- How to Copy a Directory in Linux Command Line [Beginner’s Tip]
- Copy directory in Linux command line
- A few things to note about copying directory in Linux
- The destination directory doesn’t exist? It will be created
- Can’t create nested directory while copying
- Preserve the original file attributes
- How can I Copy Files in a Folder into Another Folder on Linux Terminal
- File copying in terminal
- Cp Command
- mv command
- Rsync Command
- Final thoughts
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
- How do I copy folder with files to another folder in Unix/Linux? [closed]
- 3 Answers 3
- How to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
- Using the cp Command to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
- Additional Options
- How to Copy File to Another Directory in Linux
- Copy Multiple Files from One Directory to Another in Linux
- Copy Using rsync Command
- Other Options
How to Copy a Directory in Linux Command Line [Beginner’s Tip]
If you are new to Linux command line, you probably have this question in mind: How do I copy a directory and the files inside it to another directory in Linux command line?
Here’s how to copy a directory in Linux:
You probably already know that you can use cp command to copy files in Linux. Do you know that you can use the same cp command to copy a folder in Linux command line?
Hah! You already tried that and perhaps got this error:
Let me show you a thing or two about copying directory in Linux.
Copy directory in Linux command line
You can definitely use the same cp command but with the recursive option -r to copy a folder with its content to another folder. The above mentioned error also hints that you missed the -r option.
All you got to do is to use the command in this fashion:
And now if you use ls command on the destination directory, it should have the entire source directory inside it.
The -r option allows the recursive option. This means the entire content of the directory including its own subdirectories, everything in the directory will be copied to the destination.
A few things to note about copying directory in Linux
Here are a couple of things to note and tips about copying folders.
The destination directory doesn’t exist? It will be created
If the destination directory doesn’t exist (but the path exists), it will be created up to one level (explained in the next section). However, it will now copy the contents of the source directory, not the source directory itself.
For example, if you do this:
The non_existing_directory will be created with the content of the source_directory but it won’t have the source_directory inside it. Just the files of source_directory will be copied. It would be like non_existing_directory will be a replica of source_directory.
Can’t create nested directory while copying
You cannot use the above command to create nested directory structure.
For example, if you try to use cp -r source_dir dir1/dir2/dir3 but dir2 and dir3 don’t exist, it won’t create the nested directory structure and the command fails.
Preserve the original file attributes
One last tip to keep things short. If you use the -a option along with the -r option, it will preserve the original file information such as file permissions, file timestamps etc. It will archive the directory to the new location instead of creating it afresh.
That’s it
This much information should be enough for you to know how to copy a directory in Linux. If you have questions or suggestions, please feel free to leave a comment.
Источник
How can I Copy Files in a Folder into Another Folder on Linux Terminal
File copying in terminal
Copying the content of one directory into another is a very simple task. However, you have plenty of options of doing it. Linux is blessed with numerous tools to manipulate files and directories through various actions.
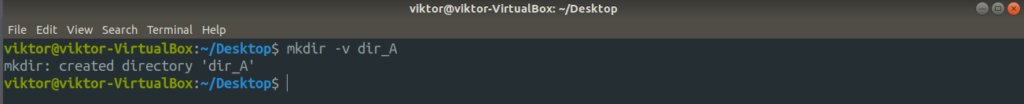
All the steps are demonstrated on Ubuntu 18.04.1. At first, let’s create a handful of dummy files to work with.
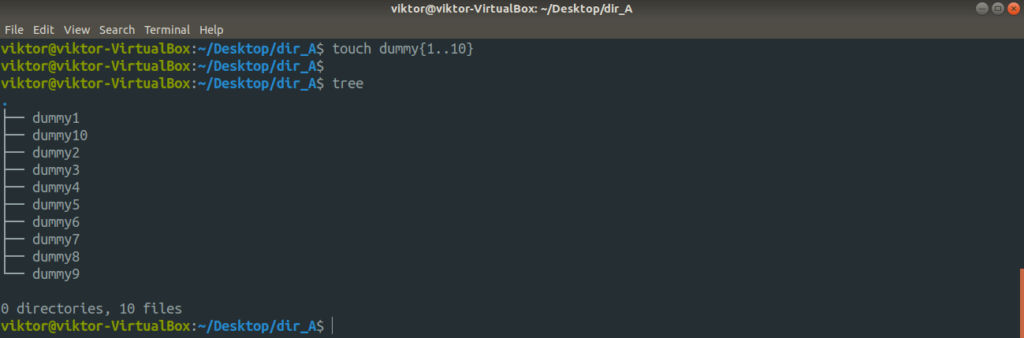
Now, let’s create the dummy files using touch.
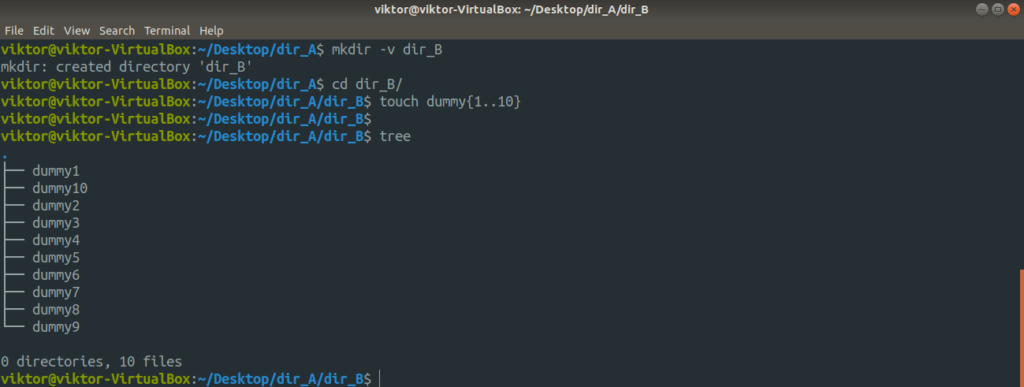
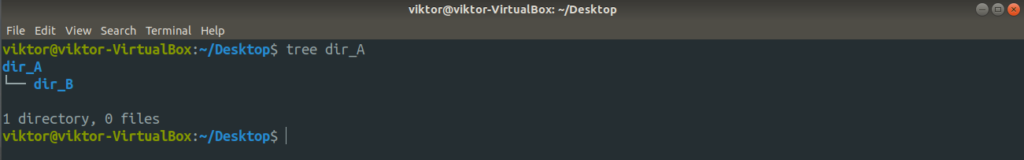
Let’s create another folder within dir_A with a handful of dummy files.
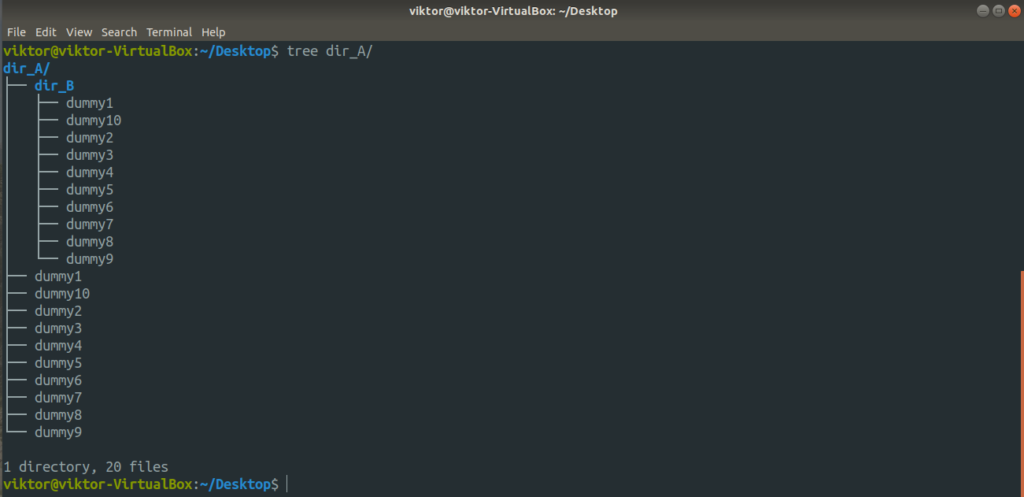
Now, the entire structure of the directory dir_A looks like this.
Cp Command
The cp command is, by far, the most common tool for copying files. It’s a tool that comes by default with any Linux system. Copying files and directories are the sole purpose of cp. It supports a wide range of features.
This is the basic structure of the cp command.
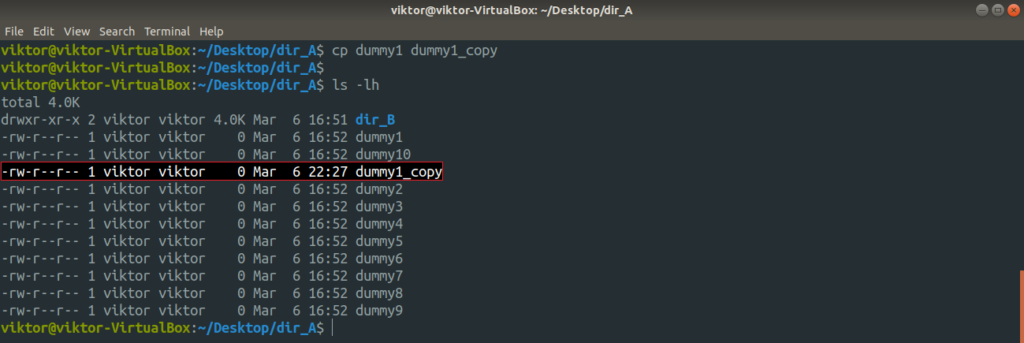
For example, let’s make a copy of the dummy1 file with the name dummy1_copy.
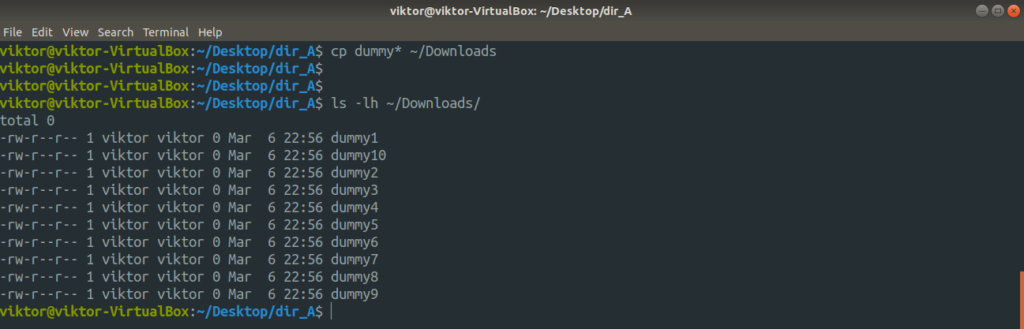
Now, let’s try copying multiple files at once. For such an operation, cp requires the destination be a directory. Here, I’ll be using wildcard expression to grab all the dummy files and put them into the
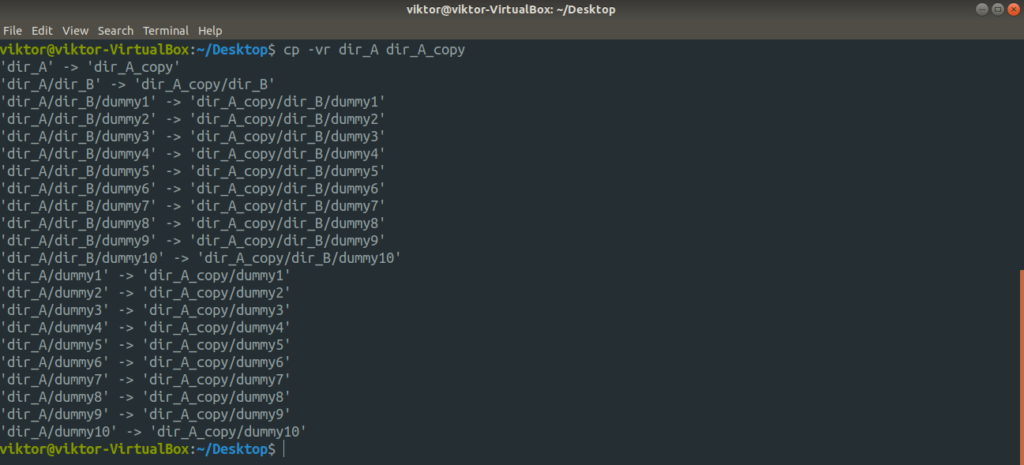
How about copying a directory?
Here, we used two different flags. Let’s have a quick breakdown of them.
- -r: Stands for a recursive copy (including any hidden file(s)). Must-have flag if copying involves an entire directory or more.
- -v: Stands for verbose. The cp tool will output every single action it’s performing.
Want to follow the symbolic links? Add the “-L” flag.
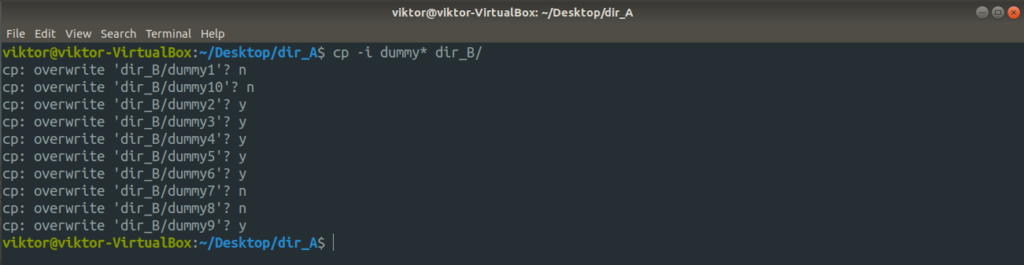
Let’s say the destination directory already has a file with the same name. If you want to avoid overwriting, use the “-n” flag. It’ll ensure that in case of conflict, cp won’t overwrite the file.
If you’re performing a sensitive copy/paste action, it’s better to have the finest control over what happens, right? In such a case, use the “-i” flag. It stands for an interactive mode where cp will ask for confirmation every time a conflict arises.
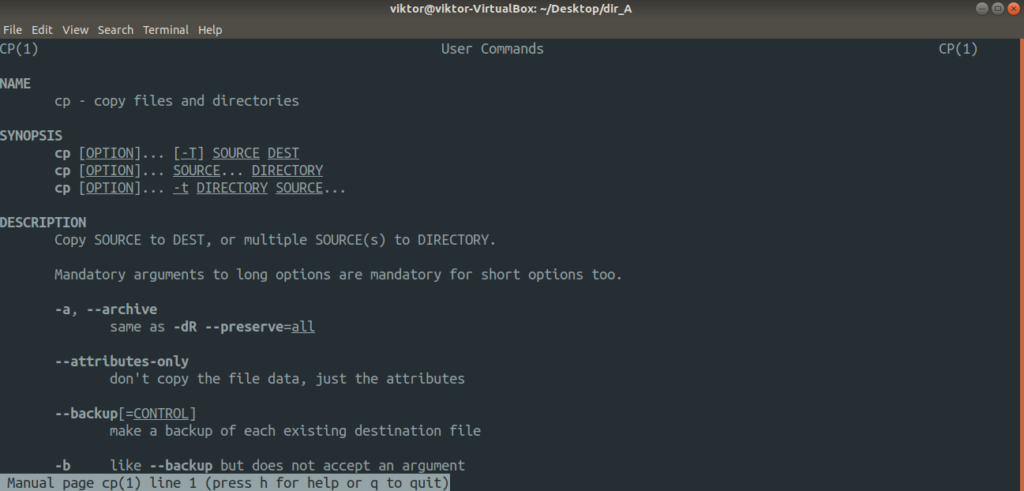
If you’re more interested, the man page is always one of the best documentation. Learn more about cp.
mv command
The mv tool is similar to the cp tool. However, instead of copying, mv moves files and directories. Compared to cp, it’s a simpler one.
The command structure of mv is similar to cp.
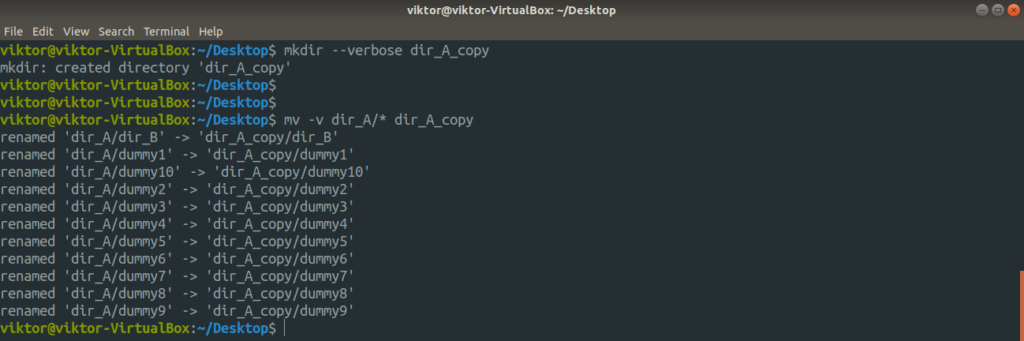
To move the contents of dir_A to dir_A_copy, run the following command.
Here, the “-v” flag is for verbose mode. If you want to move just the contents of dir_A, use the following one instead. In this case, the target directory must exist beforehand.
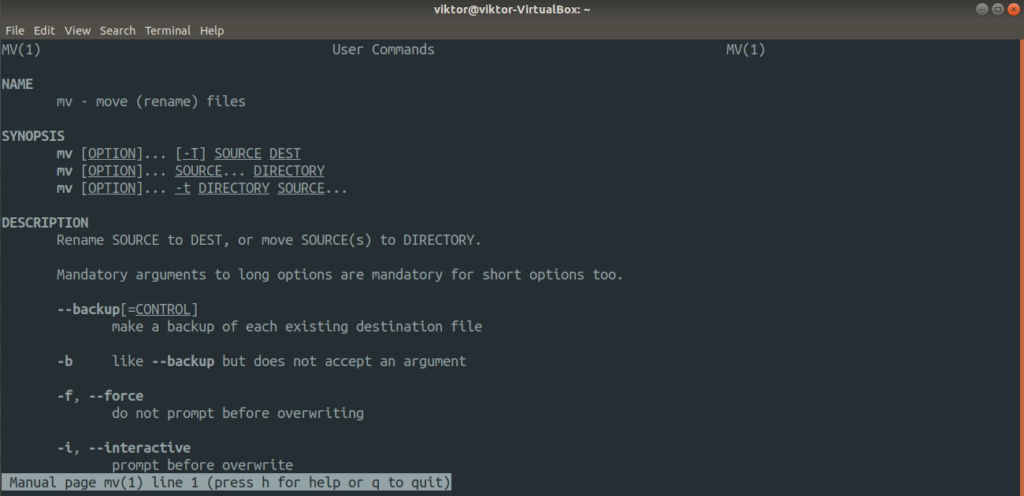
The mv tool doesn’t have much to work with. For all the available options, check out the man page.
Rsync Command
This is one of the most popular and powerful tools for file copying, used mostly for backup. It holds the ability to copy files over a remote connection. Unlike cp and mv, it also comes with a ton of advanced file copying options that offer the utmost customization of its behavior.
Rsync is mostly famous for its delta-transfer algorithm that dramatically reduces the amount of data that needs to be exchanged. In the case of remote syncing, this saves up a lot of bandwidth.
Rsync doesn’t generally come pre-installed in any Linux distro. However, because of its popularity, it’s now available on all the major Linux distros. Use Pkgs.org to find out the rsync package for your distro. Assuming that you got rsync installed, let’s get started.
First, the basic command structure of rsync. It’s quite similar to cp.
Before getting started, here are a handful of popular rsync arguments.
- -v: Verbose mode, outputs whatever action being performed on the console screen.
- -vv: Verbose mode with more details
- -r: Recursive mode, must be present if copying directories
- -z: Compress data
- -a: Archive data
- -n: Dry run, should be run in combination with verbose mode. Simply outputs the actions if the command was to run for real
- –delete: Delete the file(s) and directory(s) on the destination directory if the source directory doesn’t contain them any longer
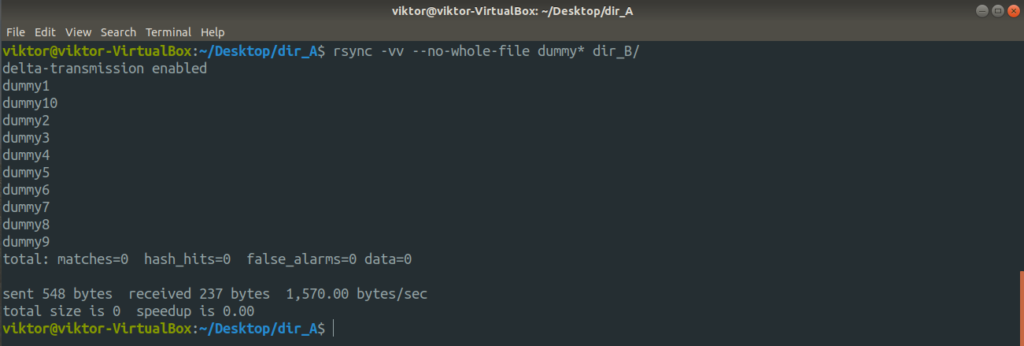
- -no-whole-file: Forces rsync to use its delta transmission algorithm, no matter what. Useful in scenarios where you must ensure the least amount of data write.
- –remove-source-file: Delete source file(s) after copying.
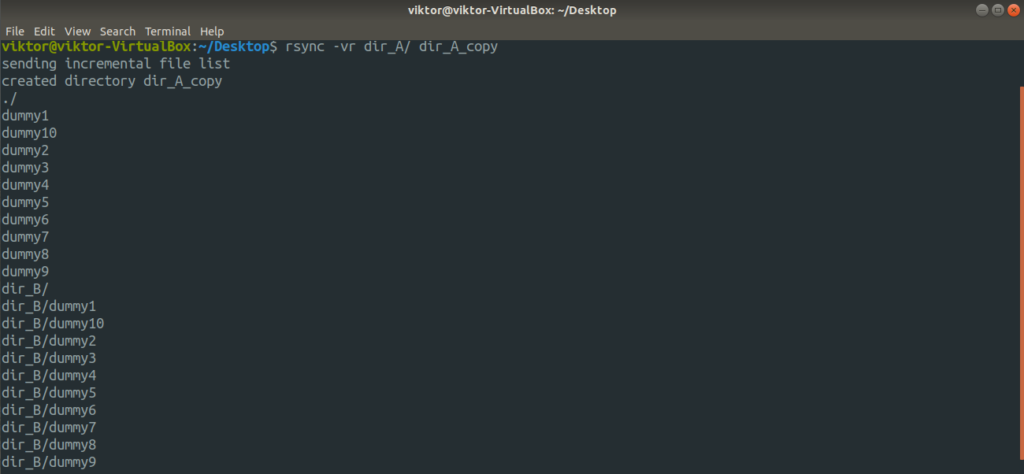
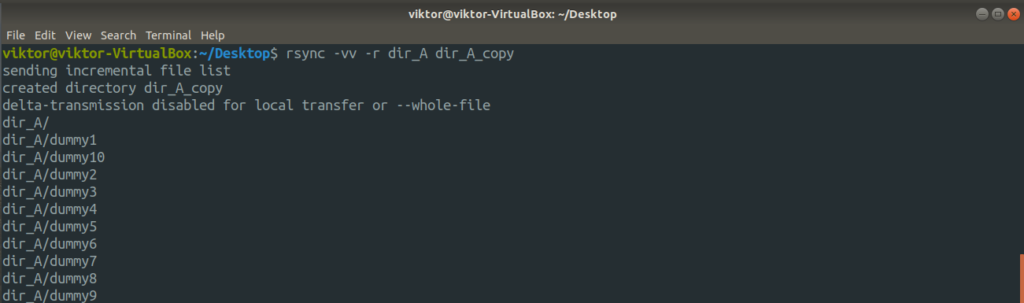
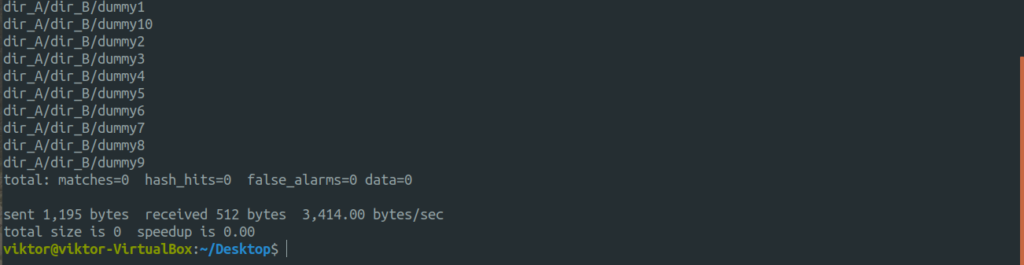
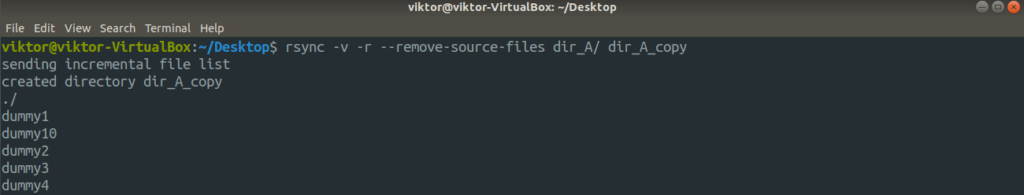
Let’s check them out in action. First, the directory copy. Run the following command.
For further detailed output, let’s use the “-vv” flag.
Now, let’s check out the cool part of rsync. We discussed how rsync intelligently copies only the files that are modified, saving bandwidth and disk write. It’s time to check it out in action. In this example, the action will be performed within the dir_A directory.
Despite delta-transmission enabled, rsync may not apply it when you’re performing local data transfer.
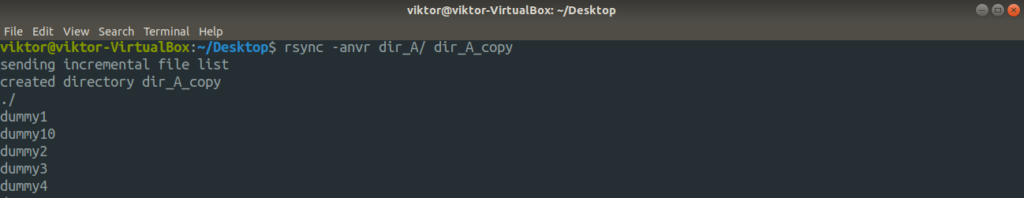
Now, let’s check out the dry run feature. Before running any rsync command for real, it’s always important that you test it out beforehand. This is where the dry run comes in. Rsync will output what will happen if the command was to actually run.
Rsync can also work with remote directories, no problem. All it needs is a proper SSH connection with SSH keys configured.
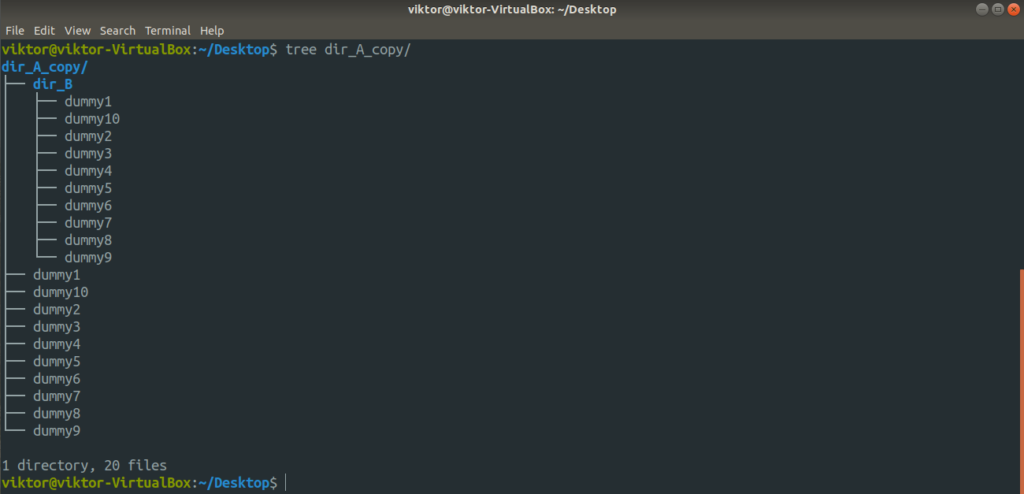
Want to perform a move operation? To put that in rsync’s perspective, rsync will copy the contents of the source directory and then, delete the source content.
Check out the result of the operation.
Final thoughts
The cp and rsync are the most common tools you can use for copying files in a folder on the Linux terminal. Both of them are also really good for scripting. Just make sure to test the functions out before implementation.
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
Источник
How do I copy folder with files to another folder in Unix/Linux? [closed]
Want to improve this question? Update the question so it’s on-topic for Stack Overflow.
Closed 8 years ago .
I am having some issues to copy a folder with files in that folder into another folder. Command cp -r doesn’t copy files in the folder.
3 Answers 3
The option you’re looking for is -R .
- If destination doesn’t exist, it will be created.
- -R means copy directories recursively . You can also use -r since it’s case-insensitive.
- To copy everything inside the source folder (symlinks, hidden files) without copying the source folder itself use -a flag along with trailing /. in the source (as per @muni764 ‘s / @Anton Krug ‘s comment):
You are looking for the cp command. You need to change directories so that you are outside of the directory you are trying to copy.
If the directory you’re copying is called dir1 and you want to copy it to your /home/Pictures folder:
Linux is case-sensitive and also needs the / after each directory to know that it isn’t a file.
is a special character in the terminal that automatically evaluates to the current user’s home directory. If you need to know what directory you are in, use the command pwd .
When you don’t know how to use a Linux command, there is a manual page that you can refer to by typing:
at a terminal prompt.
Also, to auto complete long file paths when typing in the terminal, you can hit Tab after you’ve started typing the path and you will either be presented with choices, or it will insert the remaining part of the path.
Источник
How to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
Home » SysAdmin » How to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
This guide will show you how to copy files and directories in Linux by executing commands from the command line. Furthermore, the commands listed below detail how to create system-wide backups or filter out and copy only specific files.
Note: These Linux commands can only be run from a terminal window. If your version of Linux boots to a desktop graphical interface, launch a terminal window by pressing CTRL-ALT-F2 or CTRL-ALT-T.
Using the cp Command to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
The cp command is the primary method for copying files and directories in Linux. Virtually all Linux distributions can use cp . The basic format of the command is:
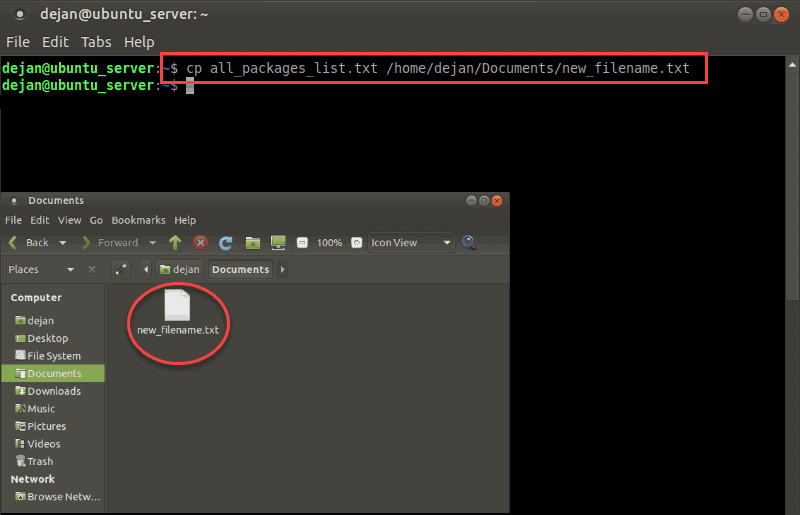
This Linux command creates a copy of the my_file.txt file and renames the new file to my_file2.txt.
By default, the cp command runs in the same directory you are working in. However, the same file cannot exist twice in the same directory. You’ll need to change the name of the target file to copy in the same location. Some users will add _old, some will add a number, and some will even change the three-letter extension (e.g., .bak instead of .txt).
You may not get a warning before Linux overwrites your file – be careful, or see below for the –i option.
Additional Options
Additional options can be used in combination with the cp command:
- –v verbose: shows the progress of multiple copied files
- –ppreserve: keeps the same attributes, like creation date and file permissions
- –f force: force the copy by deleting an existing file first
- –i interactive: prompts for confirmation, highly advised
- –Rrecursive: copies all files and subfolders in a directory
- –u update: copy only if source is newer than destination
Note: The -p (preserve) option forces the system to preserve the following source file attributes: modification time, access time, user ID (UID), group ID (GID), file flags, file mode, access control lists (ACLs), and extended attributes (EAs).
How to Copy File to Another Directory in Linux
To copy a file from the directory you’re working in to a different location, use the command:
You don’t need to rename the file unless there’s already one with the same name in the target directory.
To specify a path for the source file:
This lets you copy without having to change directories. The cp command will create the /new_directory if it doesn’t exist.
To rename and copy a file to a different path:
This option is useful for creating backups of configuration files, or for copying data to a storage device.
Note: Learn how to move directories in Linux.
Copy Multiple Files from One Directory to Another in Linux
You may need to copy more than one file at a time.
List each file to be copied before the target directory:
This example created a copy of all three files in the /new_directory folder.
Use a wildcard to specify all files that share a string of characters:
This would find all the files with the .jpg extension in the /pictures directory, and copy them into the /new_directory folder.
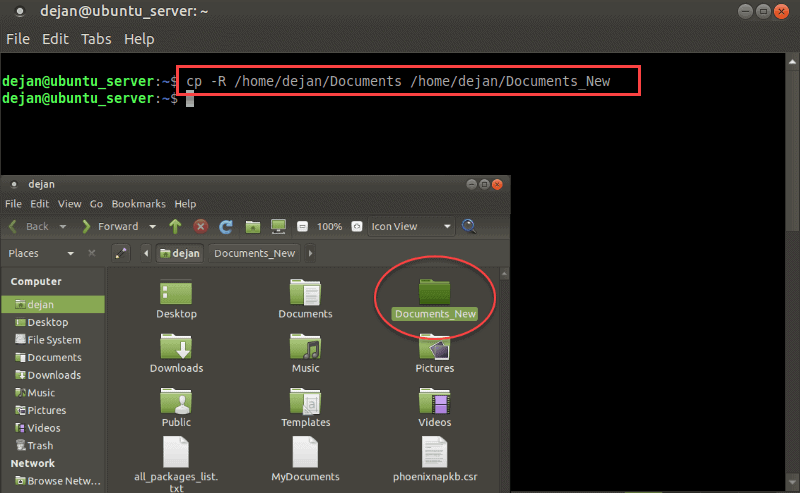
To copy an entire folder and its subfolders and files, use the –R option:
–R stands for recursive, which means “everything in that location.” This would copy all the files, as well as all the directories, to the /new_directory folder.
Copy Using rsync Command
The rsync command in Linux is used to synchronize or transfer data between two locations. Usage is similar to cp , but there are a few key differences to note.
To copy a single file, enter the following into a terminal:
- The –a option means all, and is included with rsync commands – this preserves subdirectories, symbolic links, and other metadata.
- Replace the my_file.txt file in the working directory.
- Replace /new_directory/ with the destination.
- Using my_file_backup.txt as the target indicates the file will be renamed during the copy.
To copy a directory with rsync, enter the following:
This copies the contents of the /etc/docker/ directory to /home/backup/docker/. Make sure to keep the slashes. Omitting the slash on the source directory will copy the contents into a subdirectory.
To omit files from being copied, check out our guide on how to exclude files and directories in data transfer using rsync command.
Other Options
The ls command is a handy partner to the cp command in Linux.
To list the contents of a directory enter the command:
The example above displays all the files in /directory. Use this command after copying to verify the files were copied successfully.
To change directories, use cd and the name of the directory. For example:
The command prompt will change to display that you’ve changed directories.
Now you understand how to copy files in Linux. The cp command is a versatile and powerful tool for managing and backing up files.
Источник