- How To Check Linux Disk Space?
- Check with df Command
- Check with du Command
- Sort Directories According To Their Size
- Check Disk Space Remotely
- Howto Find Out or Learn Harddisk Size in Linux or UNIX
- Task: Display Hard Disk Partition Size
- Task: Display Hard Disk Partition Size in Mega bytes or GB or TB
- Task: Display TOTAL Hard Disk Size
- Как посмотреть диски в Linux
- 1. lsblk
- 2. df -h
- 3. fdisk -l
- 4. parted -l
- 5. cfdisk
- 6. sfdisk -l
- 7. ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
- 8. lshw -class disk
- Заключение
How To Check Linux Disk Space?
Disk usage and monitoring is important aspect of Linux system administration. One of the most occurring problems is fulling disk space. Getting information about disk usage can become a nightmare if you do not know how to properly do it. How many free GB are there? or How many percentages of the disk is full?
Check with df Command
To check disk space usage df command can be used. df command will give general information about disk usage. We will also provide the -l and -h options in order to list partitions in a human-readable format.

We will get the following information about the disk space and size.
- `Size` is the complete size of the given partition or disk.
- `Used` is the size which is already used or filled in a given disk or partition.
- `Available` is the size which is spare in a given disk or partition.
- `Use` is the percentage of the used part of the given disk or partition.
Check with du Command
An alternative to df command is du command. Actually, they provide different information from a different viewpoint. Du command provides information about files and directories.

The command may seem a bit complex. We get size summary information about directories in root path level and to clear standard error messages send them to the /dev/nul
Sort Directories According To Their Size
We can list root-level directories according to their size in KB. Listing them according to their size is not so complex.

Check Disk Space Remotely
Checking disk space usage one by one connecting to the servers is a tedious task. It can be done remotely with ssh connection. By using ssh remote command execution feature disk command can be run without connecting to server.

As a standard command, we issue ssh ubu1 and then put our command to run remotely.
Источник
Howto Find Out or Learn Harddisk Size in Linux or UNIX
H ow do I find out my installed hard disk size in Linux or UNIX like operating systems?
Under Linux and UNIX operating systems you can use the df command. The df command displays the amount of disk space available on the file system containing each file name argument. If no file name is given, the space available on all currently mounted file systems is shown.
Task: Display Hard Disk Partition Size
Open a command-line terminal (select Applications > Accessories > Terminal), and then type:
$ df
Sample outputs:
Task: Display Hard Disk Partition Size in Mega bytes or GB or TB
Type the following command:
$ df -H
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Task: Display TOTAL Hard Disk Size
The fdisk command is partition table manipulator for Linux. But it can be used to display total hard disk size. You must type the following command as the root user:
# fdisk -l | grep Disk
Sample outputs:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Hello Sir,
Pls verify the other userfull command for me on linux.
Thanks for the fdisk -l tip! I’ve been wondering how to see total disk size, not just partitions. Now I know!
Nice and quick, thanks!
The following command is an improvement of the Fdisk -l command, which is actually exactly what most people are looking for:
# fdisk -l 2> /dev/null | grep Disk | grep -v identifier
Disk /dev/sda: 60.0 GB, 60011642880 bytes
Disk /dev/sdb: 60.0 GB, 60011642880 bytes
Disk /dev/sdc: 1000.2 GB, 1000204886016 bytes
Disk /dev/sdd: 1000.2 GB, 1000204886016 bytes
…..
Disk /dev/sdv: 1000.1 GB, 1000123400192 bytes
Disk /dev/md5: 18002.2 GB, 18002220023808 bytes
hi plz how put a hard disck in a server and mirror i want the comment
and you will get something simillar to it:
/dev/sda: 80.0 GB
/dev/sdb: 120.0 GB
/dev/sdc: 2000.4 GB
/dev/sdd: 250.1 GB
/dev/sde: 250.1 GB
—————–
total: 2700.6 GB
Though above logic is good, but not foolproof.
If $4 units are different then sum+=$3 will yield wrong result.
sir df is only work for mounted filesystem. and fdisk does’nt show any free space of the whole disk
why people need to show off with the linux command?
wut the heck..why dont you type a little bit more until it becomes some great bash romance..i think this website has explain pretty well..or maybe u can check this link
nice and helpful…
Hi
Thanks a lot
It’s very usefull for me.
I have one question…
below mentioned command will work on AIX, FreeBSD, HPUX, IRIX,Mac OS X, NetBSD, OpenBSD,OpenVMS, POWER HMC, IBM Hardware Management Consoles ,Solaris, Tru64,UnixWare, SCO OpenServer and SCO UNIX VMware ESX VMware ESXi ………….
fdisk -l |grep Disk
Thanks ….it worked like a charm
thank u very much, great tips !!
is there a command that shows only used hard disk size??
thanks it really helped me
dmesg | grep GiB
If using lvm, you can use pvdisplay
Our vendor has finished installing redhat OS on our servers & has submitted an installation report. When I verify the file system using df -h , the sum of the size of the file systems as shown in the output is greater than the actual HDD size allocated to that virtual machine. But when I use fdisk -l|grep Disk, the size shown in output matches with the hdd size. Can you please help me out as to how do I verify the file system ??
My aim is to match the HDD size allocated to particular Virtual machine with the total size all file systems on that VM.
lsblk is the most flexible tool for getting infos on a blockdevice:
Size, and only the size in bytes of drive sda (2TB hdd)
lsblk —nodeps —bytes —noheadings —output SIZE /dev/sda:
2000398934016
Nice. I like that one. 🙂
Hello,
I would like to ask if there is a way to find out about how a linux system was partitioned at the time of installation, as you see I installed linux but when ran this command “df” it did not give me the exact parition sizes I specified at the time of installation. I would like to know this for already existing systems as to determine the sizes in case of a problem happens and I need to build and format a new hard drive.
My disk size is 90%. can i know at what time it becomes 90%.
Источник
Как посмотреть диски в Linux
Системные администраторы ОС Linux обычно просматривают диски, чтобы проверить все дисковое пространство и его использование. Список дисков также помогает увидеть подключенные диски к системе, разделы и файловую систему, используемую дисками.
В системе Linux существует несколько способов посмотреть все жесткие диски. Из этой статьи вы узнаете, как посмотреть диски в Linux с помощью командной строки.
1. lsblk
lsblk (list block devices) используется для просмотра информации обо всех доступных блочных устройствах, таких как жесткий диск и флэш-накопители.
Просто набрав команду lsblk, вы получите список всех блочных устройств в виде древовидного формата. Это удобный и простой способ посмотреть диски.
sda 8:0 0 238.5G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 529M 0 part
├─sda2 8:2 0 100M 0 part /boot/efi
├─sda3 8:3 0 16M 0 part
├─sda4 8:4 0 165.8G 0 part
├─sda5 8:5 0 70G 0 part /
└─sda6 8:6 0 2G 0 part [SWAP]
zram0 252:0 0 8G 0 disk [SWAP]
2. df -h
Команда df используется для просмотра объема доступного дискового пространства. Так же команда df отобразит имя устройства, общее количество блоков, используемое дисковое пространство, доступное дисковое пространство, процент используемого пространства, точку монтирования файловой системы, а также покажет удаленно смонтированные файловые системы, такие как NFS.
Команда df -h покажет доступное пространство всех дисков в удобочитаемом виде.
Ответ в терминале:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 5.8G 0 5.8G 0% /dev
tmpfs 5.8G 90M 5.7G 2% /dev/shm
tmpfs 2.4G 11M 2.4G 1% /run
tmpfs 4.0M 0 4.0M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda5 69G 62G 3.1G 96% /
tmpfs 5.8G 4.7M 5.8G 1% /tmp
/dev/sda2 96M 41M 56M 43% /boot/efi
tmpfs 1.2G 200K 1.2G 1% /run/user/1000
3. fdisk -l
Команда fdisk — это текстовая утилита, используемая для управления разделами диска. С помощью fdisk вы можете отобразить разделы диска, создать новый раздел, удалить существующий раздел жесткого диска и просмотреть размер раздела.
Для этого используется команда fdisk -l отобразит все доступные разделы диска
Ответ в терминале:
Disk /dev/sda: 238.47 GiB, 256060514304 bytes, 500118192 sectors
Disk model: SK hynix SC300B
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: FF57C955-D98A-49C4-B1ED-835A44F2A0A4
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1085439 1083392 529M Windows recovery environment
/dev/sda2 1085440 1290239 204800 100M EFI System
/dev/sda3 1290240 1323007 32768 16M Microsoft reserved
/dev/sda4 1323008 349122559 347799552 165.8G Microsoft basic data
/dev/sda5 349122560 495923199 146800640 70G Linux filesystem
/dev/sda6 495923200 500117503 4194304 2G Linux swap
Disk /dev/zram0: 8 GiB, 8589934592 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk /dev/loop0: 207.15 MiB, 217214976 bytes, 424248 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop1: 99.18 MiB, 103993344 bytes, 203112 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
4. parted -l
Parted — это полезный и мощный инструмент используемый для управления разделами жесткого диска из терминала (командной строки). Обладает способностями такими как список, создание, сжатие, удаление, поиск и восстановление разделов диска. С помощью команды parted вы можете легко управлять всеми разделами жесткого диска.
команда parted-l покажет расположение разделов дисков.
Ответ в терминале:
Model: ATA SK hynix SC300B (scsi)
Disk /dev/sda: 256GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/4096B
Partition Table: gpt
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Name Flags
1 1049kB 556MB 555MB ntfs Basic data partition hidden, diag
2 556MB 661MB 105MB fat32 EFI System Partition boot, esp
3 661MB 677MB 16.8MB Microsoft reserved partition msftres
4 677MB 179GB 178GB ntfs Basic data partition msftdata
5 179GB 254GB 75.2GB ext4
6 254GB 256GB 2147MB linux-swap(v1) swap
Model: Unknown (unknown)
Disk /dev/zram0: 8590MB
Sector size (logical/physical): 4096B/4096B
Partition Table: loop
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Flags
1 0.00B 8590MB 8590MB linux-swap(v1)
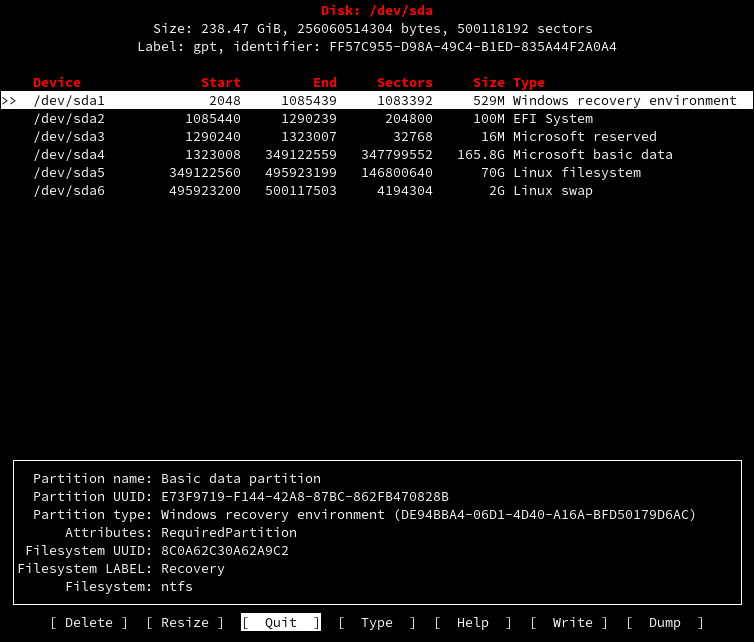
5. cfdisk
Cfdisk немного отличается от вышеприведенных команд, эта команда обеспечивает графическое представление в терминальном интерфейсе. С помощью cfdisk вы можете просматривать, создавать, удалять и изменять разделы.
Disk: /dev/sda Size: 238.47 GiB, 256060514304 bytes, 500118192 sectors Label: gpt, identifier: FF57C955-D98A-49C4-B1ED-835A44F2A0A4 Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1085439 1083392 529M Windows recovery environment
/dev/sda2 1085440 1290239 204800 100M EFI System
/dev/sda3 1290240 1323007 32768 16M Microsoft reserved
/dev/sda4 1323008 349122559 347799552 165.8G Microsoft basic data
/dev/sda5 349122560 495923199 146800640 70G Linux filesystem
/dev/sda6 495923200 500117503 4194304 2G Linux swap
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Partition name: Basic data partition │
│ Partition UUID: E73F9719-F144-42A8-87BC-862FB470828B │
│ Partition type: Windows recovery environment (DE94BBA4-06D1-4D40-A16A-BFD50179D6AC) │
│ Attributes: RequiredPartition │
│ Filesystem UUID: 8C0A62C30A62A9C2 │
│Filesystem LABEL: Recovery │
│ Filesystem: ntfs │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
[ Delete ] [ Resize ] [ Quit ] [ Type ] [ Help ] [ Write ] [ Dump ]
6. sfdisk -l
sfdisk — это редактор таблиц разделов. Он может показать разделы, показать размер раздела, проверить разделы на устройстве и подготовить устройство.
Команда sfdisk -l покажет разделы каждого диска.
Ответ в терминале:
Disk /dev/sda: 238.47 GiB, 256060514304 bytes, 500118192 sectors
Disk model: SK hynix SC300B
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: FF57C955-D98A-49C4-B1ED-835A44F2A0A4
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1085439 1083392 529M Windows recovery environment
/dev/sda2 1085440 1290239 204800 100M EFI System
/dev/sda3 1290240 1323007 32768 16M Microsoft reserved
/dev/sda4 1323008 349122559 347799552 165.8G Microsoft basic data
/dev/sda5 349122560 495923199 146800640 70G Linux filesystem
/dev/sda6 495923200 500117503 4194304 2G Linux swap
Disk /dev/zram0: 8 GiB, 8589934592 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
Disk /dev/loop0: 207.15 MiB, 217214976 bytes, 424248 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop1: 99.18 MiB, 103993344 bytes, 203112 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
7. ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
команда ls — это очень простая, но мощная команда, используемая для отображения файлов и каталогов. Мы можем посмотреть диски, посмотреть каталог /dev/disk/by-id.
$ ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
Ответ в терминале:
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9 -> ../../sda
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part1 -> ../../sda1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part2 -> ../../sda2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part3 -> ../../sda3
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part4 -> ../../sda4
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part5 -> ../../sda5
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part6 -> ../../sda6
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482 -> ../../sda
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part1 -> ../../sda1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part2 -> ../../sda2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part3 -> ../../sda3
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part4 -> ../../sda4
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part5 -> ../../sda5
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part6 -> ../../sda6
Вы также можете посмотреть:
8. lshw -class disk
lshw — это инструмент Linux, который используется для получения подробной информации об аппаратной конфигурации системы.
Используйте -class disk для просмотра информации о диске.
Ответ в терминале:
*-disk
description: ATA Disk
product: SK hynix SC300B
physical id: 0.0.0
bus info: scsi@1:0.0.0
logical name: /dev/sda
version: 0P00
serial: FI68N023911308NC9
size: 238GiB (256GB)
capabilities: gpt-1.00 partitioned partitioned:gpt
configuration: ansiversion=5 guid=ff57c955-d98a-49c4-b1ed-835a44f2a0a4 logicalsectorsize=512 sectorsize=4096
Кроме того, можно вывести class disk as-json или -html или-xml.
Ответ в терминале:
<
«id» : «disk»,
«class» : «disk»,
«claimed» : true,
«handle» : «GUID:ff57c955-d98a-49c4-b1ed-835a44f2a0a4»,
«description» : «ATA Disk»,
«product» : «SK hynix SC300B»,
«physid» : «0.0.0»,
«businfo» : «scsi@1:0.0.0»,
«logicalname» : «/dev/sda»,
«dev» : «8:0»,
«version» : «0P00»,
«serial» : «FI68N023911308NC9»,
«units» : «bytes»,
«size» : 256060514304,
«configuration» : <
«ansiversion» : «5»,
«guid» : «ff57c955-d98a-49c4-b1ed-835a44f2a0a4»,
«logicalsectorsize» : «512»,
«sectorsize» : «4096»
>,
«capabilities» : <
«gpt-1.00» : «GUID Partition Table version 1.00»,
«partitioned» : «Partitioned disk»,
«partitioned:gpt» : «GUID partition table»
>,
«children» : [
]
>
Заключение
Для всех команд, кроме lsblk и ls-l dev/disk, требуется root — доступ или разрешения суперпользователя для его запуска.
В этой статье мы узнали, как посмотреть диски в Linux с помощью командной строки.
Источник



