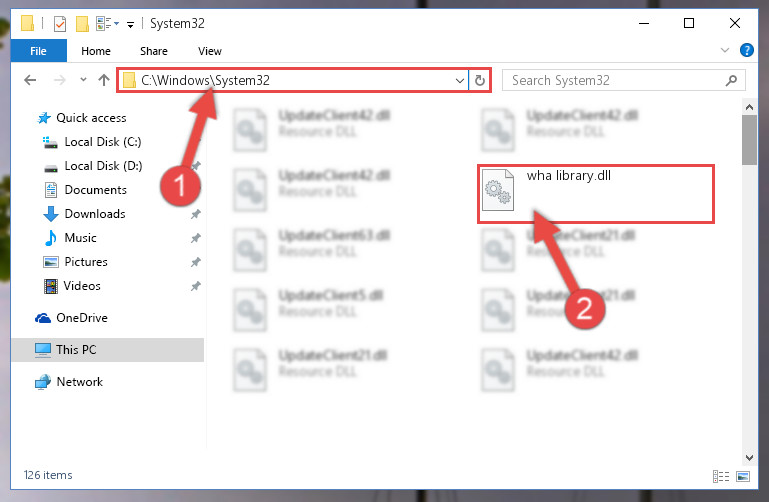 Step 4:Copying the Wha library.dll file into the Windows/System32 folder
Step 4:Copying the Wha library.dll file into the Windows/System32 folder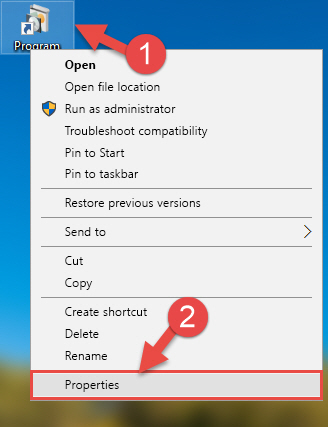 Step 1:Opening the software’s shortcut properties window
Step 1:Opening the software’s shortcut properties window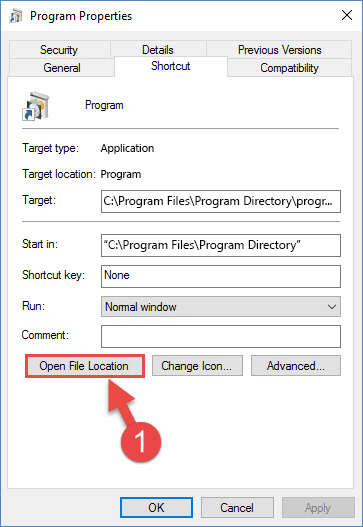 Step 2:Finding the software’s file folder
Step 2:Finding the software’s file folder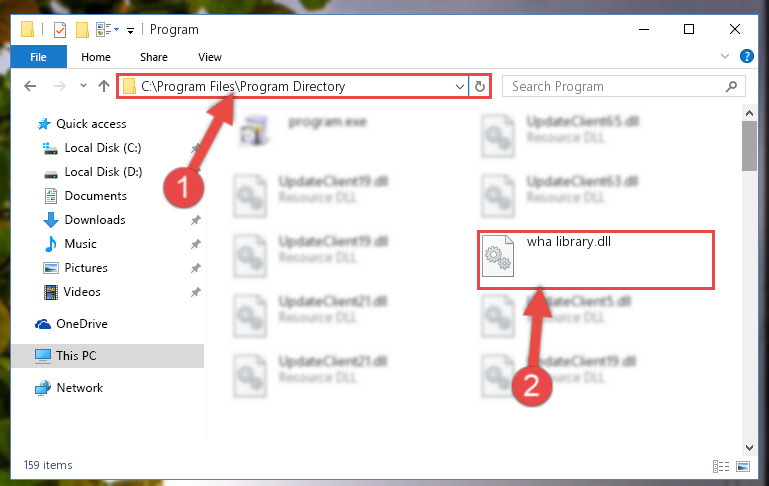 Step 3:Pasting the Wha library.dll file into the software’s file folder
Step 3:Pasting the Wha library.dll file into the software’s file folder


