- Bash permission denied Explanation and Solution
- Bash permission denied
- An Example Scenario
- The Solution
- Conclusion
- Ошибка «Permission denied» в Linux
- Изменение прав в терминале
- Изменение прав в файловом менеджере
- В заключение
- Permission denied when running .sh scripts
- 3 Answers 3
- Ubuntu says «bash: ./program Permission denied» [closed]
- 3 Answers 3
- How to resolve permission denied Linux error
- What is permission denied Linux error?
- Example of Permission denied Linux error
- How to resolve Permission denied Error
- Resolving Permission denied error related to script execution:
- Resolving permission denied Linux error while listing or writing to a file
- Resolving permission denied Linux error for specific user
- Download Free book
Bash permission denied Explanation and Solution
Files on an operating system usually have permissions, making the file accessible to a limited range of people. For instance, some files on a computer are accessible only to administrators; other files are only accessible to a particular user.
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps Get exclusive scholarships and prep courses
If you try to run a file to which you have no access on a Linux computer, you will see a permission denied error. In this guide, we’re going to talk about the cause of this error and how you can solve the error. Let’s begin.
Bash permission denied
The Bash permission denied error happens when you try to run a file which you do not have permission to run. This may happen if a file can only be executed by a particular user or a group of which you are not a member.
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps Get exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Do you want to learn more about how a coding bootcamp can help you learn to code? Get started by finding the right bootcamp for you along with unlocking additional information about bootcamp cost and reviews.
On a Linux operating system, there are three types of permissions:
You can have permission to read and write a file without having execution privileges. Thus, if you encounter a Bash permission denied be sure to check whether you are allowed to run the file. You can check if you have permissions over a file by using the following command:
This command will give you information about file permissions. We discuss the output of this command in our The Solution section later in the article. Let’s look at an example scenario featuring the permission denied error, with a corresponding solution.
An Example Scenario
We have a file called example.sh. We can see this file by running the ls command. The ls command returns the following:
Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
Find Your Bootcamp Match
We want to run our example.sh file. To do so, we can use the ./ notation:
This command lets us run the example.sh file which is present in our ./ directory (the directory we are presently viewing). Let’s see what happens when we try to run the file:
Our command returns an error.
The Solution
Our Bash shell is telling us that we do not have permissions to run our file. We can check what permissions we have by running the ls -la command:
We do not have execution privileges over any of our files. If there were an x after the rw in the first entry of the output above, we would know we can execute our file. The three characters after the first one represent read, write, and execute privileges for a user. Our group also does not have write or execute permissions.
To solve this issue, we need to give ourselves execution privileges:
This command gives our user execution (“x”) privileges over the example.sh file.
We can only run this command if we are allowed to change the privileges of the file. If this file was protected (owned by root, for example), then we would not be able to change this file.
The file is owned by the james system user so I can alter the file permissions on my james account. I could also use sudo to alter the file privileges, although this is not necessary because my user account has the necessary access.
Conclusion
The Bash permission denied error indicates you are trying to execute a file which you do not have permission to run. To fix this issue, use the chmod u+x command to give yourself permissions. If you cannot use this command, you may need to contact your system administrator to get access to a file.
Do you want to learn more about Bash? Check out our How to Learn the Command Line guide. This guide comes with top tips on how to learn Bash. You will also find a list of resources to help you accelerate your learning journey.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication.
Источник
Ошибка «Permission denied» в Linux
Все операционные системы семейства Linux имеют четко разграниченные права доступа. В своей домашней директории пользователь может делать все, что ему угодно, до тех пор, пока укладывается в отведенные рамки. Попытка выйти за них приводит к появлению ошибки «Permission Denied».
Изменение прав в терминале
Рассмотрим вариант, в котором необходимо прочесть текстовый документ, созданный другим пользователем. Файлы TXT в Linux можно просматривать непосредственно в терминале с помощью команды «cat».
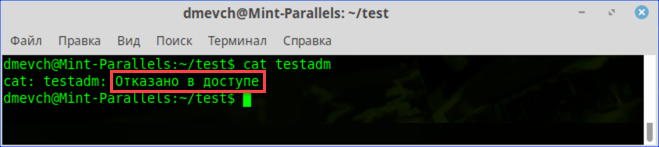
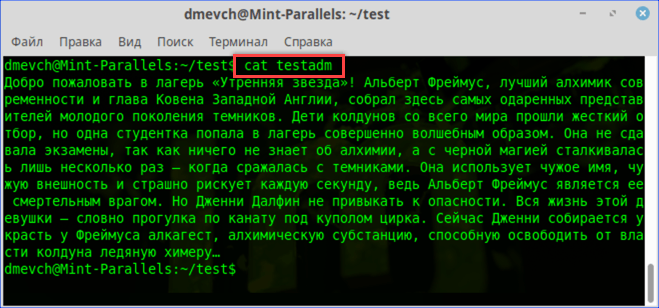
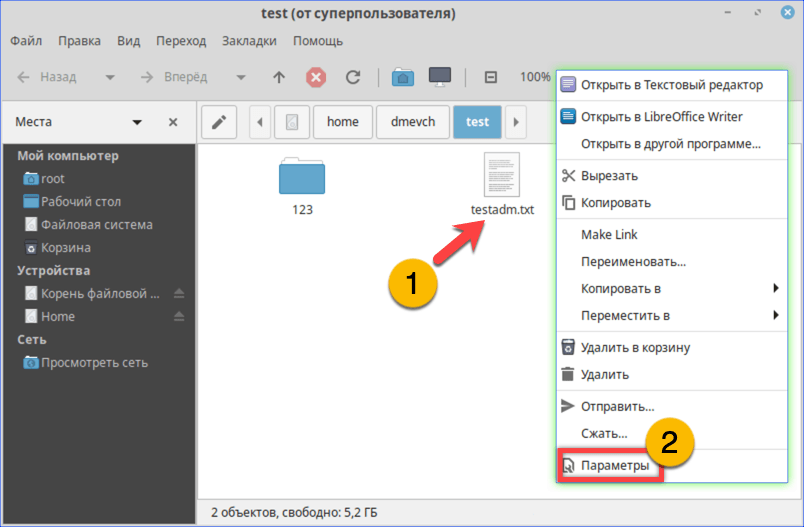
- Заходим в каталог с интересующим нас документом. Набираем команду «cat filename», подставляя вместо «filename» имя нужного файла. На скриншоте показана ошибка «Permission Denied», выглядящая в русской локализации как «Отказано в доступе».
Получаем ошибку «Permission Denied» при попытке просмотреть содержимое файла
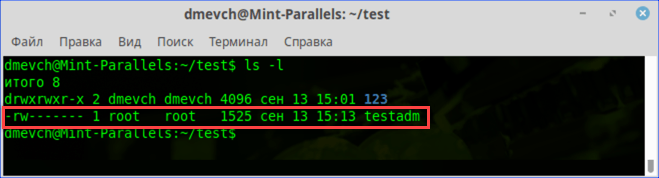
Проверяем права доступа к документу используя команду «ls -l»
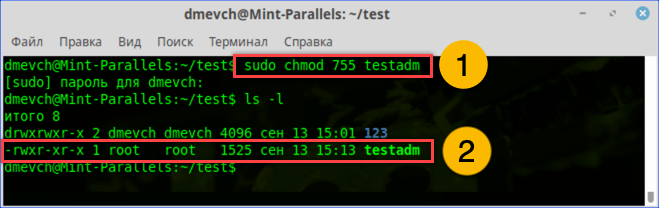
Используем команду «chmod» и административные права для получения доступа
Просматриваем содержимое текстового документа командой «cat»
Изменение прав в файловом менеджере
Разберемся, как выполнить рассмотренную выше операцию в графическом интерфейсе, используя файловый менеджер из дистрибутива.
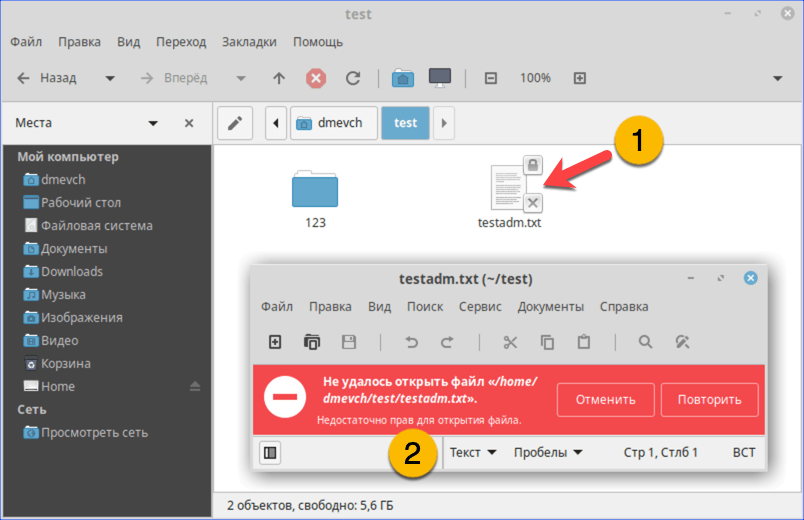
- Как видно на скриншоте, значок файла изначально имеет дополнительные символы, указывающие на то, что доступ у нему ограничен. При попытке посмотреть содержимое получаем графический вариант ошибки «Permission Denied».
При попытке открыть текстовый документ получаем ошибку «Permission Denied»
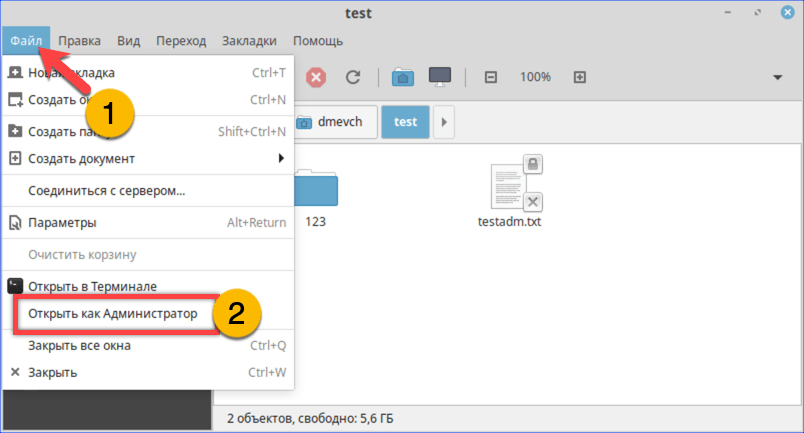
Открываем меню «Файл» и перезапускаем файловый менеджер от имени root
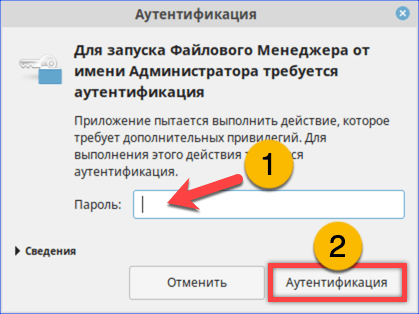
Набираем пароль root в окне аутентификации
Открываем параметры файла с помощью контекстного меню
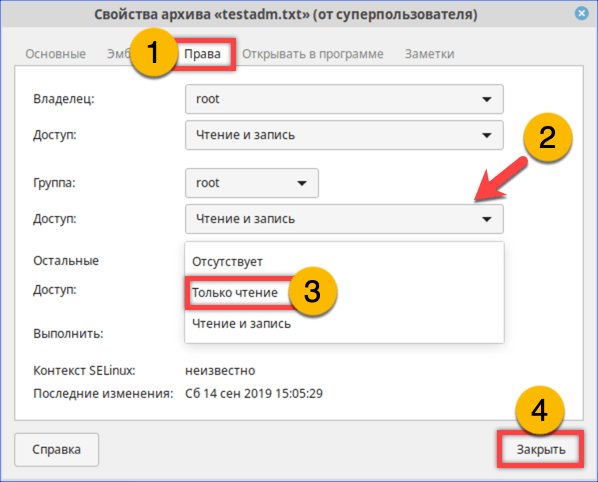
На вкладке «Права» разрешаем доступ для группы root и остальных пользователей
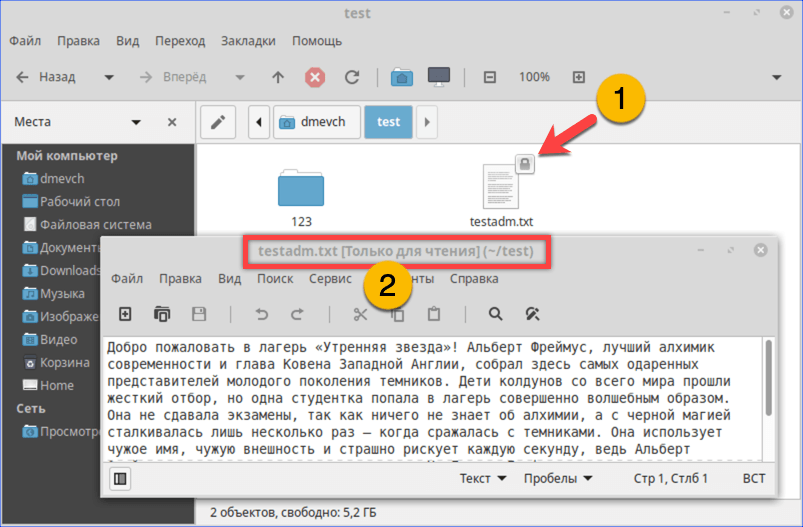
Открываем ранее недоступный файл в режиме чтения и изучаем содержимое
В заключение
Как видим, избавиться от ошибки Permission Denied достаточно просто. Решив изменить правда доступа к системным файлам, лишний раз убедитесь, что полностью уверены в своих действиях и понимаете последствия вносимых изменений.
Источник
Permission denied when running .sh scripts
program exited with code: 126 . This problem always occur when I try to execute my code. What might be the solution?
3 Answers 3
If you want to skip these (for now of course), you can create a directory/folder in your user-home directory and work on your C programmes (or others) there.
You can open the terminal (press Ctrl + Alt + T ) and cd to the target directory:
To give the file «the_file_name» execute permission (if the file-system allows you with the RW rights):
You need to give execute and read permission. Follow this:
When we make new script file then by default it has read and write permission. But if we want to execute them, then we should give execute permission by shown above.
Note that execution bit alone is not enough for shell scripts: one must be able to read the file as well to execute it (contrary to binaries which only need the execute permission bit).
Open your terminal application by pressing CTRL + ALT + T or with the apposite shortcut on the graphical enviroment (like Terminal or xTerm ).
In the uniform window which appears on the screen you’ll see a blinking character, it’s the terminal cursor : simply click on the window and write to enter text (typically commands) and press ENTER to confirm the input.
Before the cursor there is always listed your current position on the file system from the root directory («/») and your home (where your personal files are) is called «
«.
To change directory/folder use cd EXISTENTFOLDER (replace EXISTENTFOLDER with the folder name); if you feel lost, simply type cd to return to your home directory in a blink!
Now let’s solve your problem:
Use the cd command to find the directory with your source code. Use TAB to help you. If you execute ls -lh , you’ll see a list of possible paths to follow and files to execute.
When you’ve find the blocked file execute chmod +x FILENAME (replace FILENAME with the name of your source code file).
If you have multiple blocked files execute chmod +x * to unlock all files in the current directory. Never chmod +x dangerous or insecure files.
Execute ./FILENAME YOUREVENTUALARGUMENTS to execute your executable file.
Remember that if your compiled program tries to read/write outside your home directory you’ll need to execute it as root by using sudo ./FILENAME YOUREVENTUALARGUMENTS .
If you want to have a manual for a command execute man COMMAND (replace COMMAND with the exact command name, Linux is case sensitive).
Some shells have an Open terminal here command to simplify your life, search for it in the future and remember that the command shell can be your best friend, if you use it well. 😀
It’s all. If you need more help comment under here.
If I’m helping you press the UP arrow on the left; if you solve mark this answer as best answer.
Источник
Ubuntu says «bash: ./program Permission denied» [closed]
Want to improve this question? Update the question so it’s on-topic for Stack Overflow.
Closed last month .
I am running Ubuntu on computer 1 and computer 2. I compiled a C++ program on computer 1, and I can execute it from the terminal using ./program_name . It runs fine.
However, when I try to do this on computer 2, it says: bash: ./program_name: permission denied
What’s wrong and what can I do about it?
3 Answers 3
chmod u+x program_name . Then execute it.
If that does not work, copy the program from the USB device to a native volume on the system. Then chmod u+x program_name on the local copy and execute that.
Unix and Unix-like systems generally will not execute a program unless it is marked with permission to execute. The way you copied the file from one system to another (or mounted an external volume) may have turned off execute permission (as a safety feature). The command chmod u+x name adds permission for the user that owns the file to execute it.
That command only changes the permissions associated with the file; it does not change the security controls associated with the entire volume. If it is security controls on the volume that are interfering with execution (for example, a noexec option may be specified for a volume in the Unix fstab file, which says not to allow execute permission for files on the volume), then you can remount the volume with options to allow execution. However, copying the file to a local volume may be a quicker and easier solution.
Источник
How to resolve permission denied Linux error
This article will teach you quickly what is permission denied Linux error. And also what ways you can avoid permission denied error in Linux.
What is permission denied Linux error?
This error comes when you try to list files or try execute the file inside the directory where you don’t have sufficient permission. Since Linux operating system is very particular about its security aspect.
Example of Permission denied Linux error
Let’s say you are a normal user who is trying to list or trying change the directory inside the /root file-system. Since you do not have sufficient permissions system will respond with permission denied error message as below:
One way to avoid such error is to switch to root user using su – command. However this solution is not recommended since it will gain unnecessary access to all the root file system.
How to resolve Permission denied Error
Resolving Permission denied error related to script execution:
Let’s say you have created a shell script for performing any task. but when you try to execute the script you may end with below error due absence of permission denied error.
Now to avoid such case you need to add execute permission “x” to the file myshell.sh using chmod command as below:
In the last output you can see that there is “x” (execution) permission added after chmod command. So next time when you try to execute the shell script , it will execute without any error.
Resolving permission denied Linux error while listing or writing to a file
In this type of permission denied error you try to list or write the file in which you do not have sufficient permission to do so as below:
If you look at the permissions of the “myfolder” directory using ls -l command you will come to know about the permissions.
As per the permission given in above output only owner of the directory who is root can have all permission that is read, write and execute. So in such case you need to change the permission of the directory to read using below chmod command:
Now this time when normal user manmohan try to list directory he will not get the permission denied error.
In case you want to have write permission on this directory you need to specify w flag as well in chmod command as below:
Same is applicable to file level permission as well.
One more way is to changing the ownership of the directory using chown command. Since in our example we are getting error for user manmohan we will change ownership of the directory “myfolder” using below command.
Since manmohan user is now the owner of the directory he can able to do any operation on the directory. In case you want to recursive permission do not forget to add -r while chown command as below:
Resolving permission denied Linux error for specific user
In above method of changing the permission using chmod is not suitable as per my opinion. Because when you give permission to others, it will be open for all the users within the system. Which is wrong in terms of security perspective. To resolve this error specific to user you can implement it using access control list or ACL. Follow my article on Access control list ACL for the same.
Download Free book
Get your free copy of Linux command line Cheat Sheet.
Источник