- Устанавливаем Wine в Debian, Linux Mint и Ubuntu
- Зачем нужен Wine?
- Подготовка к установки Wine
- Процесс установки Wine
- Из официального репозитория операционной системы
- Сторонние репозитории для Wine
- Для Ubuntu и linux Mint
- Установка Wine в Debian 10
- PPA -репозиторий
- Как пользоваться Wine
- Как удалить Wine
- Что можно запустить с помощью Wine?
- 10 игр работающих под Wine:
- 8 программ работающих под Wine:
- Комментарии
- Как установить Wine 6.0 на Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Установка Wine 6.0 на Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Установка Wine на Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Установка Wine на Debian
- Установка Wine с использованием исходного кода на Debian, Ubuntu и Mint
- Как использовать Wine для запуска приложений и игр Windows
- Запуск программы Windows в Ubuntu
- Удаление Wine в Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Заключение
- Available versions
- Installation on Debian Jessie and newer
- Step 1: Enable multiarch
- Step 2: Installation
- Standard installation
- Installation from Stretch backports
- Installation from winehq’s repo
- Debian Bullseye
- Optional Wine dependencies
- Mono and Gecko
- Usage
- Command names (choosing between wine and wine-development)
- Configuring Wine
- Installing and removing Windows programs
- System integration
- Additional programs for Wine
- Alternatives
Устанавливаем Wine в Debian, Linux Mint и Ubuntu
Linux хорош всем, но иногда нужно запустить программу, которая существует исключительно только для Windows. На помощь приходит Wine. Все отлично, если у Вас 32-битная операционная система. Установить Wine в Linux будет просто. Но мы живем в 2019 году и уже давно используем 64-битные операционные системы?
Версия Wine на 64 бит — это еще та поделка, которая практически ничего не умеет запускать. В deb-подобных системах запустить 32-битный Wine не составит особого труда.
Приведенный ниже способ запуска 32-битного Wine в 64-битной ОС работает только в Debian, Linux Mint и других дистрибутивах основанных на Debian или Ubuntu (ElementaryOS, Deepin и т.д.)
Зачем нужен Wine?
Wine — это очень хорошее и нужное приложение, с помощью которого есть возможность использовать коммерческие Windows-приложения на своей любимой системе Debian/Ubuntu или Linux Mint. Wine не всегда используется в запуске пиратских фотошоп и корел. Есть, к примеру, официальная утилита для управления маршрутизаторами Mikrotik — Winbox, которая имеет только windows-версию. С Wine можно с легкостью пользоваться Winbox на Mint’е или Ubuntu. Даже есть порт Winbox’а для MacOS, которое тоже работает через Wine.
Подготовка к установки Wine
Перед те как начать процесс установки Wine, необходимо подготовить систему. Для этого открываем консоль и удаляем все предыдущие неудачные попытки установки:
Если Вы впервые производите установку, то выполнять этот пункт необязательно. Идем дальше.
«Объясняем» системе что будем ставить i386-пакет:
Процесс установки Wine
После этого производим установку 32-битного Wine.
Из официального репозитория операционной системы
В Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint можно установить из официального репозитория командой:
Последняя стабильная версия Wine на момент написания статьи – Wine 6.7. В Ubuntu или в linux Mint она может быть такой при установки командой выше, но в Debian — это очень наврядли. Для установки последней версии Wine в вашей ОС необходимо подключить сторонний репозиторий.
Сторонние репозитории для Wine
Для Ubuntu и linux Mint
Первым делам импортируем ключ безопасности стороннего репозитория:
Установка Wine в Ubuntu
Для того, чтобы установить Wine Ubuntu нужно добавить репозиторий:
Установка Wine в Linux Mint
Для установки на Linux Mint разработчики Wine не предоставляют отдельно репозитория, но так как Mint основан на кодовой базе Ubuntu, мы можем установить нужную версию Wine зная кодовое название своего дистрибутива.
На странице здесь ищем название вашей Ubuntu и при добавлении репозитория подставляем нужное:
Установка Wine в Debian 10
Так же как и в Ubuntu для установки Wine на Debian нужно импортировать ключ безопасности стороннего репозитория:
PPA -репозиторий
Для Ubuntu и Linux Mint есть возможность воспользоваться сторонним PPA -репозиторием:
В Debian из коробки такой трюк не прокатит. Исправить можно, но стоит ли в стабильный дистрибутив вносить нестабильные пакеты?
Как пользоваться Wine
После установки возникает закономерный вопрос: «Как запустить windows-программу через Wine?». Для этого запускаем команду:
Чтобы удалить программу:
Wine «из коробки» уже готов запускать большинство приложений. Если приложение по какой-то причине не устанавливается можно посмотреть чужой опыт здесь – appdb.winehq.org На это странице в поиске набираем нужную программу и зачастую получаем инструкция для запуска.
Для установки различного рода прикладных библиотек Windows есть замечательный скрипт — winetricks. Для его установки нужно выполнить команды:
Появится графическая оболочка, в которой мышкой можно выбрать необходимую библиотеку.
Через консоль можно быстрее выполнить установку конкретного пакета. К примеру, MS Visual C++ 6 sp6:
Как удалить Wine
Чтобы полностью удалить Wine в операционных системах Linux основанных на Debian – ubuntu, linux mint, elementaryos и т.д. необходимо выполнить команду:
Эта команда полностью удалить Wine вместе со всеми конфигурационными файлами.
Что можно запустить с помощью Wine?
С помощью Wine можно запустить большое кол-во приложений и игр.
10 игр работающих под Wine:
- World of Warcraft
- Fallout 3
- Skyrim
- EVE Online
- The Witcher
- Command & Conquer 3: Tiberium Wars
- Sid Meier’s Civilization IV
- Half-Life 2
- Deus Ex
- The Sims 3
Подробнее какие игры и как можно запустить их под Wine – здесь
8 программ работающих под Wine:
- Microsoft Office 2019
- Adobe Photoshop CC 2021
- Adobe Photoshop Lightroom
- Microsoft Edge
- KOMPAS -3D v17
- Ammy Admin
- Metatrader 5
- DirectX
Полный список программ и описание как их установить можно найти здесь – appdb.winehq.org
Комментарии
я пиздец как благодарен этой статье,единственная с помощью которой у меня получилось установить wine после трех часовой пляски с бубном
Спасибо тебе добрый гуру линя.задолбался инет рыть и читать всякий бред…а тут в двух словах и все готово!спасибо от души!
Спасибо! Кратко и толково. Только пока установить не получилось. Но думаю косяк у меня в линухе.
Класный сайт, и материал про системщика отличный
наконецто. все работает!столько всего перечитал и тольку ноль.а тут раз – и готово!
супер мт4 запустился после этих действий
Чушь полная. На 64-битной системе не будет работать 32-битный WINE . Статью в топку!
Врубель Вшнобель: Чушь полная. На 64-битной системе не будет работать 32-битный WINE . Статью в топку!
Вы хоть пробовали это делать? Все пакеты, которые предназначены для i386 можно установить для amd64. Наоборот это правило не работает.
- Денис Юрьевич прокомментировал MultiKey не устанавливается, отозван сертификат
- Павел Urman прокомментировал Как закрыть крышку часов Tissot?
- AdminWay прокомментировал kernel_task грузит проц на 100% на MacOS BigSur
- Лев прокомментировал kernel_task грузит проц на 100% на MacOS BigSur
- AdminWay прокомментировал kernel_task грузит проц на 100% на MacOS BigSur
Калибровка сенсорного экрана в Kyocera KM-3050
Как я русифицировал Kindle 4?
Если Вы используете материал моего блога, то будьте добры поставьте ссылку.
Источник
Как установить Wine 6.0 на Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint
Wine — это бесплатная и простая в использовании программа с открытым исходным кодом, которая позволяет пользователям Linux запускать приложения Windows в Unix — системах. А так же с помощью Wine можно установить и запустить почти все версии программ Windows.
Wine 6.0 наконец-то выпущен, и он поставляется с множеством многочисленных улучшений. В общей сложности в Wine внесли 40 исправлений ошибок. Вы можете узнать обо всех новых функциях и списке изменений этого нового релиза на странице проекта Wine announcement.
В этой статье описаны несколько простых шагов по установке последней стабильной версии Wine 6.0 в системах Debian 10/9, Ubuntu 20.04-18.04 и Linux Mint 20-19. А также мы увидим, как настроить wine и как установить программное обеспечение windows.
Внимание: на нашем сайте есть статьи: Установка Wine 6.0 на Debian и Установка Wine 6.0 на Ubuntu.
Установка Wine 6.0 на Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint
Если вы хотите иметь самую последнюю версию Wine 6.0, вам нужно использовать новый репозиторий Wine repository PPA. Кстати в этом репозитории есть версии разработки, и стабильные версии Wine для Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint.
Установка Wine на Ubuntu и Linux Mint
Чтобы установить Wine 6.0 на Ubuntu и Linux Mint, откройте терминал, нажав горячите клавиши ‘CTRL + ALT + T’. Выполните следующие команды для установки репозитория Wine:
————— – On Ubuntu & Linux Mint – —————
$ sudo dpkg – add-architecture i386 [Enable 32-bit Arch]
$ wget -nc https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key
$ sudo apt-key add winehq.key
[Ubuntu 20.04 & Linux Mint 20]
$ sudo add-apt-repository ‘deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/ focal main’
[Ubuntu 18.04 & Linux Mint 19.x]
$ sudo add-apt-repository ‘deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/ bionic main’
[Ubuntu 16.04 & Linux Mint 18.x]
$ sudo apt-add-repository ‘deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/ xenial main’
Далее вводим команды для установки
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install – install-recommends winehq-stable
Если у вас появится сообщение об ошибке «winehq-stable: Dependents: wine-stable (= 6.0.0
bionic)«. Тогда при установке wine необходимо добавить следующий репозиторий PPA для исправления ошибки.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:cybermax-dexter/sdl2-backport
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install – install-recommends winehq-stable
Установка Wine на Debian
Чтобы установить Wine на Debian выполните следующие команды:
$ sudo dpkg – add-architecture i386
$ wget -nc https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key
$ sudo apt-key add winehq.key
Затем добавьте следующий репозиторий в /etc/apt /sources.list или создайте *.list в разделе/etc/apt/sources.list.d / со следующим содержимым.
deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/debian/ buster main [Для Debian 10 (Buster)]
deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/debian/ stretch main [Для Debian 9 (Stretch)]
Теперь обновите базу данных репозитория пакетов и установите Wine, как показано на рисунке.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install – install-recommends winehq-stable
Установка Wine с использованием исходного кода на Debian, Ubuntu и Mint
Еще один способ получить самую последнюю стабильную версию Wine 6.0 — это построить wine из исходного кода tarball, используя следующие команды.
$ wget https://dl.winehq.org/wine/source/6.0/wine-6.0.tar.xz
$ tar-xvf wine-6.0. tar. xz
$ cd wine-6.0/ $ sudo . / configure
$ sudo . / configure – enable-win64 [для 64-битной платформы]
$ sudo make && sudo make install
Как использовать Wine для запуска приложений и игр Windows
Чтобы продемонстрировать, как можно запустить программу Windows с помощью Wine. Мы загрузили .exe файл Rufus с официальной страницы.
Чтобы запустить на Linux исполняемый файл Rufus.EXE который предназначен для Windows, выполните команду:
Запуск программы Windows в Ubuntu
Как только вы запустите программу, Wine создаст конфигурационный файл в домашнем каталоге пользователя. В моем случае,
/.wine. Это показано на рисунке.
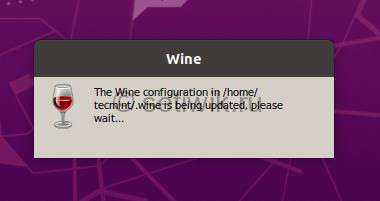
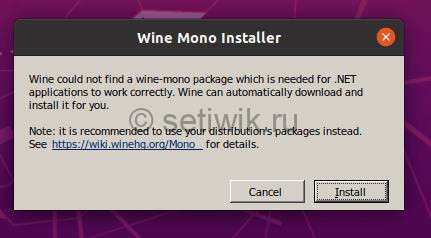
Во время настройки, Wine попросит установить .NET, нажмите кнопку «Установить«.
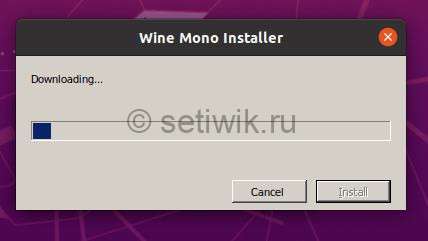
Ожидайте начала и завершения загрузки .NET
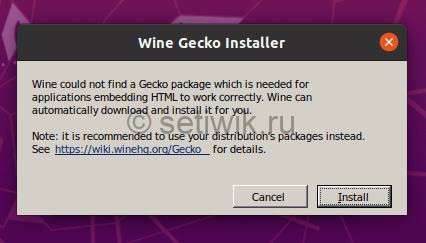
Кроме того, он также попросит вас установить пакет Gecko, который требуется для приложений, встраивающих HTML.
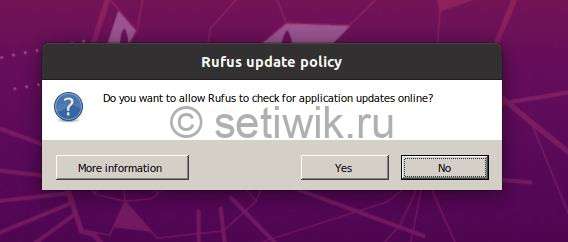
Выберите, хотите ли вы время от времени проверять наличие обновлений приложений.
И последние Rufus у вас отобразится на экране.
Вот и все мы успешно установили Wine на Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint. А так же показали вам как вы можете запускать приложения Windows в среде Linux.
Удаление Wine в Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint
Если вы недовольны программой Wine и вы хотите полностью удалить его. Это можно реализовать с помощью следующей команды.
Заключение
Надеюсь, что вы успешно установили Wine на Debian, Ubuntu и Linux Mint. А так же у вас получилось запустить приложение Windows через Wine.
Источник
Available versions
Since Debian Jessie you can choose between two sets of Wine packages: wine and wine-development.
wine tracks the stable releases from winehq.org (e.g. version 5.0.1), and wine-development the development releases (e.g. version 5.12).
Despite its name wine-development is also intended to be used by regular users. Do not mix this up with the *-dev packages which contain the header files and development libraries.
You can either install both sets at the same time, or only one of them. If you install both sets, «wine» will take precedence unless you configure your system otherwise, see «Usage» below.
Installation on Debian Jessie and newer
Step 1: Enable multiarch
On 64-bit systems you should enable a 32-bit architecture for multiarch. This is needed for running 32-bit Windows applications (many modern apps are still 32-bit), but also for large parts of the Windows subsystem itself. If in doubt, you do need it!
You can identify your architecture with the following command:
E.g. for amd64 (which most users have) you need i386. Enable it with the following command:
Step 2: Installation
You always need to install the wine (or wine-development) package. This should automatically install all other required packages if you already have enabled multiarch (step 1).
To run 32-bit Windows applications (this is the most common case, independently of your Debian architecture) make sure that wine32 (or wine32-development) is installed (requires step 1).
It’s quite easy to run into broken dependencies when installing Wine: The multiarch setup requires packages from e.g. amd64 and i386 to be in exactly the same version. Usually you already have most of the required amd64 library packages installed. These packages are the versions from your default release, e.g. Debian Stable or Testing. But if you install Wine from another suite (e.g. Debian Backports or Unstable) then some newly needed i386 packages might have another version, and you face broken dependencies. To solve this install the i386 package from the same suite as the already installed amd64 package (e.g. «sudo apt install libpulse0:i386/testing»), and then continue to install Wine.
Standard installation
Install wine on a 64-bit architecture (amd64 with i386 as foreign 32-bit architecture):
Install wine on a 32-bit architecture:
Install wine-development on a 64-bit architecture (amd64 with i386 as foreign 32-bit architecture):
Install wine-development on a 32-bit architecture:
Installation from Stretch backports
For Debian Stretch wine is available as backport. To enable stretch-backports add this line to your sources.list (or add a new file with the «.list» extension to /etc/apt/sources.list.d/):
Packages from backports are not installed automatically. But once they are installed you receive automatic updates. The following example commands make sure that all required packages are pulled from stretch-backports instead of stretch.
Do not simply use «apt install -t stretch-backports wine» instead of the following example commands. You’d end up with dependency packages installed unnecessarily from stretch-backports and have a high risk of «broken dependencies» because some new i386 dependency packages wouldn’t match the versions of their already installed amd64 counterparts.
Install wine on a 64-bit architecture (amd64 with i386 as foreign 32-bit architecture):
Install wine on a 32-bit architecture:
Install wine-development on a 64-bit architecture (amd64 with i386 as foreign 32-bit architecture):
Install wine-development on a 32-bit architecture:
Installation from winehq’s repo
Winehq offers newer builds of wine for both Buster and Bullseye. These packages are only available for the amd64 architecture. Here are the installation instructions.
Debian Bullseye
1. Add the i386 architecture:
2. Import the winehq key:
3. Add the bullseye winehq repo:
4. Update and install the latest stable version of wine:
Optional Wine dependencies
wine and wine-development consist of a suite of packages. Some are optional and might not be installed automatically:
wine and wine-development each provide essential wrappers and convenience tools for the standard Wine components, and the alternatives system to provide the usual Wine command names.
wine32 and wine32-development each provide the binary loader for 32-bit Windows applications.
wine64 and wine64-development each provide the binary loader for 64-bit Windows applications.
wine32-preloader and wine32-development-preloader each provide the prelinked loader for 32-bit Windows applications.
wine64-preloader and wine64-development-preloader each provide the prelinked loader for 64-bit Windows applications.
wine32-tools and wine32-development-tools each provide the 32-bit Wine developer tools.
wine64-tools and wine64-development-tools each provide the 64-bit Wine developer tools (capable of generating both 32- and 64-bit results since Debian Stretch).
libwine and libwine-development each provide the Wine library (one package for each architecture, e.g. libwine:i386 and libwine:amd64).
libwine-dev and libwine-development-dev each provide Wine’s C header files and development libraries (one package for each architecture, e.g. libwine-dev:i386 and libwine-dev:amd64).
wine-binfmt provides support for launching Windows executables directly (shared between both suites since Debian Stretch).
fonts-wine provides the Wine fonts (shared between both suites, available since Debian Stretch, previously part of libwine).
Users on a 64-bit system should make sure that both wine32 and wine64 (or wine32-development and wine64-development) are installed (see Step 1: Enable multiarch).
libwine and libwine-development recommend many other libraries needed for optional functionalities. These should be installed automatically, but if you don’t need them you may uninstall them. On amd64 remember that most times the i386 packages are the relevant ones.
Mono and Gecko
Windows software may require Mono for .NET, and Gecko for any HTML rendering. Debian has disabled these by default and do not provide packages.
The downloader for Wine Mono is intentionally disabled in the Debian packages. Unfortunately Wine Mono is not available in the official Debian archives.
You can find more information at: https://wiki.winehq.org/Mono
You can download the Wine Mono installer and copy them to one of the following locations:
- /usr/share/wine-mono/
- /usr/share/wine-development/mono/ (only if you are using wine-development)
- /usr/share/wine/mono/
- $XDG_CACHE_HOME/wine/
- $HOME/.cache/wine/ (if XDG_CACHE_HOME is not set)
Usage
Command names (choosing between wine and wine-development)
wine and wine-development use the Debian alternatives system to provide /usr/bin/wine and other commands. If both packages are installed it defaults to use the commands provided by wine.
You may change this by running:
You may force a version at any time (as long as the wineserver isn’t running yet), by using the suffixed command names, e.g.:
Configuring Wine
To open the Wine configuration window, enter the following command:
To open the Wine registry editor, enter the following command:
Installing and removing Windows programs
In order to install a program, launch the Windows installation file (.exe/.msi) with the following command:
In order to remove a program, launch the wine uninstaller with the following command:
Wine uninstaller does not delete menu entries and desktop icons; therefore they must be removed manually.
System integration
If you want to start Windows applications directly (with the command ./foo.exe) you have to enable binfmt support. Have a look at the README.debian for details.
Additional programs for Wine
winetricks — is a helper script to download and install various redistributable runtime libraries needed to run some programs in Wine. These may include replacements for components of Wine using closed source libraries.
To download and install, enter:
If you have both wine and wine-development installed and want to use wine-development, you should execute the following commands before running winetricks:
playonlinux — Frontend for Wine which helps to easily install Windows games and programs in Linux.
q4wine — Helps to manage wine prefixes and install applications.
gnome-exe-thumbnailer — Wine .exe and other executable thumbnailer for GNOME
winegame — Helps to easily install Windows games and programs in Linux.
Alternatives
Crossover — CrossOver is developed by CodeWeavers and based on Wine, an open-source Windows compatibility layer. CrossOver lets you run thousands of Windows apps on your favorite Linux distro like Ubuntu, Mint, Fedora, Debian, RHEL and more.
Wine Staging Wine Staging (formerly wine-compholio) is a special Wine version containing bug fixes and features, which are not yet available in regular Wine versions. The idea of Wine Staging is to provide new features faster to end users and to give developers the possibility to discuss and improve their patches before they are sent upstream.
Источник







