- Linux check the physical health of a USB stick [ Flash drive ]
- Linux check USB stick or errors
- Linux command to check the physical health of a USB stick
- Say hello to f3 tool
- How to install f3 tool on Linux
- Testing performance with f3read/f3write
- Quick capacity tests with f3probe on Linux
- How to correct capacity to actual size for my USB stick in Linux
- Conclusion
- Как в Linux посмотреть подключенные USB устройства
- Просмотр списка имен USB устройств с помощью команды df
- Список имен подключенных USB — устройств с помощью команды lsblk
- Список USB — устройств с помощью команды fdisk
- Список сведений о подключенных USB-устройствах с помощью команды lsusb
- Список USB контроллеров и устройств, использующих USB устройства
- Заключение
- How to List USB Devices in Linux
- List USB Device Names Using df Command
- List USB Device Name using lsblk Command
- List USB Device Names Using fdisk Command
- List USB Devices Details using lsusb Command
- List USB controllers and devices using usb-devices
- Conclusion
- 4 Useful Way to Know Plugged USB Device Name in Linux
- Find Out Plugged USB Device Name Using df Command
- Use lsblk Command to Find USB Device Name
- Identify USB Device Name with fdisk Utility
- Determine USB Device Name with dmesg Command
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
Linux check the physical health of a USB stick [ Flash drive ]
Linux check USB stick or errors
The procedure to check the physical health of a USB pen drive in Linux:
- Open the terminal application.
- Insert your USB stick or pen drive into Linux system.
- To test and detect bad sector in USB flash memory or pen drive, run: badblocks -w -s -o error.log /dev/sdX
- To error check USB flash drive, you can use the f3write and f3read commands, which is an alternative to h2testw app from Windows operating systems.
Let us see all commands and examples in details.
Linux command to check the physical health of a USB stick
First, find out your USB stick or flash drive name under Linux, run:
lsblk
The output indicated that I am using /dev/sda for USB and /dev/nvme0n1 for NVme pci ssd.
Warning: This will destroy any previously stored data on your USB pen/stick. Make sure you choose correct USB device name under Linux.
Once inserted the USB pen/stick, run the following command to search a device for bad blocks:
sudo badblocks -w -s -o error.log /dev/sda
Gif 01: Test usb stick health using badblocks command in Linux
Use the cat command to view error.log:
cat error.log
Say hello to f3 tool
From the project home page:
f3 is a simple tool that tests flash cards capacity and performance to see if they live up to claimed specifications.
F3 stands for Fight Flash Fraud, or Fight Fake Flash.
How to install f3 tool on Linux
First, make sure you have compilers installed and running on Linux. If not, see the following tutorilas:
Download file using the wget command:
wget https://github.com/AltraMayor/f3/archive/v7.2.tar.gz
Untar tar ball on Linux, run:
tar xvf v7.2.tar.gz
Compile it:
make
Install it:
make install
Testing performance with f3read/f3write
Use the following two command. First, f3write will write large files to your mounted USB pen disk. For example, my /dev/sda is mounted at /mnt/:
f3write /mnt/
Next, f3read will check if the flash disk contains exactly the written files:
f3read /mnt/
Zero data lost indicate that my USB pen drive working fine.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Quick capacity tests with f3probe on Linux
If you believe you have bought a fake flash drive, try the following Linux commands. The f3probe command is the fastest drive test and suitable for large disks because it only writes what’s necessary to test the drive. It operates directly on the (unmounted) block device and needs to be run as a privileged user (be careful with device names again as —destructive option deletes all data):
sudo ./f3probe —destructive —time-ops /dev/sdb
Sample outputs:
The outputs from the above indicate that I do not have fake usb drive.
Good news: The device `/dev/sdb’ is the real thing
How to correct capacity to actual size for my USB stick in Linux
Run f3fix command to creates a partition that fits the actual size of the fake drive. Only use to correct size for the fake drive. Use f3probe’s output to determine the parameters for i3fix:
sudo ./f3fix —last-sec=16477878 /dev/sdb
Conclusion
You learned how to check the health status of a USB stick in Linux and further learned how to find out the actual size of a USB pen drive in case you got a faked USB pen drive.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Как в Linux посмотреть подключенные USB устройства
В настоящее время многие компьютерные периферийные устройства, такие как веб-камеры, мыши, сканеры, принтеры, жесткие диски, USB (Pendrive) подключаются по USB. После того, как эти устройства подключены к рабочему столу или серверу, важно знать имя устройства или путь к нему. Это помогает идентифицировать USB устройства для таких задач, как форматирование или отключение.
В Linux все файлы устройств хранятся в каталоге /dev и должны быть доступны во время загрузки системы.
В этой статье я покажу вам различные способы как в ubuntu посмотреть usb устройства. Большинство команд, упомянутых здесь, должны работать практически на всех дистрибутивах Linux. Например Ubuntu, Debian, Mint.
Просмотр списка имен USB устройств с помощью команды df
Команда df — это полезная команда, которая может помочь составить список всех подключенных томов, включая USB-накопители.
Как только USB-устройство подключается в систему Linux, это устройство автоматически монтируется в раздел /media и становится готовым к использованию.
Из приведенного выше вывода следует, что у меня есть 1 USB-накопитель /dev/sdb с 2 разделами /dev/sdb1 и /dev/sdb2
Список имен подключенных USB — устройств с помощью команды lsblk
Команда Lsblk используется для перечисления всех блочных устройств в системе Linux. Из списка можно фильтровать USB-устройства с помощью команды grep.
Чтобы получить дополнительную информацию, такую как UUID, производитель и тип файловой системы, используйте команду blkid, как показано на рисунке ниже.
Список USB — устройств с помощью команды fdisk
Вы можете использовать старую добрую команду fdisk, которая используется для разбиения томов на разделы, чтобы перечислить все разделы в системе Linux, включая USB-накопители.
Запятая будет отображать подробную информацию о вашем USB-томе, включая разделы , размер тома, секторы и тип файловой системы.
Список сведений о подключенных USB-устройствах с помощью команды lsusb
Команда lsusb, также известная как команда “List USB”, используется в Linux для перечисления всех USB-устройств, подключенных к системе.
На выводе выше отображается идентификатор шины, идентификатор устройства, идентификатор USB, а также поставщик или производитель USB-устройств
Команда lsusb перечисляет подключенные устройства и не предоставляет дополнительной информации о USB-устройствах.
Для получения дополнительной информации о подключенных USB устройствах используйте команду dmesg. Команда dmesg, также известная как “сообщение драйвера” или “показать сообщение”, используется для проверки загрузочных сообщений. Кроме того, эта команда используется для отладки проблем, связанных с оборудованием и печати сообщений, генерируемых драйверами устройств.
Вы можете использовать команду dmesg и grep, чтобы сузиться до USB-устройств.
Кроме того, вы можете передать вывод команды dmesg в less для облегчения прокрутки.
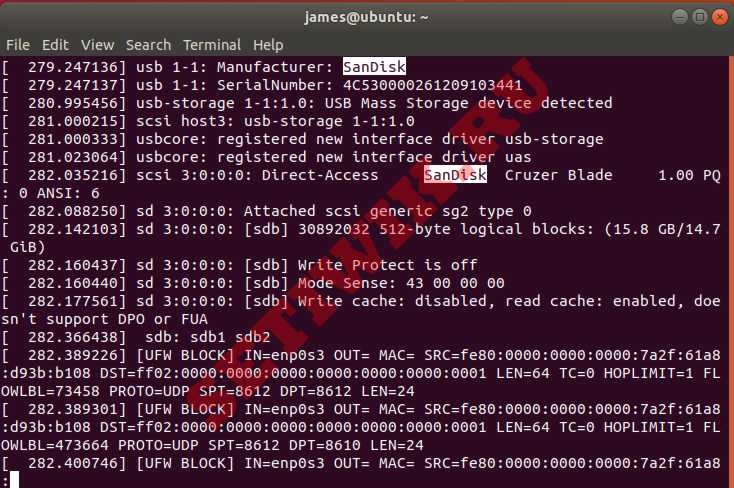
На выходе вы можете найти определенную строку, нажав клавишу прямой косой черты ( / ) на клавиатуре, а затем имя или идентификатор устройства USB-устройства.
В моем случае я ищу дополнительную информацию о USB устройстве под названием SanDisk.
Список USB контроллеров и устройств, использующих USB устройства
Команда usb-devices-это сценарий оболочки, который позволяет вам перечислить все USB-контроллеры и USB-устройства, подключенные к вашему компьютеру. Он печатает детали USB-устройства, такие как производитель, название продукта, серийный номер и многое другое. Вот вывод команды:
Заключение
В этой статье мы продемонстрировали различные способы просмотра USB-устройств, подключенных к системе Linux.
Источник
How to List USB Devices in Linux
Nowadays, many computer peripherals such as webcams, mice, scanners, printers, hard drives, USB (Pendrive) now come as USB devices. Once these devices are connected to the Desktop or server it’s important to know the device name or device path. This helps to identify USB devices for the tasks such as formatting.
In Linux, all device files are stored in /dev directory and must be available to the OS during the system boot.
In this tutorial, I will show you the various ways to list USB devices on Linux. Most commands mentioned here should work on all Linux distributions.
List USB Device Names Using df Command
The df command is a useful command that can help list all mounted volumes, including your USB drives.
Once a USB device is plugged into a Linux system especially for Desktop, it is automatically mounted in the /media partition and becomes ready for use.
From the output above, I have 1 USB drive /dev/sdb with 2 partitions /dev/sdb1 and /dev/sdb2
List USB Device Name using lsblk Command
Lsblk command is used to list all block devices on a Linux system. From the list, you can filter USB devices using the grep command.
To retrieve additional information such as the UUID, manufacturer and filesystem type, use the blkid command as shown.
List USB Device Names Using fdisk Command
You can use the good old fdisk command that is used for partitioning volumes to list all the partitions on the Linux system, including the USB drives.
The comman will display detailed information about your USB volume including the partitions, size of the volume , sectors and the filesystem type.
List USB Devices Details using lsusb Command
The lsusb command, also known as the “List USB” command, is used in Linux to list all the USB devices attached to the system.
The output above displays the Bus ID, Device ID, USB ID, and the vendor or manufacturer of the USB devices
The lsusb command simply lists the connected devices and does not provide further information about the usb devices.
For more information about the attached USB devices use the dmesg command. The dmesg command also known as “driver message” or “display the message” is used for examining the boot messages. Additionally, it is used for debugging hardware-related issues and printing messages generated by device drivers.
You can use the dmesg command and grep to narrow down to USB devices.
Also, you can pipe the output of dmesg command to less for easier scrolling.
On the output, you can search for a specific string by pressing the forward slash key ( / ) on your keyboard followed by the name or Device ID of the USB device.
In my case, I’m searching for more information regarding a USB device called SanDisk, which is actually my removable pen drive.
List USB controllers and devices using usb-devices
The usb-devices command is a shell script that allows you to list all the USB controllers and the USB devices connected to your PC. It prints out details of the USB device such as the manufacturer, product name, serial number, and so much more. Here’s the output of the command:

Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have demonstrated different ways to list the USB devices attached to the Linux system.
Источник
4 Useful Way to Know Plugged USB Device Name in Linux
As a newbie, one of the many things you should master in Linux is identification of devices attached to your system. It may be your computer’s hard disk, an external hard drive or removable media such USB drive or SD Memory card.
Using USB drives for file transfer is so common today, and for those (new Linux users) who prefer to use the command line, learning the different ways to identify a USB device name is very important, when you need to format it.
Once you attach a device to your system such as a USB, especially on a desktop, it is automatically mounted to a given directory, normally under /media/username/device-label and you can then access the files in it from that directory. However, this is not the case with a server where you have to manually mount a device and specify its mount point.
Linux identifies devices using special device files stored in /dev directory. Some of the files you will find in this directory include /dev/sda or /dev/hda which represents your first master drive, each partition will be represented by a number such as /dev/sda1 or /dev/hda1 for the first partition and so on.

Now let’s find out device names using some different command-line tools as shown:
Find Out Plugged USB Device Name Using df Command
To view each device attached to your system as well as its mount point, you can use the df command (checks Linux disk space utilization) as shown in the image below:

Use lsblk Command to Find USB Device Name
You can also use the lsblk command (list block devices) which lists all block devices attached to your system like so:

Identify USB Device Name with fdisk Utility
fdisk is a powerful utility which prints out the partition table on all your block devices, a USB drive inclusive, you can run it will root privileges as follows:

Determine USB Device Name with dmesg Command
dmesg is an important command that prints or controls the kernel ring buffer, a data structure which stores information about the kernel’s operations.
Run the command below to view kernel operation messages which will as well print information about your USB device:

That is all for now, in this article, we have covered different approaches of how to find out a USB device name from the command line. You can also share with us any other methods for the same purpose or perhaps offer us your thoughts about the article via the response section below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник





