- ИТ База знаний
- Полезно
- Навигация
- Серверные решения
- Телефония
- Корпоративные сети
- Как сменить mac – адрес в Linux
- Находим текущий mac – адрес сетевого интерфейса
- Меняем MAC с помощью Macchanger. Установка
- Меняем MAC с помощью iproute
- Итоги
- Changing Your MAC Address/Linux
- Making Changes Permanent — Surviving a Reboot [ edit | edit source ]
- How to Change MAC Address in Linux
- Changing MAC address in Linux
- Step 1: Find your MAC address and network interface
- Method 1: Change MAC address using Macchanger
- How to Use Macchanger to change MAC address
- Method 2: Changing Mac address using iproute2 [intermediate knowledge]
- Dimitrios Savvopoulos
- How To Permanently Change The MAC Address On Linux
- How to check the original and new MAC addresses
- How to disable changing the MAC on each reboot with systemd
ИТ База знаний
Курс по Asterisk
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Как сменить mac – адрес в Linux
Меняем физический адрес
3 минуты чтения
Усаживайтесь на кушетку поудобнее. Зачем, в первую очередь, вы хотите сменить mac – адрес у вашего сервера на базе Linux? Может хотите блочить его на фаерволе, или попробовать совершить «магию» с лицензиями, которые привязаны к маку?
Мини — курс по виртуализации
Знакомство с VMware vSphere 7 и технологией виртуализации в авторском мини — курсе от Михаила Якобсена
В целом, дело ваше. Мы покажем способ, как это сделать. Давайте по шагам.
Находим текущий mac – адрес сетевого интерфейса
Сначала давайте посмотрим на текущий mac вашего сервера. Сделать это можно командой:
Вывод сервера будет примерно таким. Он будет содержать параметры (mac — адреса всех ваших интерфейсов):
Как мы видим, например, у интерфейса enp0s12e2 текущий mac – адрес это 33:23:f8:8b:d7:65 . Давайте поменяем его.
Меняем MAC с помощью Macchanger. Установка
Macchanger — это ну очень простая утилита, чтобы смотреть, менять и управлять MAC – адресами на ваших сетевых интерфейсах. Она доступна на почти всех Linux – подобных системах.
Например, чтобы установить Macchanger на Fedora, CentOS или RHEL используйте команду:/p>
А если у вас Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint или даже Kali Linux, то установить ее можно вот так:
Как использовать Macchanger
Помните имя интерфейса, которое мы обсудили чуть раньше? Ага, мы про enp0s12e2
Например, чтобы присвоить этому интерфейсу рандомный mac, используйте команду:
После смены, проверьте, что мак – адрес поменялся командой:
Он стал другим, не так ли? Теперь, чтобы присвоить конкретный (нужный вам) мак интерфейсу, примените команду:
Где, как не сложно догадаться, XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX — mac, который вам нужен. Кстати, если вы поняли, что сделали что-то не то, то вернуть mac – адрес устройства к его изначальному значению можно вот так:
Меняем MAC с помощью iproute
Делать это через macchanger, честно говоря, правильнее. Однако, если не получилось/не хотите, то можно поступить вот так. Первое, выключаем интерфейс:
Далее, присваиваем новый mac выключенному интерфейсу:
Не забываем включить интерфейс обратно:
Итоги
В статье мы обсудили два способа смены адреса: через утилиту macchanger и встроенную команду ip. Мы рекомендуем использовать macchanger, как более надежный способ. Однако, решать вам.
Онлайн курс по Linux
Мы собрали концентрат самых востребованных знаний, которые позволят тебе начать карьеру администратора Linux, расширить текущие знания и сделать уверенный шаг к DevOps
Источник
Changing Your MAC Address/Linux
Under GNU/Linux, the MAC address of a network interface card (NIC) can be changed by following the procedures below.
NOTE: MAC addresses used within this article are provided for example only. Substitute according to your requirements.
NOTE: Commands below MUST be executed with root privileges (e.g. prepended with «sudo «), in order for things to work!
/etc/init.d/networking stop ifconfig eth0 hw ether 02:01:02:03:04:08 /etc/init.d/networking start
Execute » ifconfig eth0 » to confirm.
The above should work on Debian, Ubuntu, and similar distributions. Alternatively, under RHEL/Fedora and possibly other GNU/Linux distributions (incl. CentOS and Scientific Linux), to disable and restart networking, one must stop and start /etc/init.d/network , instead of /etc/init.d/networking .
If you have iproute2 utilities installed, you may prefer to use the » ip » command, as follows:
/etc/init.d/network stop ip link set eth0 address 02:01:02:03:04:08 /etc/init.d/network start
To confirm your setting, you may prefer to execute » ip link ls eth0 » or » ip addr ls eth0 » instead of » ifconfig eth0 «.
NOTE: You may not be able do this if using a DSL modem (depending on modem vendor or ISP).
Making Changes Permanent — Surviving a Reboot [ edit | edit source ]
In openSUSE and other SUSE-based systems (SUSE enterprise desktop\server, etc.) you can make changes «permanent» across reboots by adding an appropriate entry to the /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-ethN file (ifcfg-eth0 for the first Ethernet interface config file, ifcfg-eth1 — for the second, etc.):
In Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and other similar systems (Fedora, CentOS, etc.) an easy way to make changes «permanent» across reboots is to add an appropriate entry to the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ethN file (ifcfg-eth0 for the first Ethernet interface config file, ifcfg-eth1 — for the second, etc.):
Note: in the file is a value HWADDR — This is not the same thing. Use MACADDR for permanent changes.
The HWADDR «directive is useful for machines with multiple NICs to ensure that the interfaces are assigned the correct device names regardless of the configured load order for each NIC’s module. This directive should not be used in conjunction with MACADDR.» . The MACADDR «directive is used to assign a MAC address to an interface, overriding the one assigned to the physical NIC. This directive should not be used in conjunction with HWADDR.»
Upper and lower case letters are accepted when specifying the MAC address, because the network function converts all letters to upper case.
You can test changes without restarting the system by executing:
service network restart
(WARNING: doing this will break all existing network connections!)
On Debian, Ubuntu, and similar systems, place the following in the appropriate section of /etc/network/interfaces (within an iface stanza, e.g., right after the gateway line) so that the MAC address is set when the network device is started:
hwaddress ether 02:01:02:03:04:08
On Gentoo you may achieve the same result by adding an entry to the global configuration file /etc/conf.d/net for each Ethernet card. Example for the eth0 device:
You can also use the tool «GNU MACChanger» to change the MAC address under GNU/Linux.
To change MAC address during boot time with MACChanger, add the following line to your /etc/network/interfaces (example for the eth0 interface):
pre-up macchanger -m 12:34:56:78:90:AB eth0
Источник
How to Change MAC Address in Linux
Last updated October 29, 2020 By Community 5 Comments
Before I show you how to change Mac address in Linux, let’s first discuss why would you change it in the first place.
You may have several reasons. Maybe you don’t want your actual MAC address (also called physical address) to be exposed on a public network? Other case can be that the network administrator might have blocked a particular MAC address in the router or firewall.
One practical ‘benefit’ is that some public network (like Airport WiFi) allows free internet for a limited time. If you want to use the internet beyond that, spoofing your Mac address may trick the network in believing that it’s a new device. It’s a famous meme as well.
I am going to show the steps for changing MAC address (also called spoofing/faking MAC address).
Changing MAC address in Linux
Let’s go through each step:
Step 1: Find your MAC address and network interface
Let’s find out some details about the network card in Linux. Use this command to get the network interface details:
In the output, you’ll see several details along with the MAC address:
As you can see, in this case, my network interface is called enp0s31f6 and its MAC address is 38:42:f8:8b:a7:68.
You may want to note it down on a secure place to revert to this original MAC address later on.
Now you may proceed to changing the MAC address.
If you do this on a network interface which is currently in use, probably your network connection will be terminated. So either try this method on an additional card or be prepared to restart your network.
Method 1: Change MAC address using Macchanger
Macchanger is simple utility to view, modify, and manipulate MAC addresses for your Network interface cards. It is available in almost all GNU/Linux operating systems and you can install is using the package installer of your distribution.
On Arch Linux or Manjaro:
On Fedora, CentOS, RHEL:
On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Kali Linux:
Important! You’ll be asked to specify whether macchanger should be set up to run automatically every time a network device is brought up or down. This gives a new MAC address whenever you attach an Ethernet cable or re-enable WiFi.
I recommend not to run it automatically, unless you really need to change your MAC address every time. So, choose No (by pressing tab key) and hit Enter key to continue.
How to Use Macchanger to change MAC address
Do you remember your network interface name? You got it in the Step 1 earlier.
Now, to assign any random MAC address to this network card, use:
After changing the MAC id, verify it using command:
You will now see that MAC has been spoofed.
To change the MAC address to a specific value, specify any custom MAC address using command:
Where XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX is the new MAC id that you want to change.
Finally, to revert the MAC address to its original hardware value, run the following command:
However, you don’t have to do this. Once you reboot the system, the changes will be automatically lost, and the actual MAC address will be restored again.
You can always check the man page for more details.
Method 2: Changing Mac address using iproute2 [intermediate knowledge]
I would recommend using Macchanger but if you don’t want to use it, there is another way to change the MAC address in Linux.
First, turn off the network card using command:
Next, set the new MAC using command:
Finally, turn the network back on with this command:
Now, verify new MAC address:
That’s it. You have successfully changed the MAC address in true Linux style. Stay tuned with It’s FOSS for more Linux tutorial and tips.
Dimitrios Savvopoulos
Dimitrios is an MSc Mechanical Engineer but a Linux enthusiast in heart. He is well settled in Solus OS but curiosity drives him to constantly test other distros. Challenge is part of his personality and his hobby is to compete from 5k to the marathon distance.
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
How To Permanently Change The MAC Address On Linux
This article explains how to permanently change / spoof the MAC addresses of network interfaces. For this purpose, we’ll use Macchanger, an utility for manipulating MAC addresses, for which we’ll create a systemd unit to start it automatically on boot.
Macchanger, the tool that we’re going to use in this article to change the MAC address, has a service that asks if you want it to change your MAC each time your computer boots, but this fails to work for me on Ubuntu 18.04. Since any change made by Macchanger resets when you reboot the system, this article includes instructions for creating a systemd unit to automatically run Macchanger when your Linux computer boots up, changing the MAC address each time.
To use this guide, your Linux system needs to use systemd, obviously.
1. Install Macchanger
Macchanger should be in the repositories for major Linux distributions. To install it in Debian / Ubuntu / Linux Mint, use:
2. Find out the network interface for which you want to change the MAC address
For this, you can use the following command:
If you’re using a system where this no longer work, you can run this command instead:
Your network interfaces should now be displayed like this:
- For ifocnfig -a :
- For ip link show :
Here, the wired network interface is enp10s0 and wireless network interface is wlp3s0 (previously, eth0 , 1, etc. was used for wired interfaces, and wlan0 , 1, and so on for wireless). Note down the network interface for which you want to spoof the MAC address.
3. Check if Macchanger actually works on your system
Before creating the systemd unity to change the MAC address automatically on each reboot, check to see if Macchanger can actually change your MAC address (I’ve seen cases in which it doesn’t work for some reason). To temporarily change your MAC address (the change is reverted after a system reboot), run Macchanger as follows:
NETWORK-INTERFACE is the network interface for which you want to change the MAC, as listed by step 2 in this article (e.g. enp10s0, wlp3s0).
If Macchanger works, the -r option should change the MAC to a random MAC address, and the command should output the original and new MAC addresses.
4. Create a systemd unit to run Macchanger automatically each time the system starts (so the MAC address changes each time your system boots up)
We’ll create the /etc/systemd/system/changemac@.service systemd unit file and open it as root with a text editor:
If you don’t have Gedit installed, replace it in the command above with another text editor that’s installed on your system.
Paste the following in the changemac@.service file:
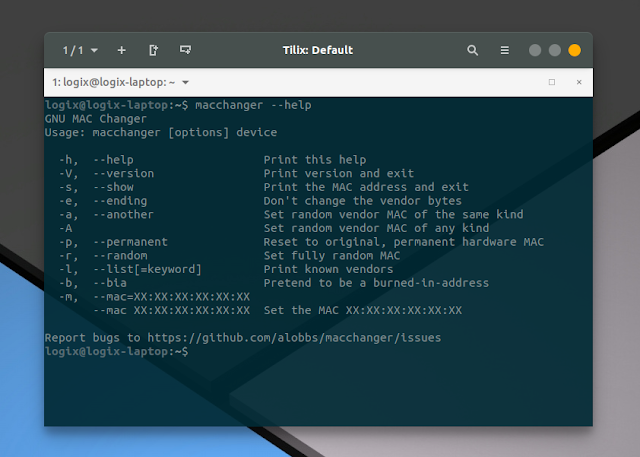
The systemd unit uses macchanger -r to change the MAC. -r sets a fully random MAC address. You can change -r to -e to change the MAC but preserve the original NIC vendor bytes, -a to set random vendor MAC of the same kind, and so on. You can see all the available options by running:
You can set a custom, non-random MAC address as well. For this, change the ExecStart=/usr/bin/macchanger -r %I line to something like this:
Replacing XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX with the new MAC address.
5. Enable the Macchanger systemd service
It’s now time to enable the systemd service so its starts on boot. For this, use:
Replacing enp10s0 with the network address from step 2.
You can use the same command to enable changing the MAC address for multiple network interfaces.
6. Reboot the system
Your network interface(s) should now have a new MAC address. For how to check the old (original) and new MAC address, see below.
How to check the original and new MAC addresses
Macchanger can be used to find out the original MAC and new MAC address, by running this command:
Where NETWORK-INTERFACE is the network interface you found out by using the commands from step 2.
How to disable changing the MAC on each reboot with systemd
To undo the changes, start by disabling the systemd MAC changer service(s):
Replacing enp10s0 with the network address from step 2 (from the initial setup instructions). Do this for each network interface for which you previously enabled the service.
Now you can remove the MAC changer systemd service file:
Источник