- Set Time, Date Timezone in Linux from Command Line or Gnome | Use ntp
- Set Time/Date/Timezone in Ubuntu Linux
- Check Current Time
- Using the date command
- Using timedatectl command
- Changing Time
- using date command
- Change Date
- Create custom date format
- List/Change time zone
- Set the Local-rtc
- Check/Change CMOS Time
- Conclusion
- Установка времени Linux
- Как работает время на компьютере?
- Установка времени Linux
- Установка времени через терминал
- Выводы
- Linux Set Date and Time From a Command Prompt
- Linux Display Current Date and Time
- Linux Display The Hardware Clock (RTC)
- Linux Set Date Command Example
- Linux Set Time Examples
- How do I set the Hardware Clock to the current System Time?
- A note about systemd based Linux system
- timedatectl: Display the current date and time
- How do I change the current date using the timedatectl command?
- How do I set the current time only?
- How do I set the time zone using timedatectl command?
- How do I synchronizing the system clock with a remote server using NTP?
Set Time, Date Timezone in Linux from Command Line or Gnome | Use ntp
Written by Guillermo Garron
Date: 2012-04-19 15:55:00 00:00
To have the correct time and date in Linux is very important, a lot of things depends on it. It does not matter if you are using Linux to power your personal computer or you have a Linux server. The server and system clock needs to be on time.
Set date from the command line
Set time from the command line
Set time and date from the command line
Linux check date from command line
Will show you something like this:
Set hardware clock
The hardware clock is the clock that runs in you PC hardware even if you disconnect it from the main power supply. This is because it has a lithium battery in the modern computers and another type of battery in the old ones.
We’ll see differences between hardware clock and system clock
Will output something like this:
Now check the system clock
Will output something like this:
Let’s set the hardware clock to local time:
If you want to set it to UTC time use:
Set the timezone
To set the timezone of your system clock do the following:
Choose the right timezone for you.
Automatically adjust your computer clock
To have your system to automatically adjust time we need to install ntp . Get it from your repository. Once installed you can configure it this way:
Edit the file /etc/ntpd.conf . It will look like this:
Be sure to start the daemon, and to make it start automatically when the system boots.
On Arch Linux is: /etc/rc.d/ntpd start on Debian and derivatives /etc/init.d/ntpd start
Update from the command line against a time server
You can update the clock manually, without the need of the daemon with ntpdate
You will get something like this:
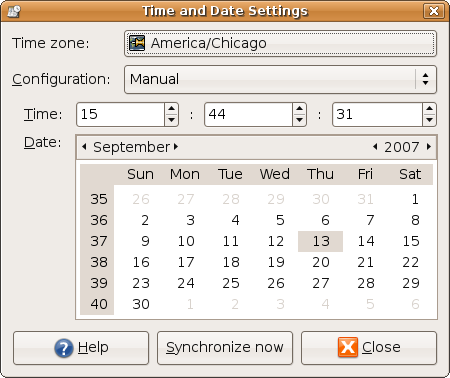
Bonus: Set the time and Date on Gnome
If you are using Gnome right click on the clock and select adjust, or go to: System > Administration > Time and Date (You may be asked for root password)
You will see a window similar to this one:
If you enjoyed the article, please share it
Источник
Set Time/Date/Timezone in Ubuntu Linux
Time is an important aspect in Linux systems especially in critical services such as cron jobs. Having the correct time on the server ensures that the server operates in a healthy environment that consists of distributed systems and maintains accuracy in the workplace.
In this tutorial, we will focus on how to set time/date/time zone and to synchronize the server clock with your Ubuntu Linux machine.
Check Current Time
You can verify the current time and date using the date and the timedatectl commands. These linux commands can be executed straight from the terminal as a regular user or as a superuser. The commands are handy usefulness of the two commands is seen when you want to correct a wrong time from the command line.
Using the date command
Log in as a root user and use the command as follows
Output
You can also use the same command to check a date 2 days ago
Output
Using timedatectl command
Checking on the status of the time on your system as well as the present time settings, use the command timedatectl as shown
Changing Time
We use the timedatectl to change system time using the format HH:MM: SS. HH stands for the hour in 24-hour format, MM stands for minutes and SS for seconds.
Setting the time to 09:08:07 use the command as follows (using the timedatectl)
using date command
Changing time means all the system processes are running on the same clock putting the desktop and server at the same time. From the command line, use date command as follows
Where,
• 10: Hour (hh)
• 13: Minute (mm)
• 13: Second (ss)
To change the locale to either AM or PM use the %p in the following format.
Change Date
Generally, you want your system date and time is set automatically. If for some reason you have to change it manually using date command, we can use this command :
It will set your current date and time of your system into ‘January 25, 2014′ and ’09:17:00 AM’. Please note, that you must have root privilege to do this.
You can use timedatectl to set the time and the date respectively. The accepted format is ‘YYYY-MM-DD’, ‘YYYY’ represents the year, ‘MM’ the month in two digits and ‘DD’ for the day in two digits.
Changing the date to ’15 January 2019′, you should use the following command:
Create custom date format
To create custom date format, use a plus sign (+)
%D format follows Year/Month/Day format.
You can also put the day name if you want. Here are some examples :
List/Change time zone
Changing the time zone is crucial when you want to ensure that everything synchronizes with the Network Time Protocol. The first thing to do is to list all the region’s time zones using the list-time zones option or grep to make the command easy to understand
The above command will present a scrollable format.
Recommended timezone for servers is UTC as it doesn’t have daylight savings. If you know, the specific time zones set it using the name using the following command
To display timezone execute
Set the Local-rtc
The Real-time clock (RTC) which is also referred to as the hardware clock is independent of the operating system and continues to run even when the server is shut down.
Use the following command
In addition, the following command for the local time
Check/Change CMOS Time
The computer CMOS battery will automatically synchronize time with system clock as long as the CMOS is working correctly.
Use the hwclock command to check the CMOS date as follows
To synchronize the CMOS date with system date use the following format
Conclusion
To have the correct time for your Linux environment is critical because many operations depend on it. Such operations include logging events and cron jobs as well.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment.
Источник
Установка времени Linux
Время от времени часы на компьютере могут сбиваться по различным причинам, время может быть установлено изначально неправильно или неправильно выбран часовой пояс. Хотя в системе по умолчанию настроена синхронизация времени с интернетом и я уже давно забыл что значит постоянно перенастраивать часы, если они отстают, такая необходимость может появиться.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим как выполняется установка времени Linux различными способами, через терминал, графический интерфейс и так далее. Но сначала нам нужно понять как работает время.
Как работает время на компьютере?
Статья ориентирована на новичков, в первую очередь на них, потому что профессионалы уже и так знают как это сделать. Поэтому сначала рассмотрим как работает время в Linux. Когда компьютер работает часы идут, это ясно, но когда вы его отключаете, а затем включаете снова часы показывают не то время, на котором остановились, а правильное время. Это происходит потому, что часы на материнской плате идут постоянно. Таймер питается от той же батарейки, что и энергозависимая память BIOS.
Операционная система передает значение таймера в память BIOS при выключении и берет его оттуда при включении. Отсюда берутся проблемы со временем при двойной загрузке Windows и Linux, но эта тема раскрыта в другой статье — сбивается время в Ubuntu и Windows. Другая проблема почему может сбиваться время — это неверно установленный часовой пояс. Если вы установили часовой пояс linux неверно, то часы будут постоянно синхронизироваться через интернет и идти неверно.
Когда все проблемы с временем будут устранены, можно перейти установить нужное время и быть уверенным что оно не будет сбиваться. Дальше рассмотрим как это сделать.
Установка времени Linux
Вы можете видеть текущее время прямо на вашем рабочем столе, в KDE часы добавлены на панель, да и в Gnome, они размещены по центру панели по умолчанию:
Если навести курсор на время, вы увидите более подробную информацию, область уведомлений и календарь.
Но настроить время здесь уже не получится. Для этого нужно открывать настройки системы. Мы будем рассматривать настройки для Gnome. Откройте меню Dash и наберите в строке поиска «Параметры»:
Дальше откройте «Дата и время»:
Как видите, здесь уже установлено значение по умолчанию «Автоматическое определение даты и времени», а внизу есть пункт, который отвечает за часовой пояс.
Вы можете просто поменять часовой пояс чтобы время синхронизировалось правильно, если что-то не так. Также можно задать время вручную. Для этого сначала отключите автоматическую синхронизацию, а затем выберите дату и время:
Никаких кнопок нажимать не нужно, закройте окно выбора и новое время будет применено. Вы всегда можете вернуть настройки до значения по умолчанию.
Установка времени через терминал
Кроме графического интерфейса, у вас есть возможность делать все необходимые действия через терминал. Для этого есть утилита date. Сначала смотрим текущее время:
У утилиты есть множество опций отображения и настроек, но мы не будем их рассматривать. Есть еще одна команда, которая позволяет посмотреть системное время linux:
Чтобы установить время можно использовать ту же команду date. Для этого ей нужно передать строку со временем и датой, например:
В качестве строки можно брать ту, которую возвращает команда date без параметров, только она должна быть на английском, поэтому сразу смотрим:
sudo date —set «Wed Sep 6 20:43:36 EEST 2017»
Если у вас включена коррекция даты через интернет, то ее нужно отключить перед этим, потому что вы даже заметить изменений не успеете, как сервер времени linux установит правильное время. Можно сократить эту строку:
sudo date —set «Sep 6 20:43:36 2017»
Это даст тот же результат. Еще один вариант — указать формат данных, которые вы собираетесь передавать с помощью модификаторов, например, изменить время linux:
sudo date +%T -s «20:43:36»
Здесь формат очень прост — часы:минуты:секунды. Можно давать время в 12 часовом формате, для этого добавьте модификатор %p:
date +%T%p -s «8:43:36PM»
Вы изменяете текущее время, но аппаратное системное время linux не изменяется, чтобы сохранить изменения используйте команду:
Еще один новый инструмент от systemd для управления временем — timedatectl. С помощью него можно выполнить те же операции, сначала смотрим доступную информацию о времени:
Текущее системное время отображается в строке Local Time. Чтобы изменить дату, используйте опцию -set-time. Синтаксис передаваемого ей параметра такой: ГГГГ-ММ-ДД ЧЧ:ММ:СС. Думаю тут понятно и без комментариев. Например:
sudo timedatectl —set-time «2017-09-06 20:43:36»
Можно задать только время, тогда нужно использовать синтаксис времени ЧЧ:ММ:СС, например:
sudo timedatectl —set-time «20:43:36»
Еще раз говорю, что если включена синхронизация по сети, то вы не сможете изменить время. Но с помощью timedatectl ее можно отключить:
sudo timedatectl set-ntp no
Или включить обратно:
sudo timedatectl set-ntp yes
C помощью этой же команды можно не только установить время linux, но и настроить часовой пояс, для этого используйте опцию set-timezone:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone ‘Russia/Moscov’
Вы можете посмотреть список доступных часовых поясов командой:
Видео о настройке времени с помощью timedatectl:
Выводы
Вот и все. Теперь вы знаете как выполняется установка времени linux. Как видите, это очень просто, вы можете использовать различные способы, в зависимости от того, что вам будет удобнее. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Источник
Linux Set Date and Time From a Command Prompt
H ow can I set the system date and time from the command prompt (bash shell)? I don’t have GUI installed and I am login over ssh session. How can I set date under Linux operating systems?
Use the date command to display the current date and time or set the system date / time over ssh session. You can also run the date command from X terminal as root user.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | None |
| Est. reading time | 2m |
This is useful if the Linux server time and/or date is wrong, and you need to set it to new values from the shell prompt.
You must login as root user to use date command.
Linux Display Current Date and Time
Just type the date command:
$ date
Sample outputs:
Linux Display The Hardware Clock (RTC)
Type the following hwclock command to read the Hardware Clock and display the time on screen:
# hwclock -r
OR
# hwclock —show
$ sudo hwclock —show —verbose
OR show it in Coordinated Universal time (UTC):
# hwclock —show —utc
Sample outputs:
Linux Set Date Command Example
Use the following syntax to set new data and time:
date —set=»STRING»
For example, set new data to 2 Oct 2006 18:00:00, type the following command as root user:
# date -s «2 OCT 2006 18:00:00»
OR
# date —set=»2 OCT 2006 18:00:00″
You can also simplify format using following syntax:
# date +%Y%m%d -s «20081128»
Linux Set Time Examples
To set time use the following syntax:
# date +%T -s «10:13:13»
Where,
Use %p locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM, enter:
# date +%T%p -s «6:10:30AM»
# date +%T%p -s «12:10:30PM»
How do I set the Hardware Clock to the current System Time?
Use the following syntax:
# hwclock —systohc
OR
# hwclock -w
A note about systemd based Linux system
With systemd based system you need to use the timedatectl command to set or view the current date and time. Most modern distro such as RHEL/CentOS v.7.x+, Fedora Linux, Debian, Ubuntu, Arch Linux and other systemd based system need to the timedatectl utility. Please note that the above command should work on modern system too.
timedatectl: Display the current date and time
Type the following command:
$ timedatectl
Fig.01: Systemd Linux timedatecetl command to display the current date and time
How do I change the current date using the timedatectl command?
To change the current date, type the following command as root user:
# timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD
OR
$ sudo timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD
For example set the current date to 2015-12-01 (1st, Dec, 2015):
# timedatectl set-time ‘2015-12-01’
# timedatectl
Sample outputs:
To change both the date and time, use the following syntax:
# timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
Where,
- HH : An hour.
- MM : A minute.
- SS : A second, all typed in two-digit form.
- YYYY: A four-digit year.
- MM : A two-digit month.
- DD: A two-digit day of the month.
For example, set the date ’23rd Nov 2015′ and time to ‘8:10:40 am’, enter:
# timedatectl set-time ‘2015-11-23 08:10:40’
# date
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
How do I set the current time only?
The syntax is:
# timedatectl set-time HH:MM:SS
# timedatectl set-time ’10:42:43′
# date
Sample outputs:
How do I set the time zone using timedatectl command?
To see list all available time zones, enter:
$ timedatectl list-timezones
$ timedatectl list-timezones | more
$ timedatectl list-timezones | grep -i asia
$ timedatectl list-timezones | grep America/New
To set the time zone to ‘Asia/Kolkata’, enter:
# timedatectl set-timezone ‘Asia/Kolkata’
Verify it:
# timedatectl
How do I synchronizing the system clock with a remote server using NTP?
Simply type the following command:
# timedatectl set-ntp yes
Verify it:
$ timedatectl
Sample outputs:
Conclusion
Linux users can use date command to print or set the system date and time. Systemd based Linux users can use timedatectl to control the system time and date.
- You can also set new timzone using this mini-howto.
- Man pages – timedatectl(8)
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник