- Linux Check IDE / SATA SSD Hard Disk Transfer Speed
- How to measure hard disk data transfer speed using hdparm
- dd Command
- Linux and Unix Test Disk I/O Performance With dd Command
- Use dd command to monitor the reading and writing performance of a disk device:
- Understanding dd command options
- Finding server latency time
- But why the server throughput and latency time are so low?
- Use hdparm command to see buffered and cached disk read speed
- Use dd command on Linux to test read speed
- Linux Laptop example
- Apple OS X Unix (Macbook pro) example
- Not a fan of the command line tools…?
- Graphical method
- Running Disks tool under Ubuntu 20.04 LTS:
- Which method and command do you recommend to use to test disk I/O performance?
- Conclusion
- Как измерить скорость жесткого диска
- Проверка скорости чтения диска
- Проверка скорости записи на диск
Linux Check IDE / SATA SSD Hard Disk Transfer Speed
S o how do you find out how fast is your hard disk under Linux? Is it running at the SATA I (150 MB/s) or SATA II (300 MB/s) or SATA III (6.0Gb/s) speed without opening computer case or chassis?
You can use the hdparm or dd command to check hard disk speed. It provides a command line interface to various hard disk ioctls supported by the stock Linux ATA/IDE/SATA device driver subsystem. Some options may work correctly only with the latest kernels (make sure you have cutting edge kernel installed). I also recommend compiling hdparm with the included files from the most recent kernel source code.
How to measure hard disk data transfer speed using hdparm
Login as the root user and enter the following command:
$ sudo hdparm -tT /dev/sda
OR
$ sudo hdparm -tT /dev/hda
Sample outputs:
For meaningful results, this operation should be repeated 2-3 times. This displays the speed of reading directly from the Linux buffer cache without disk access. This measurement is essentially an indication of the throughput of the processor, cache, and memory of the system under test. Here is a for loop example, to run test 3 time in a row:
for i in 1 2 3; do hdparm -tT /dev/hda; done
Where,
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- -t :perform device read timings
- -T : perform cache read timings
- /dev/sda : Hard disk device file
To find out SATA hard disk link speed, enter:
sudo hdparm -I /dev/sda | grep -i speed
Output:
Above output indicate that my hard disk can use 1.5Gb/s, 3.0Gb/s, or 6.0Gb/s speed. Please note that your BIOS / Motherboard must have support for SATA-II/III:
$ dmesg | grep -i sata | grep ‘link up’
dd Command
You can use the dd command as follows to get speed info too:
Источник
Linux and Unix Test Disk I/O Performance With dd Command
- dd command : It is used to monitor the writing performance of a disk device on a Linux and Unix-like system.
Tutorial details Difficulty level Intermediate Root privileges Yes Requirements dd Est. reading time 15m - hdparm command : It is used to get/set hard disk parameters including test the reading and caching performance of a disk device on a Linux based system.
In this tutorial you will learn how to use the dd command to test disk I/O performance .
Use dd command to monitor the reading and writing performance of a disk device:
- Open a shell prompt.
- Or login to a remote server via ssh.
- Use the dd command to measure server throughput (write speed) dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test1.img bs=1G count=1 oflag=dsync
- Use the dd command to measure server latency dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test2.img bs=512 count=1000 oflag=dsync
The dd command is useful to find out simple sequential I/O performance.
Understanding dd command options
In this example, I’m using RAID-10 (Adaptec 5405Z with SAS SSD) array running on a Ubuntu Linux 14.04 LTS server. The basic syntax is as follows to find out server throughput:
Fig.01: Ubuntu Linux Server with RAID10 and testing server throughput with dd
Finding server latency time
In this example, 512 bytes were written one thousand times to get RAID10 server latency time:
Please note that server throughput and latency time depends upon server/application load too. So I recommend that you run these tests on a newly rebooted server as well as peak time to get better idea about your workload. You can now compare these numbers with all your devices.
But why the server throughput and latency time are so low?
Low values does not mean you are using slow hardware. The value can be low because of the HARDWARE RAID10 controller’s cache.
Use hdparm command to see buffered and cached disk read speed
I suggest you run the following commands 2 or 3 times Perform timings of device reads for benchmark and comparison purposes:
To perform timings of cache reads for benchmark and comparison purposes again run the following command 2-3 times (note the -T option):
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
OR combine both tests:
Fig.02: Linux hdparm command to test reading and caching disk performance
Use dd command on Linux to test read speed
To get accurate read test data, first discard caches before testing by running the following commands:
Linux Laptop example
Run the following command:
Apple OS X Unix (Macbook pro) example
GNU dd has many more options but OS X/BSD and Unix-like dd command need to run as follows to test real disk I/O and not memory add sync option as follows:
So I’m getting 635346520 bytes (635.347 MB/s) write speed on my MBP.
Not a fan of the command line tools…?
You can use disk utility (gnome-disk-utility) on a Linux or Unix based system to get the same information. The following screenshot is taken from my Fedora Linux v22 VM and Ubuntu 20.04 desktop:
Graphical method
Click on the “Activities” or press the “Super” key to switch between the Activities overview and desktop. Type “Disks”
Fig.03: Start the Gnome disk utility
Fig.04: Benchmark disk/partition
Fig.05: Final benchmark result
Running Disks tool under Ubuntu 20.04 LTS:
- First, open Disks from the Activities overview.
- Next choose the disk from the list in the left pane.
- Select the menu button and select Benchmark disk… from the menu.
- Click Start Benchmark… and adjust the Transfer Rate and Access Time parameters as desired.
- Finally click Start Benchmarking to test how fast data can be read from the disk. Administrative privileges may be required. Enter your password, or the password for the requested system administrator account.
Test the performance of your hard disk using ‘Disks’
Which method and command do you recommend to use to test disk I/O performance?
- I recommend dd command on all Unix-like systems ( time sh -c «dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testfile bs=100k count=1k && sync»
- If you are using GNU/Linux use the dd command ( dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testALT.img bs=1G count=1 conv=fdatasync )
- Make sure you adjust count and bs arguments as per your setup to get a good set of result.
- The GUI method is recommended only for Linux/Unix laptop users running Gnome 2 or 3 desktop.
- For detailed I/O performance benchmarking use the fio command
- We use the IOzone. It is a filesystem benchmark tool. The benchmark generates and measures a variety of file operations.
Conclusion
You learned how to use the dd under Linux or Unix for testing simple and sequential I/O performance measurement. For detailed I/O performance benchmarking try the «The Flexible I/O Tester (FIO)» for Unix or Linux. See How To Linux Check IDE / SATA Hard Disk Transfer Speed and man pages: hdparm(1) for more information.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
looking at that strange uneven graph I think that Virtualbox can be blamed maybe? ,, but the numbers are impresive nevertheless 🙂 Thanks for great post
Hi,
Very useful article
Thanks a lot
As a file system developer, I believe there should be a special place in hell for people who test storage performance using dd. At its very best, it tells you about one rarely-relevant kind of performance – sequential single-stream write bandwidth. It won’t reveal anything about performance with multiple threads or deeper queues, latency, variability, etc. “I tested with dd and it was
Agreed but dd is still a good place to start.
AGREEED. and that place will be full of “DD peoples” thinking why they are there!
This type of dd checks are useless… if you do it, in 99% of cases you will see a wonderfull timings and you finish thinking why you still having poor performace in your app or service…
DO NOT USE DD if you want REAL data of I/O or FILE benchmarks! USE FIO!
Not if you’re shuffling around mainly large files, like multimedia, one at a time (like a file manager will for a mechanical HDD). I very much care for this use case and I’m almost sure that DD approximates this well with file sizes that are >2 GB.
JDarcy, you are an idiot. Seriously? Are you “that” upset.
Источник
Как измерить скорость жесткого диска
Иногда хочется быстро прикинуть, как работает дисковая подсистема, либо сравнить 2 жестких диска. Очевидно, что измерить реальную скорость дисков практически невозможно, она зависит от слишком большого числа параметров. Но получить некое представление о скорости дисков можно.
Проверка скорости чтения диска
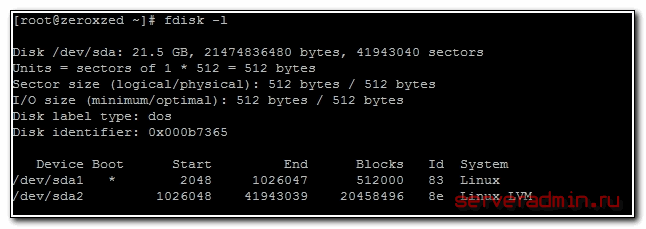
Проще всего измерить скорость диска с помощью программы hdparm. Установить ее очень просто:
Теперь нужно вывести список дисков и разделов в системе:
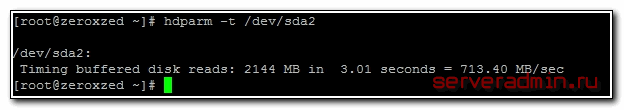
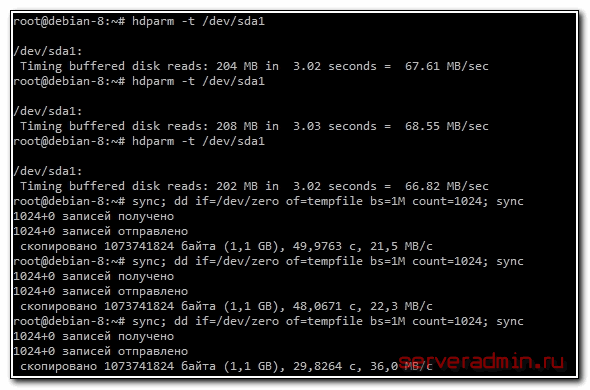
Выбираем нужный раздел и проверяем скорость чтения:
Проверка скорости записи на диск
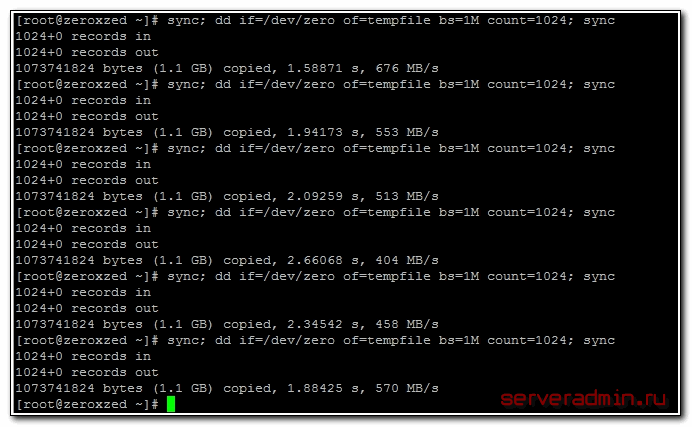
Для того, чтобы измерить скорость записи на диск, можно воспользоваться стандартной утилитой linux — dd. С ее помощью мы создадим на диске файл размером 1 Gb частями по 1Mb.
Измеряем скорость записи на диск:
Я измерял скорость на виртуальной машине, диск которой был размещен на RAID5, собранным из 5-ти дисков SAS 10к. В принципе, неплохой результат. Можно изменить размер файла и блоков, из которого он записывается. Если сделать файл побольше, результат скорости диска может получиться более приближенный к реальности.
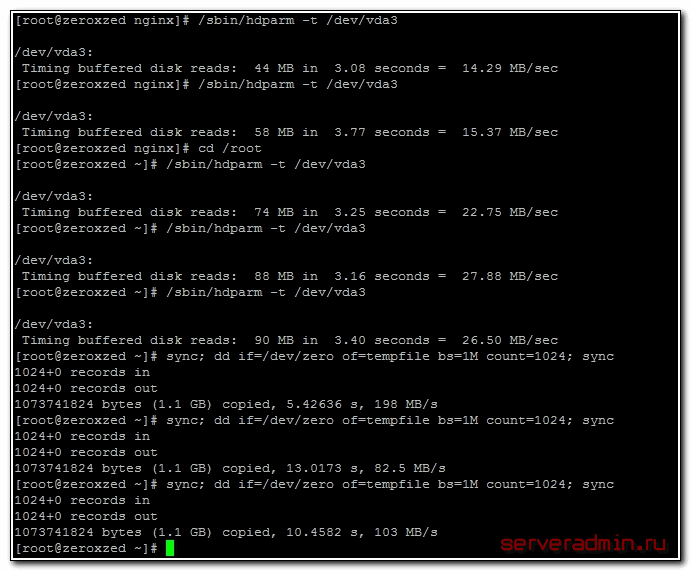
А вот скорость диска на VDS, который я арендую. Результат в разы хуже:
Скорость диска на виртуальной машине, расположенной на втором SATA диске моего рабочего ноутбука:
Результат не очень, надо разбираться в чем дело. Давно возникли подозрения, что с диском что-то не то, заметно подтормаживают виртуальные машины, хотя раньше это было не заметно. Жаль, результатов более ранних тестов не сохранилось.
Интересно было бы посмотреть на ваши результаты тестов. Если же вы хотите серьезно измерить скорость дисков, то вам сюда — Как правильно мерять производительность диска.
Источник