- How to Switch between Multiple PHP Version on Debian 9
- Enable PHP 7.2 as Default
- Enable PHP 5.6 as Default
- Как переключаться между несколькими версиями PHP в Ubuntu
- Переключение между несколькими версиями PHP
- Переключитесь с PHP7.x на PHP5.x
- Переключитесь с PHP5.x на PHP7.x
- Жонглируем версиями PHP в системе
- HowTo: Change the PHP version on Apache or Nginx
- Checking the current PHP version
- Why Update to PHP 7?
- How to change the PHP version?
How to Switch between Multiple PHP Version on Debian 9
On your system, if you have installed multiple versions of PHP (eg PHP 7.2, 7.1 and 5.6). PHP 7.2 is running as default PHP for Apache and CLI. For any requirement, you need to use PHP 5.6. Then you don’t need to remove PHP 7.2. You can simply switch your PHP version to default used for Apache and command line.
We assume you have installed multiple PHP version on your Debian system. Now you need to switch the active PHP version for CLI and Apache2. This tutorial will help you to switch between multiple PHP versions for Apache server and CLI on Debian.
Here are two examples for PHP 7.2 and PHP 5.6. You can use the same for other PHP versions by changes commands accordingly.
Enable PHP 7.2 as Default
You need to set PHP 7.2 as your active PHP version for CLI and Apache2 both. You can do this by disabling Apache2 modules for all other installed PHP versions and configure CLI using the update-alternatives command. Run the following commands to make changes.
Apache:-
Command Line:-
Note – The phpize7.2 and php-config7.2 command is available in php7.2-dev package. This is more useful for compiling PHP modules using pecl.
Enable PHP 5.6 as Default
You need to set PHP 5.6 as your default version for CLI and Apache2 both. Run the following commands to disable other PHP versions like (php7.2, php7.1, or php7.0 etc) for Apache and command line.
Apache:-
Command Line:-
Note – The phpize5.6 and php-config5.6 command is available in php5.6-dev package. This is more useful for compiling PHP modules using pecl.
Источник
Как переключаться между несколькими версиями PHP в Ubuntu
Иногда самая последняя версия установленного пакета может работать не так, как вы ожидали.
Приложение может не соответствовать обновленному пакету и поддерживать только определенную старую версию пакета.
В таких случаях вы можете просто отказаться от проблемного пакета до его ранней рабочей версии в кратчайшие сроки
Однако вам не нужно понижать некоторые пакеты.
Мы можем использовать несколько версий одновременно.
Например, скажем, вы тестируете приложение PHP в стек LAMP, развернутое в Ubuntu 18.04 LTS.
Через некоторое время вы обнаружите, что приложение отлично работает в PHP5.6, но не в PHP 7.2 (Ubuntu 18.04 LTS устанавливает PHP 7.x по умолчанию).
Вы собираетесь снова установить PHP или весь пакет LAMP? Не обязательно.
Вам даже не нужно понижать PHP до более ранней версии.
В этом кратком уроке я покажу вам, как переключаться между несколькими версиями PHP в Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. Это не так сложно, как вы думаете.
Полное обучение PHP вы всегда можете пройти здесь : https://webshake.ru/php-training-course
Переключение между несколькими версиями PHP
Чтобы проверить установленную по умолчанию версию PHP, запустите:
Как вы можете увидеть, установленная версия PHP – 7.2.7.
После тестирования вашего приложения пару дней вы узнаете, что ваше приложение не поддерживает PHP7.2.
В таких случаях неплохо иметь версию PHP5.x и версию PHP7.x, так что вы можете в любой момент легко переключаться между любой поддерживаемой версией.
Вам не нужно удалять PHP7.x или переустанавливать стек LAMP. Вы можете использовать как версии PHP5.x, так и 7.x вместе.
Я предполагаю, что вы еще не удалили php5.6 в своей системе.
На всякий случай, вы удалили его уже, вы можете установить его снова, используя PPA, как показано ниже.
Вы можете установить PHP5.6 из PPA:
Переключитесь с PHP7.x на PHP5.x
Сначала отключите модуль PHP7.2, используя команду:
Затем включите модуль PHP5.6:
Установите PHP5.6 в качестве версии по умолчанию:
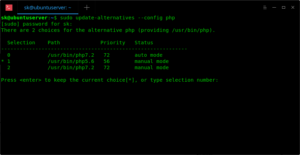
Кроме того, вы можете запустить следующую команду, чтобы установить, какую версию PHP по всей системе вы хотите использовать по умолчанию.
Введите номер, чтобы установить его как версию по умолчанию или просто нажмите ENTER, чтобы сохранить текущий выбор.
В случае, если вы установили другие расширения PHP, установите их как по умолчанию.
Наконец, перезапустите веб-сервер Apache:
Теперь проверьте, является ли версия PHP5.6 версией по умолчанию или нет:
Переключитесь с PHP5.x на PHP7.x
Аналогично, вы можете переключиться с PHP5.x на версию PHP7.x, как показано ниже:
Источник
Жонглируем версиями PHP в системе

Что делать, если хочется сменить системную версию PHP на одну из кастомных сборок? Давайте отталкиваться от того, что у вас на сервере уже установлено несколько версий PHP и вы хотите, чтобы в консоли команда php была конкретной версии, отличающаяся от той, что шла с системой. В этой статье я расскажу, как правильно это настроить, чтобы не было проблем с будущими пакетными обновлениями.
В качестве примера возьмём сервер на CentOS 7, где установлен родной PHP:
Также на сервере установлен наш Plesk с парой своих сборок PHP:
Допустим, мы хотим переключить систему на использование PHP 5.6 по умолчанию (переключать глобально PHP с версии 5.4 на 7 как-то сс… страшно — чему-то в системе может поплохеть от такого). Бинарь PHP 5.6 лежит у нас тут:
Как же сделать так, чтобы система использовала эту, нужную нам, версию PHP?
Сначала посмотрим на системную переменную PATH
В ней перечислен список директорий, в которых ищутся программы по имени. Главный нюанс — поиск в директориях происходит последовательно и используется первый найденный результат. Текущий путь до текущего бинарника PHP мы можем увидеть с помощью команды:
Как видно из PATH , /usr/local/bin находится в списке раньше, чем /usr/bin . Значит, если мы поместим ссылку на альтернативную версию PHP “пораньше”, в /usr/local/bin , то именно она и будет использоваться при вызове команды php вместо /usr/bin/php . Мы можем создать эту ссылку руками (и всё даже будет работать), но правильнее использовать специально созданную для этих целей утилиту update-alternatives (в CentOS это просто alternatives , но есть симлинка update-alternatives , поэтому дальше будем оперировать именно этой командой, как универсальной для Debian/Ubuntu/CentOS/и т.д.).
Теперь, давайте зарегистрируем все доступные версии PHP с помощью этой команды:
Цифры 10, 20 и 30 — это приоритет. Он работает для автоматического выбора, если администратор сам не выбрал конкретную версию. Самое большое число определяет выбор «по умолчанию».
Проверим, что php теперь указывает на созданную командой симлинку:
Давайте разберемся, что же update-alternatives сделала для нас:
Как видно, она создала цепочку симлинок и теперь по требованию просто меняет промежуточную симлинку на нужный нам бинарь.
То есть, мы успешно настроили группу PHP в update-alternatives , где по умолчанию в автоматическом режиме выбран системный PHP. Сейчас у нас есть возможность переключить команду PHP на любую другую версию..
Давайте переключимся на PHP версии 5.6, которая идет в поставке с Plesk’ом:
Проверяем, что переключение произошло:
Все отлично работает. Теперь в системе используется нужная нам версия PHP и я не опасаюсь, что эта настройка слетит при следующих пакетных обновлениях.
С помощью update-alternatives можно выбирать не только версию PHP, но и многие другие вещи, например разные версии phpunit или редактор по умолчанию в системе. Подход этот универсален для различных систем. Не изобретая своего велосипеда, используя существующие инструменты, вы можете быть уверенным, что не устроили для ваших коллег квеста “Ну почему оно так работает?!”. Настраивайте свою систему правильно.
Источник
HowTo: Change the PHP version on Apache or Nginx
New versions of PHP bring new features and fixes for security issues and bugs. Migrating from one version to another can often lead to incompatibilities. As of writing this article, PHP 7.2 is the latest stable release and PHP 7.3 is expected to be released in December 2018. Drupal.org currently recommends PHP 7.1+ for new projects and encourages the community to plan an upgrade for older versions.
Drupal, as we know, is a CMF written in PHP. It uses various PHP libraries and components including the Symfony framework, the Twig template engine, PHPUnit, Guzzle, etc. Hence, it is always recommended to do a compatibility check with all the components, libraries and core/contributed modules of your Drupal site before upgrading to newer versions of PHP.
Now, the process of changing the PHP version of your Drupal site may vary with your hosting provider and the access level that you have on the server. But for this tutorial, Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS with Apache 2.4.18 and Nginx 1.10.3 was used. Few commands, configuration files, and directory paths may differ with your system and the version of web servers.
Checking the current PHP version
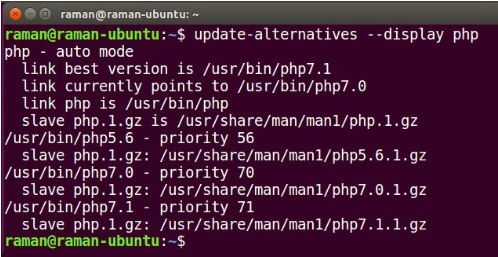
First and foremost, let us see what all versions of PHP are currently installed on our system.
You may also check all the installed PHP packages along with its extensions using:
By default, the one with the highest priority will be the command line version. That is, if we use the interactive shell or parse a PHP file through the terminal, this version will be used.
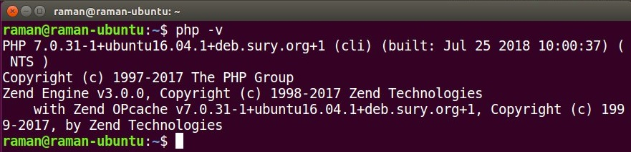
However, this selected command line version may/may not be the configured with your web server. To check the PHP version configured with the web server, you may create a phpinfo() page or echo out the PHP_VERSION_ID constant / phpversion() function.
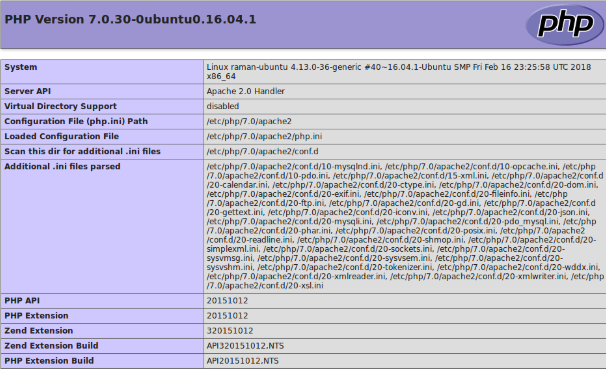
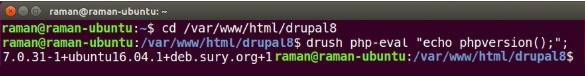
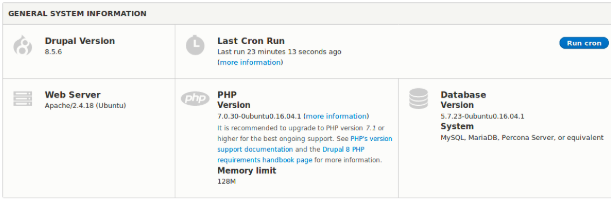
If you do not have the access to your server through SSH, you may also view the current PHP version using the Status Reports of your Drupal site available under /admin/reports/status.
Why Update to PHP 7?
Here are some of the reasons why you need to upgrade from PHP 5 to PHP 7:
- PHP 7 is twice as fast as PHP 5. The huge upward shift in performance is one of the reasons why an upgrade is important. This means your website loads in lesser time, giving your web users another reason to stay on your website.
- PHP 7 supports simultaneous execution of asynchronous tasks. Tasks such as networks, access to the database, timers and perform events related to I/O operations can be done asynchronously by putting in place a single PHP event-loop.
- It is mobile-first. Of course, you need to offer a better value proposition to your users. And mobile users cant be ignored here. PHP 7 offers exactly what businesses need to do to cater to the needs of mobile device users.
It offers reduced memory usage, execution engine improvements, and native local threat storage which are specifically suited to mobile devices that have limited browsing features.
How to change the PHP version?
Since Apache and Nginx are the most popular web servers in the market, we will have a quick look on how to change the PHP version on them. Also, it is highly recommended to have a backup of your Drupal site before tinkering around with any of the configurations on your server.
Now, in my case, I have PHP 7.0 configured on the web server and Drupal is giving a nice recommendation to upgrade it. But I do not have the latest PHP 7.2 installed on my system, so, I will first download it along with the required PHP extensions.
These include extensions for URL, JSON, Image, Library, Mbstring, Open SSL, and XML. But, just to ensure that all the extensions get installed, let’s install them manually.
You may view the packages using dpkg -l php7.2* to confirm.
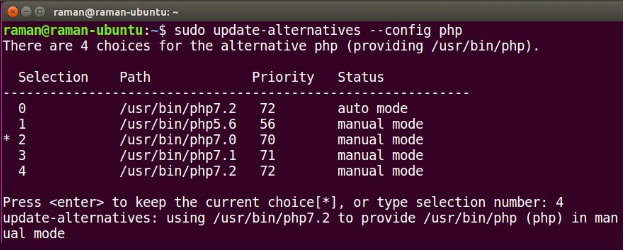
I. Command Line Version
To change the command line version of PHP you may use the following command. Again, changing this won’t affect the version used by the web server.
Enter the choice number mentioned besides the desired PHP version
II. Apache
For Apache web server, the a2enmod and a2dismod scripts can be used for enabling and disabling the PHP modules.
Disable all the previously enabled PHP modules
Enable the new PHP version module
Restart the web server
PHP version for a specific website can also be set through to the .htaccess file in the following way.
III. Nginx
For Nginx, we simply need to update the PHP-FPM socket in its configuration file. But before that make sure that the PHP-FPM is installed for your version and is running as a service.
Take a backup of the default configuration file and then open it up in your favourite text editor.
Change the FastCGI backend to use the new PHP-FPM socket, save and exit the file
Run the configuration test
Restart the web server
We have now successfully changed the PHP version of our Drupal site. Now, navigate to Manage → Reports → Status report to ensure that the version has been changed and there are no errors or warning from any Drupal module or PHP library.
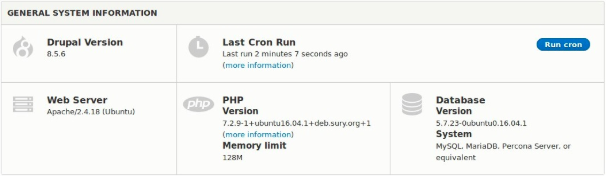
As expected, it did not produce any errors or warnings on a raw Drupal 8 installation. If you face any issues, make sure you installed all the required PHP extensions for your PHP version, check the log messages and refer the issue queues of the core and contrib modules.
In case of any queries or suggestions, feel free to drop down a comment.
Источник