- Как создавать символические ссылки (Symlinks) в системе Windows
- Что такое символические ссылки
- Как создать символические ссылки с mklink
- Как создать символическую ссылку с помощью графического инструмента
- Как удалить символические ссылки
- Как создать символьную ссылку в Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7
- Add custom Folders to Favorite Links in Windows File Explorer
- Add or Remove Folders to Favorite Links in Explorer
- Symlinks in Windows 10!
- Overview
- Background
- What drove this change?
- How to use Symlinks
- How do I try it?
Как создавать символические ссылки (Symlinks) в системе Windows
Windows 10, 8, 7 и Vista поддерживают символические ссылки, которые указывают на файл или папку в вашей системе. Вы можете создать их с помощью командной строки или стороннего инструмента под названием Link Shell Extension.
Что такое символические ссылки
Символические ссылки – это, по сути, расширенные ярлыки. Создайте символическую ссылку на отдельный файл или папку, и эта ссылка будет выглядеть так же, как файл или папка для Windows, хотя это только ссылка, указывающая на файл или папку.
Например, предположим, что у вас есть программа, которая использует файлы в папке C:\Program. А Вам хотелось бы сохранить этот каталог в D:\Refuse, но программа требует, чтобы её файлы были в C:\Program. Вы можете перенести исходный каталог из C:\Program в D:\Refuse, а затем создать символическую ссылку C:\Program, указав на D:\Refuse. Когда вы перезапустите программу, она попытается получить доступ к своему каталогу в C:\Program. Windows автоматически перенаправит её на D:\Refuse, и всё будет работать так, как если бы оно было в C:\Program.
Этот трюк можно использовать для всех целей, включая синхронизацию любой папки с такими программами, как Dropbox, Google Drive и OneDrive.
Существует два типа символических ссылок: жесткая и мягкая. Мягкие символические ссылки работают аналогично стандартным ярлыкам. Когда вы открываете мягкую ссылку на папку, вы будете перенаправлены в папку, где хранятся файлы. Однако, жесткая ссылка заставляет его выглядеть так, как будто файл или папка действительно существуют в местоположении символической ссылки, и ваши приложения не будут знать о подмене. В большинстве ситуаций жесткие символические ссылки более полезны.
Обратите внимание, что Windows фактически не использует термины «жесткая ссылка» и «мягкая ссылка». Вместо этого используются термины «жесткая ссылка» и «символическая ссылка». В документации Windows «символическая ссылка» – это то же самое, что «мягкая ссылка». Тем не менее, mklink-команда может создавать как жесткие ссылки, так и софт-ссылки (известные как «символические ссылки» в Windows).
Как создать символические ссылки с mklink
Вы можете создавать символические ссылки, используя команду mklink в окне командной строки в качестве администратора. Чтобы открыть её, найдите ярлык «Командная строка» в меню «Пуск», щелкните его правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
В Windows Creators Update вы можете использовать обычное окно командной строки, не запуская его как администратор. Однако, чтобы сделать это без окна командной строки администратора, вы должны сначала включить режим разработчика в Параметры → Обновление и безопасность → Разработчики.
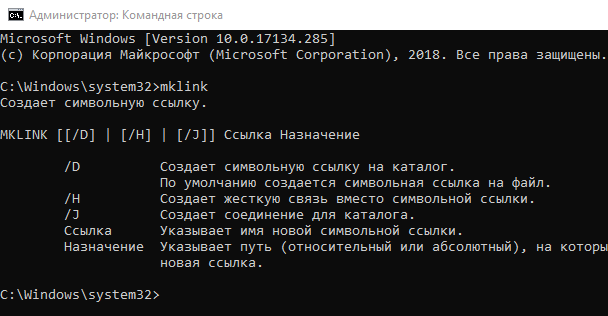
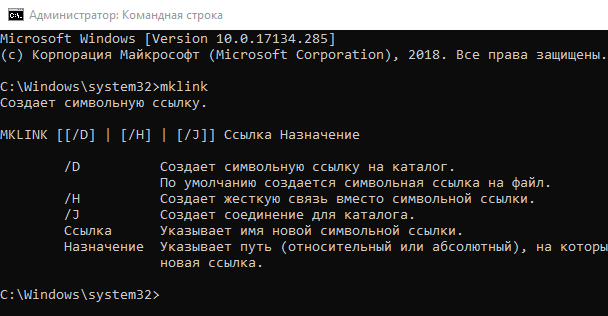
Без каких-либо дополнительных опций mklink создает символическую ссылку на файл. Команда ниже создает символическую или «мягкую» ссылку (Link) на объект Target:
Используйте /D, если вы хотите создать символическую ссылку, указывающую на каталог:
Используйте /H, если вы хотите создать жесткую ссылку, указывающую на файл:
Используйте /J для создания жесткой ссылки, указывающую на каталог:
Так, например, если вы хотите создать жесткую ссылку в C:\LinkToFolder, которая указывала бы на C:\Users\Name\OriginalFolder, вы должны выполнить следующую команду:
Вам нужно будет помещать в кавычки пути с пробелами. Например, если папка называется C:\Link To Folder и C:\Users\Name\Original Folder, вы должны использовать следующую команду:
Если вы увидите сообщение «У вас недостаточно прав для выполнения этой операции», Вам следует запустить Командную строку как Администратор.
Как создать символическую ссылку с помощью графического инструмента
Если вы хотите создавать символические ссылки с помощью инструмента с графическим интерфейсом, загрузите Link Shell Extension. Обязательно загрузите соответствующий пакет необходимых библиотек – найдёте их на странице загрузки инструмента.
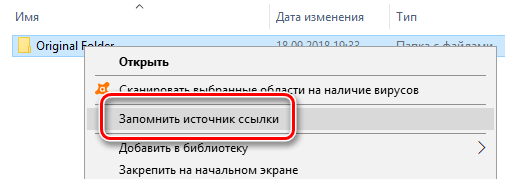
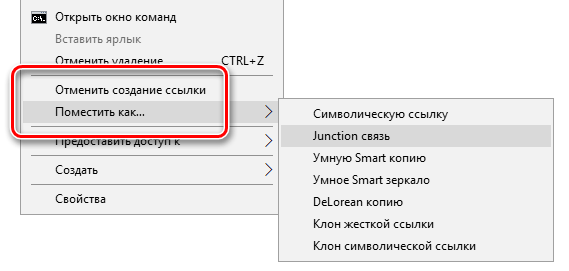
После установки найдите файл или папку, для которой вы хотите создать ссылку, щелкните её правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Запомнить источник ссылки» в контекстном меню.
Затем вы можете щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши в другой папке, указать на меню «Поместить как» и выбрать тип создаваемой ссылки.
Как удалить символические ссылки
Чтобы избавиться от символической ссылки, вы можете просто удалить её, как и любой другой файл или каталог. Только будьте осторожны: удаляйте ссылку, а не файл или каталог, к которому она привязана.
Как создать символьную ссылку в Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7
Товарищи, добрый день. Хотя эта тема и не самая популярная, но она мне очень много раз выручала, поэтому я не могу о ней не написать. Итак, что значит термин «символьная ссылка» я возьму из энциклопедии Wikipedia:
Символьная ссылка (также симлинк от англ. Symbolic link, символическая ссылка) — специальный файл в файловой системе, для которого не формируются никакие данные, кроме одной текстовой строки с указателем. Эта строка трактуется как путь к файлу, который должен быть открыт при попытке обратиться к данной ссылке (файлу). Символьная ссылка занимает ровно столько места в файловой системе, сколько требуется для записи её содержимого (нормальный файл занимает как минимум один блок раздела).
По своей сути же, симлинк — это ярлык, который позволяет системе думать, что это не ярлык, а настоящий файл (или папка). К примеру, частое применение символьной ссылок для папок — это установка игры на SSD, с последующем переносом файлов графики на жесткий диск, с целью экономия места на SSD и создание символьной ссылки до исходного места. Игра будет думать, что все файлы находятся в исходной папке. Так же символьные ссылки можно применять когда используются одинаковые файлы в нескольких каталогах, чтобы не вносить правки во все файлы, можно создать с одного файла символьные ссылки и вносить изменения один раз.
Создать символьную ссылку очень просто и сейчас я вам это докажу. Открываем командную строку, нажимаем Win+R, вводим cmd и жмём ОК. Хотя если вы собираетесь работать с системными файлами, может понадобиться командная строка с правами администратора.
Дальше нам нужно ввести команду для создания символьной ссылки, выглядит она следующем образом:
где /j — атрибут создания соединения для каталога. Если вы создаете ссылку на файл, атрибут ставить не надо.
К примеру, если я хочу создать символьную ссылку на папку mklink на локальном диске E, как папку mk на диске С, мне нужно ввести следующую команду (и да, символьная ссылка может называться не так, как исходный файл (папка):
В результате мы получим вот это.
Если же мы хотим создать символьную ссылку на файл, например на файл 1.txt, хранящийся в корне диска E. для использования в виде файла 2.txt. скажем в папке mslink на диске C, команда будет выглядеть вот так:
А на выходе получим вот это.
Резюмируя скажу, что знание возможностей данной функции, открывает большие возможности. С помощью неё я выходил из нескольких ситуаций, когда не хватало свободного пространства, на моем старом SSD, позволяя быстро перенести игру из папки origin на другой диск. Но вариантов использования её гораздо больше, к примеру перенос кэша браузеров, о котором мы поговорим в одной из будущих статей.
Вроде всё. Надеюсь эта статья оказалась вам полезной, обязательно нажмите одну из кнопок ниже, чтобы рассказать о ней друзьям. Также подпишитесь на обновления сайта, введя свой e-mail в поле справа или подписавшись на группу во Вконтакте и канал YouTube.
Спасибо за внимание
Add custom Folders to Favorite Links in Windows File Explorer
When you open Windows File Explorer or whenever you create a new file, open a new file or save a new file, you are presented with a File Dialog Box, where you can save the files. On the left side, in the Navigation Pane, you will see standard locations or places like Desktop, Computers, Pictures, etc, mentioned, which are easily accessible. This is called the Places Bar or the Favorites Links in Windows 10/8/7/Vista. If needed, you can with this tip, add your desired custom shortcuts to Open and Save dialog boxes in Windows.
Add or Remove Folders to Favorite Links in Explorer
There are several ways to add custom Folders to Favorite Links in Windows 10 File Explorer:
- Create a Shortcut
- Use Add current location to Favorites link
- Use Drag and Drop
- Tweak the Registry
- Using Group Policy Editor
- Using a third-party tool.
Let us look at these options in detail.
1] Open Explorer and navigate to the following folder:
Right-click in the window pane and choose New > Create Shortcut. Paste the path of the folder, which you are desirous of adding > Next > Give Shortcut a Name > Finish. Or else you can simply cut-paste its shortcut in this location.
Your Favorites will now show the custom desired place.
2] You may navigate to the folder you want to add here, then right-click on Favorites
Then select Add current location to Favorites.
3] Simply drag and drop the folder in this Favorites link.
4] Open Registry Editor and navigate to the following key:
Right-click on the Place0 in RHS pane and click on Modify. Add the desired folder path in Value Data and click OK. Do so similarly for other places.
5] The Places bar can also be changed using Group Policy.
To do so, Type gpedit.msc in Start Search bar and hit Enter. Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Explorer or File Explorer > Common Open File Dialog > Items Displayed In Places Bar.
Click on Display Properties, to open its Dialog Box. Select Configured, and add the folder paths in the boxes provided. Click Apply > OK.
The valid items you may display in the Places Bar are:
- Shortcuts to local folders — (ex. C:\Windows)
- Shortcuts to remote folders — (\\server\share)
- FTP folders
- web folders
- Common Shell folders.
The list of Common Shell Folders that may be specified: Desktop, Recent Places, Documents, Pictures, Music, Recently Changed, Attachments and Saved Searches.
If you disable or do not configure this setting the default list of items will be displayed in the Places Bar.
In Windows 10/8/7/Vista, this policy setting applies only to applications that are using the Windows XP common dialog box style. This policy setting does not apply to the new Windows Vista common dialog box style.
6] Use some small freeware applications which are available, like the PlacesBar Editor, where you can customize Windows as well as Office Dialog Places. Some other freeware are Shell Places Bar Editor, PlaceBar Constructor, & PlacesBar Tweaker.
Symlinks in Windows 10!
Overview
Symlinks, or symbolic links, are “virtual” files or folders which reference a physical file or folder located elsewhere, and are an important feature built in to many operating systems, including Linux and Windows.
The Windows’ NTFS file system has supported symlinks since Windows Vista. However, it hasn’t been easy for Windows developers to create symlinks. In our efforts to continually improve the Windows Developer experience we’re fixing this!
Starting with Windows 10 Insiders build 14972, symlinks can be created without needing to elevate the console as administrator. This will allow developers, tools and projects, that previously struggled to work effectively on Windows due to symlink issues, to behave just as efficiently and reliably as they do on Linux or OSX.
Background
A symlink is essentially a pointer to a file or folder located elsewhere, consumes little space and is very fast to create (compared to copying a file and its contents).
Because of this, developers often replace duplicate copies of shared files/folders with symlinks referencing physical files/folders. Replacing redundant copies of files can save a great deal of physical disk space, and significantly reduce the time taken to copy/backup/deploy/clone projects.
In UNIX-compatible operating systems like Linux, FreeBSD, OSX, etc., symlinks can be created without restrictions.
However, for Windows users, due to Windows Vista’s security requirements, users needed local admin rights and, importantly, had to run mklink in a command-line console elevated as administrator to create/modify symlinks. This latter restriction resulted in symlinks being infrequently used by most Windows developers, and caused many modern cross-platform development tools to work less efficiently and reliably on Windows.
Now in Windows 10 Creators Update, a user (with admin rights) can first enable Developer Mode, and then any user on the machine can run the mklink command without elevating a command-line console.
What drove this change?
The availability and use of symlinks is a big deal to modern developers:
Many popular development tools like git and package managers like npm recognize and persist symlinks when creating repos or packages, respectively. When those repos or packages are then restored elsewhere, the symlinks are also restored, ensuring disk space (and the user’s time) isn’t wasted.
Git, for example, along with sites like GitHub, has become the main go-to-source code management tool used by most developers today.

The use of package managers in modern development has also exploded in recent years. For example, node package manager (npm) served
400 million installs in the week of July 1 st 2015, but served more than 1.2 billion installs just one year later – a 3x increase in just one year! In late June 2016, npm served more than 1.7 billion node packages in just seven days!

There are clear drivers demanding that Windows enables the ability to create symlinks to non-admin users:
- Modern development projects are increasingly portable across operating systems
- Modern development tools are symlink-aware, and many are optimized for symlinks
- Windows developers should enjoy a development environment that is at least the equal of others
How to use Symlinks
Symlinks are created either using the mklink command or the CreateSymbolicLink API
mklink
- There is no change in how to call mklink. For users who have Developer Mode enabled, the mklink command will now successfully create a symlink if the user is not running as an administrator.
CreateSymbolicLink
- To enable the new behavior when using the CreateSymbolicLink API, there is an additional dwFlags option you will need to set:
| Value | Meaning |
| SYMBOLIC_LINK_FLAG_ALLOW_UNPRIVILEGED_CREATE 0x2 | Specify this flag to allow creation of symbolic links when the process is not elevated |
Example Use
In the example below:
- A subfolder folder called “animals” containing three files (cat.txt, dog.txt, and fish.txt)
- (green) The mklink command is executed to create a symlink called “pet.txt” pointing at the “animalsdog.txt” file
- (blue) When the contents of the current folder are listed, the symlink can be seen (yellow)
- (purple) When contents of pet.txt are queried, the content of the referenced file (“dog.txt”) is displayed
Once created, symlinks can be opened, loaded, deleted, etc., just like any other file. Here, the pet.txt symlink is being opened in Notepad (red):
How do I try it?
This new symlinks support first shipped in Windows 10 Insiders Build 14972, and will be formally delivered in Windows 10 Creators Update. We are also working with the owners of open-source community tools such as Git and npm so they know symlink improvements are coming and can make the necessary changes to better support symlinks on Windows.
We encourage you to take this new feature for a spin and be sure to let us know via the Windows 10 Feedback hub or on Twitter etc. (see below). Please sign up for the Windows Insiders program if you haven’t already to try out symlinks!