- Disk cloning
- Contents
- Using dd
- Using ddrescue
- File system cloning
- Using e2image
- Disk cloning software
- Клонирование разделов жестких дисков в Linux
- Как клонировать раздел Linux
- Клонирование всего жесткого диска
- Создание резервной копии MBR в Linux
- How to clone the partition table on Linux with sfdisk
- Disk cloning in Linux using dd command
- How to clone a partition from one disk to another
- How to clone an entire disk
- How to create a disk image
- Compressed disk image
- Send disk image to remote system
- Split the disk image by size
- Restoring disk image
- How to Clone a Partition or Hard drive in Linux
- How to Clone Linux Partition
- How to Clone Linux Hard Drive
- How to Backup MBR in Linux
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
Disk cloning
Disk cloning is the process of making an image of a partition or of an entire hard drive. This can be useful for copying the drive to other computers or for backup and recovery purposes.
Contents
Using dd
Using ddrescue
ddrescue is a tool designed for cloning and recovering data. It copies data from one file or block device (hard disc, cdrom, etc) to another, trying to rescue the good parts first in case of read errors, to maximize the recovered data.
To clone a faulty or dying drive, run ddrescue twice. For the first round, copy every block without read error and map the errors to rescue.map .
where X is the partition letter of the source and Y of the target block device.
For the second round, copy only the bad blocks and try 3 times to read from the source before giving up.
Now you can check the file system for corruption and mount the new drive.
File system cloning

Using e2image
e2image is a tool included in e2fsprogs for debugging purposes. It can be used to copy ext2, ext3, and ext4 partitions efficiently by only copying the used blocks. Note that this only works for ext2, ext3, and ext4 filesystems, and the unused blocks are not copied so this may not be a useful tool if one is hoping to recover deleted files.
To clone a partition from physical disk /dev/sda , partition 1, to physical disk /dev/sdb , partition 1 with e2image, run
Disk cloning software
These applications allow easy backup of entire filesystems and recovery in case of failure, usually in the form of a Live CD or USB drive. They contain complete system images from one or more specific points in time and are frequently used to record known good configurations. See Wikipedia:Comparison of disk cloning software for their comparison.
See also Synchronization and backup programs for other applications that can take full system snapshots, among other functionality.
Источник
Клонирование разделов жестких дисков в Linux
Оригинал: How to Clone Linux Partition
Автор: Marin Todorov
Дата публикации: 18 декабря 2018 года
Перевод: А. Кривошей
Дата перевода: октябрь 2019 г.
Существует множество причин, по которым вы можете захотеть клонировать раздел Linux или даже весь жесткий диск, большинство из которых связаны с созданием резервных копий ваших данных. Есть несколько способов сделать это в Linux, используя внешние утилиты, такие как partimage или Clonezilla.
Однако в этом руководстве мы рассмотрим клонирование дисков Linux с помощью утилиты dd, которая чаще всего используется для преобразования или копирования файлов и предустановлена в большинстве дистрибутивов Linux.
Как клонировать раздел Linux
С помощью команды dd вы можете скопировать весь жесткий диск или отдельный раздел Linux. Начнем с клонирования одного из наших разделов. В моем случае у меня есть следующие диски: /dev/sdb, /dev/sdc. Я буду клонировать /dev/sdb1 / в /dev/sdc1.
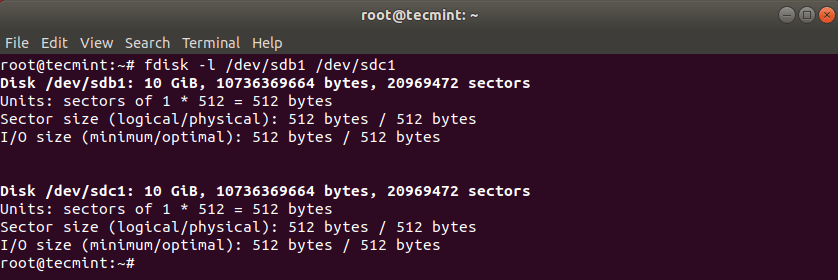
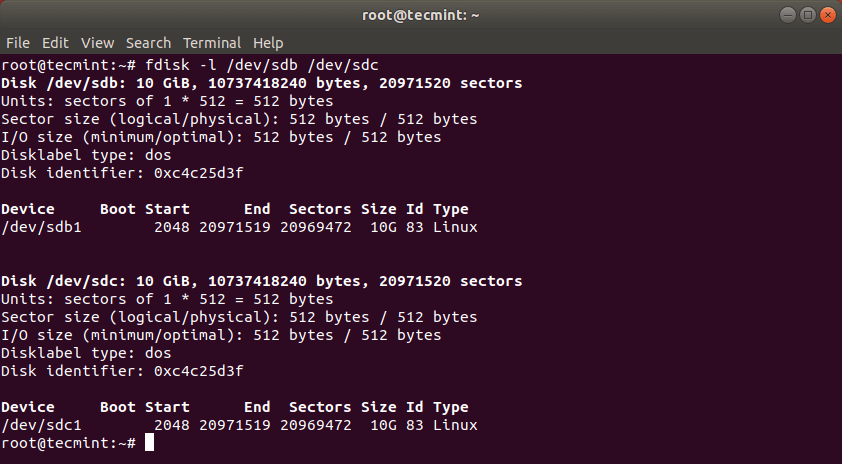
Сначала выведите список разделов диска, используя команду fdisk, как показано ниже.
Теперь клонируем раздел /dev/sdb1/ в /dev/sdc1 с помощью команды dd:
Приведенная выше команда указывает dd использовать /dev/sdb1 в качестве входного файла и записать его в выходной файл /dev/sdc1.
После клонирования раздела Linux вы можете проверить оба раздела с помощью команды:
Клонирование всего жесткого диска
Клонирование жесткого диска Linux похоже на клонирование раздела. Однако вместо указания раздела вы просто используете весь диск. Обратите внимание, что в этом случае рекомендуется, чтобы целевой жесткий диск был такого же размера (или больше), что и исходный диск.
Эта команда должна была скопировать диск /dev/sdb с его разделами на целевой жесткий диск /dev/sdc. Вы можете проверить изменения на обеих дисках с помощью команды fdisk.
Создание резервной копии MBR в Linux
Команда dd также может быть использована для резервного копирования MBR, которая находится в первом секторе диска перед первым разделом. Поэтому, если вы хотите создать резервную копию вашей MBR, просто выполните команду:
Источник
How to clone the partition table on Linux with sfdisk
Sometimes you need to clone partitions on your hard drive for various reasons, hd damaged, creating a RAID 1 or something similar, then it is often tedious and impractical to perform the operation using the normal tools like fdisk, in this case you can use sfdisk.
As reported in the manual:
sfdisk is a non-interactive program to edit the partition table, which is useful for creating scripts. The normal use of this service program involves the preparation of a file containing the instructions on the partitions to be created within a disk specified explicitly. Even if there is a special syntax for these instructions, it may be convenient to use since it is obtained from a query with the same sfdisk, as will be shown.
In practice sfdisk is nothing but a tool that allows you to perform simple tasks in Linux on the partition table
In our case through the -d option will be able to clone partitions , in fact, this option create a report on the partitions of the hard disk defined as a parameter.
Bringing the output to a file you can then perform the inverse operation and recreate the partition table to another disk , or even on the same .
Cloning the partition table
For example, assuming that our disk is /dev/sda , to save the partition table we can give the command:
sfdisk -d /dev/sda > partitions.txt
while to restore it, assuming that the destination disk is /dev/sdb and we want to clone the partition table, we can use the command
sfdisk /dev/sdb
If you get told by sfdisk that “sfdisk: I don’t like these partitions – nothing changed”, it is because the installer for some modern distributions, including CentOS6, create partitions that are the size you specify and do not necessarily end at cylinder boundaries.
This shouldn’t cause any problems during day to day running but does when manually partitioning disks.
Fortunately we can force sfdisk to do this, with the option –force
At this point we have two disks with partitions of the same size, of course, the passage of data, if you would like it, or sync the disks or even RAID reconstruction now it’s up to you.
Источник
Disk cloning in Linux using dd command
The dd command utility is a simple yet powerful and useful command available in Unix and Linux systems which is used to convert and copy files. Unix like systems treat all devices as files and these device files are located in the /dev directory in your system. So typically your hard disk drive is a file in the /dev directory with the prefix of hd or sd (depending on IDE or SCSI driver). This concept of device as files makes dd a perfect candidate for backup and restore of disk images or cloning some partitions or the entire disk.
This article shows you some examples of how to use the dd command to backup or clone drive partitions and entire drives.
You can use the fdisk command or check the /proc/partitions to view all the disk partitions in your system.
From the above output we can deduce that you have hard disks on your system and their device file names are sda and sdb. There are two partitions in sda which are sda1 and sda2 and we also know that sda1 is a boot partition.
How to clone a partition from one disk to another
The following are the steps to create a clone of a partition from one disk to another disk, lets say for example you want to clone sda1 partition to sdb1 . In this case sda is your source disk and sdb is the destination disk.
Step 1: Create a new partition in the destination disk if it does not already exist. You can use the fdisk command to create the new partition.
Step 2: Run the dd command.
- conv=sync,noerror tells dd command to continue copying after read errors and fill input block with nulls in case partial records.
- status=progress shows progress of the copy.
- bs=64M set the block size to copy at a time. Adjust this value could improve the copying speed
How to clone an entire disk
To clone an entire disk, say for example sda to sdb , run:
When you clone a entire disk, the destination disk will get all the partitions that are on the source disk.
How to create a disk image
Before you create a disk image backup, make sure no partitions on that disk are mounted and run the following command
where sdb is the disk file name and /path/to/backup.img is the path and filename of the backup image.
Compressed disk image
You could also compress the backup image with gzip as shown in the example below
Send disk image to remote system
You could send the backup image to a remote machine using ssh as in the below example.
Split the disk image by size
You can split the disk image in to smaller pieces of any size that you specify by passing the dd output through split command.
The above command splits the backup image file to smaller files of size 50MB or less. A two letter suffix will be added to the files. The resulting files will have names backup.img.gz.aa, backup.img.gz.ab, backup.img.gz.ac.
To join the split files into a single image file, you run the command
Restoring disk image
The below command restores the disk sdb from the image file backup.img .
To restore from a compressed backup image, use the gunzip command with dd
To restore from a backup image that is compressed and split, run:
Источник
How to Clone a Partition or Hard drive in Linux
There are many reasons why you may want to clone a Linux partition or even hard drive, most of which are related to creating backups of your data. There are multiple ways you can achieve this in Linux by using some external tools such as partimage or Clonezilla.
However in this tutorial we are going to review Linux disk cloning with tool called dd, which is most commonly used to convert or copy files and it comes pre-installed in most Linux distributions.
How to Clone Linux Partition
With dd command you can copy entire hard drive or just a Linux partition. Lets start with cloning one of our partitions. In my case I have the following drives: /dev/sdb, /dev/sdc.. I will clone /dev/sdb1/ to /dev/sdc1.
First list the these partitions using the fdisk command as shown.

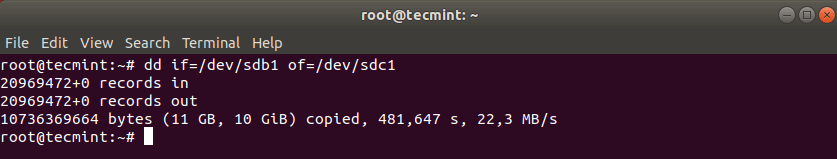
Now clone a partition /dev/sdb1/ to /dev/sdc1 using the following dd command.
The above command tells dd to use /dev/sdb1 as input file and write it to output file /dev/sdc1.

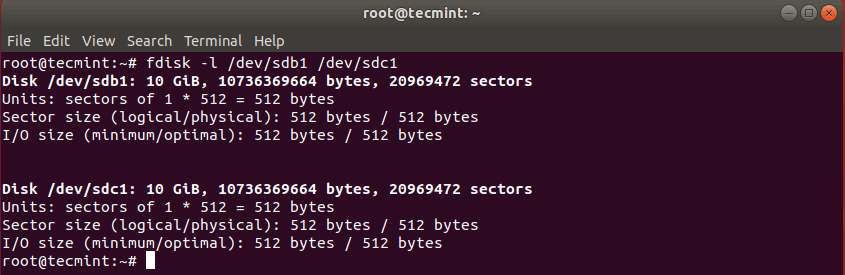
After cloning Linux partition, you can then check both partitions with:

How to Clone Linux Hard Drive
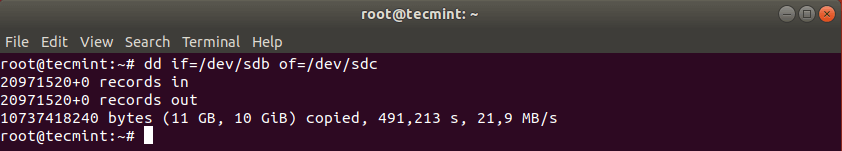
Cloning a Linux hard drive is similar to cloning a partition. However, instead of specifying the partition, you just use the entire drive. Note that in this case it is recommended that the hard drive is same in size (or bigger) than the source drive.

This should have copied the drive /dev/sdb with its partitions on the target hard drive /dev/sdc. You can verify the changes by listing both drives with fdisk command.

How to Backup MBR in Linux
dd command can also be used to backup your MBR, which is located at the first sector of the device, before the first partition. So if you want to create backup of your MBR, simply run:
The above command tells dd to copy /dev/sda to /backup/mbr.img with step of 512 bytes and the count option tells to copy only 1 block. In other words you tell dd to copy the first 512 bytes from /dev/sda to the file you have provided.

That’s all! dd command is a powerful Linux tool that should be used with caution when copying or cloning Linux partitions or drives.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник