- Using ‘apt search’ and ‘apt show’ Commands to Search and Find Details of Packages in Ubuntu
- Why would you want to use apt search or apt show command?
- Search for available packages using apt search command
- Use apt search for package name only
- Get detailed information on a package using apt show command
- Conclusion
- Команда apt в Linux
- Обновление индекса пакета ( apt update )
- Обновление пакетов ( apt upgrade )
- Полное обновление ( apt full-upgrade )
- Установка пакетов ( apt install )
- Удаление пакетов ( apt remove )
- Удалить неиспользуемые пакеты ( apt autoremove )
- Листинг пакетов ( apt list )
- Поиск пакетов ( apt search )
- Информация о пакете ( apt show )
- Выводы
- How to use apt-cache search to find packages
- Search Packages using apt-cache search
- Alternative ways
- Search Packages using apt Search
- Search Packages using aptitude
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
Using ‘apt search’ and ‘apt show’ Commands to Search and Find Details of Packages in Ubuntu
Last updated October 29, 2020 By Abhishek Prakash 11 Comments
This is a detailed beginners guide to apt search command. Using apt search and apt show commands, you can get details of the available versions, dependencies, repositories and other important information about packages in Ubuntu.
Have you ever wondered if a certain package is available to install via apt package manager?
Have you wondered if the package offered by Ubuntu repositories are the latest one or not?
The apt package manager in Ubuntu and many other distribution provides two handy apt command options for this purpose.
The apt search command looks for the provided string in the name and description of the packages.
The apt show command provides detailed information on a package:
The commands don’t require you to be root in Ubuntu. Here’s an example of these commands:
Why would you want to use apt search or apt show command?
Let’s say you want to install Gambas programming language in Ubuntu. You are happy with your knowledge of the apt command so you decided to use the command line for installing application.
You open a terminal and use the apt command to install gambas but it results in unable to locate package error.
Why did Ubuntu not find the gambas package? Because there is no such package called gambas. Instead, it is available as gambas3. This is a situation where you could take the advantage of the apt search command.
Let’s move to apt show command. This command provides detailed information about a package, its repository, dependencies and a lot more.
Knowing what version of a package is available from the official repository could help you in deciding whether you should install it from some other sources.
The apt package manager works on a local database/cache of available packages from various repositories. This database contains the information about the available package version, dependencies etc. It doesn’t contain the entire package itself. The packages are downloaded from the remote repositories.
When you run the sudo apt update command, this cache is created/updated in the /var/lib/apt/lists/ directory. The apt search and apt show commands utilize this cache.
The term package is used for an application, program, software.
Search for available packages using apt search command
Let me continue the gambas example. Say, you search for
It will give you a huge list of packages that have “gambas” in its name or description. This output list is in alphabetical order.
Now, you’ll of course have to make some intelligent prediction about the package you want. In this example, the first result says “Complete visual development environment for Gambas”. This gives you a good hint that this is the main package you are looking for.
Why so many packages associated with gambas? Because a number of these gambas packages are probably dependencies that will installed automatically if you install the gambas3 package. If you use the ‘apt show gambas3‘ command, it will show all the dependencies that will be installed with gambas3 package.
Some of these listed packages could be libraries that a developer may need in some special cases while developing her/his software.
Use apt search for package name only
By default, apt search command looks for the searched term in both the name of the package and its description.
You may narrow down the search by instructing the apt command to search for package names only.
If you are following this as a tutorial, give it a try. Check the output with search term ‘transitional’ with and without –names-only option and you’ll see how the output changes.
Bonus Tip: You can use ‘apt list –installed’ command to look for installed packages in Ubuntu.
Get detailed information on a package using apt show command
The output of the apt search commands a brief introduction of the packages. If you want more details, use the apt show command.
The apt show command works on the exact package name and it gives you a lot more information on the package. You get:
- Version information
- Repository information
- Origin and maintainer of the package information
- Where to file a bug
- Download and installation size
- Dependencies
- Detailed description of the package
- And a lot more
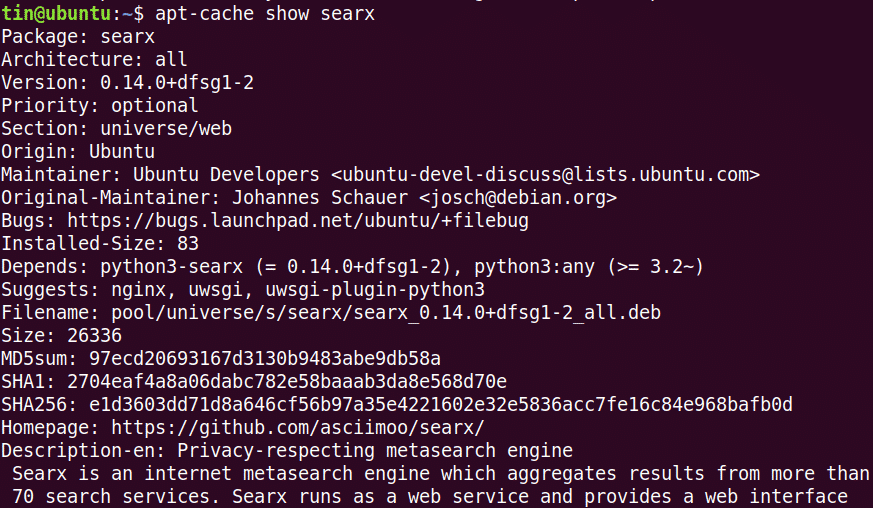
Here’s an example:
You need to give the exact package name otherwise the apt show won’t work. The good thing is that tab completion works apt show command.
As you can see in the previous image, you have plenty of information that you may found helpful.
The apt show command also works on installed packages. In that case, you can see which source the package was installed from. Was it a PPA or some third-party repository or universe or the main repository itself?
Personally, I use apt show a lot. This helps me know if the package version provided by Ubuntu is the latest or not. Pretty handy tool!
Conclusion
If you read my detailed guide on the difference between apt and apt-get commands, you would know that this ‘apt search’ command works similar to ‘apt-cache search‘. There is no such command as “apt-get search”.
The purpose of creating apt command is to give you one tool with only enough option to manage the packages in your Debian/Ubuntu system. The apt-get, apt-cache and other apt tools still exist, and they can be used in scripting for more complex scenarios.
I hope you found this introduction to apt search and apt show commands useful. I welcome your questions and suggestions on this topic.
If you liked it, please share it on various Linux forums and communities you frequent. That helps us a lot. Thank you.
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
Команда apt в Linux
apt — это утилита командной строки для установки, обновления, удаления и иного управления пакетами deb в Ubuntu, Debian и связанных дистрибутивах Linux. Он сочетает в себе наиболее часто используемые команды из инструментов apt-get и apt-cache с различными значениями по умолчанию некоторых параметров.
apt разработан для интерактивного использования. Предпочитайте использовать apt-get и apt-cache в своих сценариях оболочки, поскольку они обратно совместимы между различными версиями и имеют больше параметров и функций.
Большинство команд apt необходимо запускать от имени пользователя с привилегиями sudo .
Это руководство служит кратким справочником по командам apt .
Обновление индекса пакета ( apt update )
Индекс пакетов APT — это в основном база данных, в которой хранятся записи о доступных пакетах из репозиториев, включенных в вашей системе.
Чтобы обновить индекс пакета, выполните команду ниже. Это приведет к получению последних изменений из репозиториев APT:
Всегда обновляйте индекс пакета перед обновлением или установкой новых пакетов.
Обновление пакетов ( apt upgrade )
Регулярное обновление вашей системы Linux — один из наиболее важных аспектов общей безопасности системы.
Чтобы обновить установленные пакеты до последних версий, выполните:
Команда не обновляет пакеты, требующие удаления установленных пакетов.
Если вы хотите обновить один пакет, передайте имя пакета:
Полное обновление ( apt full-upgrade )
Разница между upgrade и full-upgrade заключается в том, что при последующем удаляются установленные пакеты, если это необходимо для обновления всей системы.
Будьте особенно осторожны при использовании этой команды.
Установка пакетов ( apt install )
Установить пакеты так же просто, как запустить следующую команду:
Если вы хотите установить несколько пакетов с помощью одной команды, укажите их в виде списка, разделенного пробелами:
Для установки локальных файлов deb укажите полный путь к файлу. В противном случае команда попытается получить и установить пакет из репозиториев APT.
Удаление пакетов ( apt remove )
Вы также можете указать несколько пакетов, разделенных пробелами:
Команда remove удалит указанные пакеты, но при этом могут остаться некоторые файлы конфигурации. Если вы хотите удалить пакет, включая все файлы конфигурации, используйте purge вместо remove :
Удалить неиспользуемые пакеты ( apt autoremove )
Каждый раз, когда в системе устанавливается новый пакет, который зависит от других пакетов, также будут установлены зависимости пакетов. Когда пакет будет удален, зависимости останутся в системе. Эти оставшиеся пакеты больше не используются ничем и могут быть удалены.
Чтобы удалить ненужные зависимости, используйте следующую команду:
Листинг пакетов ( apt list )
Команда list позволяет вывести список доступных, установленных и обновляемых пакетов.
Чтобы вывести список всех доступных пакетов, используйте следующую команду:
Команда напечатает список всех пакетов, включая информацию о версиях и архитектуре пакета. Чтобы узнать, установлен ли конкретный пакет, вы можете отфильтровать вывод с помощью команды grep .
Чтобы вывести список только установленных пакетов, введите:
Перед фактическим обновлением пакетов может быть полезно получить список обновляемых пакетов:
Поиск пакетов ( apt search )
Эта команда позволяет вам искать данный пакет в списке доступных пакетов:
В случае обнаружения команда вернет пакеты, имя которых соответствует поисковому запросу.
Информация о пакете ( apt show )
Информация о зависимостях пакетов, размере установки, источнике пакета и т. Д. Может быть полезна перед удалением или установкой нового пакета.
Чтобы получить информацию о данном пакете, используйте команду show :
Выводы
Умение управлять пакетами — важная часть системного администрирования Linux.
apt — это менеджер пакетов для дистрибутивов на основе Debian. Чтобы узнать больше о команде apt откройте терминал и введите man apt .
Не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии, если у вас есть вопросы.
Источник
How to use apt-cache search to find packages
In Ubuntu and Debian systems, you can search for any package just by a keyword related to its name or description through the apt-cache search. The output returns you with a list of packages matching your searched keyword. Once you find the exact package name, you can then use it with the apt install for installation. It’s also helpful when looking for information about a specific package. Note that with apt-cache search, you can search for any apt package that is installed or yet to be installed.
This article will explain you how to search for a package through the apt-cache search command in your system repositories. We will also learn some other commands: apt search and aptitude through which you can also search for any package.
Note: We have performed the procedure explained in this article on the Ubuntu 18.04 LTS system Terminal. To open the Terminal in Ubuntu, use the Ctrl+Alt+T keyboard shortcut.
Before performing any of the following methods, we will recommend you to update the repository index as follows:
Search Packages using apt-cache search
Apt-cache is a command-line tool used for searching apt packages on a Ubuntu or Debian based systems. With apt-cache search, you can search for any package using the keyword related to its name or description. In the output, it displays all the packages matching the search criteria.
With apt-cache search, you can search and display the information about the available packages from the internet repositories. It can also be used to search for information about the packages which are already installed on your system. It obtains information about the packages from different sources and saves them in the local database which is updated by running the apt update operation.
In order to search for packages, type apt-cache search followed bt the relevant keyword. Here is the syntax to do so:
Replace the keyword with any of installed or installable package name. Note that the keyword can be exact or a part of the package name or it can be any word related to package description. In the output, you will see a list of packages matched with the mentioned keyword and a brief description of each package.
For instance, we want to install a storage management solution ZFS. To find the exact package name, let’s search it using apt-cache search as follows:
From the output, you can identify the exact package name that is “zfsutils-linux” along with a short description. As you can see the list it displayed is too long. You can use the less command to view output one line or one screen at a time.
Similarly, the apt-cache search can be helpful if you want to install a web server but do not remember the name of the package. In this case, you can search for the package using any keyword related to the package description. For instance, I found it really helpful once I needed to install the search engine about which I only know that it’s a meta search engine that protects the privacy of its users. However, i did not remember the name of that search engine, so i have entered the search term as follows:
When the result appeared, I found the required search engine name that was “Searx”. After that, I simply used the apt install searx command to install it.
Similarly, if we use apt-cache with show flag, it will display basic information about the package including the version, size, dependencies, description and much more. To find information about a certain package, use the show flag as follows:
Alternative ways
Here are some other ways which can also be used to search for an installed or installable package in a system.
Search Packages using apt Search
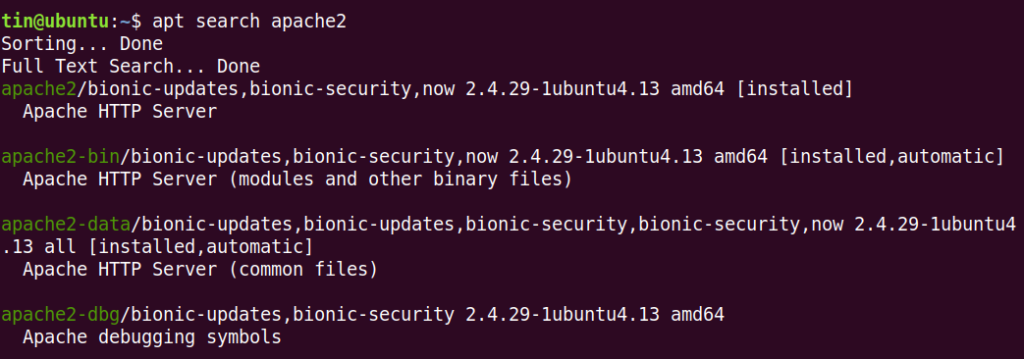
Apt search is the apt equivalent of apt-cache search in older apt-get command. Some users prefer the apt search command because of its well presented display of results. It displays the packages list along with their latest available versions and a short description. The best thing about apt search is that it highlights the packages name and maintains some space among different packages. Also, you will see the Installed label at the end of the already installed packages.
In order to search for a package, type apt search followed by the keyword related to the package name.
An example of this would be searching for the Apache2 package using the following command:
Search Packages using aptitude
Aptitude is the front end of the apt command in Linux used for installing, upgrading, and removing packages. It can also be used for searching a package in a Linux system.
Aptitude is not installed by default in Linux, so you will have to manually install it. To do so, execute the install command as follows:
The system might ask for confirmation by providing you with a Y/n option. Hit y and then Enter to confirm, after that the Aptitude will be installed on your system.
Now, in order to search for a package through aptitude, type apt search followed by the keyword related to the package name.
You will see the results similar to the following:
That is all there is to it! In this article, we have learned how to search for a package using the apt-cache search command. In addition, we also learned the use of apt search and the aptitude command to search for a package. I hope it will be helpful whenever you need to search for either an installed or installable package in your system.
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.
Источник