- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- How to change the desktop environment in Kali Linux without reinstalling the operating system
- Table of contents
- Kali Linux desktop environments
- GNOME 3
- By the way, where is Cinnamon?
- Desktop environment selection during Kali Linux installation
- How to change Kali Linux desktop environment without reinstalling the system. Desktop environment metapackages
- How to install a new desktop in Kali Linux
- How to switch between desktop environments
- How to remove the desktop environment
- How to install a desktop for which the meta-package is missing
- What Changes When Switching Desktop Environment
- Support Articles
- Table of Contents
- Desktop Environment (Change)
- Different Desktop Environments
- Cinnamon
- GNOME
- KDE Plasma
- Troubleshooting
- Customize Notification Dialog
- Remove Duplicate Options From Login Screen
- Change Automatic Startup Programs
- Double Lock Screen Passwords
- Enable Cinnamon Lock Screen
- Removing Desktop Environments
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
How to change the desktop environment in Kali Linux without reinstalling the operating system
Table of contents
In Linux, the appearance of the operating system (desktop environment) is just a package with a set of programs, so on any Linux distribution, you can change the default desktop environment. This is done by literally a few commands.
Kali Linux desktop environments
This desktop environment is currently installed by default.
This, as well as the next two, are lightweight environments – they are not demanding on resources and are recommended for low-power (legacy) computers.
On a cursory acquaintance (booted just to take a screenshot) – this desktop environment seemed very cute.
GNOME 3
Previously, it was the default (“classic”) desktop environment. GNOME 3 has strange limitations (for example, you cannot create a shortcut on the desktop in the usual way), and in general (in my opinion) it is the most inconvenient and unfortunate desktop environment.

This environment gives room for customization and various custom widgets and plugins.

Mate is, in fact, the actual GNOME 2. The transition to GNOME 3 brought too drastic changes that not everyone accepted. For example, I personally still don’t like GNOME 3. By the way, GNOME 3 is also used in Ubuntu.
So, developers who did not agree with the concept of GNOME 3 forked GNOME 2 and called it Mate. This environment is still kept up to date and has a classic and possibly a bit outdated look.
If you ask my opinion which desktop environment is better, then I will answer, the best desktop environment is Cinnamon.
By the way, where is Cinnamon?
Cinnamon is not among the desktops offered during installation, but this desktop can be installed later.
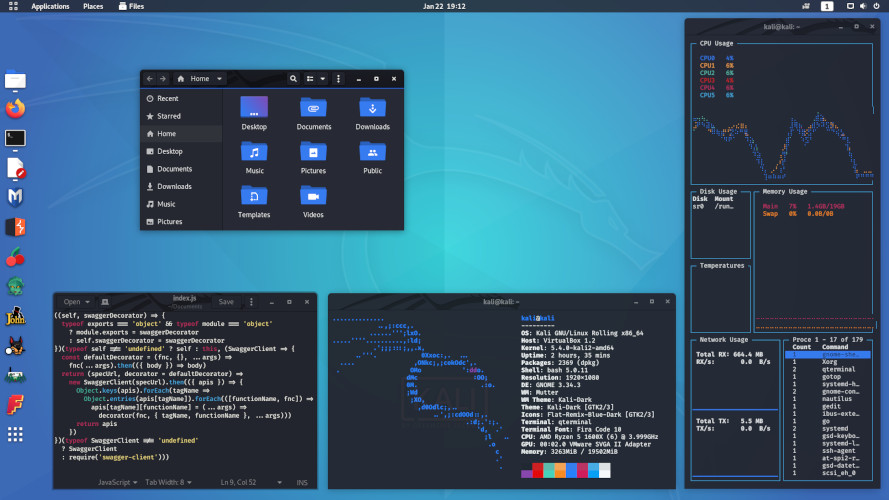
Desktop environment selection during Kali Linux installation
Therefore, when installing Kali Linux, you can choose any of the available desktops or window managers:
How to change Kali Linux desktop environment without reinstalling the system. Desktop environment metapackages
Desktop environments are full-fledged graphical shells like GNOME, Cinnamon, KDE and others.
Window managers perform only some of the functions of the graphical interface, in fact, they only allow you to open a few windows, add a desktop background, and can have a simple menu. Due to this simplicity, window managers consume a minimum of resources. But from the point of view of user convenience, they are inferior to a full-fledged desktop environment.
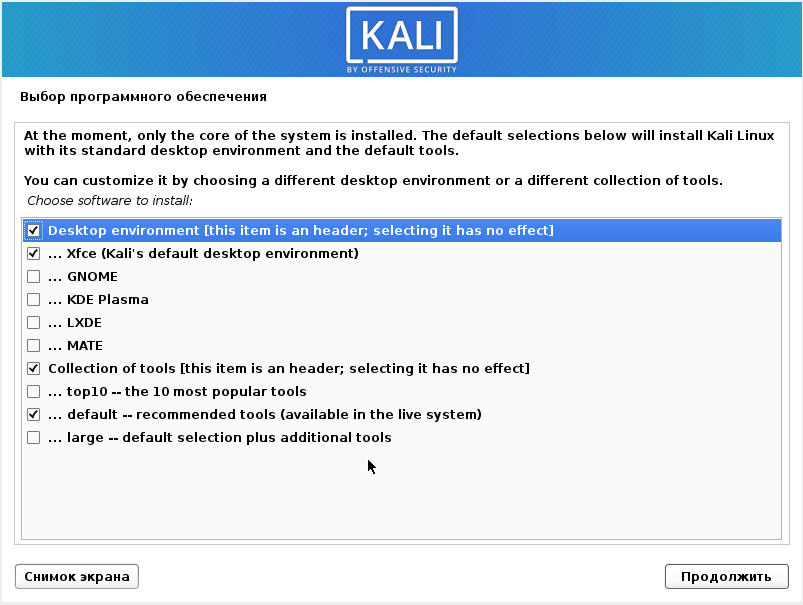
Kali Linux has the following metapackages that make it easy to install desktops:
- kali-desktop-e17: Enlightenment (window manager)
- kali-desktop-gnome: GNOME (desktop environment)
- kali-desktop-i3: i3 (window manager)
- kali-desktop-kde: KDE (desktop environment)
- kali-desktop-lxde: LXDE (window manager)
- kali-desktop-mate: MATE (desktop environment)
- kali-desktop-xfce: XFCE (window manager)
How to install a new desktop in Kali Linux
Installing a new desktop environment is done with a command like:
For example, to install GNOME, run the following command:
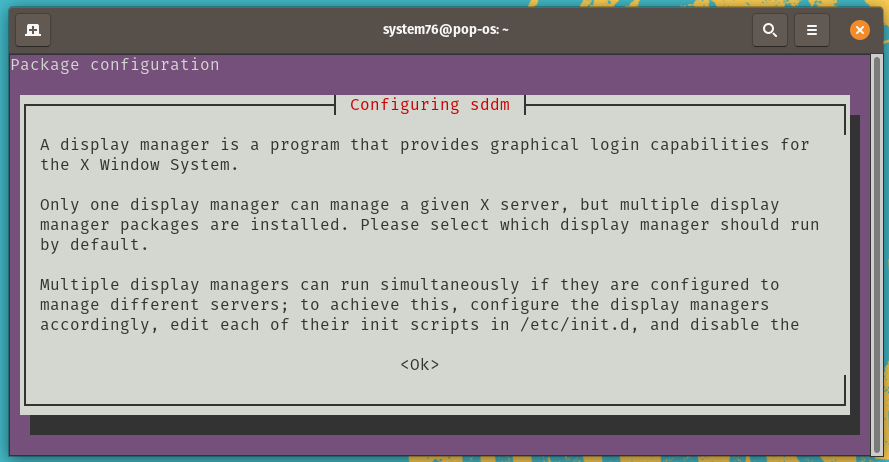
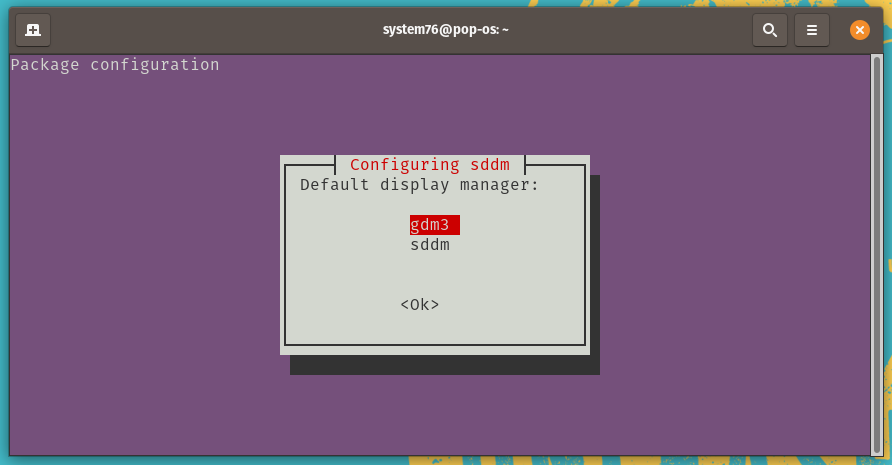
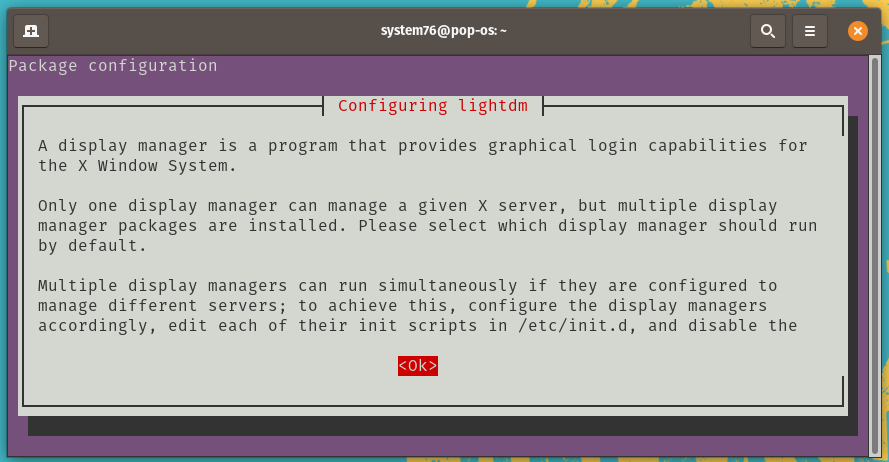
During installation, you will be prompted to select Display Manager, which is a program that provides graphical login capabilities for the X Window System. Basically, it launches in front of a graphical desktop environment (GNOME, XFCE, and others), shows a user login form and prompts you to select the desired desktop.
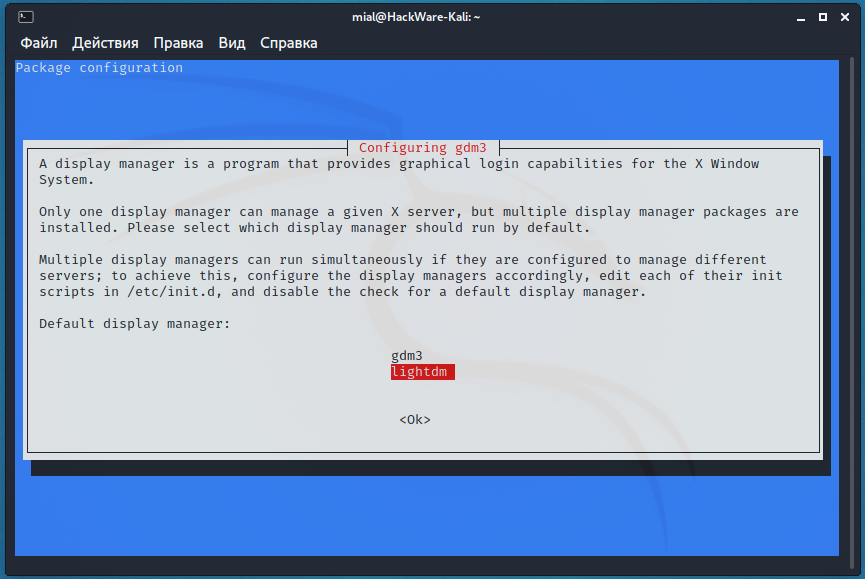
You can switch between Display Managers at any time by running the command:
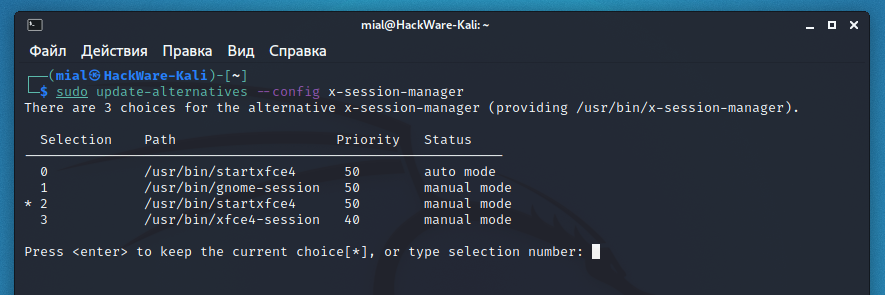
How to switch between desktop environments
To switch to the new desktop environment, run the command:
Enter the number corresponding to the desired desktop.
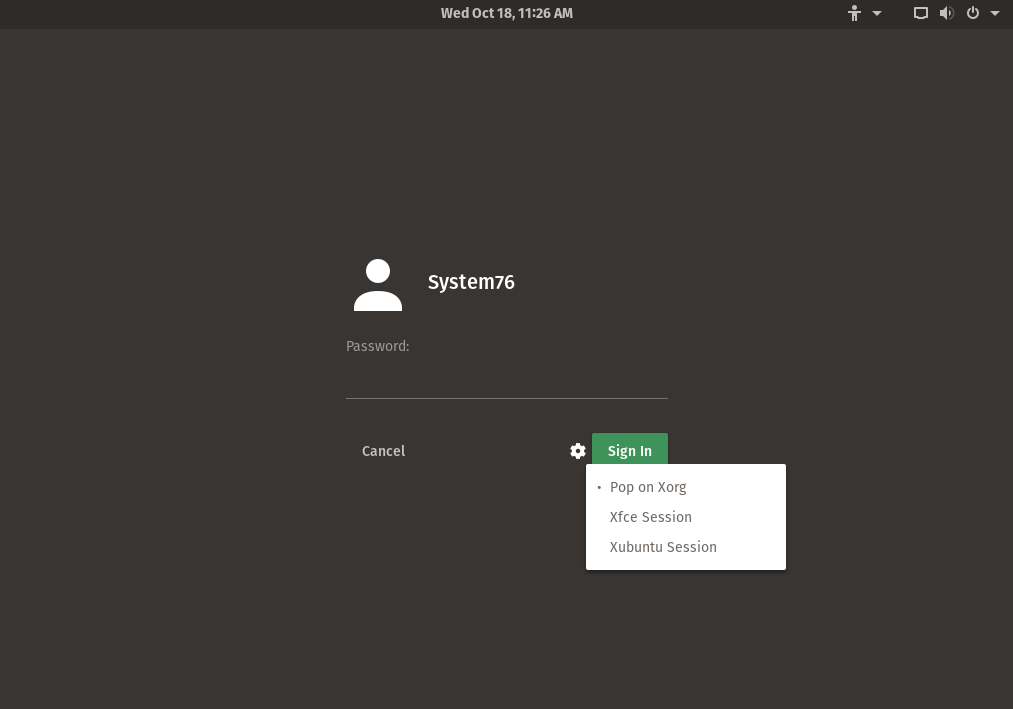
You can also select the desktop environment when the user logs on to the system.

How to remove the desktop environment
If you want to be able to switch between different window managers and desktop environments, then you do not need to uninstall previously installed packages – you can have as many graphical shells on one system as you like.
But if you finally switched to a new desktop and want to free up space, then run a command like:
For example, to remove XFCE:
How to install a desktop for which the meta-package is missing
If the Kali Linux maintainers did not provide a meta-package for any desktop environment, this does not mean that this desktop cannot be installed. If it is in the distribution repository, then it can be installed like any other package.
For example, there is no meta-package for Cinnamon (for some reason, Kali Linux maintainers don’t like Cinnamon), but you can install this desktop and switch to it, see the article “How to replace Default Desktop Environment with Cinnamon in Kali Linux” for details.
What Changes When Switching Desktop Environment
Despite the fact that when you change the desktop environment, the OS starts to look completely different, in fact, apart from the appearance, not much changes.
The most important thing is that all user files and manually installed programs remain in place, even the history of commands entered into the console remains.
But a change can happen with the tools that come with the desktop environment. Terminal, network management software, System settings can be changed. Familiar programs such as System Monitor and Screenshot may look different or may not be available in some desktop environments.
To find out, for example, which applications will be affected when moving from Xfce, type in a terminal
and press Enter.
You will be shown programs specific to Xfce.
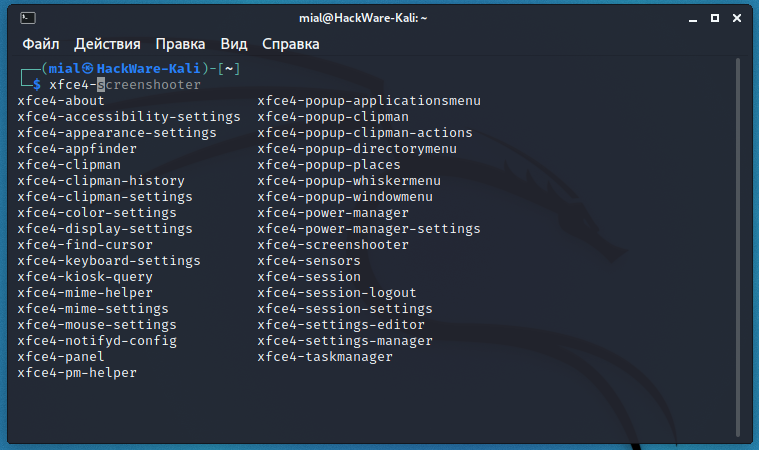
To view GNOME-specific programs, type in a terminal:
and press Enter.
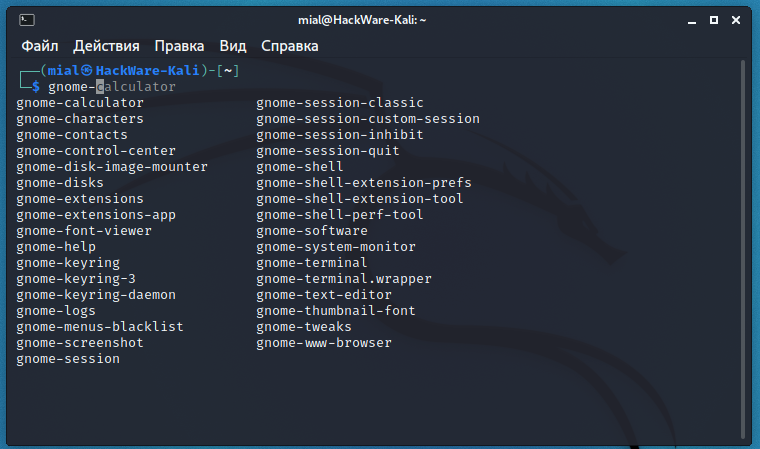
Similarly, you can check for other installed desktop environments.
In fact, if you have not removed the previous desktop environment, then you can run the programs included in it. For example, while working in Xfce, you can run programs included with GNOME:
The menu may also change if the Kali Linux developers have not created a menu for this desktop (window manager) or close to it. For example, Kali Linux maintainers do not make menus for Cinnamon, but when switching to Cinnamon, you may find that it still has a structured Kali Linux menu in which all the tools are collected and organized. Apparently Cinnamon uses a menu made for Mate, or Kali Linux has a universal menu that works in any desktop environment.
The set of wallpapers in different desktop environments may differ.
Different desktops consume a different amount of computer resources (primarily, it refers to RAM).
In all other respects, the operating system does not change and you can always return to the old desktop or try a new one.
By the way, the above applies not only to Kali Linux, that is, on any Linux distribution, you can change the desktop to your liking. If you downloaded Linux Mint with Cinnamon, you can install MATE, Xfce, Enlightenment, and others there.
Источник
Support Articles
Table of Contents
Desktop Environment (Change)
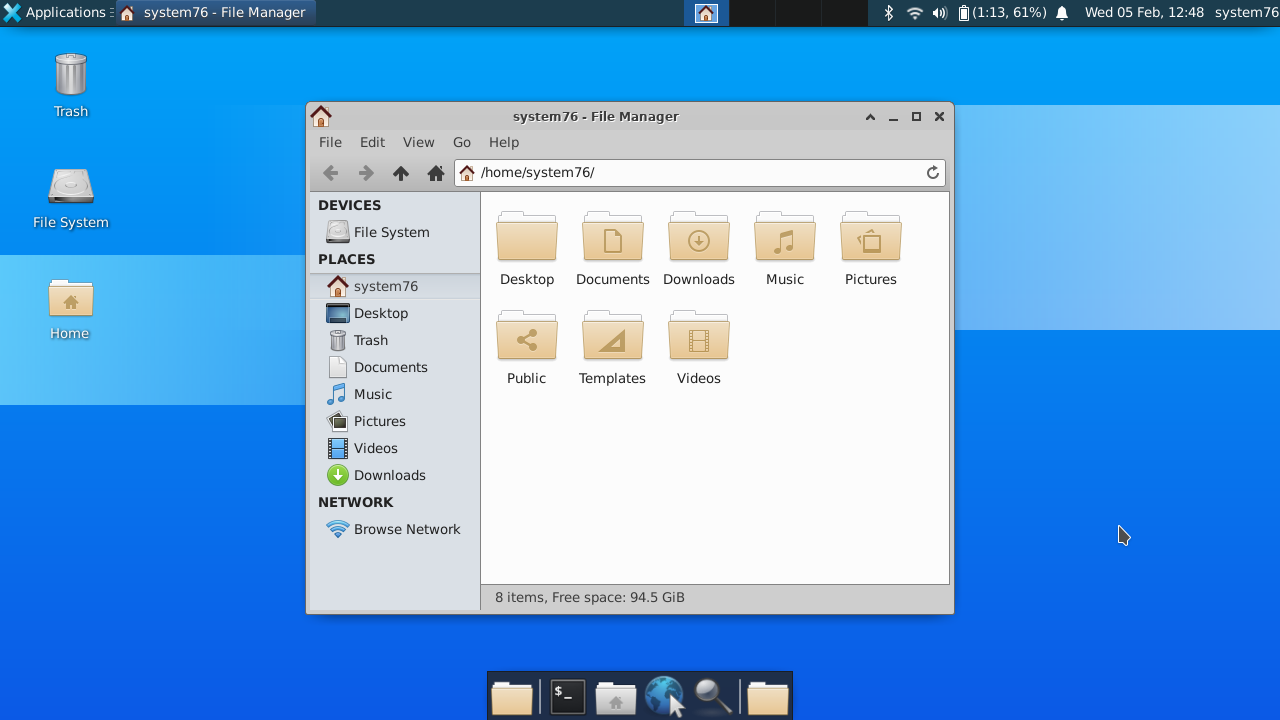
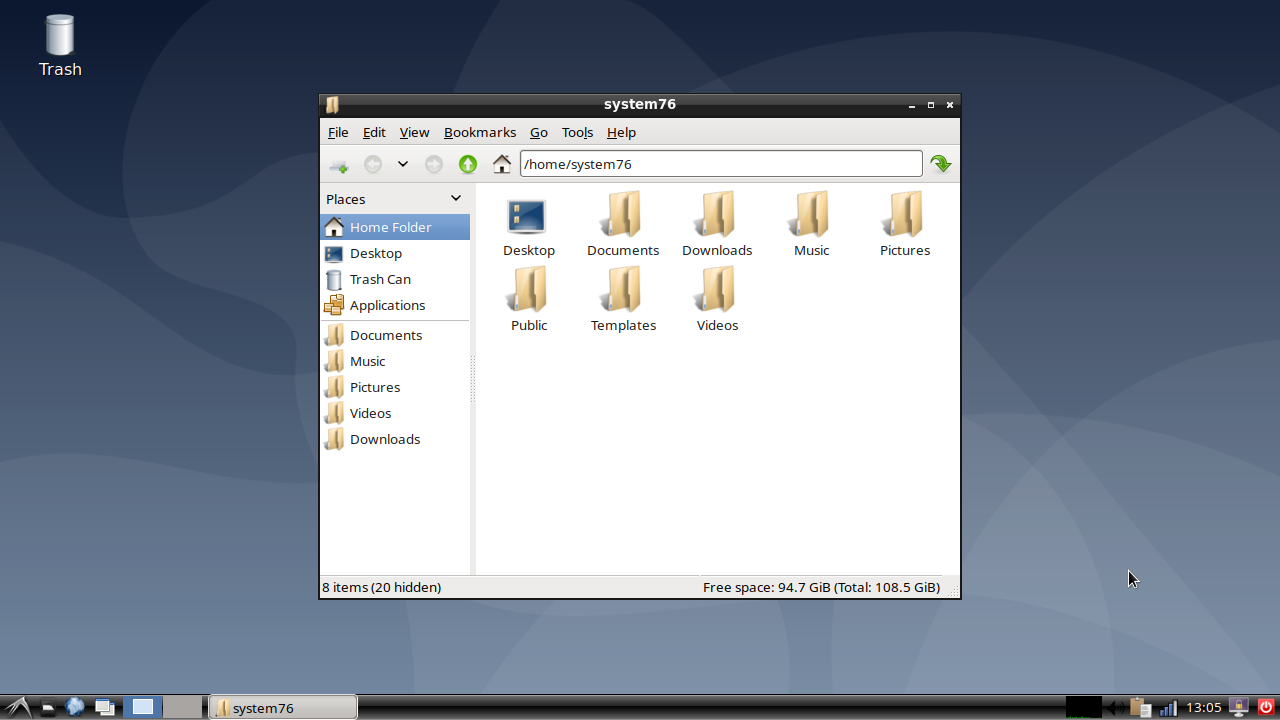
Pop!_OS and Ubuntu both include the GNOME desktop environment by default. A desktop environment is responsible for the look and feel of the graphical desktop, and includes many of the key programs that get used every day.
You can install an alternative desktop environment using the instructions below. If you run into trouble while using an alternative desktop environment, you may wish to revert to the default environment. To ensure the default GNOME desktop environment is installed in Pop!_OS, install the pop-desktop package:
For Ubuntu, install the ubuntu-desktop package instead:
The desktop environment is basically the top graphical layer of the OS. The desktop environment is launched by a display manager; Pop!_OS and Ubuntu both use GDM (GNOME Display Manager) by default.
If multiple desktop environments are installed, GDM will display a gear icon, which will allow you to select the desktop environment you want to launch. You will need to either reboot or restart your display manager using sudo systemctl restart gdm before a newly-installed desktop environment will show up in the list of options.
Different Desktop Environments
MATE is a simple and attractive desktop using traditional concepts. MATE is a fork of GNOME 2.
This command will install MATE and its dependencies:
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is used in Linux Mint by default. Cinnamon strives to provide a traditional experience and is a fork of GNOME 3.
Cinnamon is installed with:
GNOME
While Pop and Ubuntu contain GNOME by default, both include a number of customizations to GNOME. You can also install a vanilla GNOME session to get the upstream GNOME experience.
You can install the vanilla GNOME session using this command:
KDE Plasma
The KDE Plasma desktop environment is a familiar working environment and looks similar to Windows’ desktop. It is highly customizable and looks clean.
The KDE Plasma desktop and its dependencies can be installed with this command:
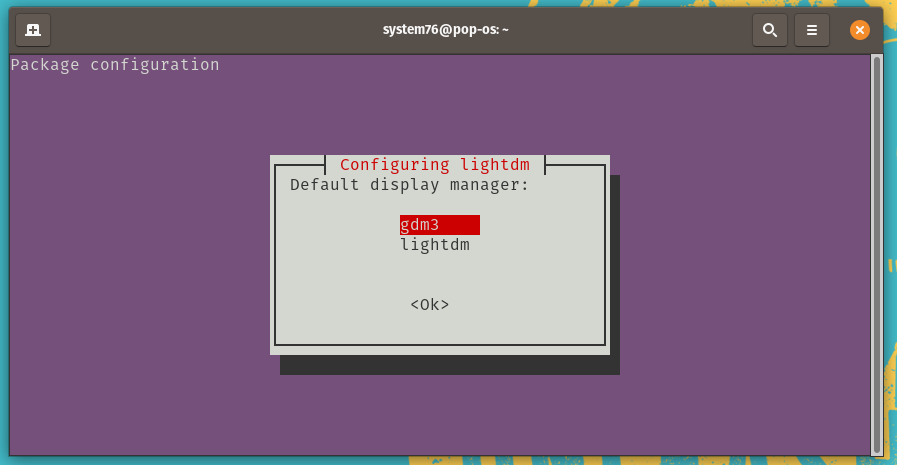
While installing KDE, you’ll be prompted to choose a display manager:
Press Enter to select the OK option. (If the OK option is not selected, press Tab to select it.) At the list, press Enter again to keep gdm3 as your display manager:
UKUI is a lightweight desktop environment based on a pluggable framework for Linux and other UNIX-like distributions. It provides a simple experience for browsing, searching, and managing your computer. It is developed using GTK and Qt.
UKUI can be installed with:
XFCE embodies the traditional UNIX philosophy of modularity and re-usability. This environment provides a good amount of conformity for the programs written for it. XFCE also provides a highly customizable environment, while being leaner on resources.
You can install XFCE and its dependencies with this command:
While installing XFCE, you’ll see a prompt to select your default display manager:
Press Enter to select the OK option. (If the OK option is not selected, press Tab to select it.) At the list, press Enter again to keep gdm3 as your display manager:
The Lightweight X11 Desktop Environment is a fast and energy-saving desktop environment. It looks similar to older versions of Windows. This is a lean desktop environment and can help extend battery life in laptops.
LXDE can be installed with:
While installing LXDE, you’ll see a prompt to select your default display manager:
Press Enter to select the OK option. (If the OK option is not selected, press Tab to select it.) At the list, press Enter again to keep gdm3 as your display manager:
LXQt is a lightweight Qt desktop environment. It’s being developed as a successor to LXDE. It is focused on being a classic desktop with a modern look and feel.
LXQt can be installed with:
Troubleshooting
Desktop environments can interfere with each other or change system-wide settings. Issues with a desktop environment’s appearance can generally be fixed by changing the theme in the Appearance control panel.
Customize Notification Dialog
Xfce will change the notification dialog to its own. It can be configured with this command:
Remove Duplicate Options From Login Screen
Some desktop environments provide more than one session. For example, Cinnamon provides both a 2D and a 3D session. The options available at login are located in the /usr/share/xessions directory, and unneeded options can be removed by deleting the corresponding files. For example, to remove Cinnamon’s extra option:
Change Automatic Startup Programs
Some desktop environments configure additional programs to start at boot. To change them, run the Startup Applications program and turn off any unwanted startup programs.
Double Lock Screen Passwords
GNOME does not use a screensaver (only a lock screen), but other desktop environments may install the classic GNOME screensaver package as a dependency. If you’re being prompted for a password twice after suspending or locking the screen, disable the second prompt with this command:
Or, if that doesn’t stop the second prompt, uninstall the redundant screensaver with this command:
Enable Cinnamon Lock Screen
If Cinnamon’s desktop lock screen isn’t functioning, this command will re-enable it:
Removing Desktop Environments
If you no longer want to use a desktop environment, it can be removed by using:
Источник